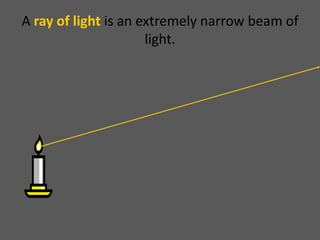
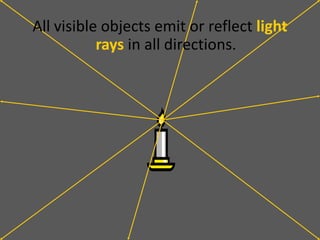
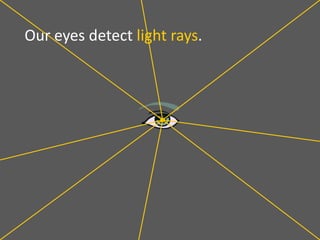
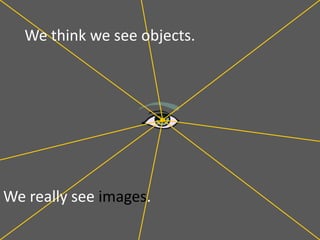
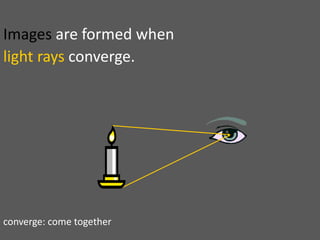
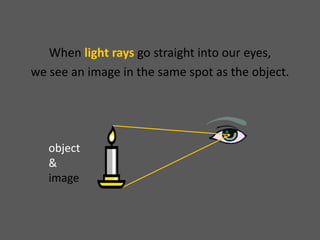
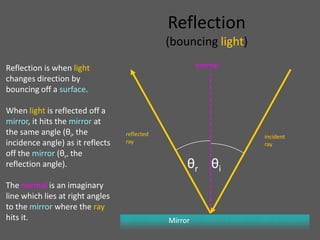
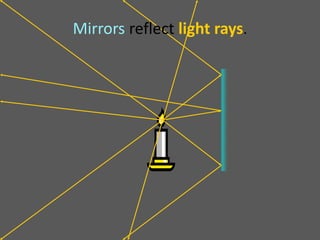
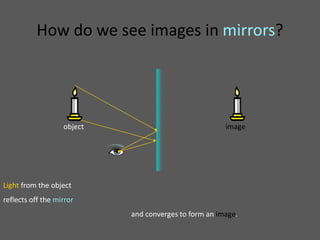
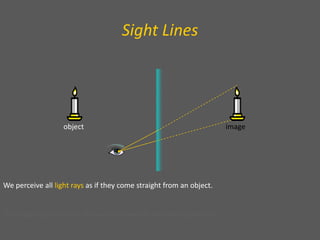
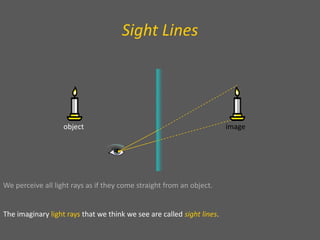
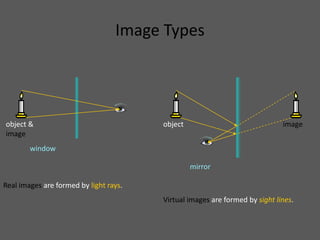
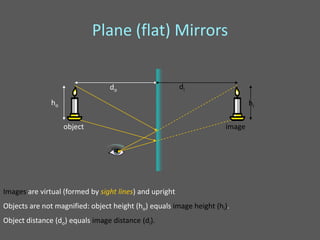
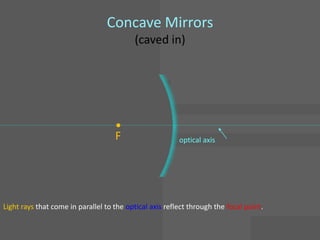
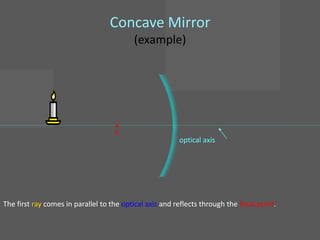
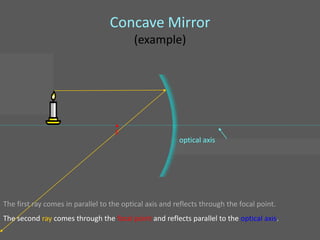
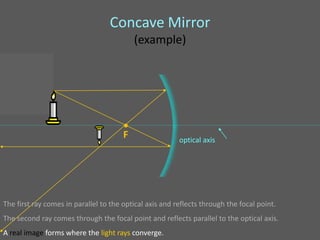
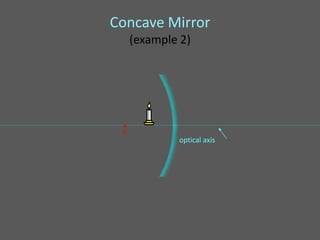
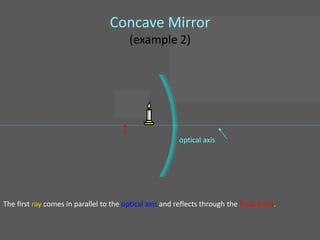
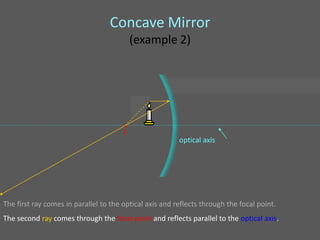
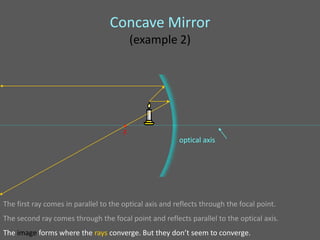
