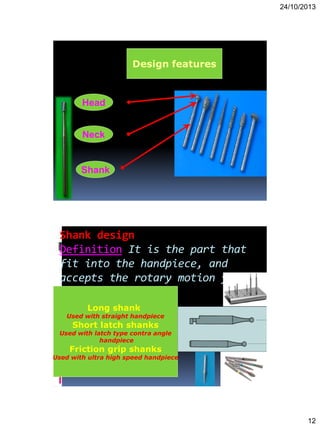
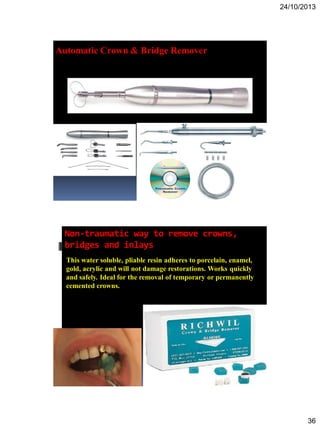
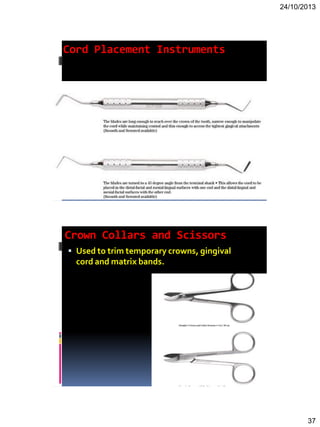
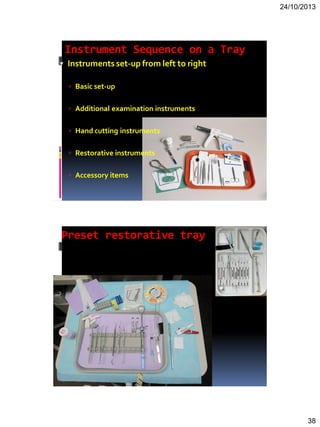
Here are the key steps in making an impression:
1. Select the appropriate tray size based on the area needing to be impressioned. Common tray types are quadrant, sectional, and full arch.
2. Apply a thin layer of impression material, like alginate or polyvinyl siloxane, to the tray.
3. Seat the loaded tray in the patient's mouth and have them close gently into maximum intercuspation. Apply gentle pressure to ensure proper seating.
4. Allow the material to set fully based on manufacturer instructions before removing the set impression from the mouth.
5. Rinse off any excess material and evaluate the impression for accuracy and completeness. Make any needed