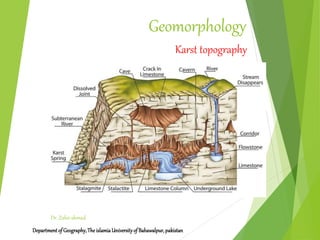
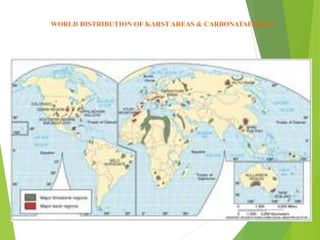
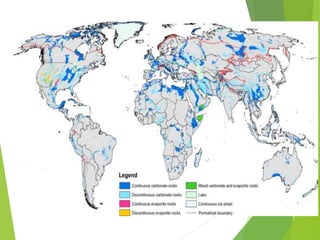
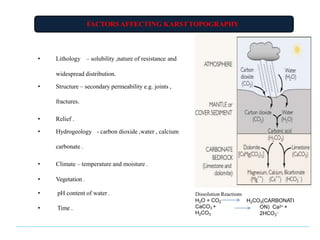
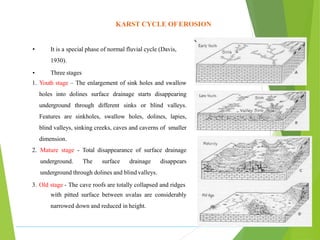
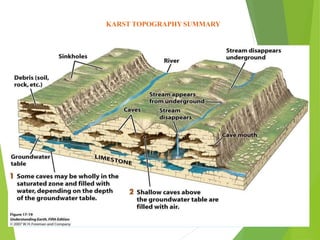
Karst topography refers to landscapes formed by the dissolution of soluble rocks like limestone and dolostone by groundwater. It is characterized by features like sinkholes, caves, underground streams, and disappearing streams. Karst landscapes are widespread globally in areas underlain by carbonate rocks, including regions in the United States, Europe, Asia, Australia, and Cuba. The development of karst topography depends on factors like the lithology of soluble bedrock, structure of the bedrock like joints and fractures, climate, hydrogeology, and time.