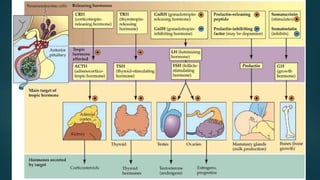
This document provides an overview of the major endocrine glands and their functions. It describes how the hypothalamus and pituitary gland regulate hormone production and release from other glands like the thyroid, parathyroid, adrenals, gonads and more. Key hormones are identified for each gland along with their roles in processes like metabolism, growth, reproduction and maintaining homeostasis. Histology slides are also included to illustrate the cellular structure of the different endocrine tissues.