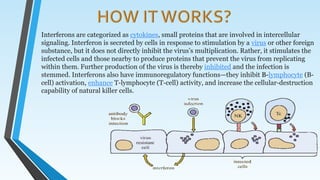
Interferons are proteins produced by cells that help the immune system fight viruses, bacteria, tumors and other foreign substances. There are two main types - Type I produced by almost any cell to induce viral resistance, and Type II produced by immune cells to signal the immune system to respond. Interferons were discovered in the 1950s and have been used to treat conditions like hepatitis C, some cancers, and multiple sclerosis by stimulating immune cells to attack infected or cancerous cells and prevent their growth and spread. Common side effects include flu-like symptoms.