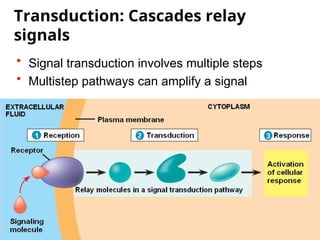
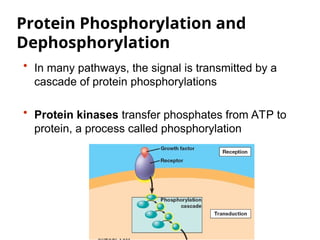
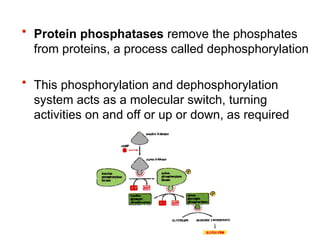
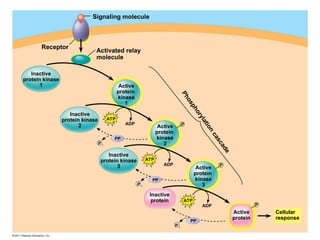
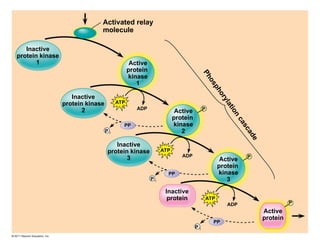
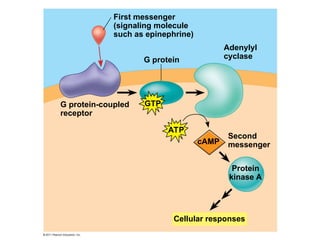
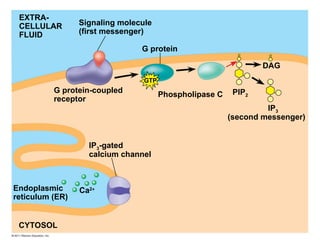
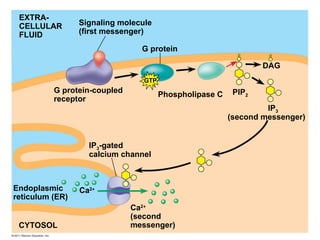
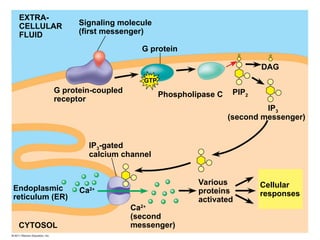
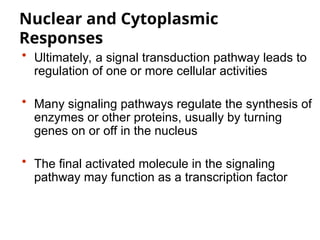
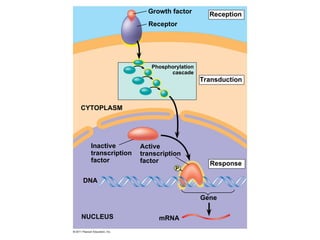
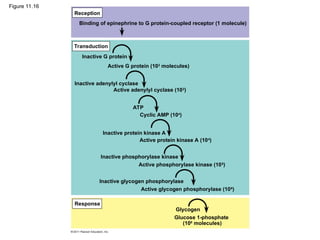
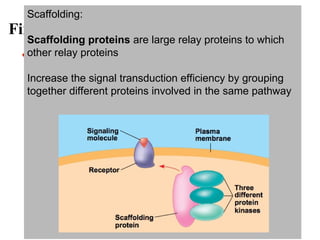
Cell-to-cell communication primarily occurs through signal transduction pathways, involving multiple steps that amplify signals and result in cellular responses. These pathways often use protein phosphorylation and dephosphorylation as molecular switches and involve first and second messengers to relay signals within a cell. The effectiveness of these pathways can be fine-tuned through amplification, specificity, efficiency via scaffolding proteins, and signal termination.