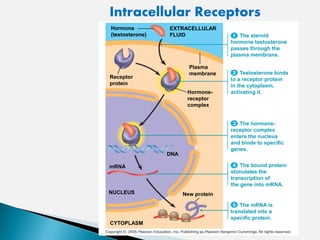
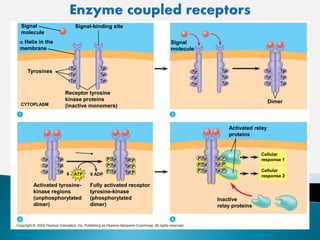
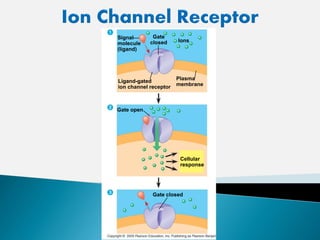
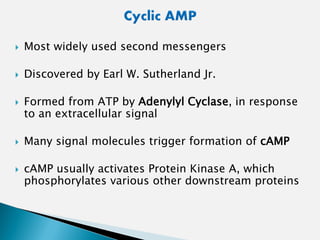
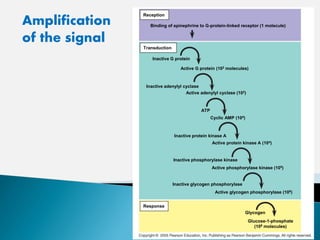
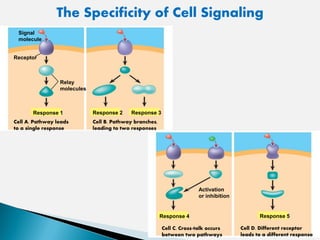
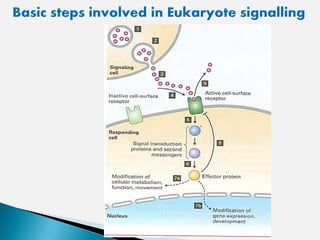
Cell signaling involves three main stages - reception, transduction, and response. Reception involves signaling molecules binding to membrane receptors, which leads to conformational changes. Transduction refers to the activation of intracellular signaling pathways through second messengers. Response occurs when downstream effectors are activated, bringing about cellular responses like metabolism, gene expression, and cell differentiation. Precise regulation of cell signaling pathways is essential for normal cell function, and defects can lead to diseases.