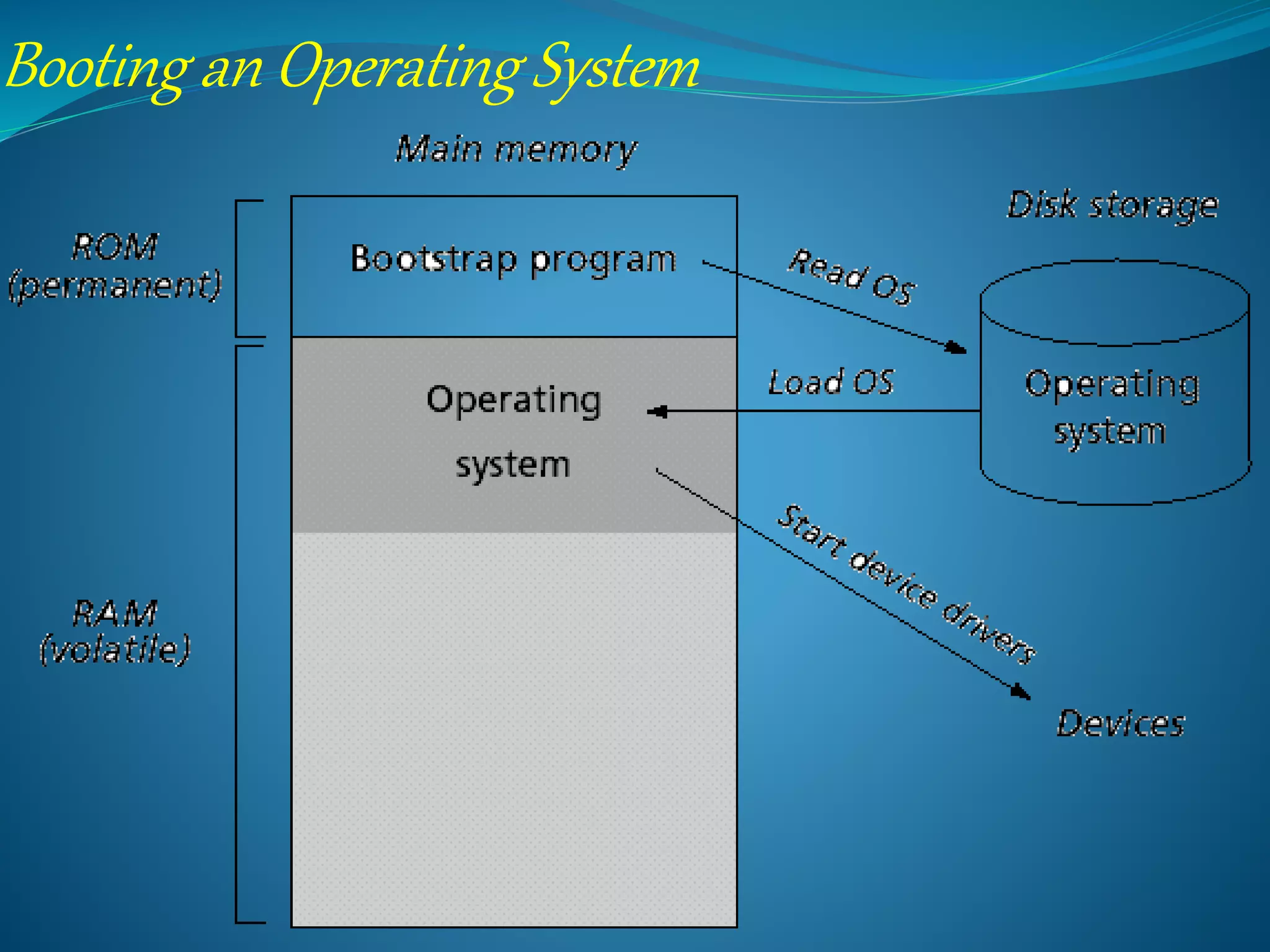
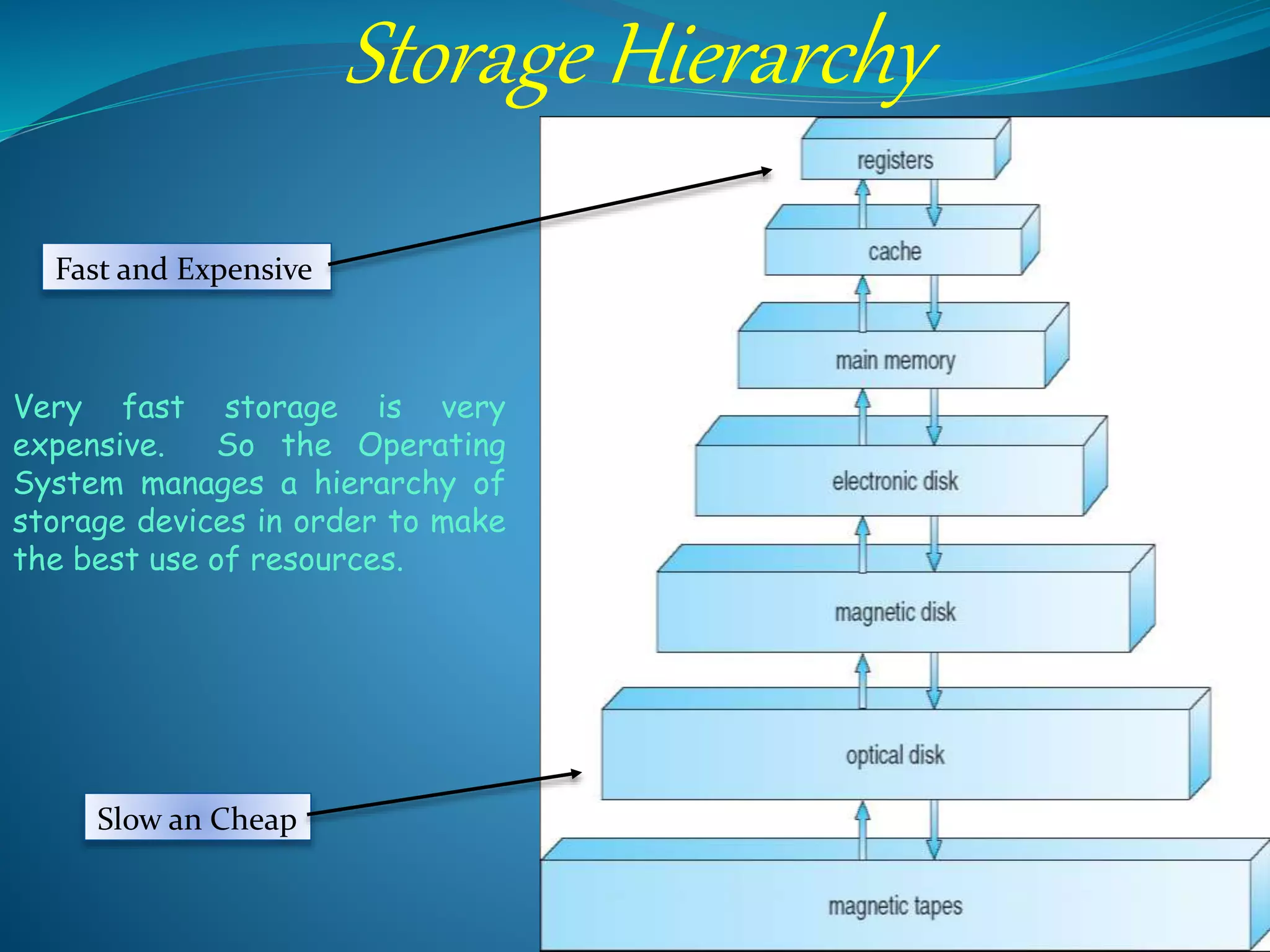
The operating system is the most important program that runs on a computer. It performs basic tasks like input/output processing and memory management. It also acts as an interface between the user and hardware. For large systems, the operating system ensures programs and users do not interfere with each other and handles security. Operating systems are classified based on attributes like whether they support single/multiple users, CPUs, tasks and threads. Examples of operating systems discussed are Windows, Linux, and Android. Their advantages and disadvantages are provided.