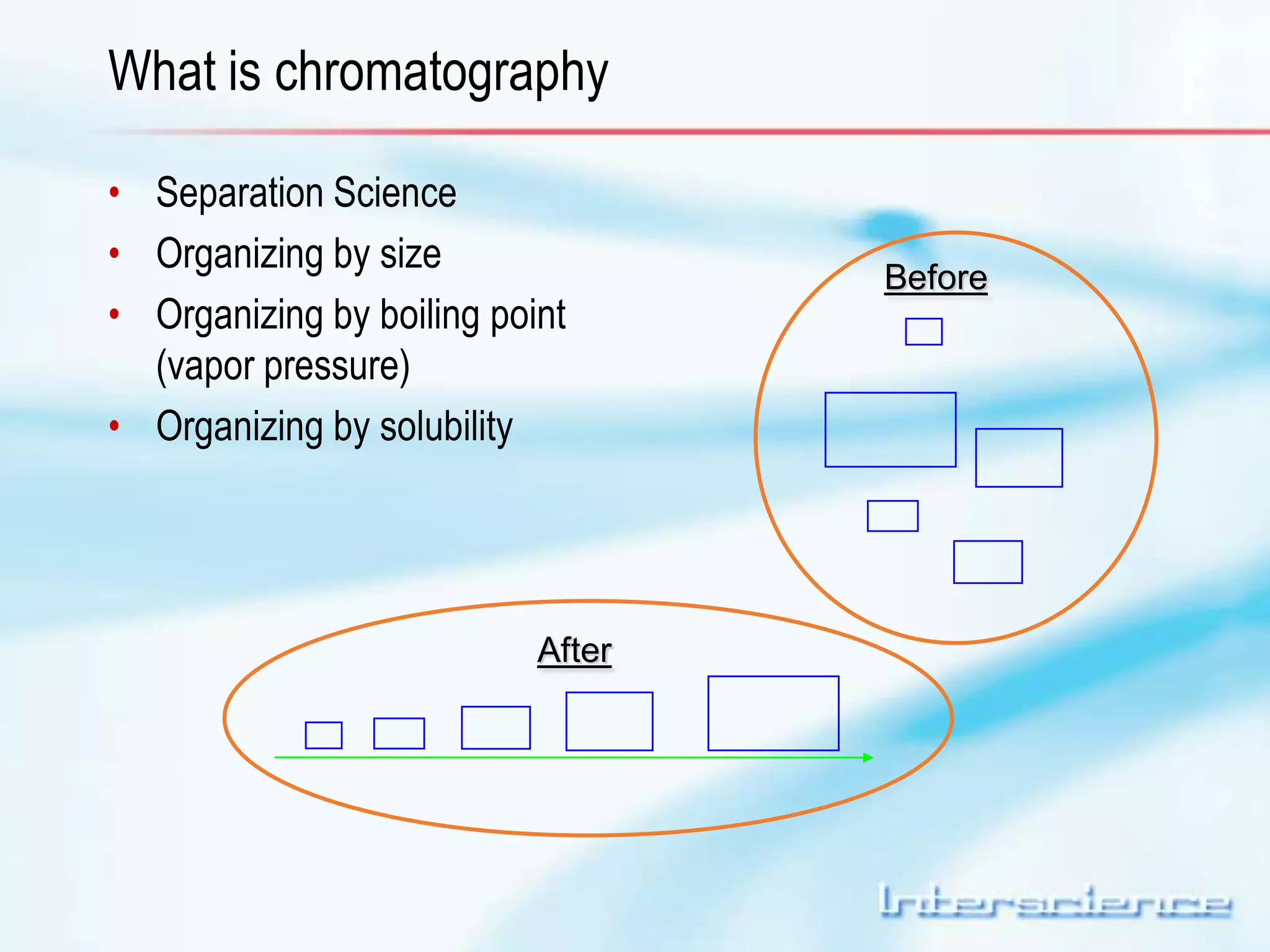
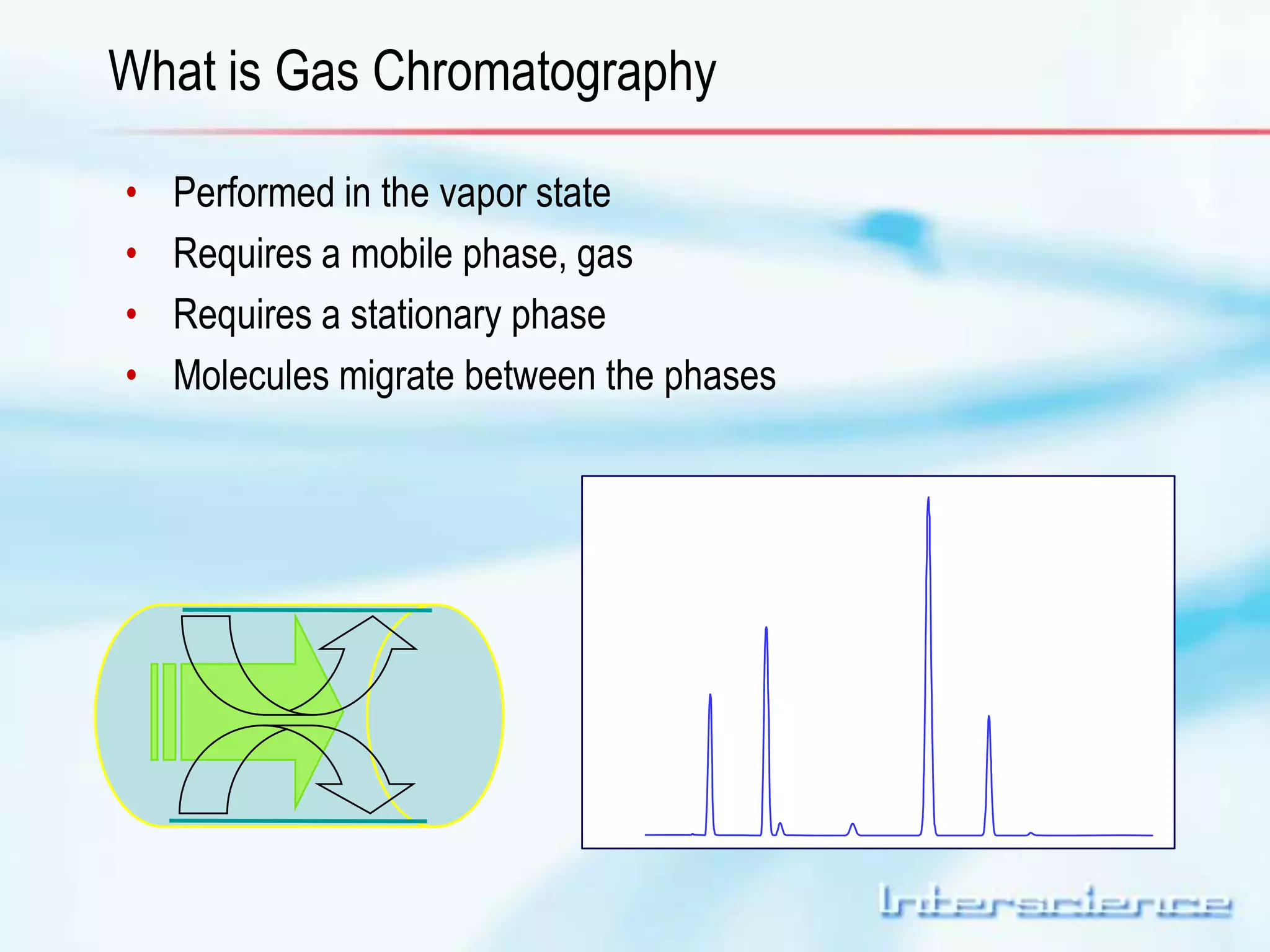