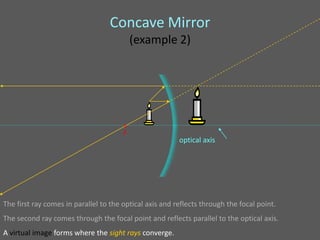
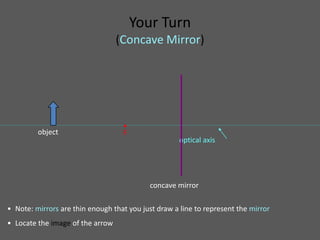
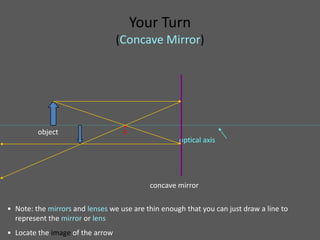
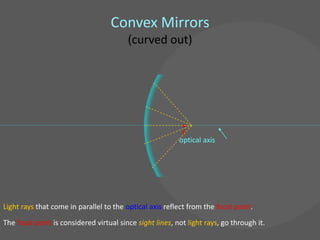
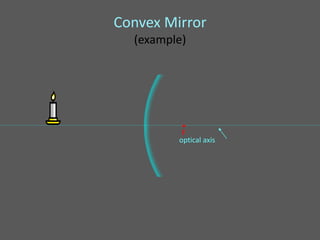
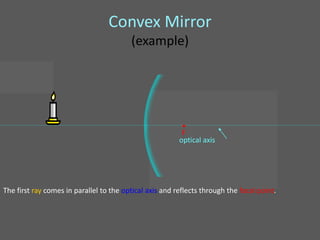
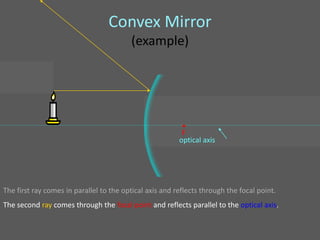
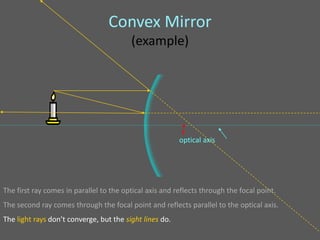
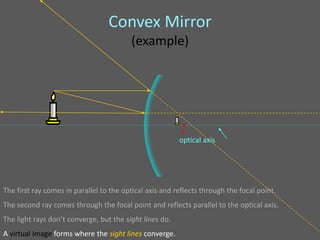
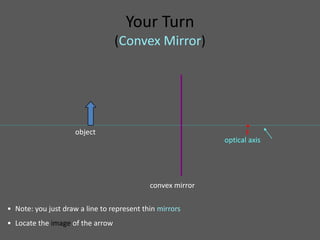
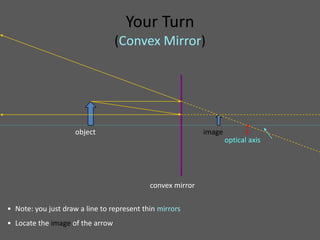
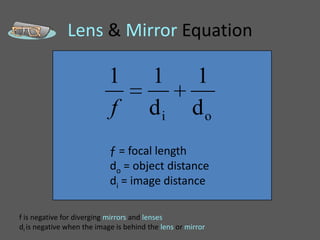
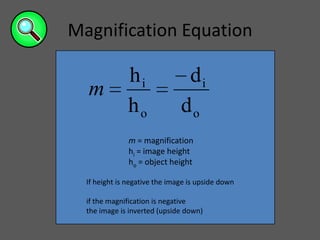
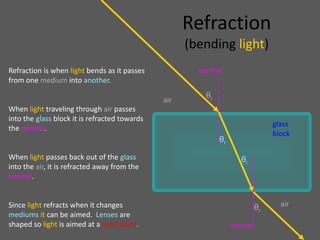
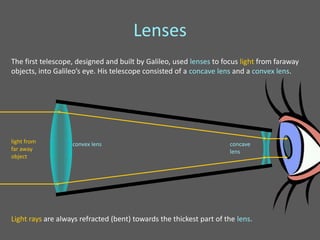
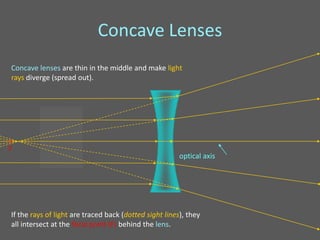
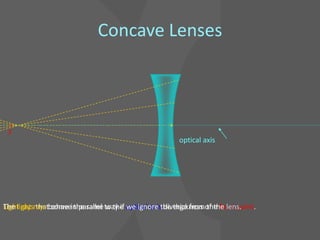
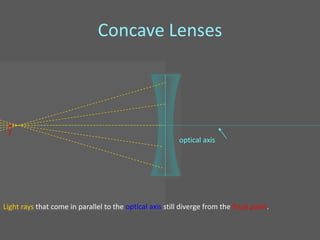
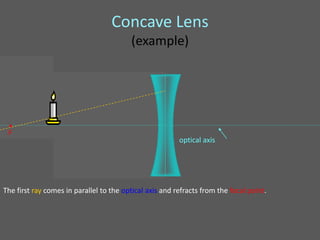
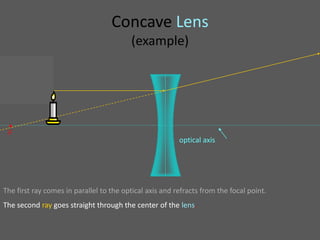
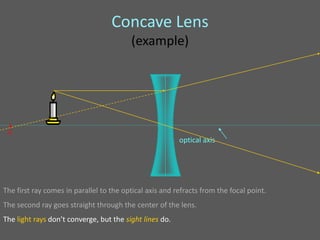
