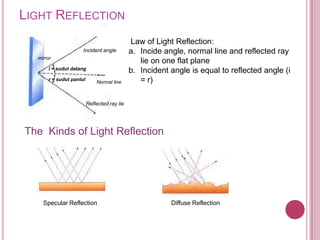
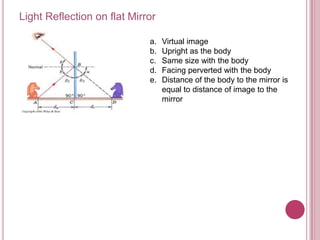
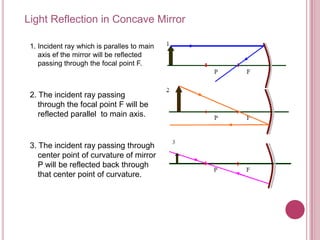
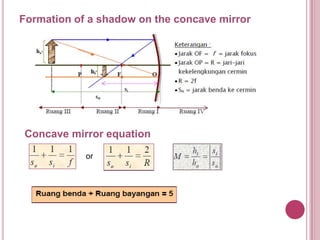
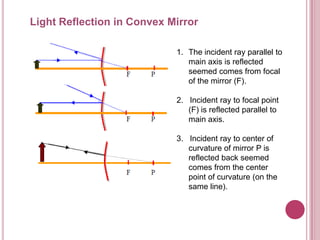
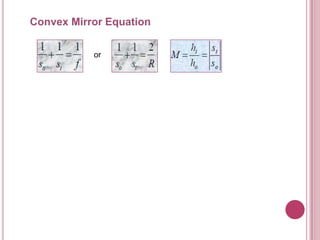
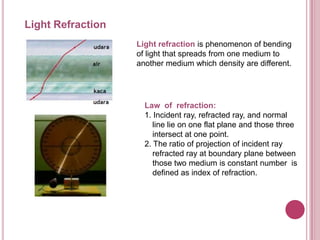
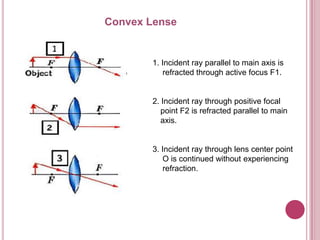
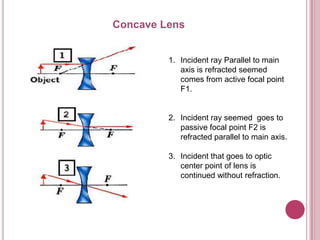
The document discusses properties of light and optics. It explains that light is an electromagnetic wave that can travel through a vacuum. It then covers the laws of reflection, including that the incident angle equals the reflection angle. Mirror image properties are described for flat, concave, and convex mirrors. Refraction and lens image formation are also covered, including the use of lens equations and examples of image distances and magnifications.