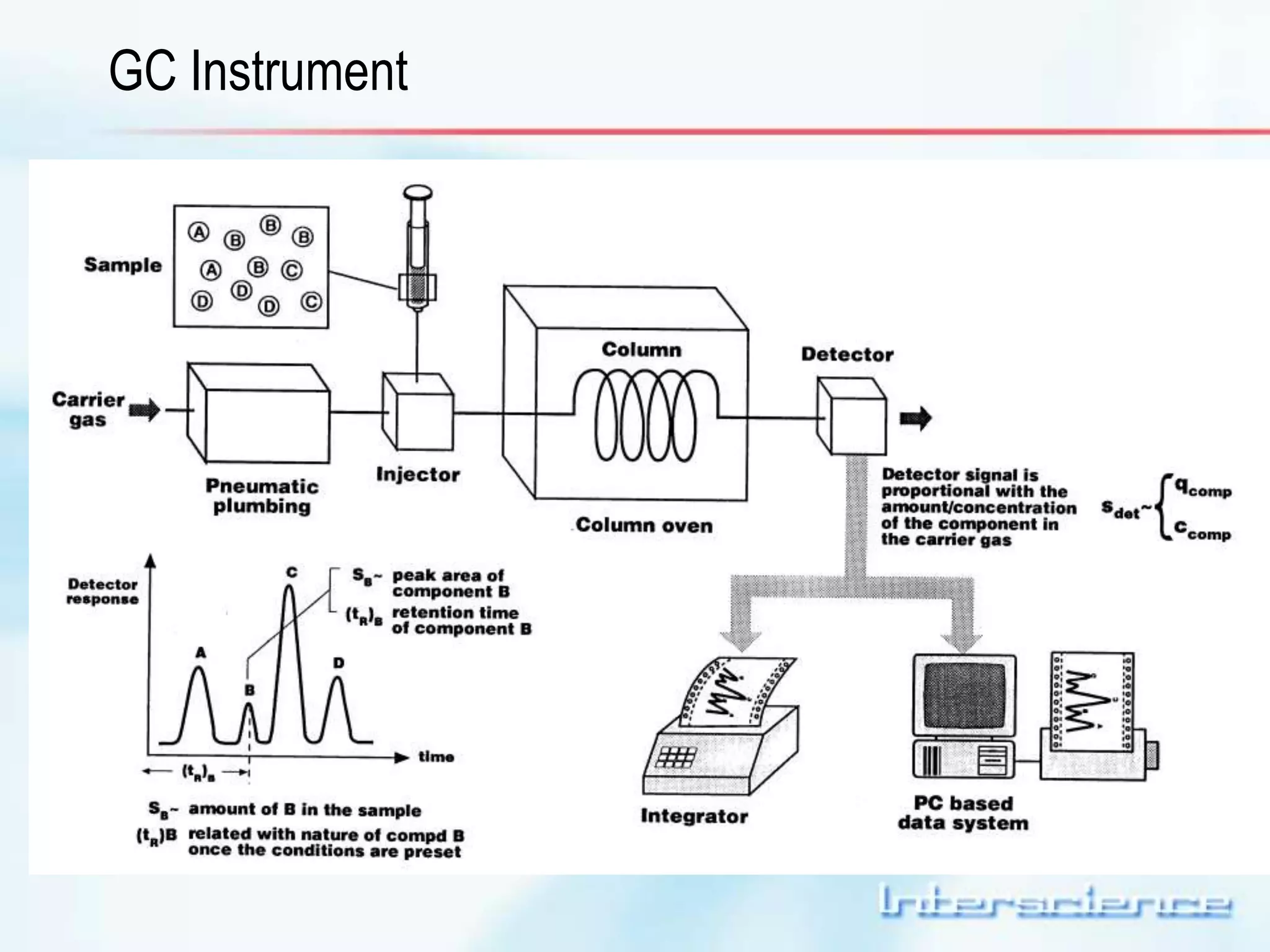
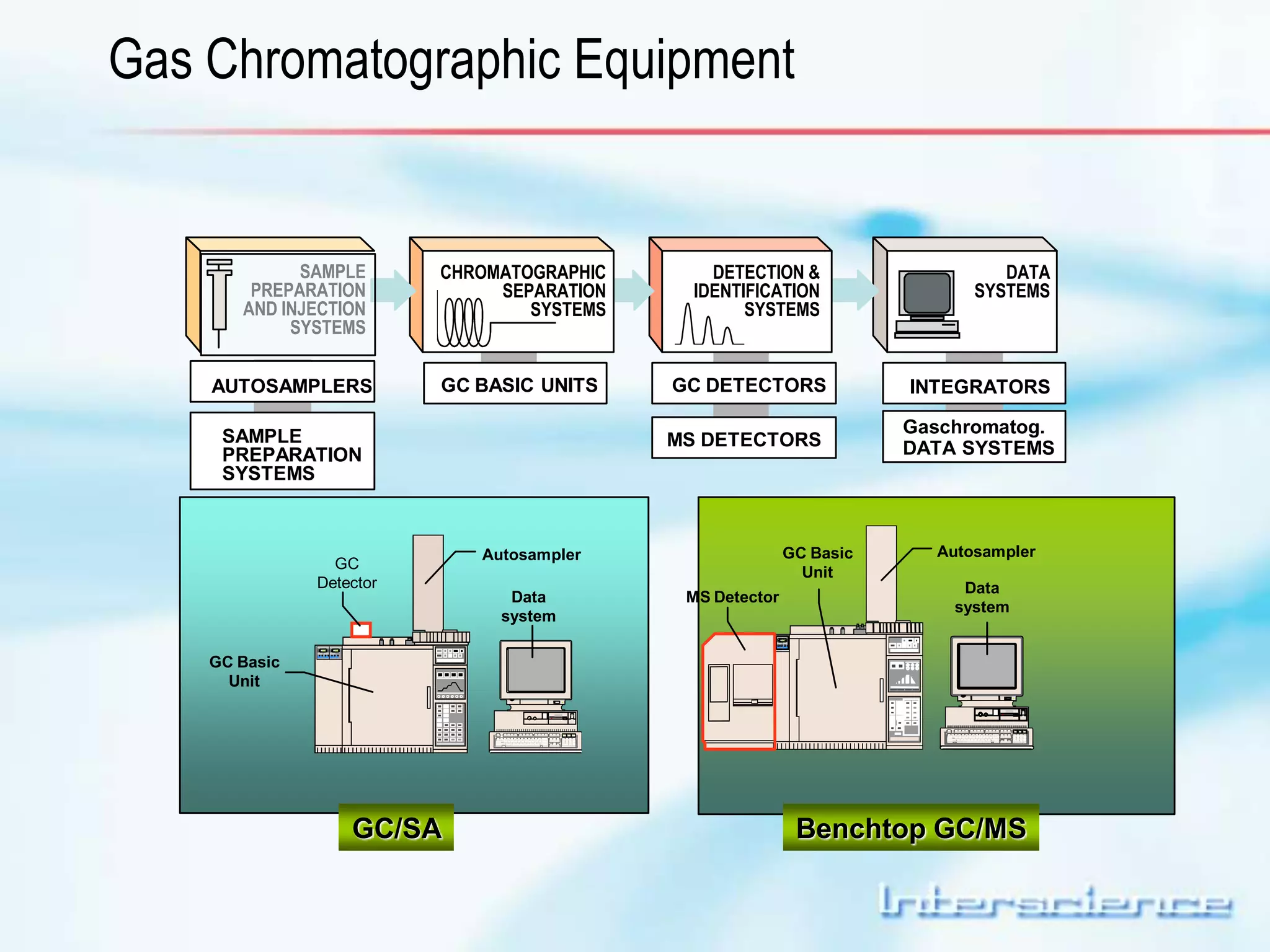
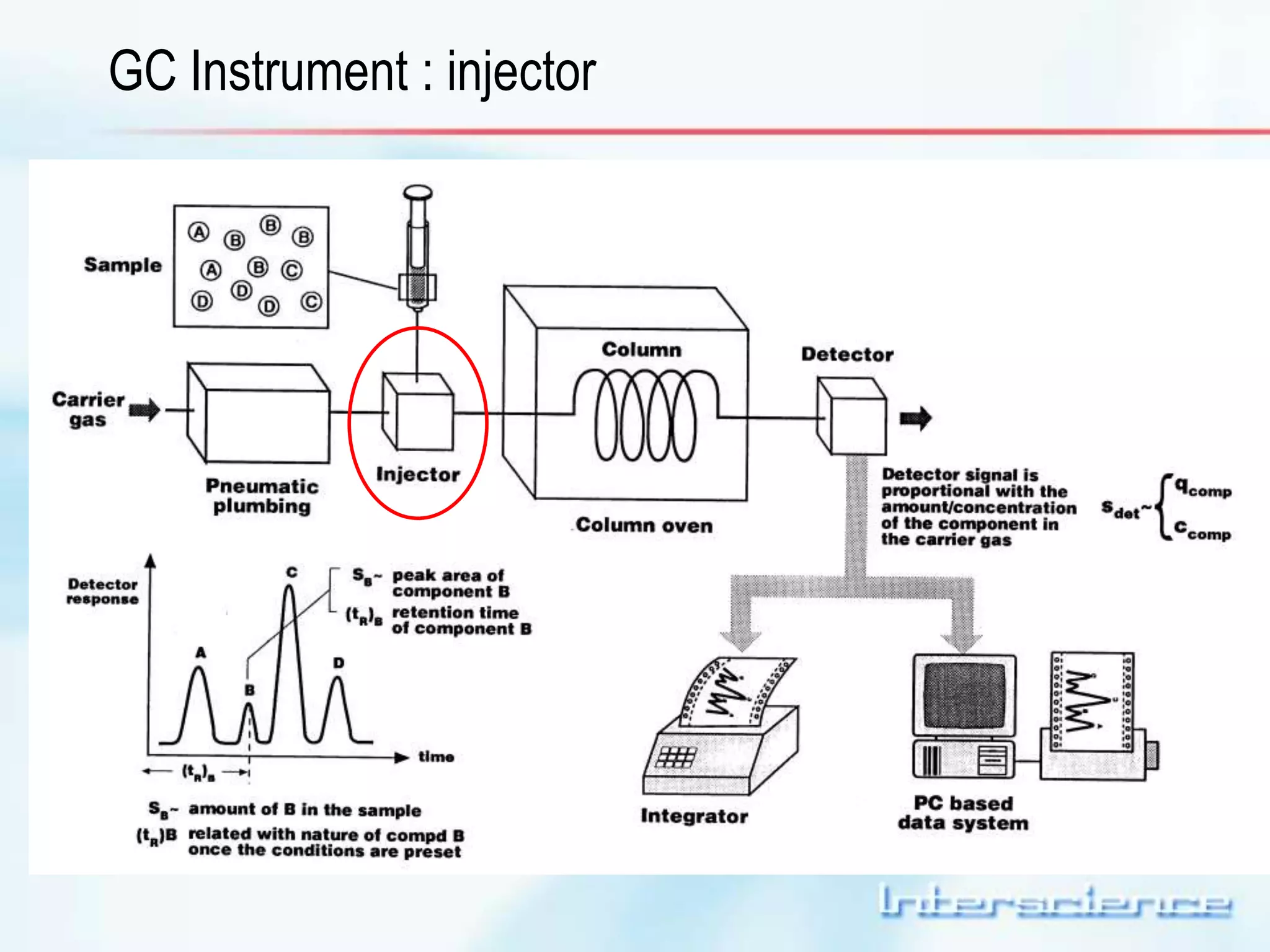
