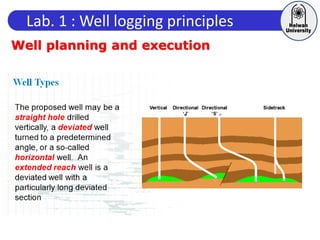
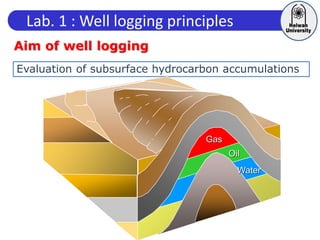
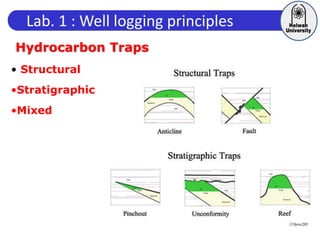
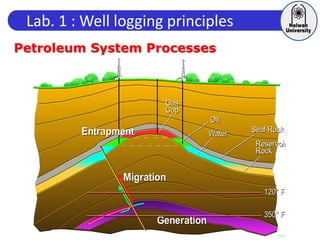
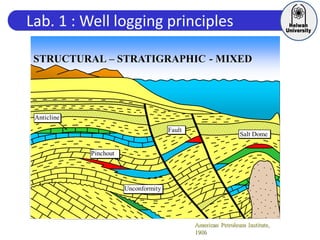
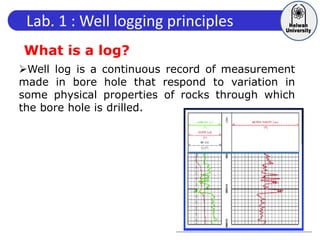
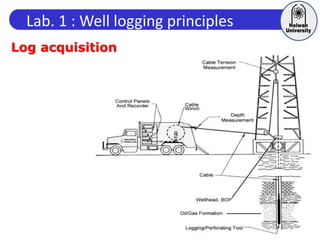
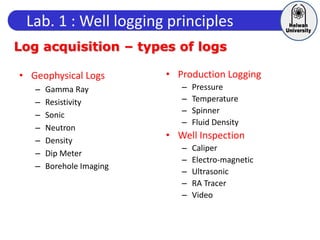
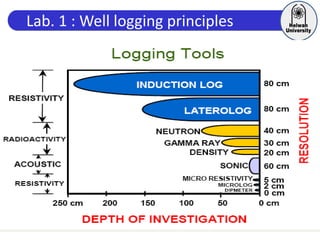
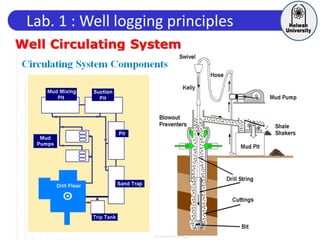
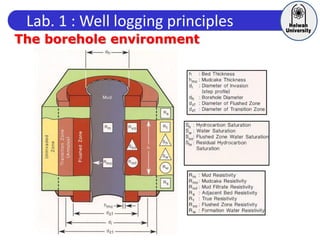
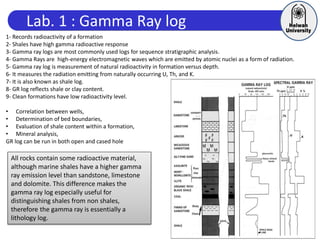
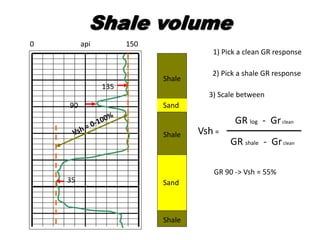
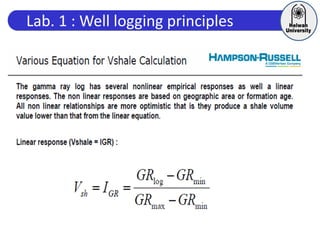
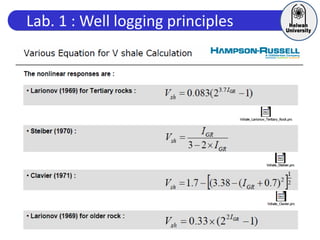
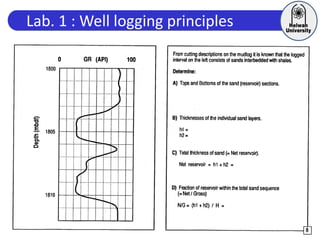
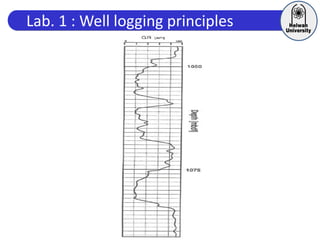
This document discusses principles of well logging. It describes how well logging aims to evaluate subsurface hydrocarbon accumulations through measuring properties in boreholes. It outlines different types of hydrocarbon traps and elements in a petroleum system. It then explains what a well log is and different types of logs used, including gamma ray, resistivity, sonic, and neutron logs. Gamma ray logs specifically measure natural radioactivity to distinguish between lithologies like sandstone and shale. The document provides details on interpreting gamma ray logs and calculating shale volume from gamma ray readings.