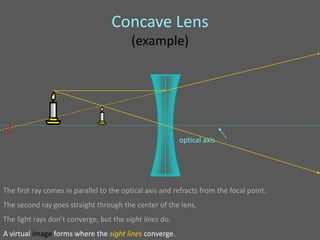
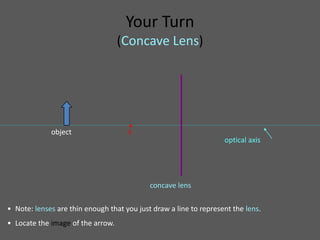
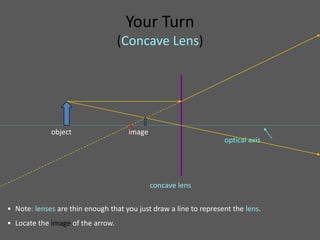
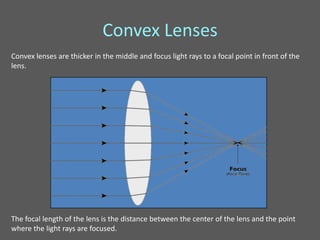
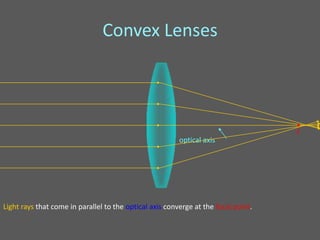
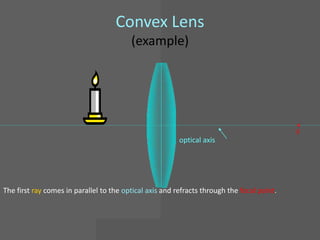
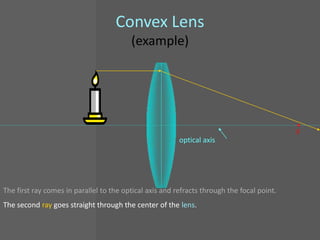
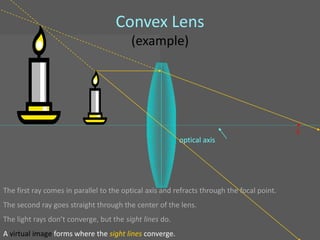
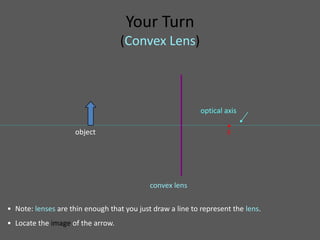
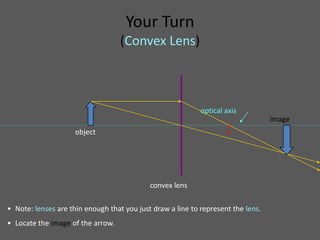
This document provides an overview of geometric optics, including reflection, mirrors, refraction, and lenses. It discusses how light rays reflect off mirrors according to the law of reflection, forming real images with plane mirrors and virtual images with spherical mirrors, whether concave or convex. Concave mirrors bring parallel rays to a focus at their focal point, while convex mirrors cause parallel rays to appear to diverge from a virtual focal point.