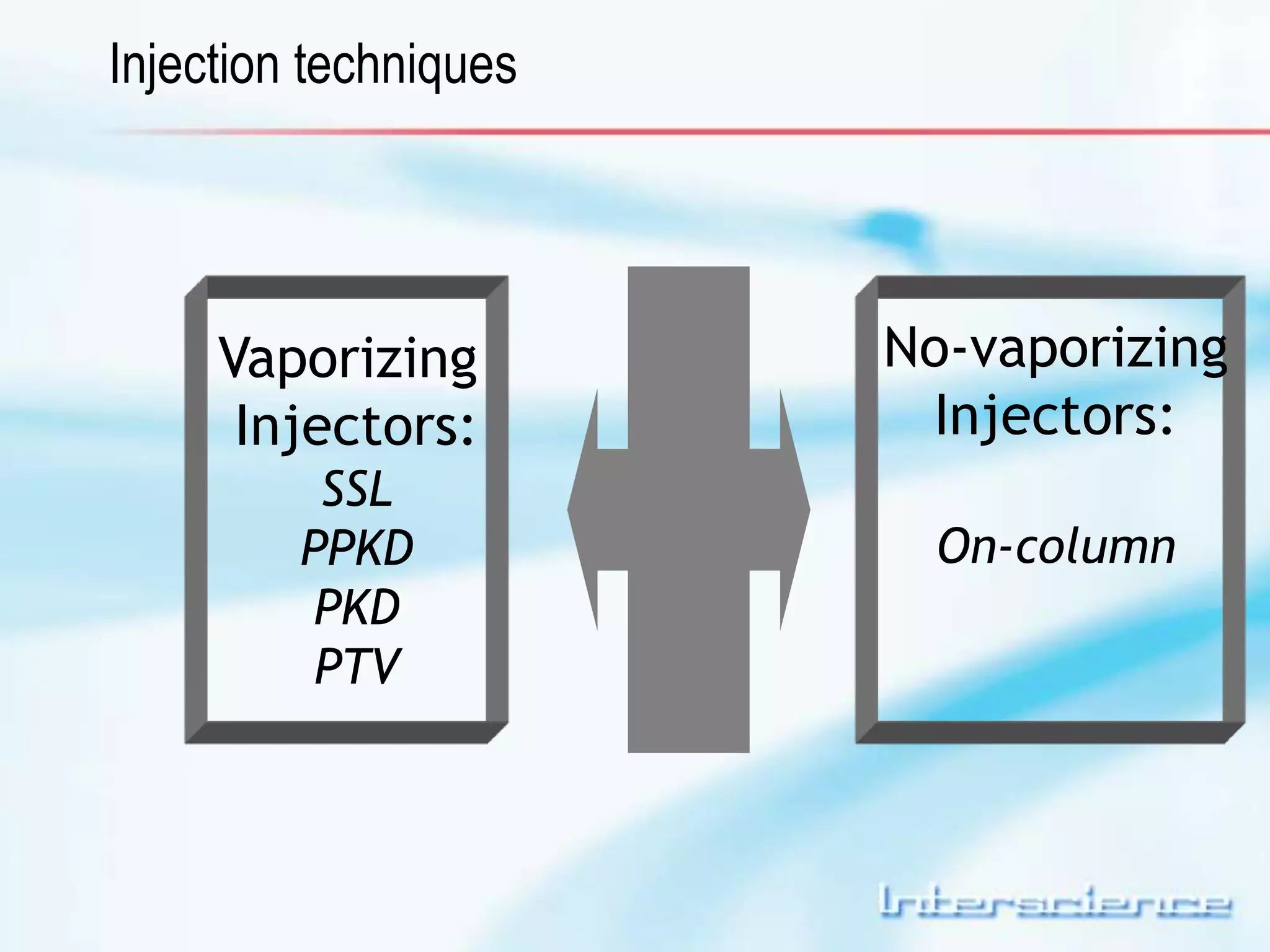
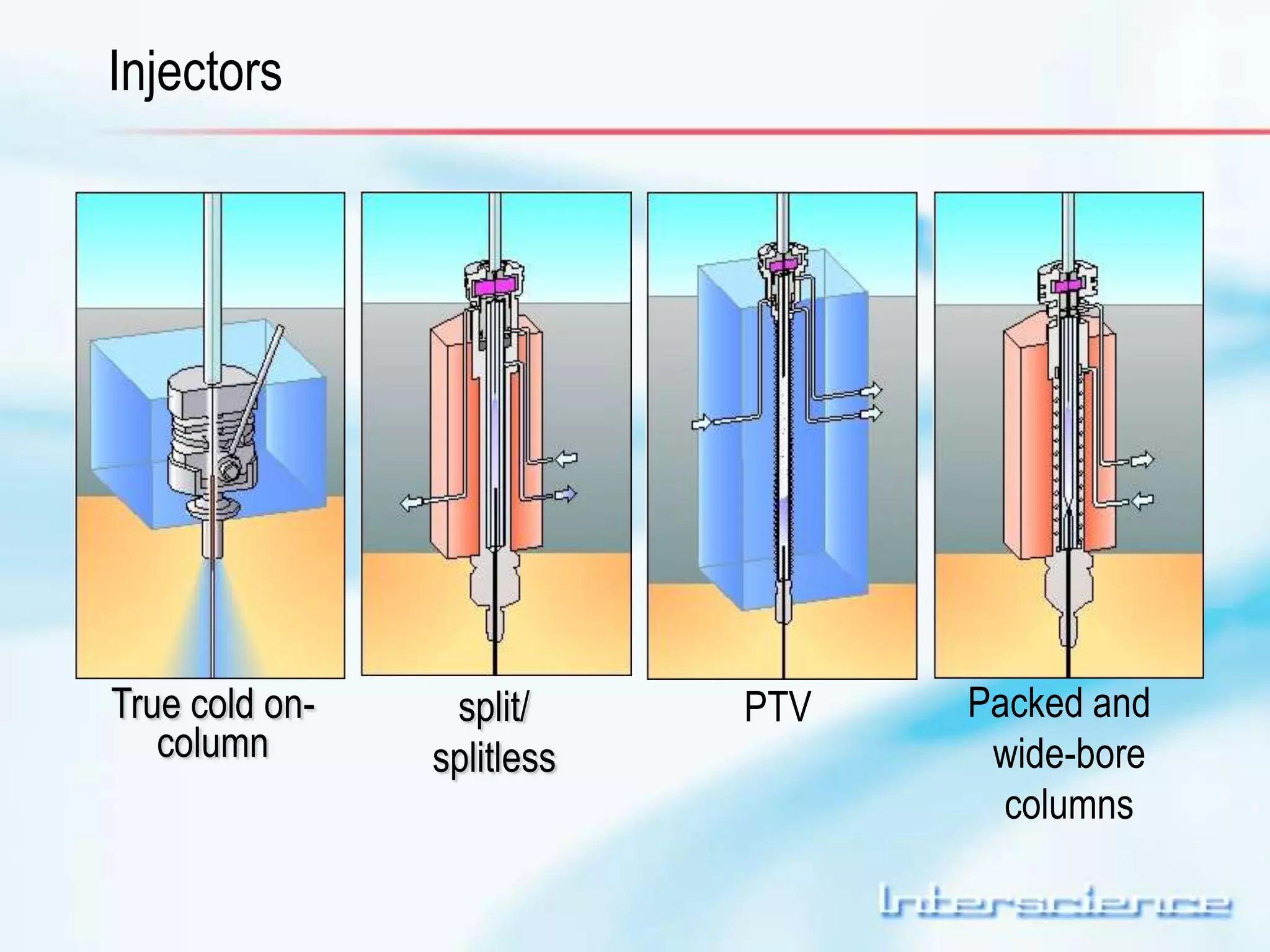
