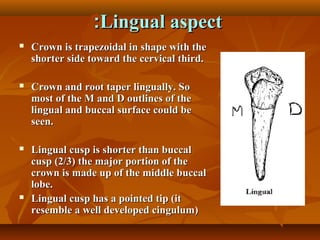
The document provides details on the chronology, characteristics, and anatomical features of the mandibular first premolar tooth. It discusses the tooth's development timeline, similarities to other teeth, and descriptions of its features from various aspects including buccal, lingual, mesial, distal, and occlusal views. Key points covered in the summary include the tooth's eruption timeline between ages 10-12 years, similarities in shape to both the mandibular canine and second premolar, and having multiple cusps visible on its occlusal surface.