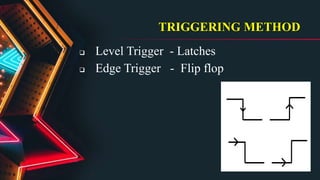
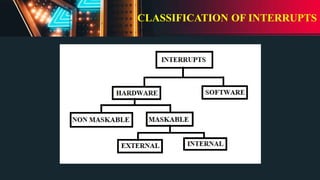
This document describes the components and software used in a microwave oven embedded system project. It includes a microcontroller, matrix keypad, 7-segment display, cooler fan, digital keyboard, LEDs, relay, reset button, buzzer, heater, LCD, and potentiometer. The document discusses how these components are interfaced with the microcontroller and the software programs used, including a host PC, target PIC microcontroller, and MPLAB X IDE compiler. It also provides details on programming concepts like interrupts, timers, triggering methods, and interfacing the keypad, LEDs, LCD, and other components with the microcontroller.