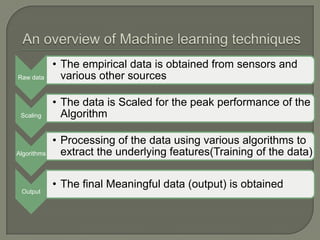
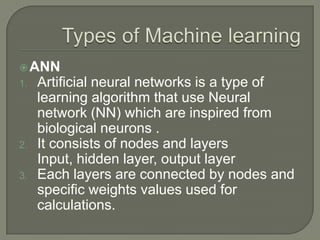
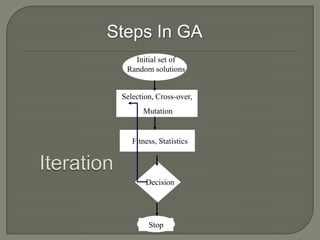
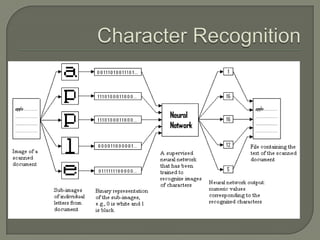
This document discusses machine learning and artificial intelligence. It provides an overview of the machine learning process, including obtaining raw data, preprocessing the data, applying algorithms to extract features and train models, and generating outputs. It then describes different types of machine learning, including supervised learning, unsupervised learning, reinforcement learning, and semi-supervised learning. Specific algorithms like artificial neural networks, support vector machines, genetic algorithms are also briefly explained. Real-world applications of machine learning like character recognition and medical diagnosis are listed.