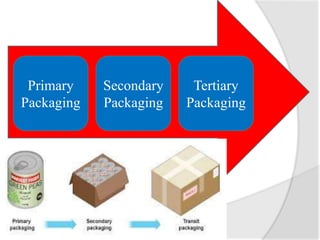
This document discusses different types of packaging used in product distribution. It describes primary, secondary, and tertiary packaging. Primary packaging makes direct contact with the product and includes shrink wrap, vacuum packaging, bubble wrap, and preservation packaging. Secondary packaging protects the primary packaging from damage and includes crates, pallets, and shock mounts. Tertiary packaging is for bulk handling, storage, and shipping and does not include shipping containers. Common packaging materials include plastic, metal, cardboard, glass, and foam.