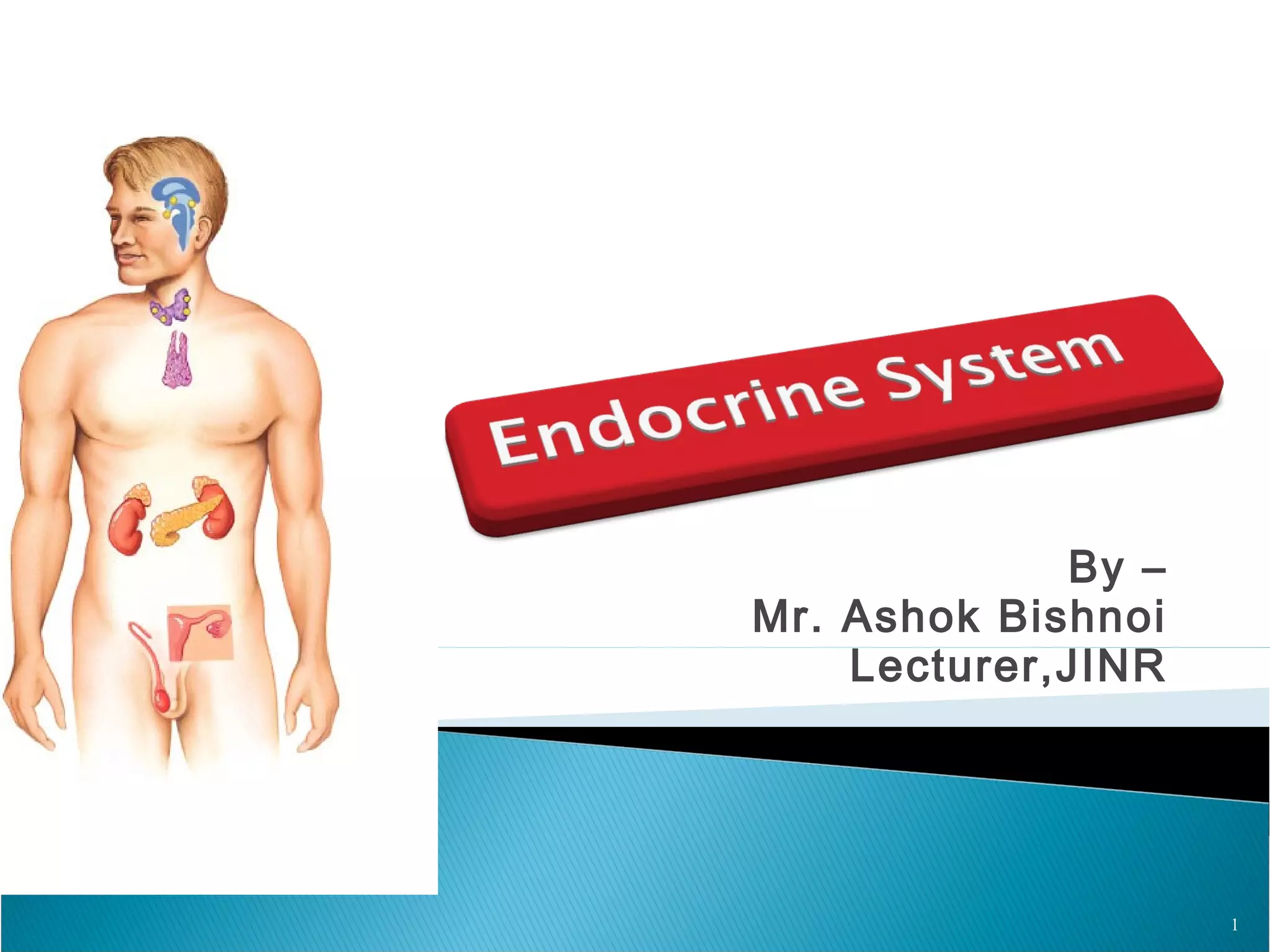
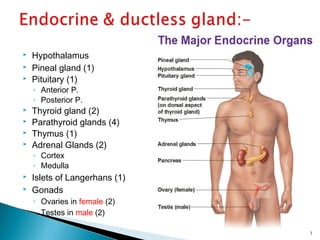
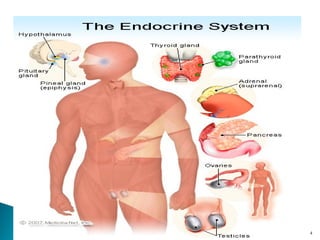
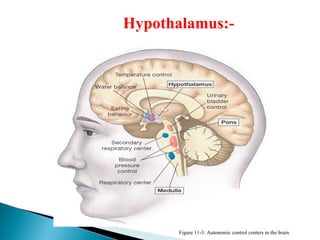
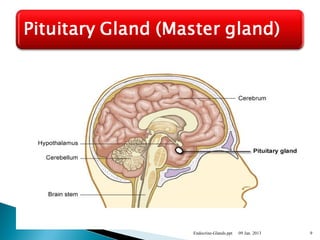
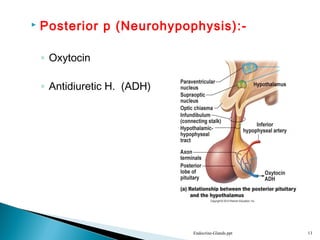
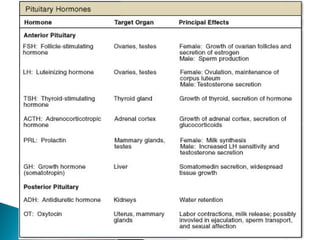
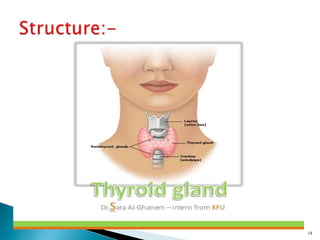
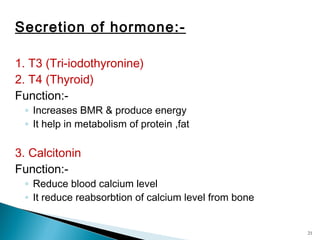
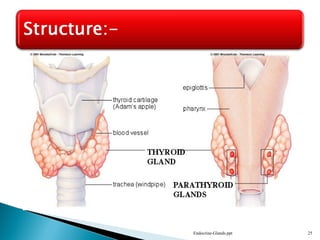
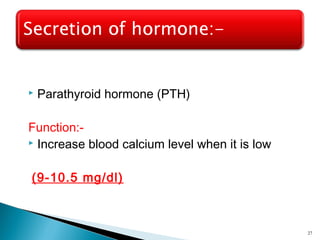
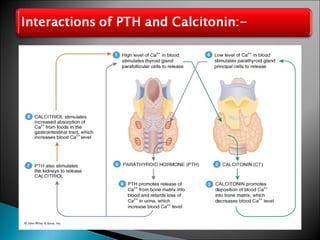
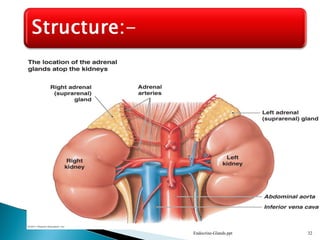
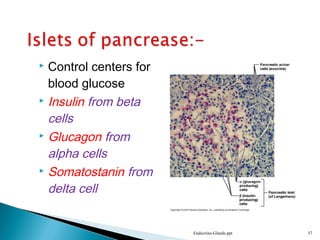
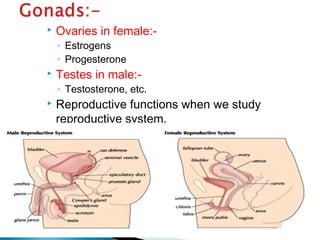
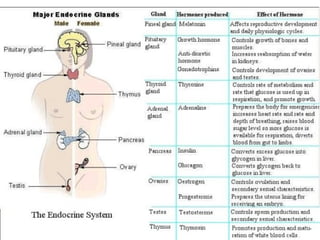
This document discusses the major endocrine glands in the human body, including their locations, secretions, and functions. It describes the hypothalamus and pituitary gland which regulate other endocrine glands. The thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal glands, pancreas, gonads and thymus are also summarized in terms of their hormone productions and roles in metabolism, growth, and development.