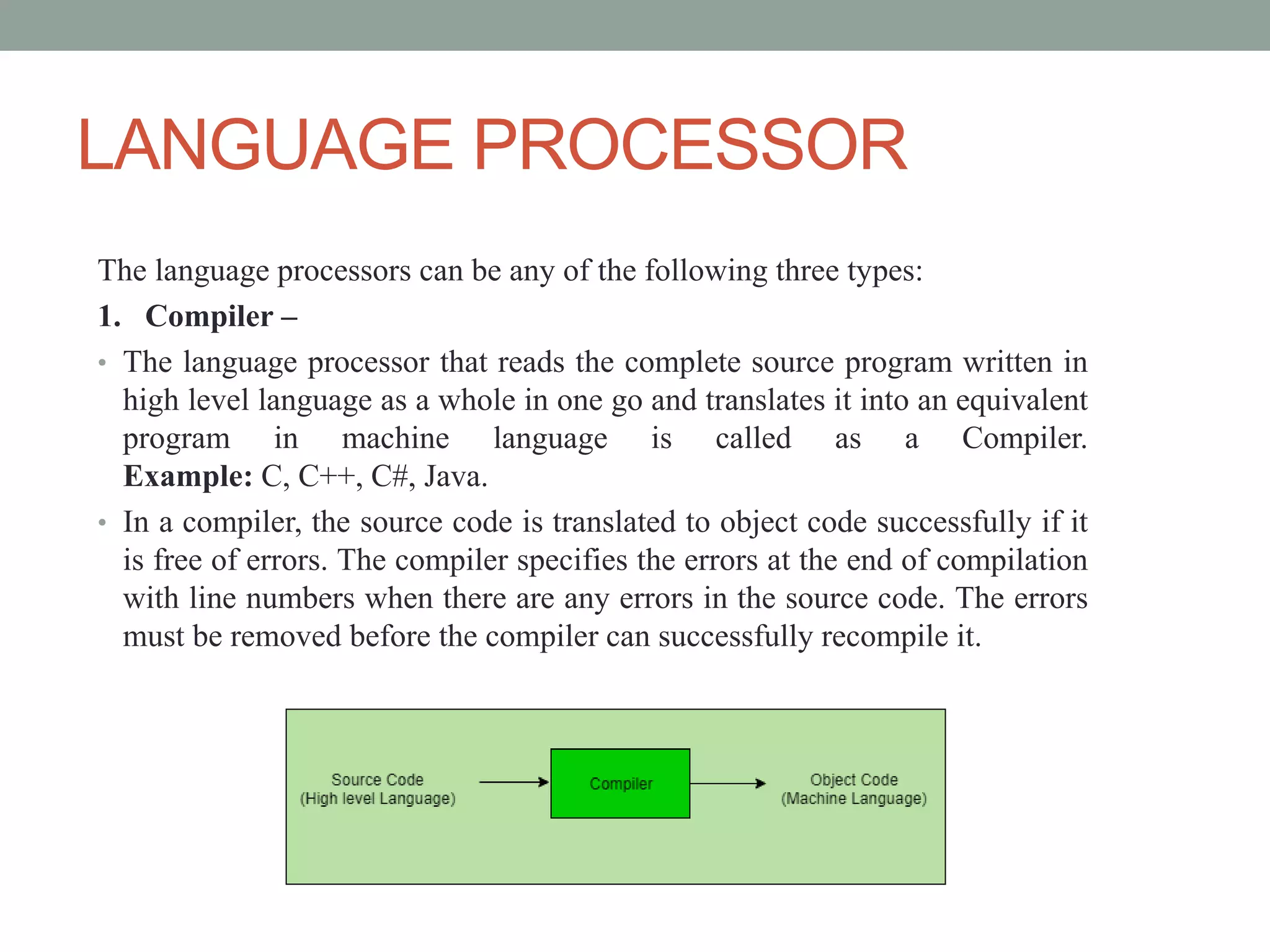
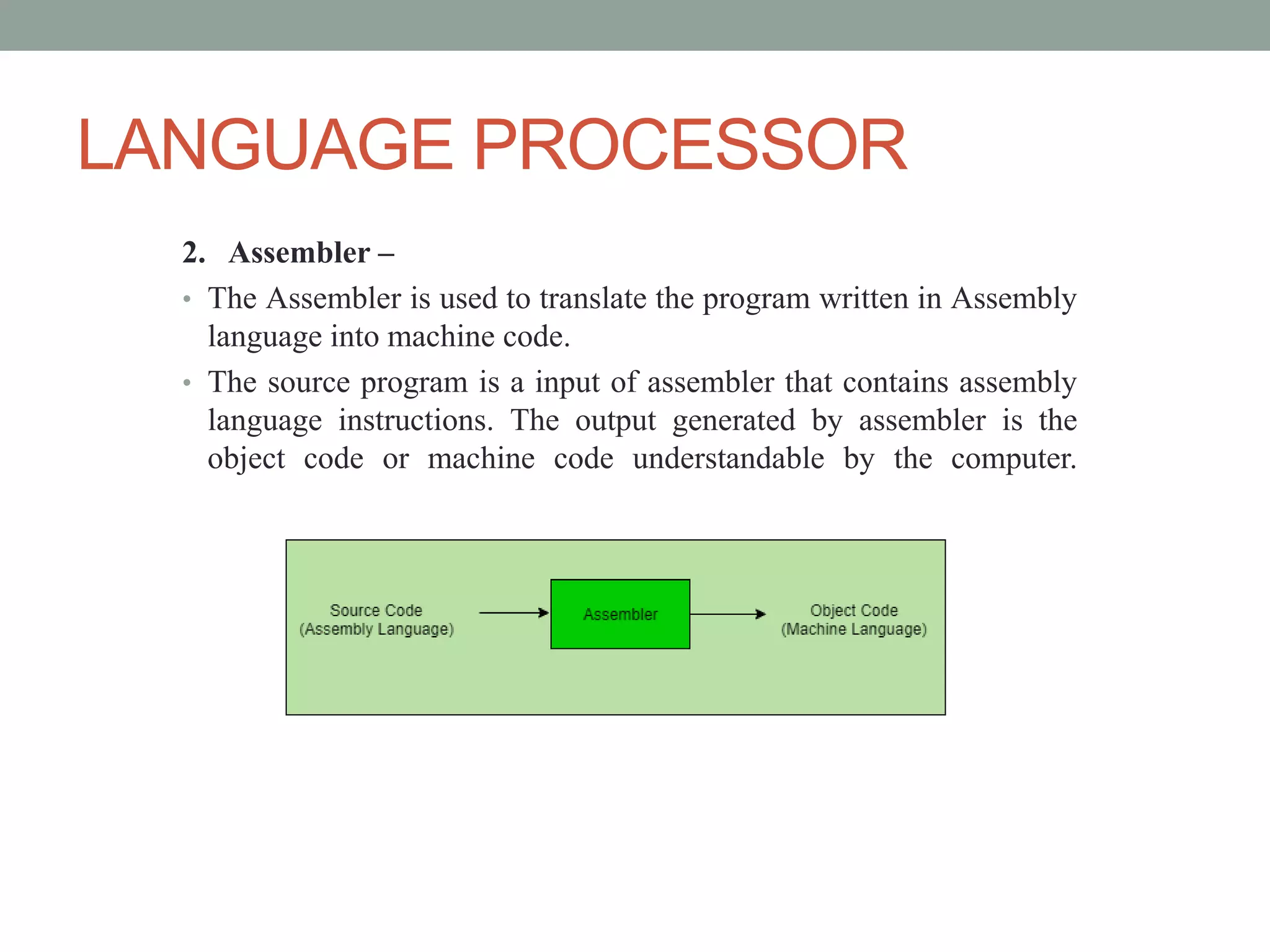
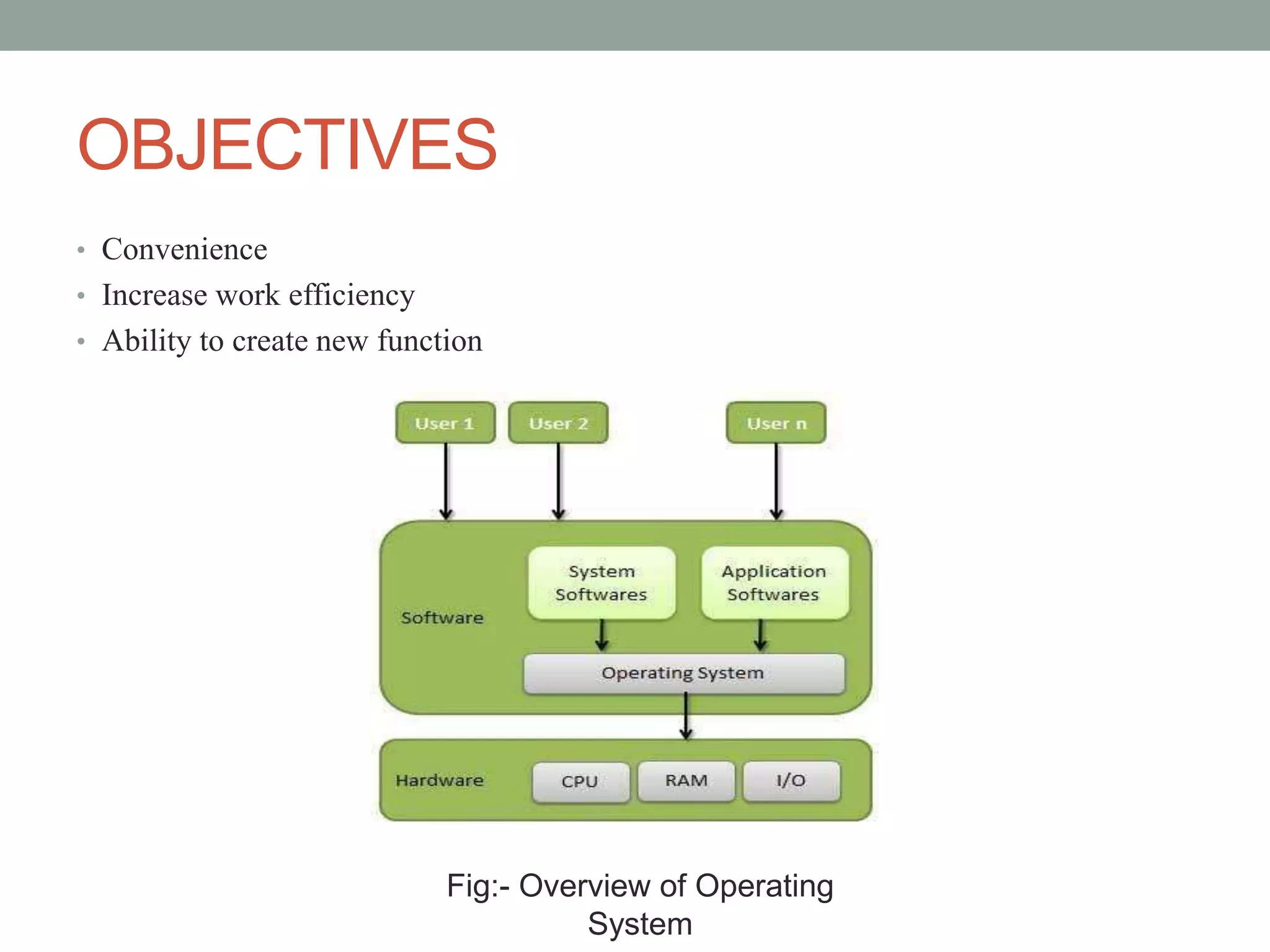
This document discusses operating systems and system software. It defines system software as programs that interface between hardware and application programs. The operating system (OS) is provided as the key example of system software, as it manages all other programs on a computer. The main types of system software discussed are operating systems, language processors, and device drivers. Language processors are further broken down into compilers, assemblers, and interpreters. Device drivers enable interaction between hardware devices and the operating system. The functions of an operating system include process management, memory management, input/output management, device management, and security management.