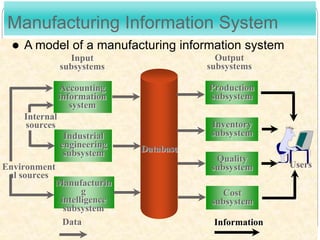
This document discusses the application of management information systems (MIS) in the manufacturing sector. It outlines the goals of an MIS, which include providing managers with information to help regular operations, control, organize and plan better. It then describes the typical inputs and outputs of an MIS and how MIS can help different functional areas like finance, manufacturing, marketing, etc. Finally, it discusses how MIS supports various management goals like financial management, human resource management, materials management, production management and marketing management in a manufacturing organization.