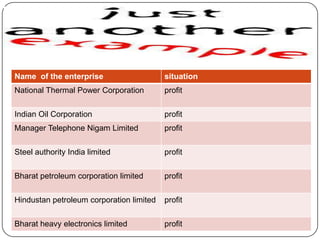
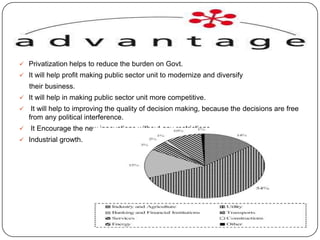
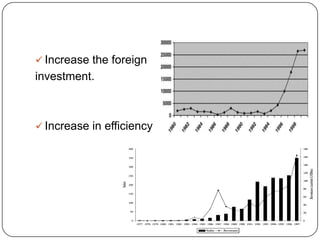
The document discusses India adopting the policy of liberalization, privatization and globalization (LPG) in 1991 to reform its economy. It introduced 3 key changes: 1) Liberalizing trade and industry, removing licenses and tariffs. 2) Extending privatization of public sector companies. 3) Globalizing the economy by opening it to foreign investments and trade. The reasons for LPG were issues like high government debt, inefficiencies, and losses in public sector firms. Liberalization deregulated industry and trade. Privatization sold public companies to private owners. Globalization integrated India's economy globally through foreign investments and trade. The goal of LPG was to make India's economy more efficient and competitive through market-oriented