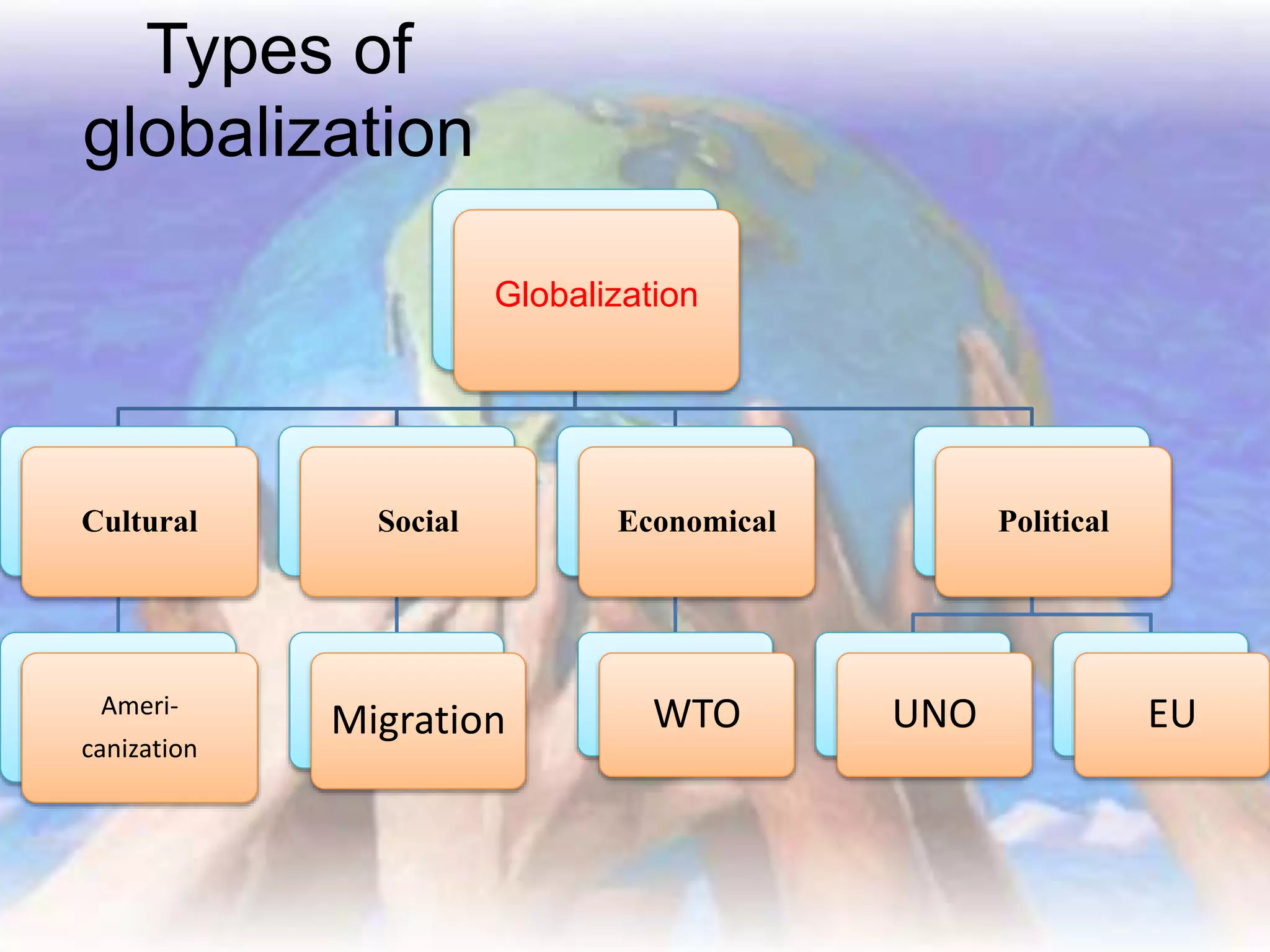
This document discusses various aspects of globalization including definitions, types, and key organizations. Globalization refers to the increasing interconnectedness of markets around the world as investment funds and businesses move beyond domestic markets. Types of globalization include cultural, social, economic, political, and others. Key topics covered include Americanization, migration, the World Trade Organization (WTO), United Nations (UNO), and European Union (EU).