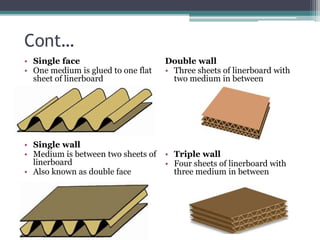
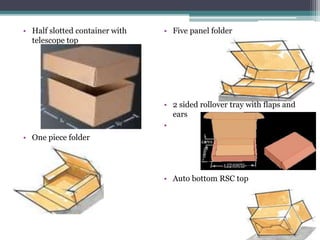
Corrugated fiberboard is made from three components - two linerboards bonded to either side of fluted corrugating medium. It provides cushioning and protection for packaged items. Different flute types provide varying strengths for packaging uses like canned goods, furniture or consumer goods. Quality is ensured through tests like flat crush resistance, bursting strength and puncture resistance. Recycling of corrugated fiberboard involves collection, sorting, shredding and reprocessing into new fiber.