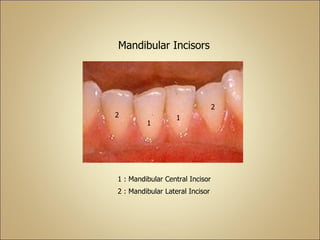
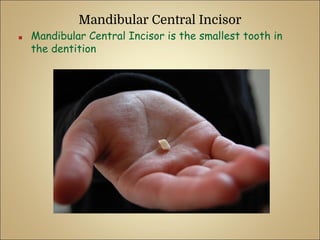
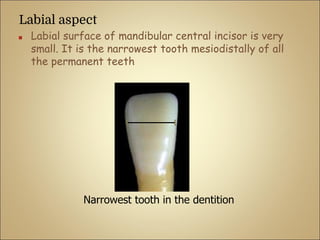
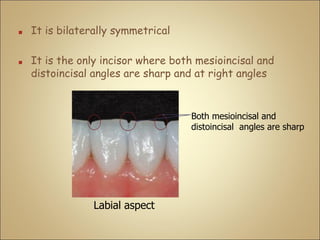
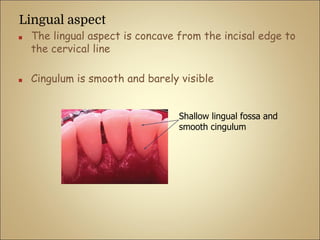
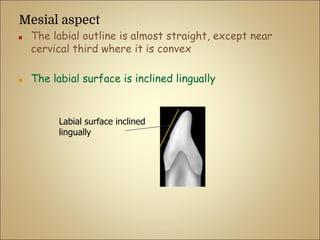
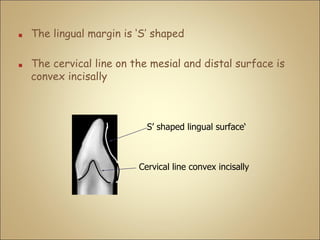
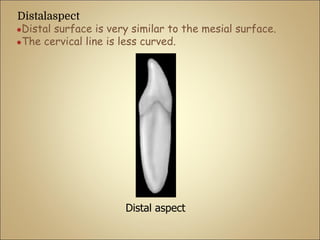
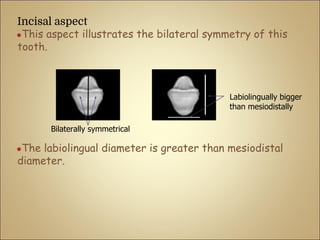
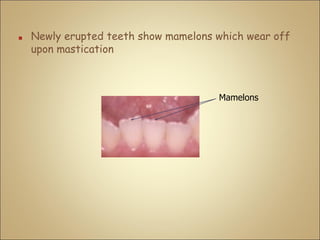
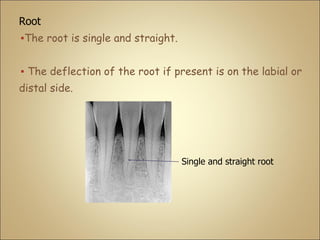
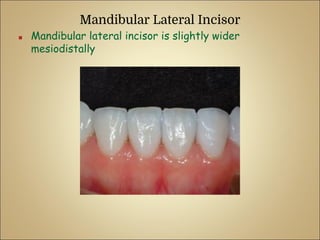
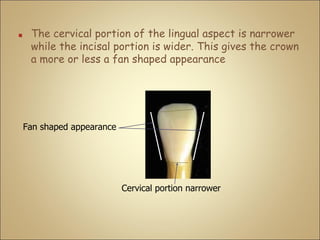
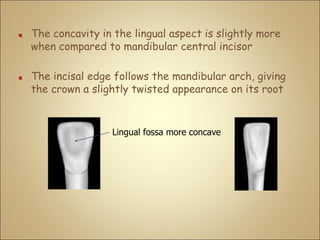
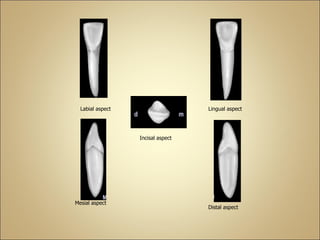
This document discusses the morphology and dimensions of the mandibular central and lateral incisors. It describes the labial, lingual, mesial, distal, and incisal surfaces of the central incisor and provides its average dimensions. The central incisor is the smallest tooth with a narrow labial surface and bilaterally symmetrical sharp mesioincisal and distoincisal angles. It also briefly outlines the morphology of the lateral incisor, noting it is slightly wider with a fan-shaped crown. The objectives are to identify the mandibular incisors and understand their morphology and distinguishing surfaces.