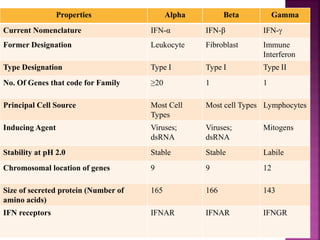
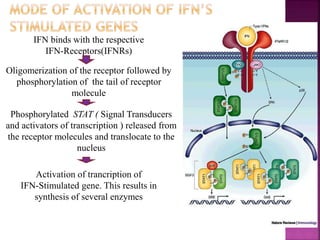
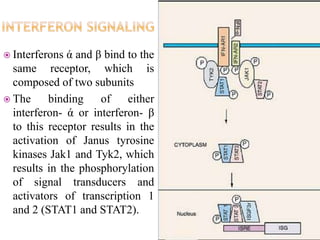
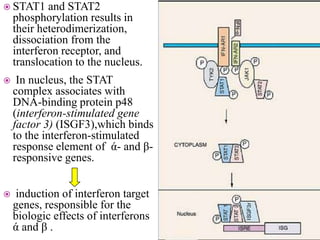
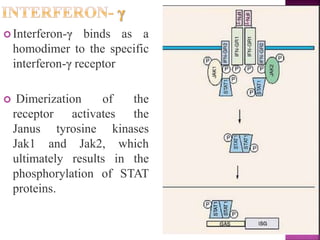
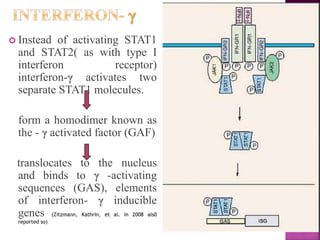
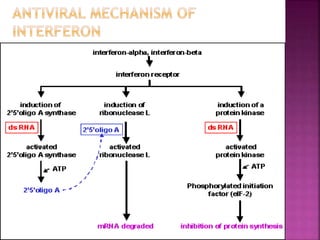
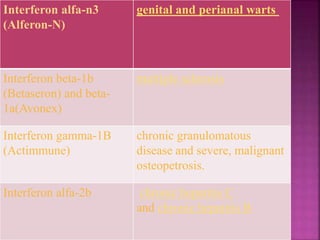
This document discusses interferons, which are proteins naturally produced in response to viral infections. There are three main types of interferons - alpha, beta, and gamma. Interferons work by binding to receptors on cells and activating signaling pathways that turn on genes to produce antiviral proteins. This inhibits viral replication and helps the immune system clear infections. Interferons are now produced recombinantly for use in treating certain viral infections and cancers. The document provides details on the structure, function, signaling, and clinical applications of the different interferon types.