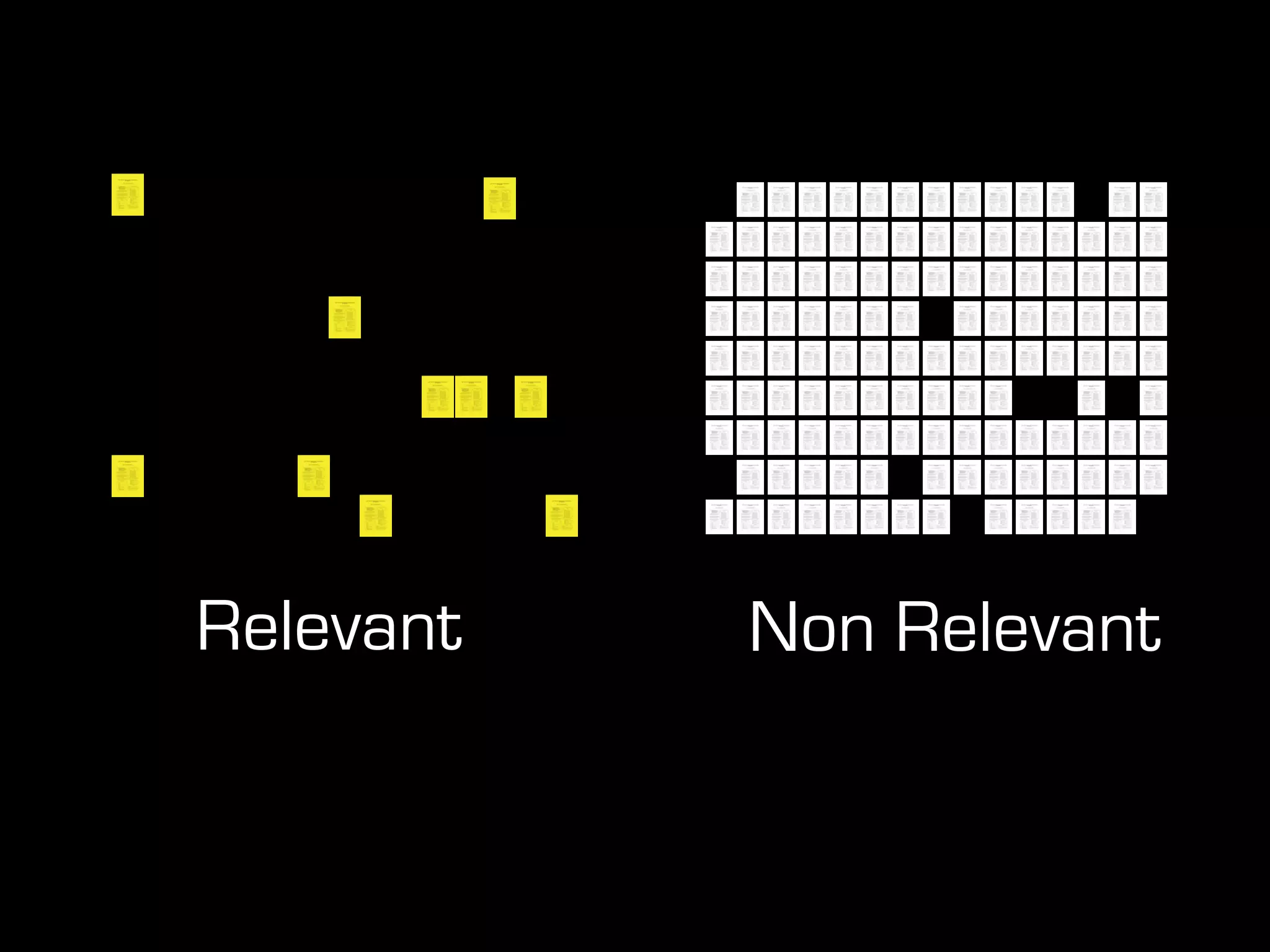
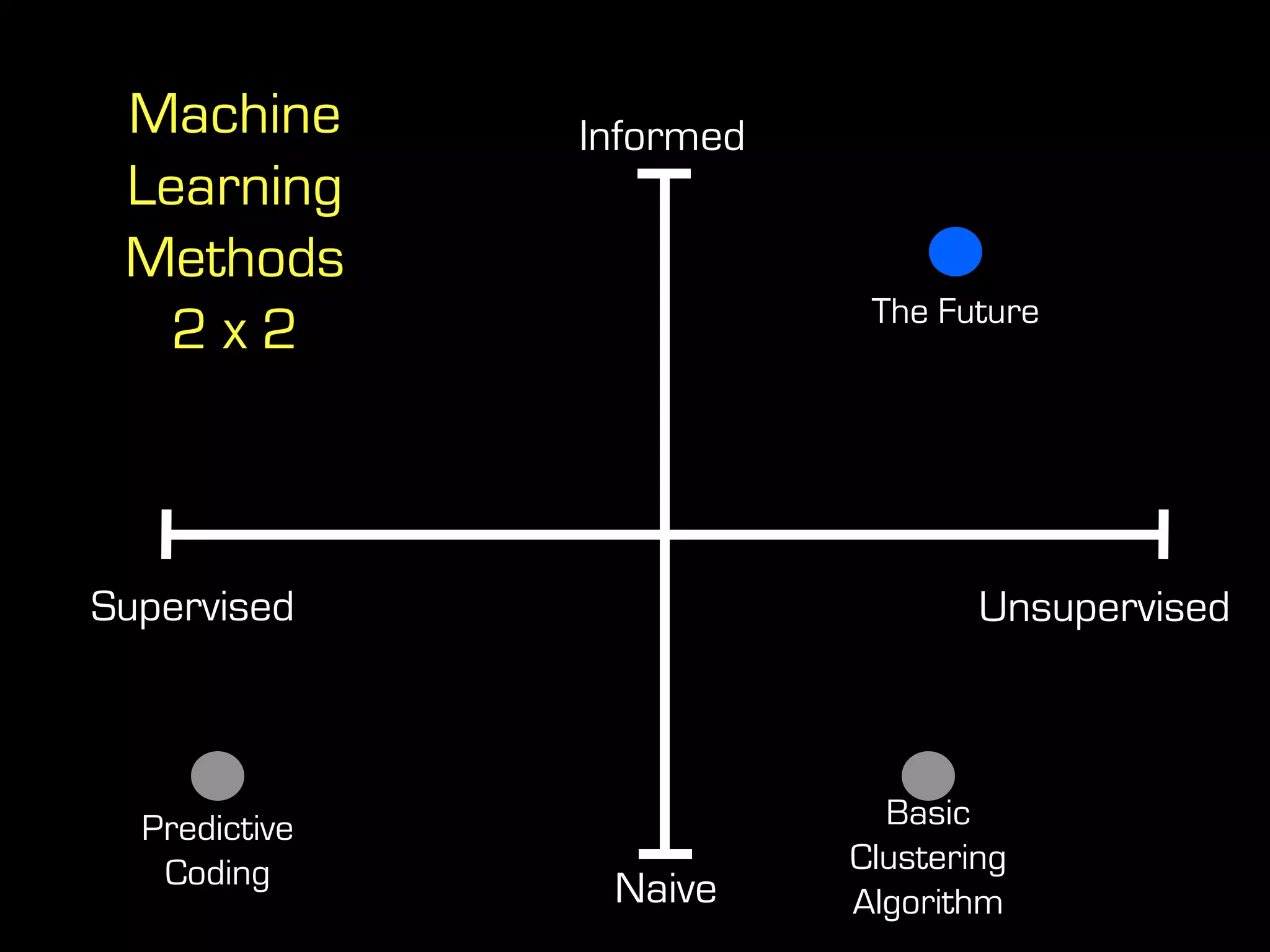
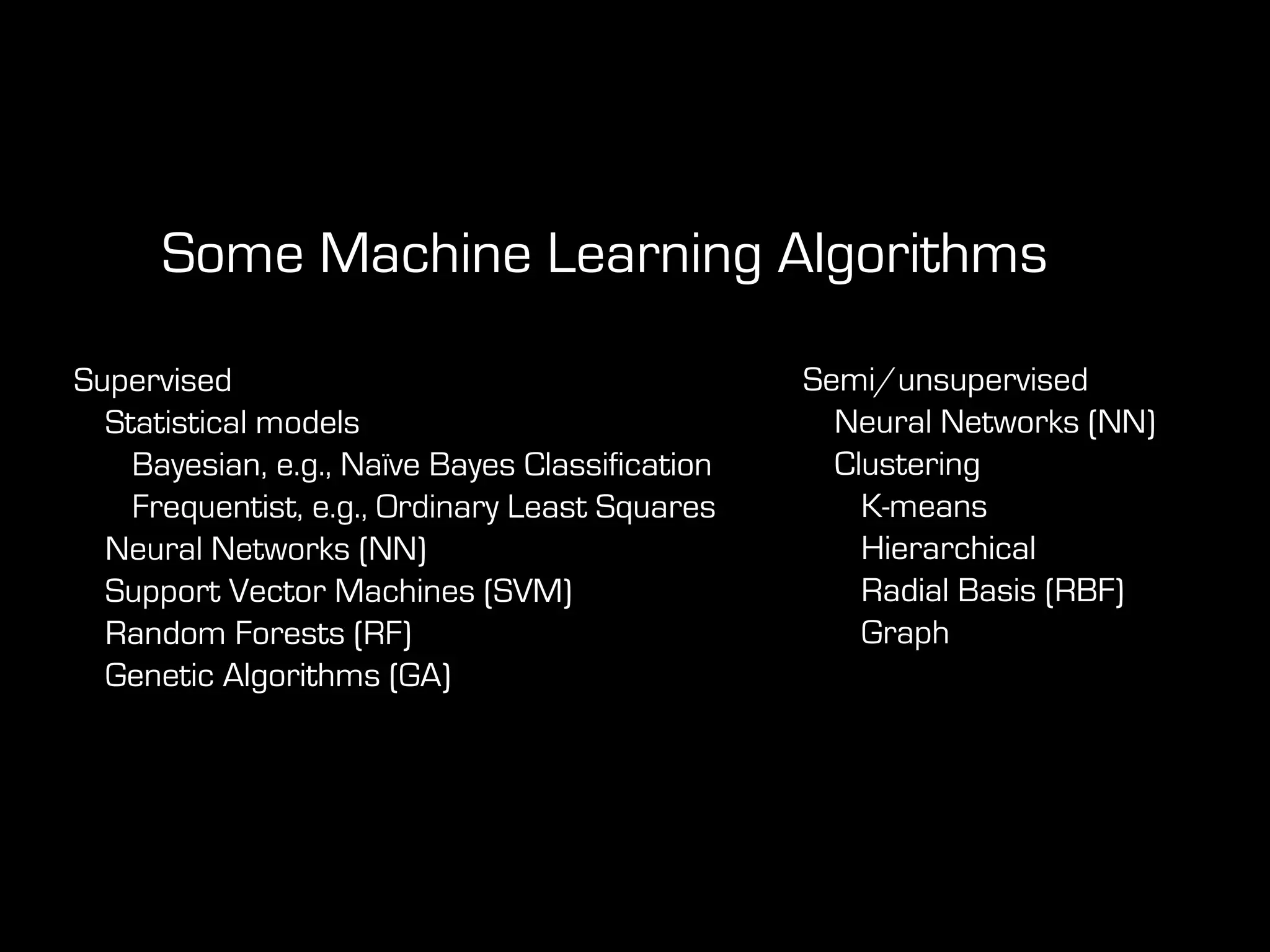
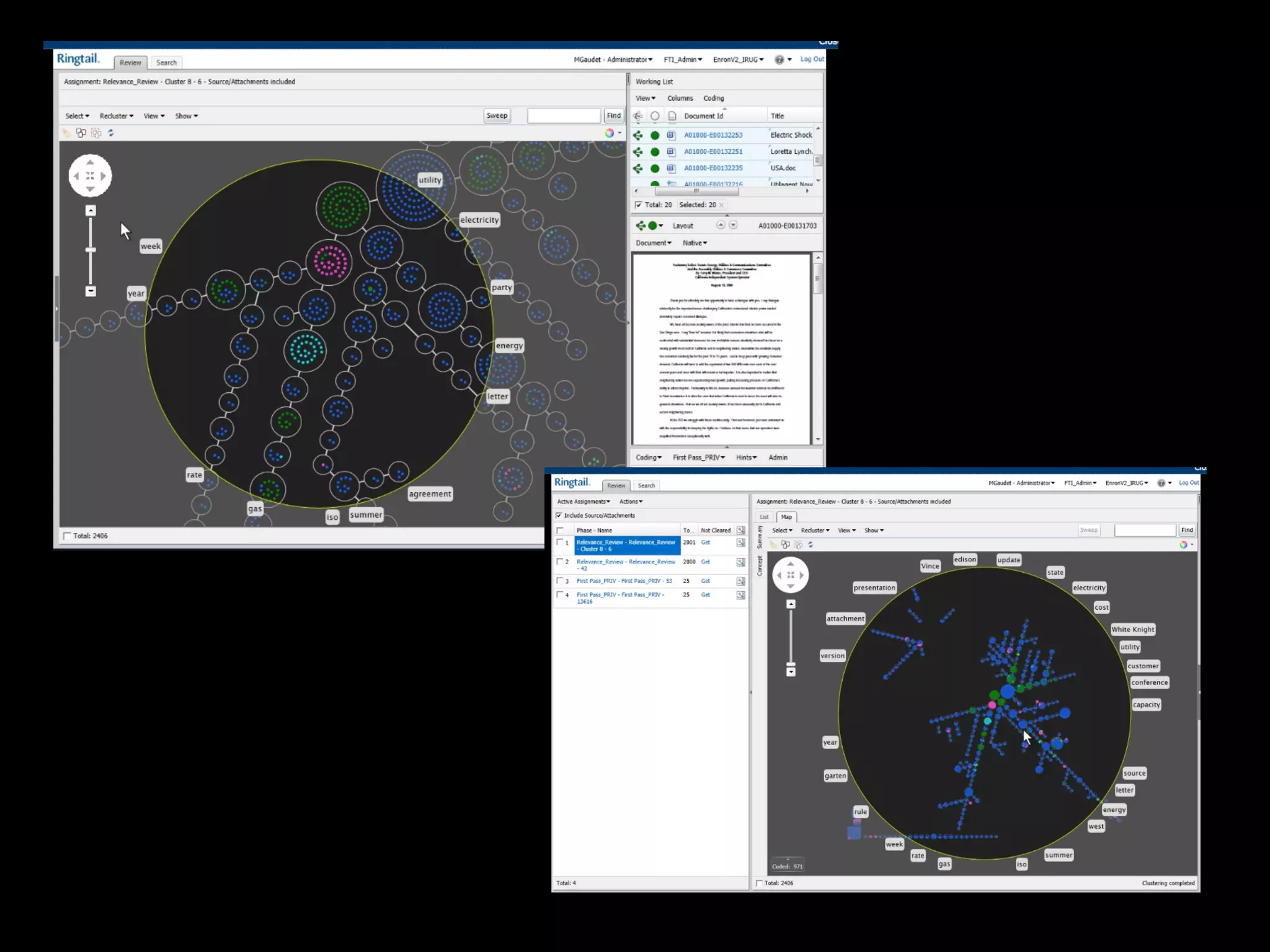
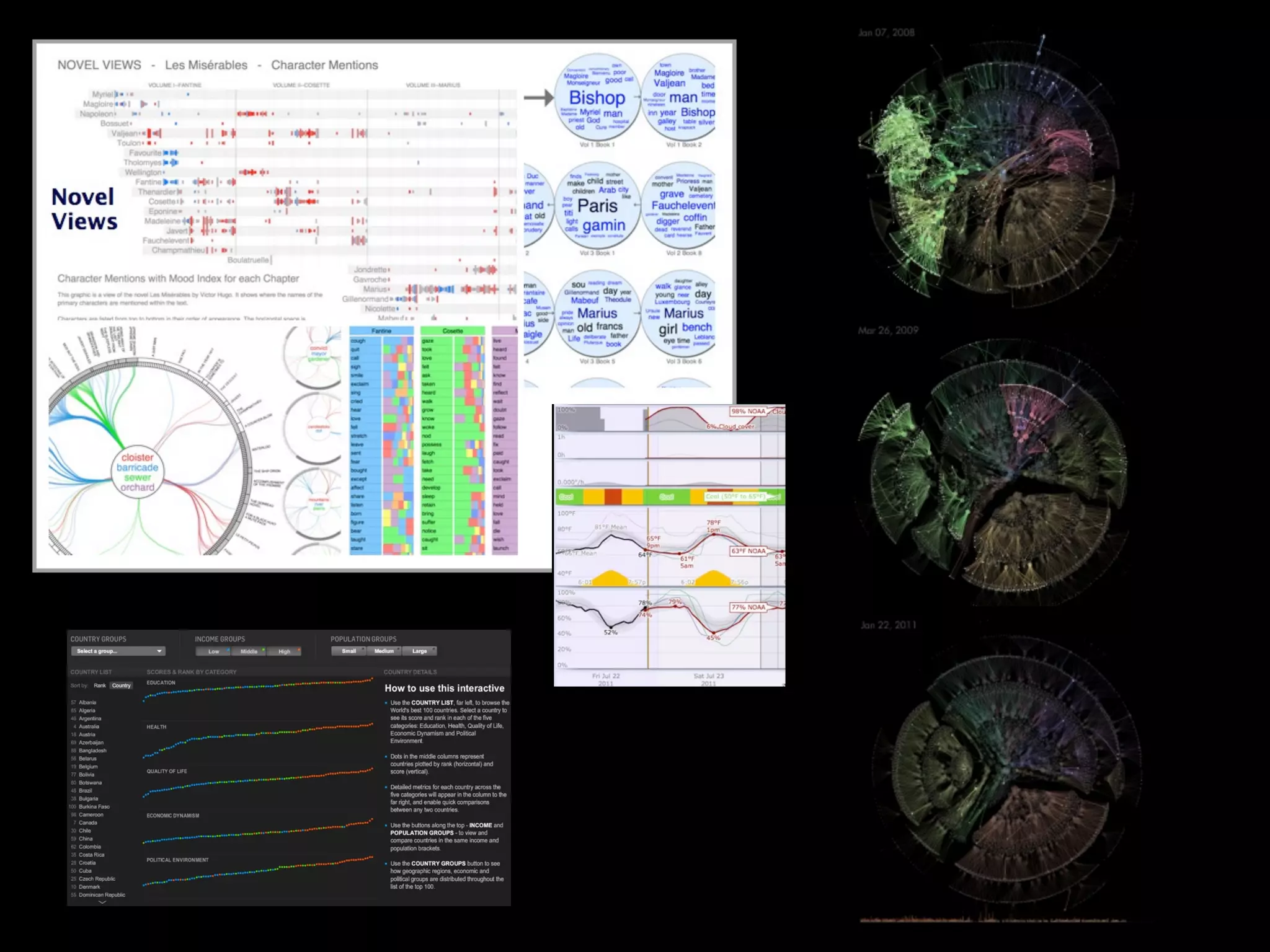
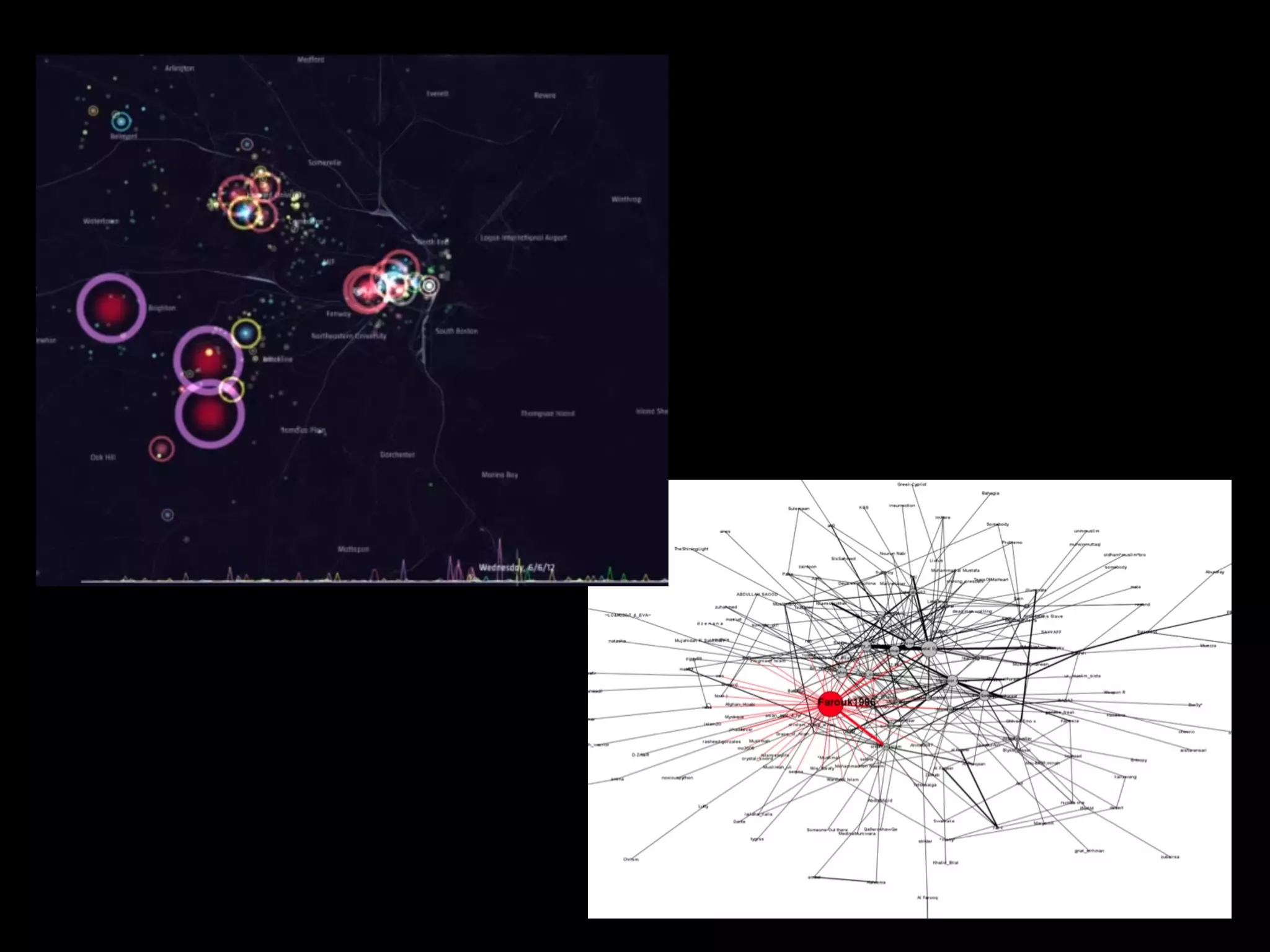
This document discusses predictive coding and machine learning methods for e-discovery. It begins by explaining that predictive coding relies on supervised machine learning methods, which use human-coded training sets to classify documents as relevant or non-relevant. The document then discusses different types of supervised and unsupervised machine learning algorithms that could be used for predictive coding. It suggests that using prior cases to inform feature selection and weightings could make algorithms "smarter." Finally, it considers whether discovery costs will eventually be reduced due to scaling relationships for cost per gigabyte and long-term rates of electronic data growth.

















































![“[I]n 2001, a 300 Gb legal matter would take 200 attorneys a full
year to review, at a cost of about $15 million.
In 2003, a similar-sized matter took 100 attorneys 3 weeks to
complete, at a cost of $6 million.
And in 2006, a 300 Gb investigation took 65 attorneys only 2.5
days to complete, at a cost of $2 million.
And now, cases with several hundreds of Gbs are routine.”
Improving Document Review in E-Discovery
FTI Consulting](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ediscoveryin2015-130130155258-phpapp02/75/Predictive-Coding-and-E-Discovery-in-2015-and-Beyond-LegalTechNYC-2013-Daniel-Martin-Katz-Michael-J-Bommarito-II-62-2048.jpg)