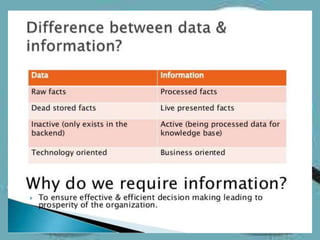
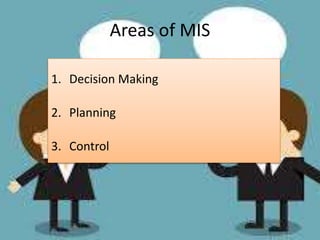
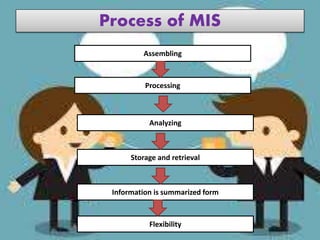
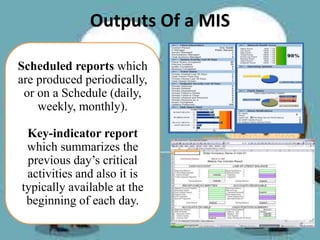
Management Information Systems (MIS) are designed to provide timely, accurate, and relevant information to managers to help them make effective decisions. An MIS involves collecting data from various business functions, processing and analyzing the data, and distributing reports to managers. The goal of an MIS is to improve decision-making, planning, and organizational control. It provides managers with operating, status, resource, and other types of information on a scheduled basis, on demand, or when exceptions occur.