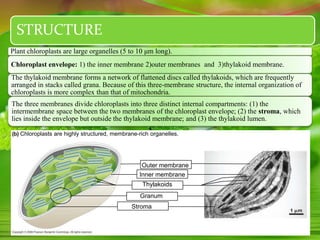
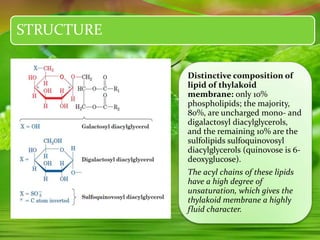
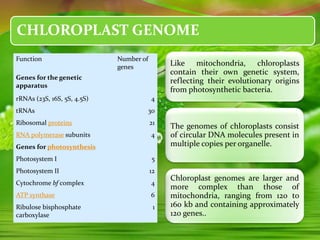
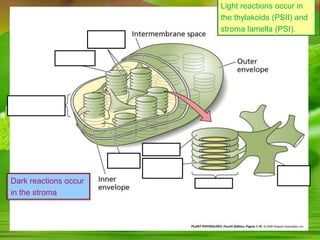
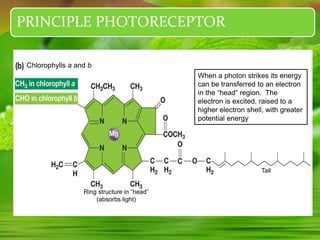
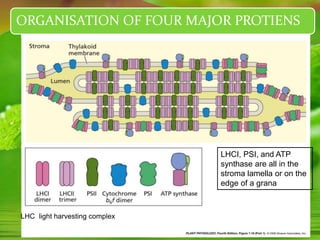
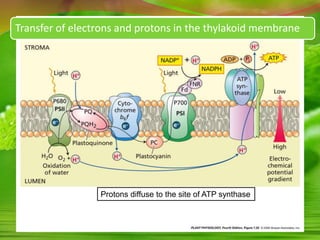
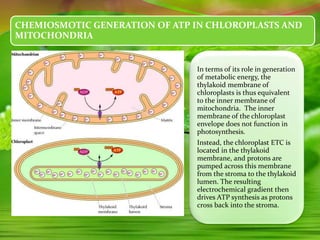
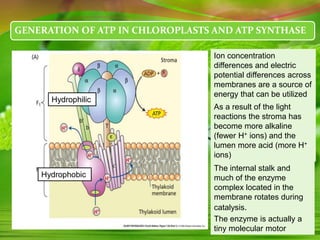
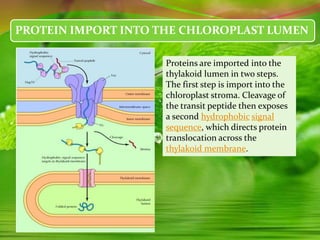
Chloroplasts, essential organelles for photosynthesis in plants and eukaryotic organisms, are complex structures composed of three membranes that create distinct internal compartments. They contain their own circular DNA, which encodes proteins necessary for photosynthesis, including the enzyme ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase (rubisco). Photosynthesis in chloroplasts occurs in two phases: light reactions in the thylakoid membrane and dark reactions in the stroma, with ATP synthesis driven by an electrochemical gradient created during these processes.