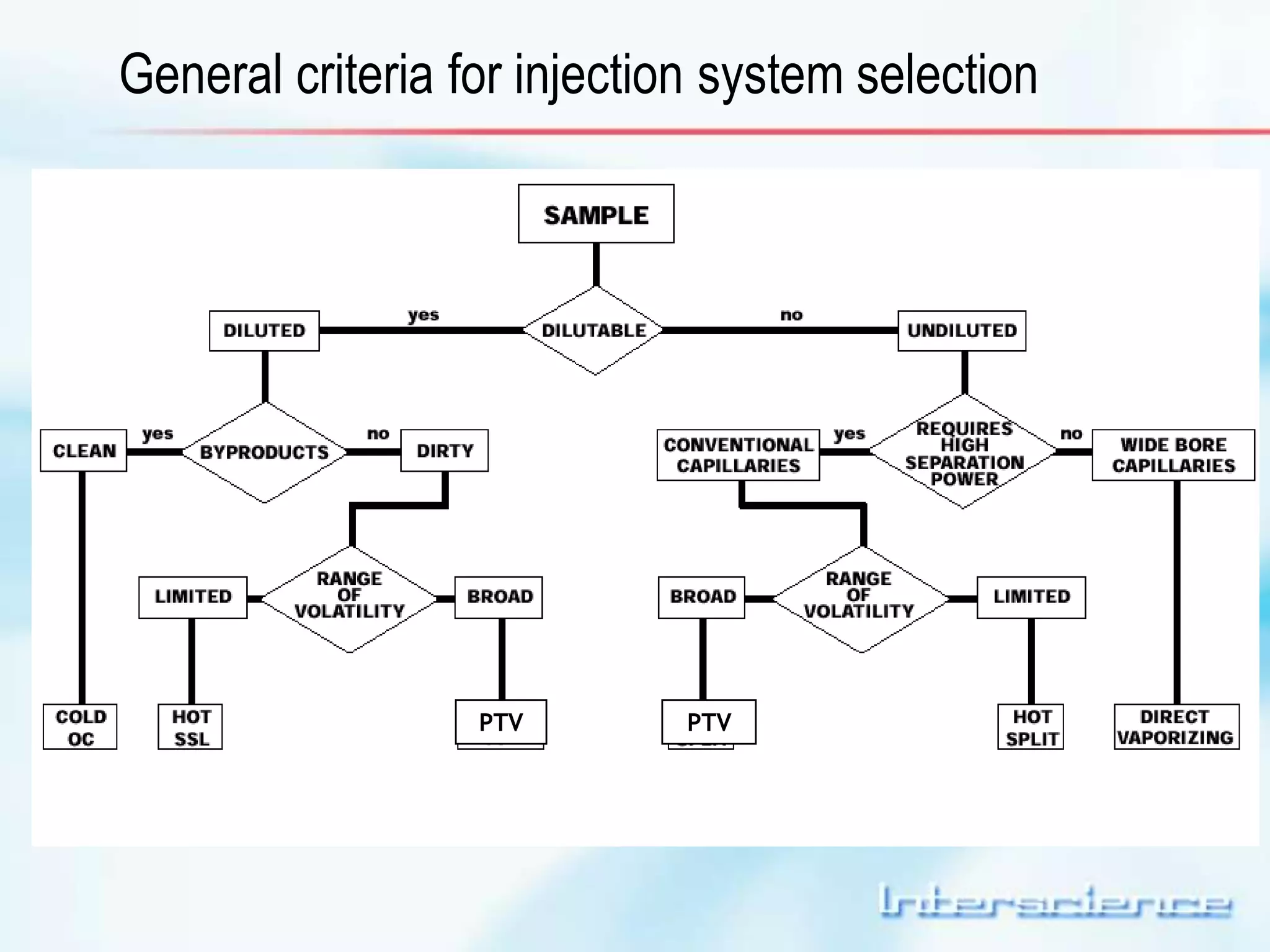
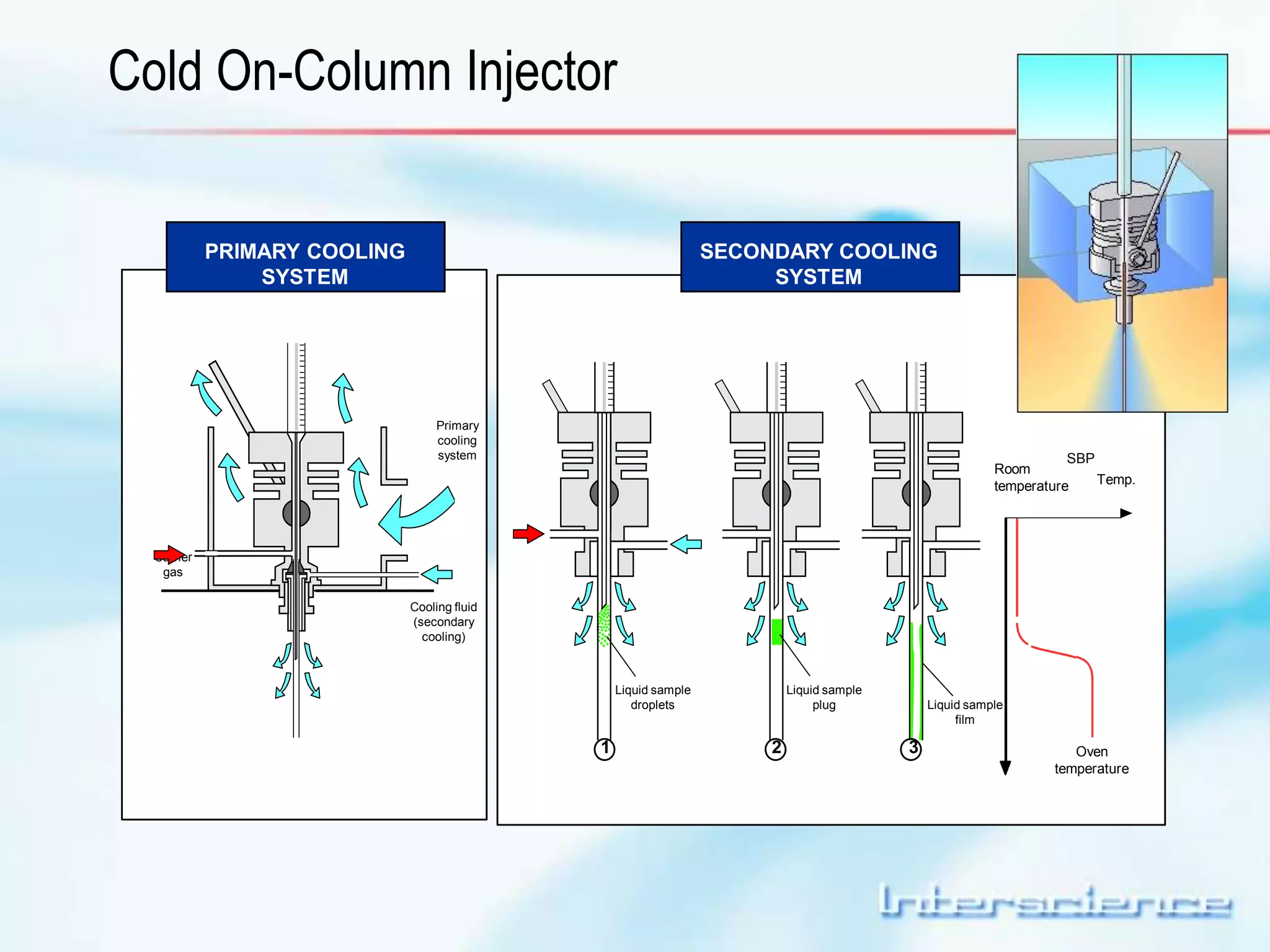
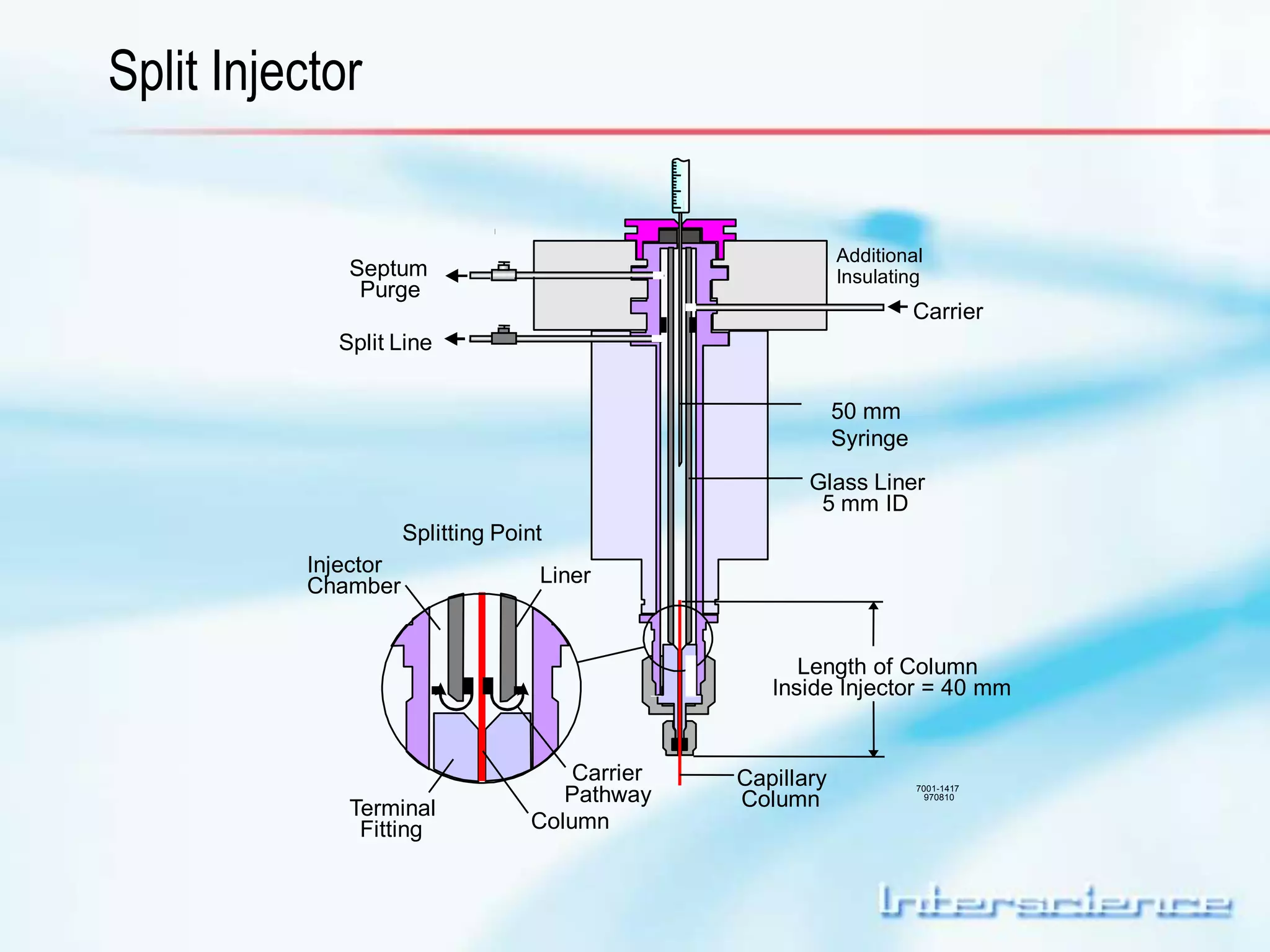
