Embed presentation



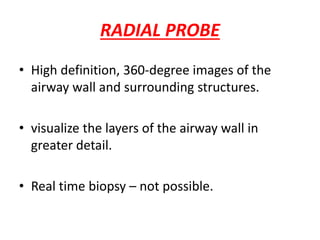
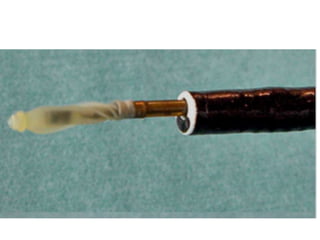

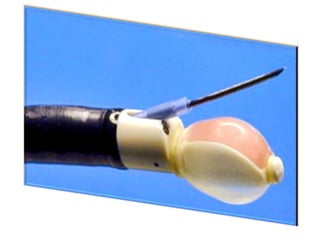
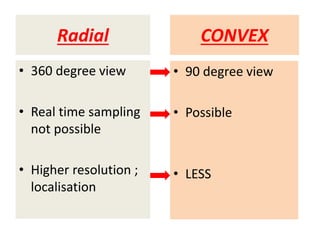



EBUS is a bronchoscopic technique that uses ultrasound to visualize structures within the airway wall, lung, and mediastinum. It uses radial or convex probes. Radial probes provide 360-degree images of the airway wall and surrounding structures at high definition but do not allow for real-time biopsy. Convex probes have a 90-degree angle of view and allow for real-time EBUS-guided biopsy. EBUS is used to diagnose and stage lung cancers and mediastinal masses and can guide procedures like airway stenting. It has advantages of being minimally invasive and having a high diagnostic yield.













