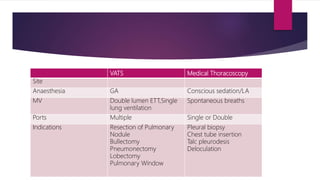
Thoracoscopy was developed in the early 1900s to break adhesions in tuberculosis patients and diagnose pleural lesions. There are two main types - medical thoracoscopy using one or two ports, and VATS which uses multiple ports and often single lung ventilation. Thoracoscopy is used to diagnose undiagnosed pleural effusions, establish malignancy, or for pleurodesis in malignant effusions. It is also used to treat parapneumonic effusions, pneumothorax by treating bullae or creating pleurodesis, and can remove retained blood clots in haemothorax. Complications are generally low but include prolonged air leak, bleeding, pneumonia and empyema.