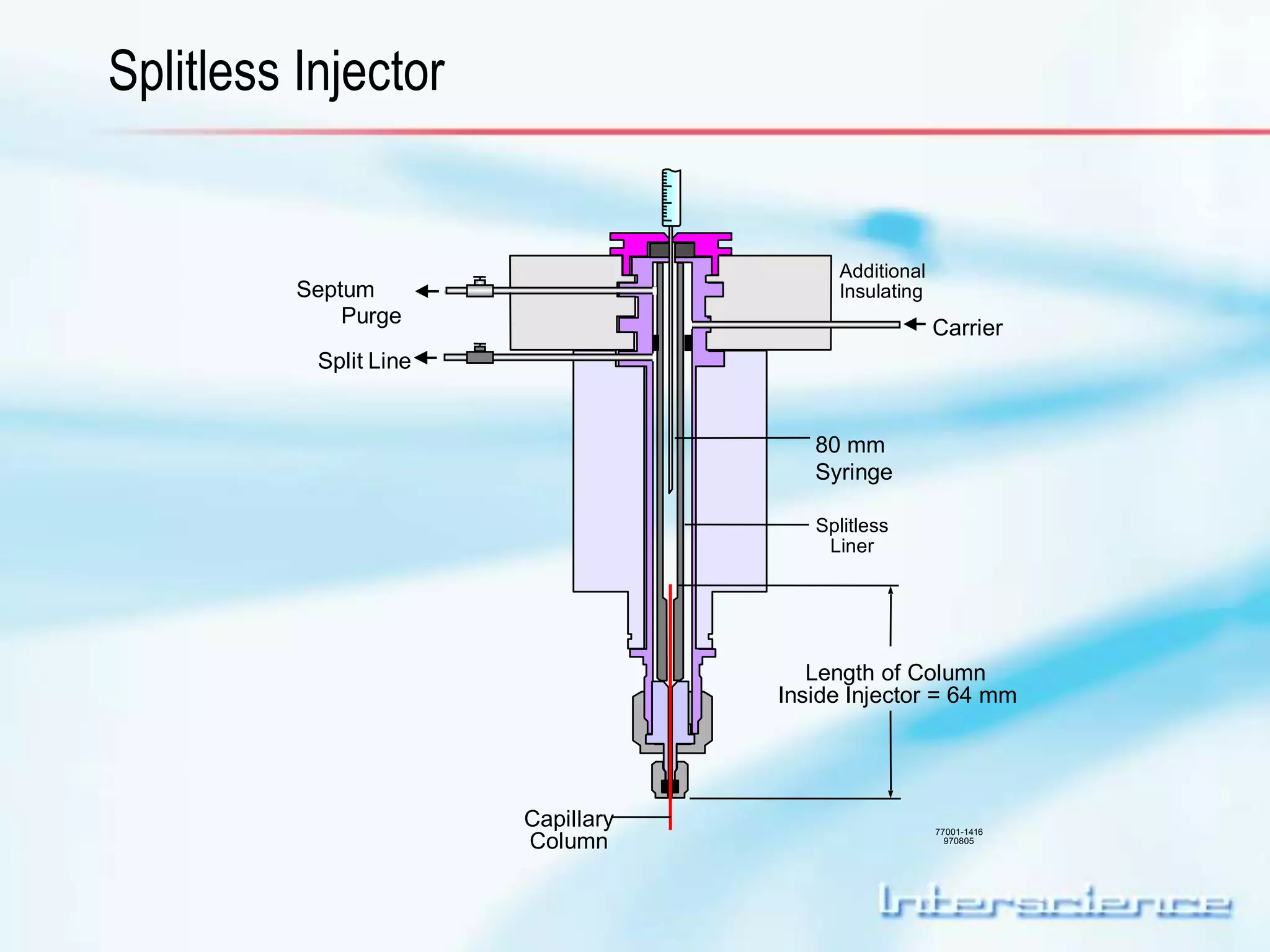
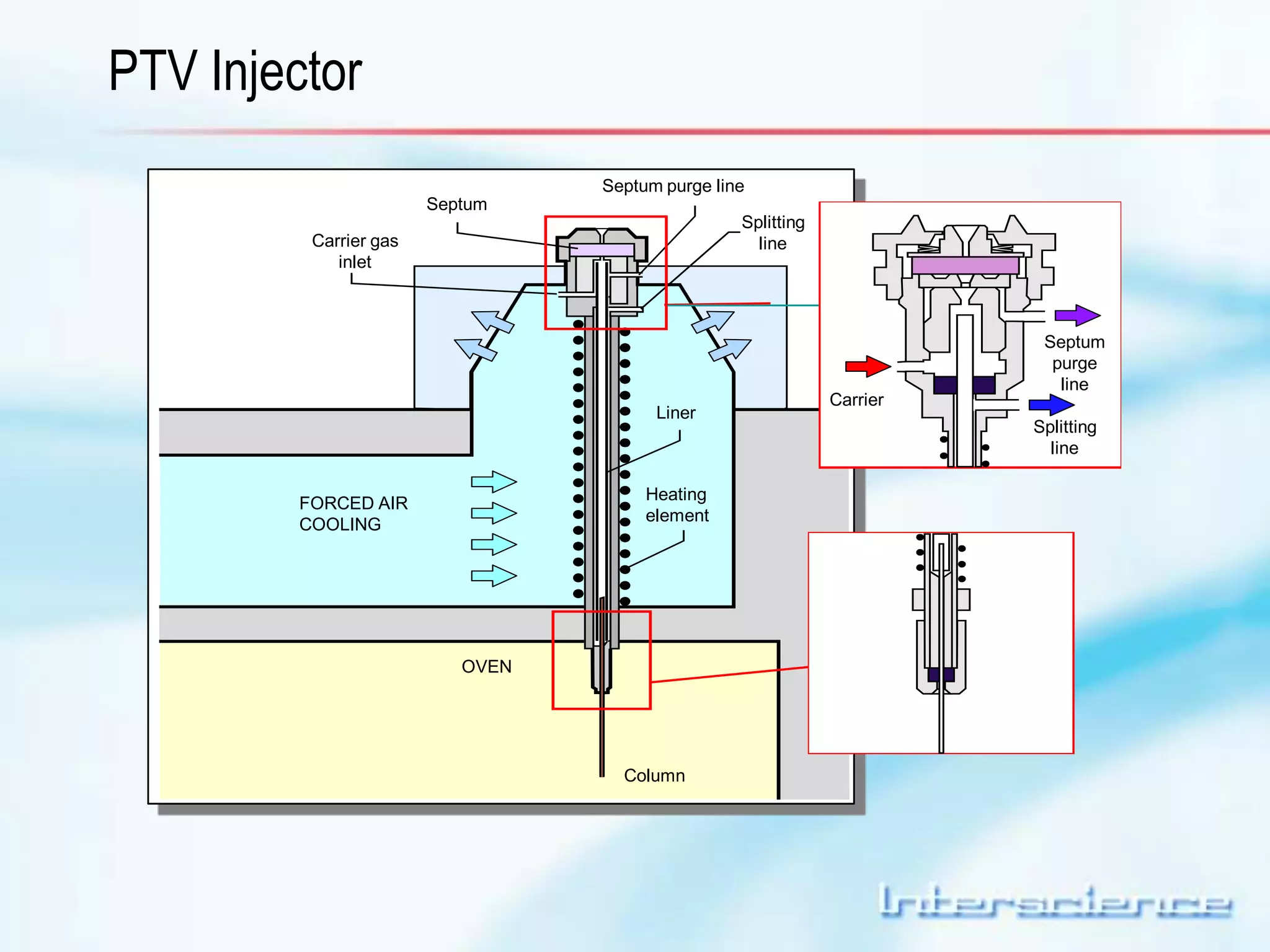
