Cell membbrane
- 5. The Plasma Membrane, the flexible boundary between the cell and its environment, allows a steady supply of nutrients to come into a cell no matter what the external conditions are. Too much of any of these nutrients or substances can be harmful to the cell. If levels become too high, excess is removed through plasma membrane
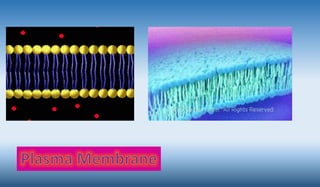
- 6. Cell Membrane • A semipermeable membrane that surround cytoplasm of cell • Encloses the entire cell • Composed of a phospholipid bilayer with embeded proteins Plasma Membrane • A semipermeable barrier that surrounds cells or cellular compartments • Encloses cells or organelles • Composition may change based on requirements of cellular compartments
- 8. Models of Plasma Membrane
- 9. Gorter and Grendel Model- 1925: • Evert Gorter and François Grendel (Dutch physiologists) • Phospholipid Bilayer • Hydrophobic tails and hydrophillic heads
- 10. Davson–Danielli model-1935: • By Hugh Davson and James Daniell. • A phospholipid bilayer that lies between two layers of globular proteins which is trilaminar and lipoprotinious. • Also called Bimolecular Leaflet Model.
- 11. Robertson Model- Unit Membrane Model -1959: • J. David Robertson. • Suggested that all cellular membranes share a similar underlying structure, the unit membrane. • Three layers- Outer Protein layer, Middle Lipid layer and Inner Molecule layer. • Glycoproteins are also present.
- 12. Fluid Mosaic Model- 1972: • By Singer and Nicholson. • Disproved Robertson, Davson and Danielli Models. • Lipid bilayer kept • Protein coat lost • Two components of this model are: • Fluid- all components are free to diffuse in the plane of membrane • Mosaic- Heterogeneity membrane (proteins and lipids interspersed and because of fluidity of plasm membrane they are randomly distributed)
- 18. Composition: • Membrane Lipids- 90-99% • Primary lipids- phospholipids • Secondary lipids- Cholesterol/Sphingolipids( Fluidity- less cholesterol more fluidity-depends on type of cell- like RBCs require more flexibility so have less cholesterol ) • Glycolipids- 5% Of Lipids (on extracellular side- Glycocalyx{Cell to Cell adhesion}) • Membrane Proteins- About 2% (essential for two membrane functions-Sensitivity, Selective Permeability) • Two types- Transmembrane proteins(Cross totally) & Peripheral proteins (towards or outwards to cell side/ Partially cross membrane) • A little percentage of Carbohydrates. (Fluidity is due to main membrane components held by non-covalent interactions)
- 23. Eukaryotes resemble prokaryotes in membrane structure and functions except for sterols.
- 24. Peripheral proteins • Loosely associated with proteins/lipids • Functions- Anchorage, Intracellular signalling molecules Integral proteins • Partially attached • Glycoproteins with sugar • Extend to outside • Function- Glycocalyx Formation
- 26. A transmembrane protein (TP) is a type of integral membrane protein that spans the entirety of the cell membrane to which it is permanently attached. There are five types of trans membrane proteins: 1. Receptor proteins 2. Channel proteins (always open) 3. Gate Channel proteins (closed-checkers-have gate but open) 4. Transport proteins- Carrier proteins (in pairs) 5. Glycocalyx attached proteins – Cam (Cell adhesion molecules (CAMs)-cell adhesion proteins located on the cell surface) Trans-Membrane Proteins:
- 27. Types of transmembrane proteins on basis of function:
- 31. Glycocalyx: • The fuzzy coat external to plasma membrane on all animal cells, including humans • Acts as on “identification” tag that enables the body to distinguish its own healthy cells from transplanted tissue, invading organism, diseased cells.
- 32. Functions: •Transport • Non facilitated Transport & Facilitated Transport(Facilitated Active transport, Facilitated passive transport {Diffusion, Osmosis}) •Mechanical Support •Homeostasis
- 33. • Integrity of the cell- size and shape • Controls transport- Since it is Selectively permeable • Excludes unwanted materials from entering the cell • Forms a physical barrier with the external environment • Allows the cell to create different environments outside and inside • Maintains the ionic concentration of cell and Osmotic pressure of the cytosol • Allows for the creation of gradients- electrical and chemical • Forms contacts with neighboring cells i.e. help in forming tissues • Sensitivity- First part of cell that is affected by changes in the extracellular environment
- 39. Properties of Plasma Membrane Allows small molecules either polar (CO2 AND H2O) or non polar( oxygen and ethanol)to pass through freely Don’t allow macromolecules( Glucose) and ions (K+ and Na+) to pass through freely Have specific trans membrane proteins to regulate ion (ion channel) and molecules (Transporter proteins) movements The property of Plasma membrane to selectively allow some molecules to pass through is termed as semipermeable
- 42. Passive mediated transport, or Facilitated diffusion- A specific molecule flows from high to low concentration Active transport- Transport from low to high concentration i.e. against concentration gradient.
- 44. Na- K pump (Active Transport)
- 54. As a part of ENDOMEMBRANE SYSTEM: • Vesicle formation • Transport Information- Proteins out or into cell • Uses Energy- ATP • Exocytosis,Endocytosis • Golgi body produces vesicles, fuses with membrane materials (hormones etc.), released out of cell
- 57. Intracellular Membranes: • Nuclear Membrane • Mitochondrial Membranes • Chloroplast Membranes • E.R as a part of endomembrane system • Golgi as part of endomembrane system
- 58. • Campbell Biology by Urry, Cain, Wasserman Minorsky, Reese. • M. Lodish (2003), Molecular cell biology, Chapter 3 Bio-membranes and cell architecture, 5th edition • Alberts B et al. (2002) in “The Molecular biology of the cell”, 4th edition. Garland Science, New York. • file:///E:/BOOKS/Cell%20Biology.pdf • file:///E:/BOOKS/cellular_organization.pdf • file:///E:/BOOKS/cholesterol.pdf • https://bioproxnoob.files.wordpress.com/2011/03/propeertiesofplasm amembrane.jpg
- 59. THANK YOU MY PUPILS