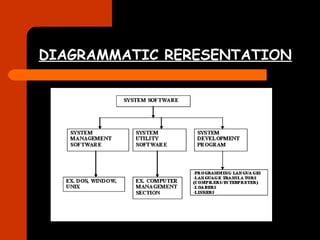
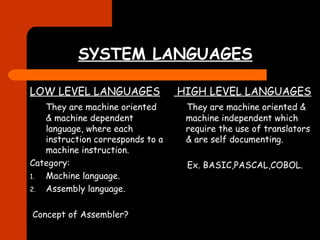
This document discusses different types of system software. It defines system software as software that operates computer hardware and provides a platform for running application software. It describes operating systems, system languages including low-level languages like machine language and assembly language and high-level languages. It also discusses translators like compilers and interpreters, loaders, linkers, and system utility software which help analyze, configure, optimize and maintain the computer.