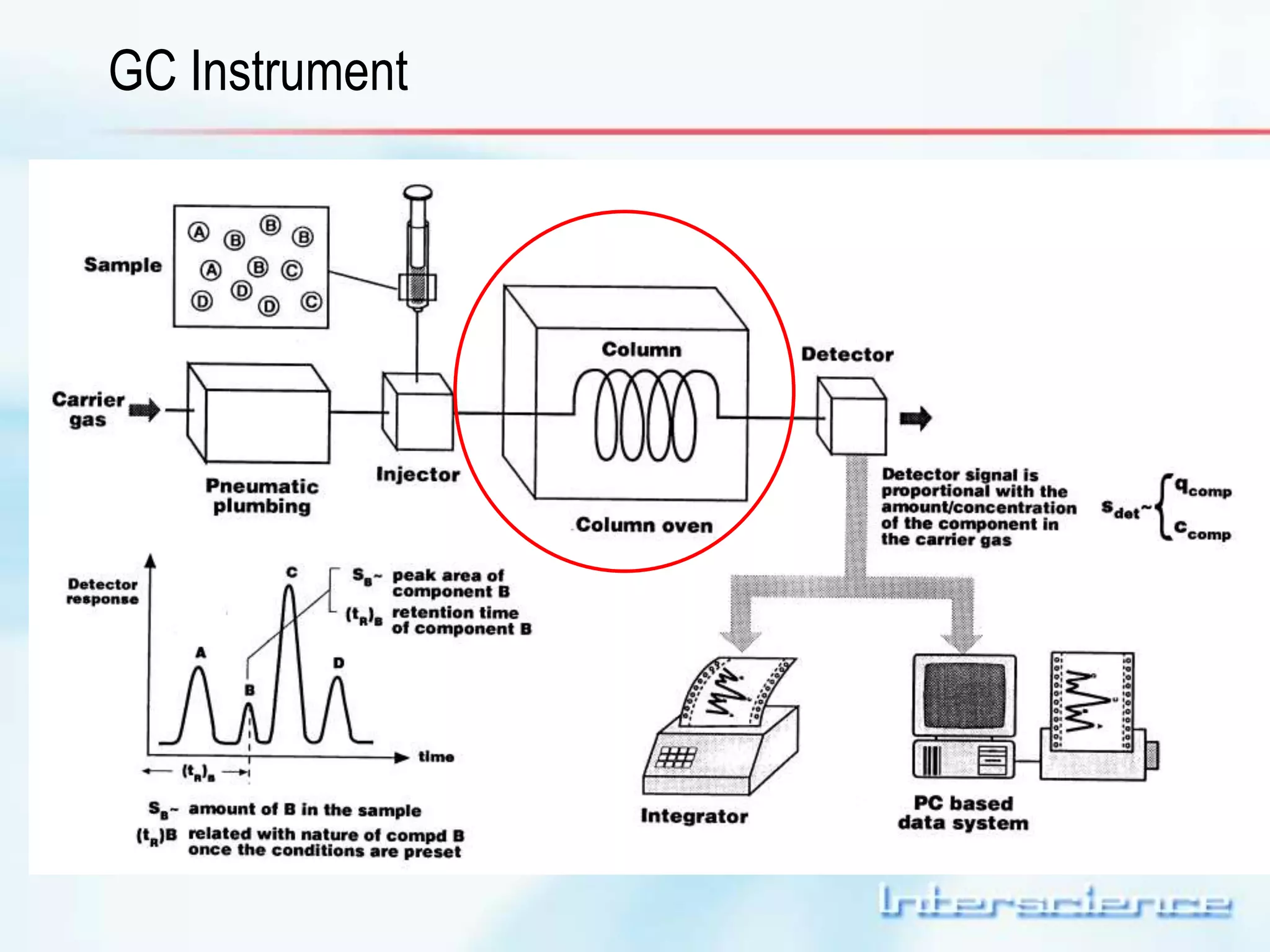
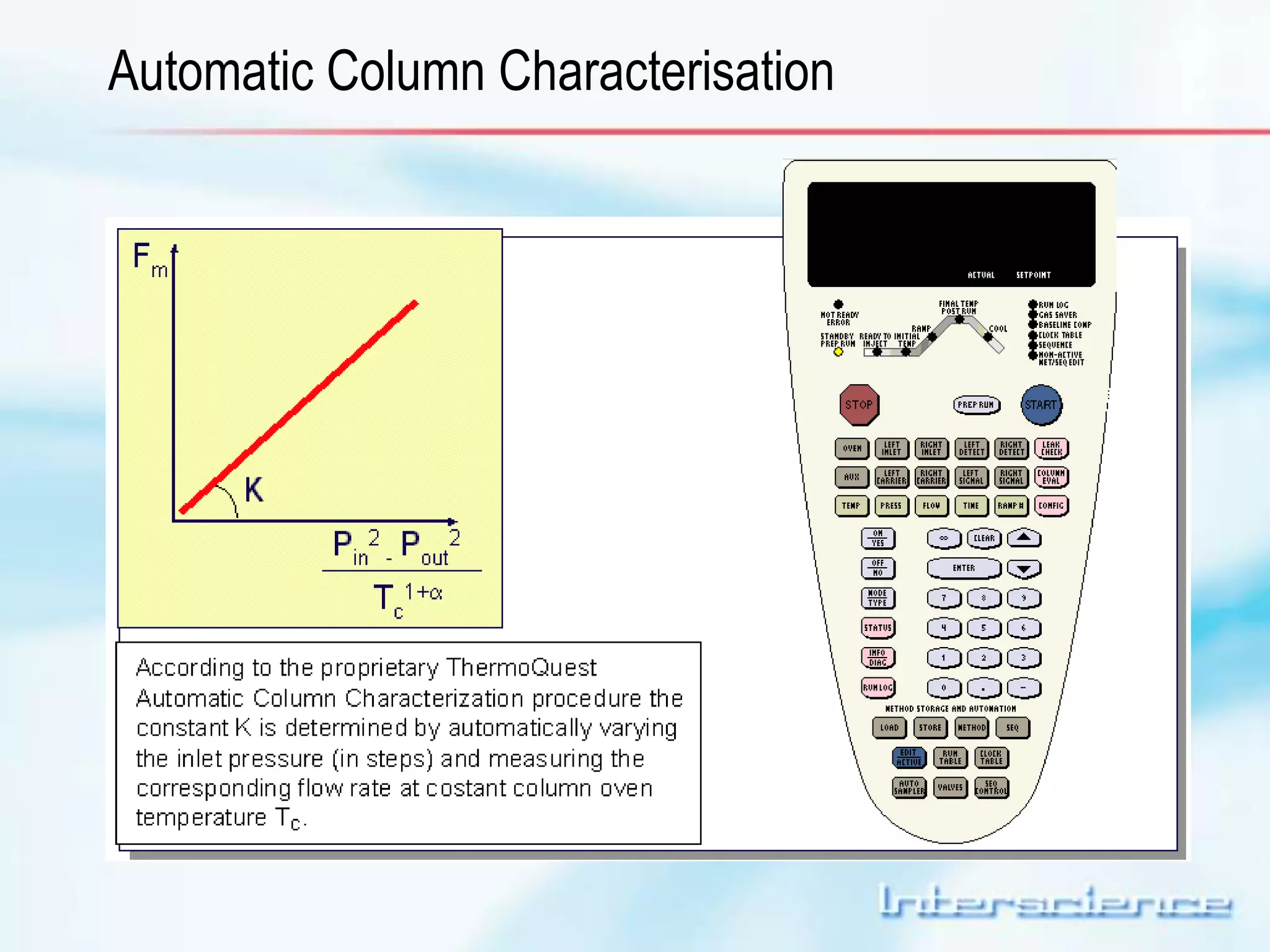
