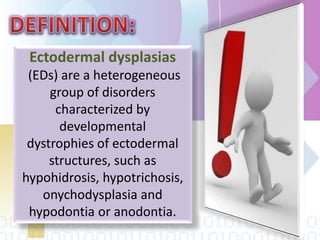
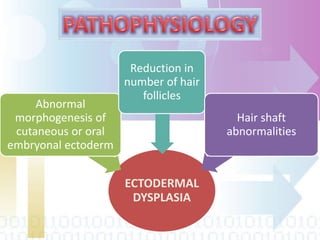
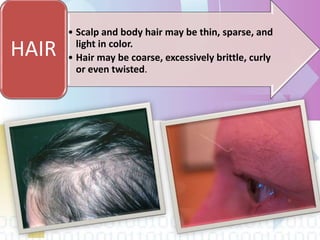
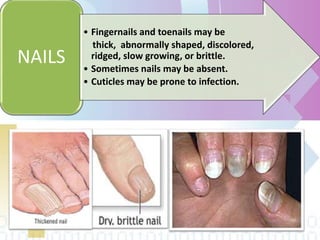
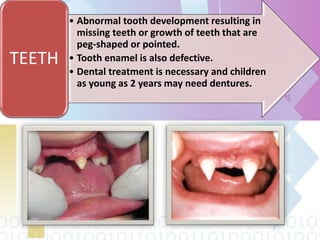
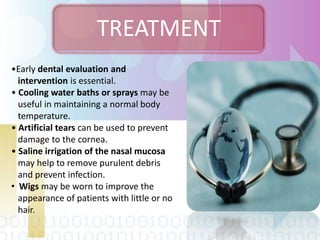
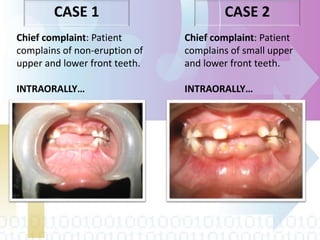
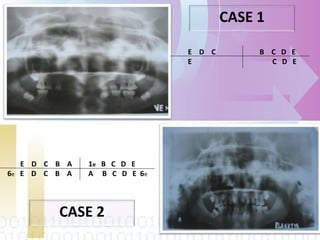
Ectodermal dysplasia is a genetic condition characterized by abnormal development of structures derived from embryonic ectoderm such as hair, teeth, nails and sweat glands. The most common types are hypohidrotic (anhidrotic) and hydrotic ectodermal dysplasia. Symptoms include sparse hair, abnormal nails, missing or malformed teeth, lack of sweat glands and dry skin prone to infection. Treatment focuses on dental care, temperature regulation, artificial tears and infection prevention. The condition is caused by mutations in genes controlling ectodermal development and can be diagnosed through clinical features, imaging and genetic testing.