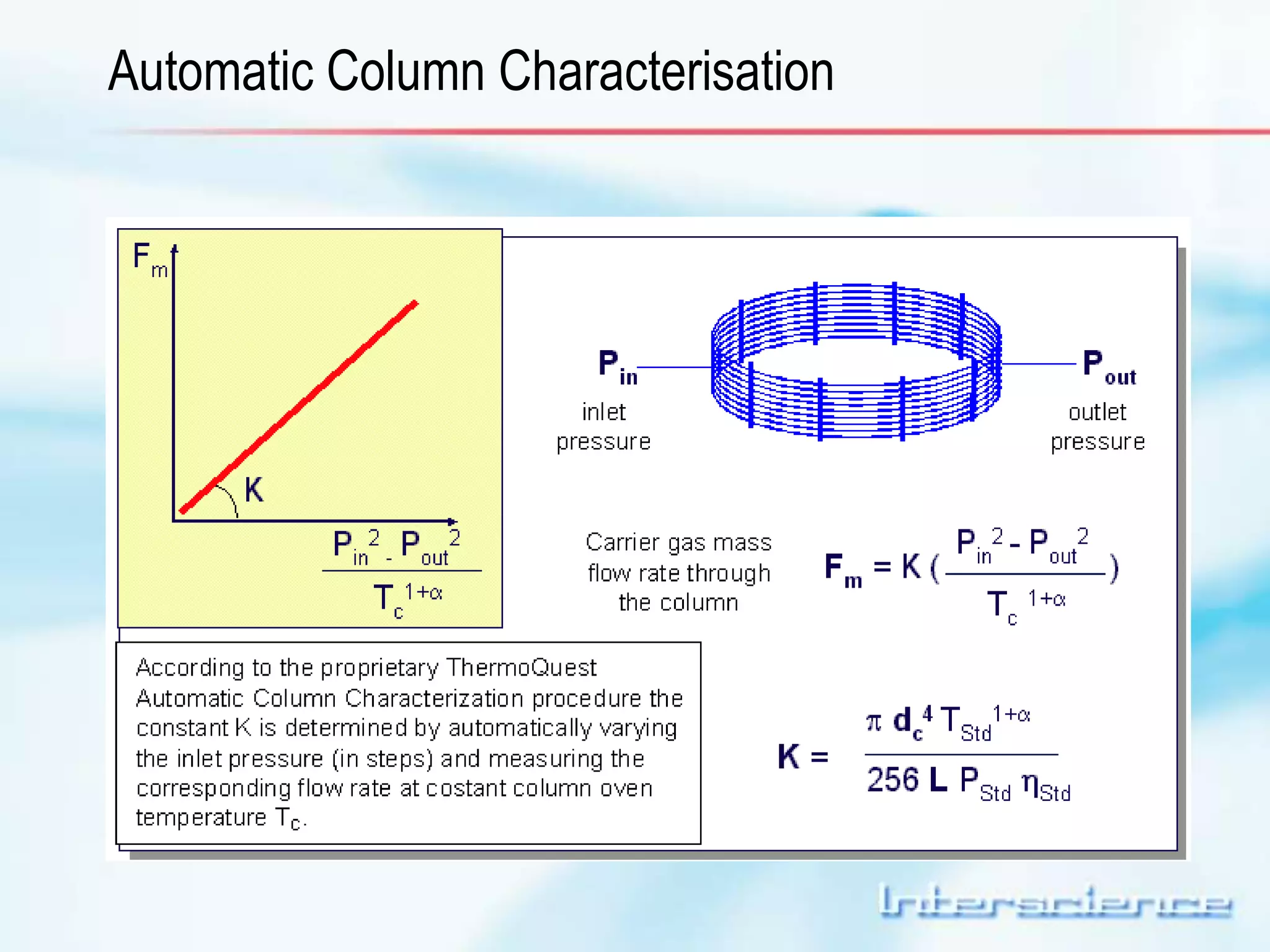
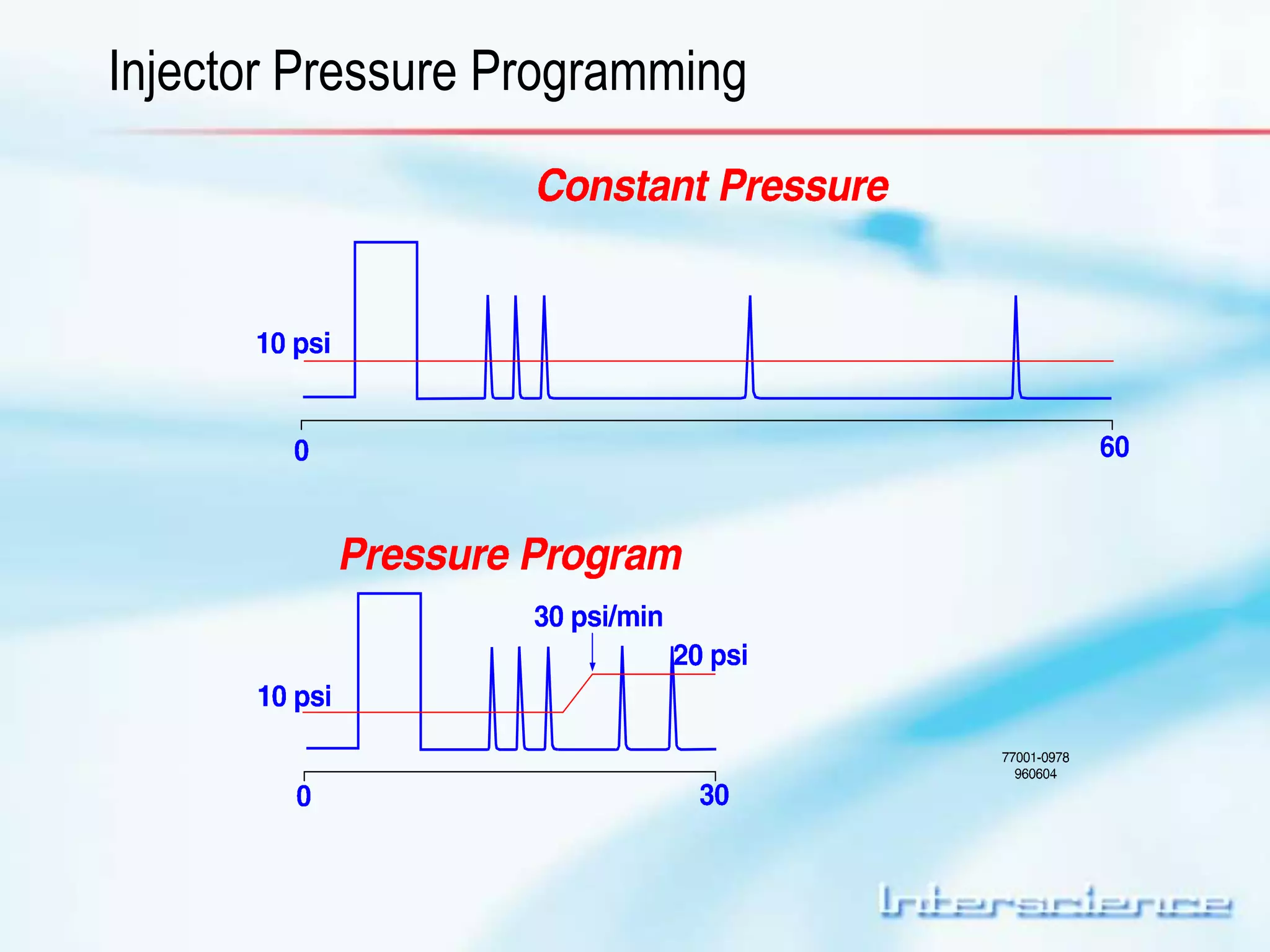
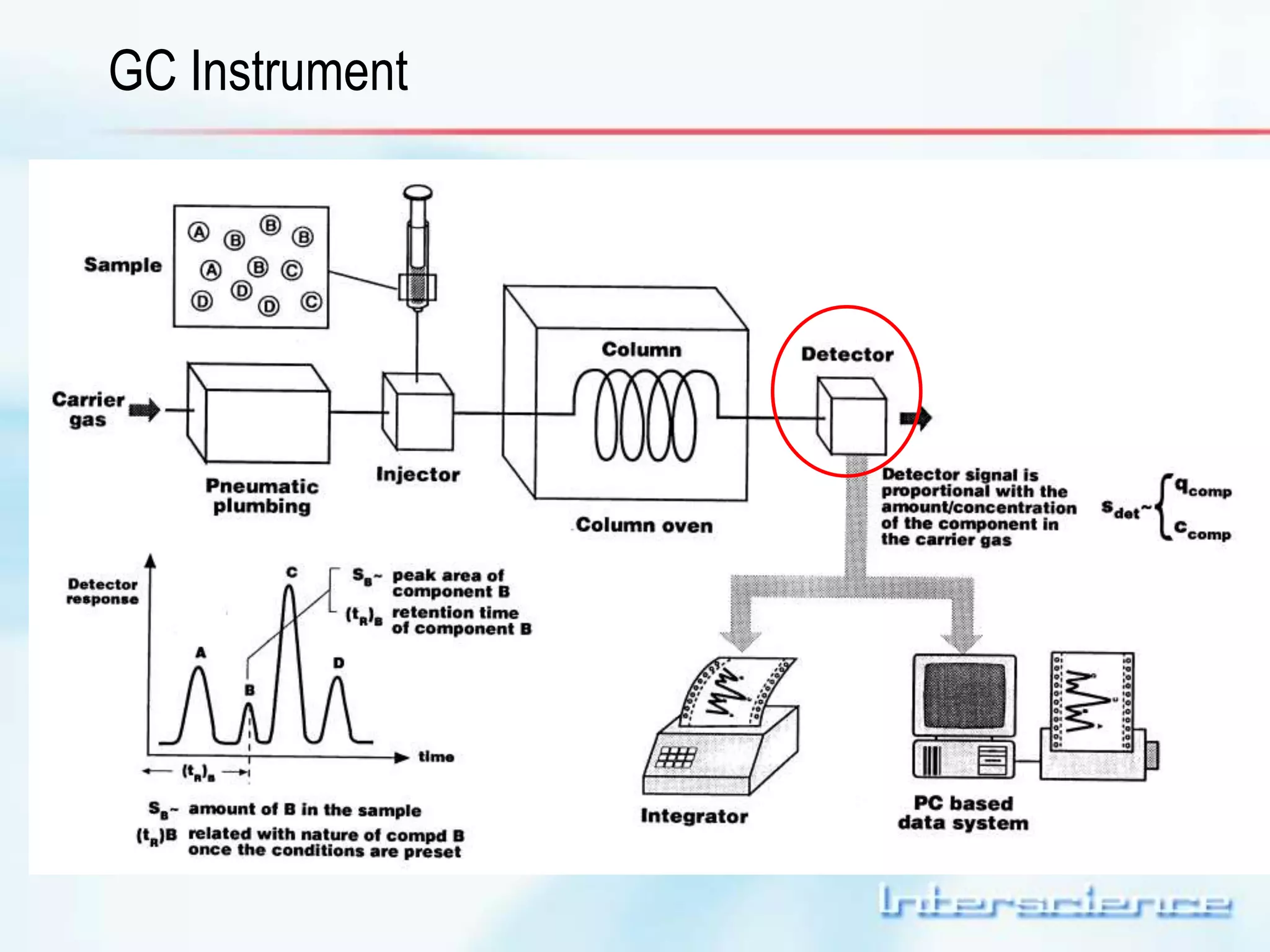
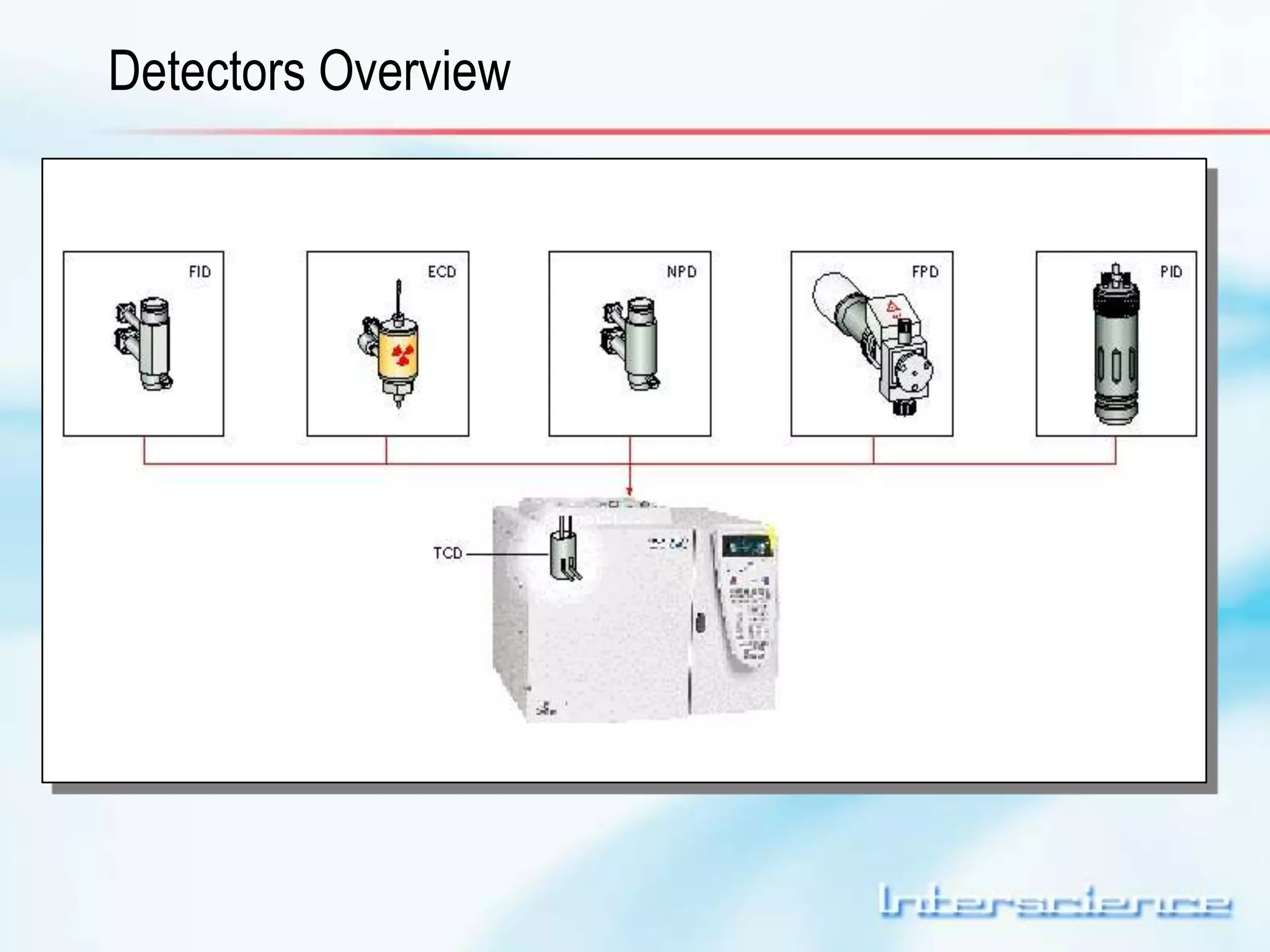
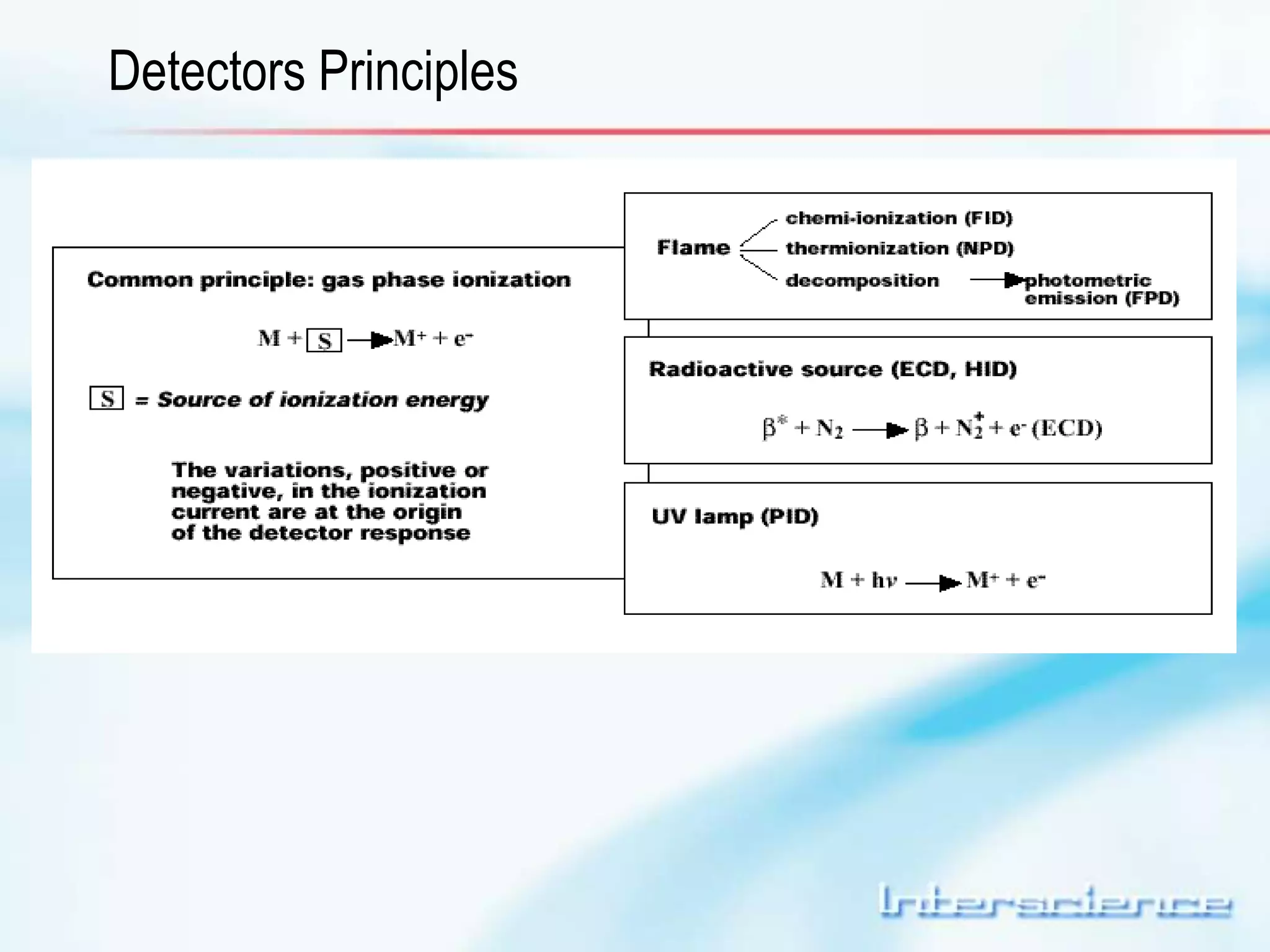
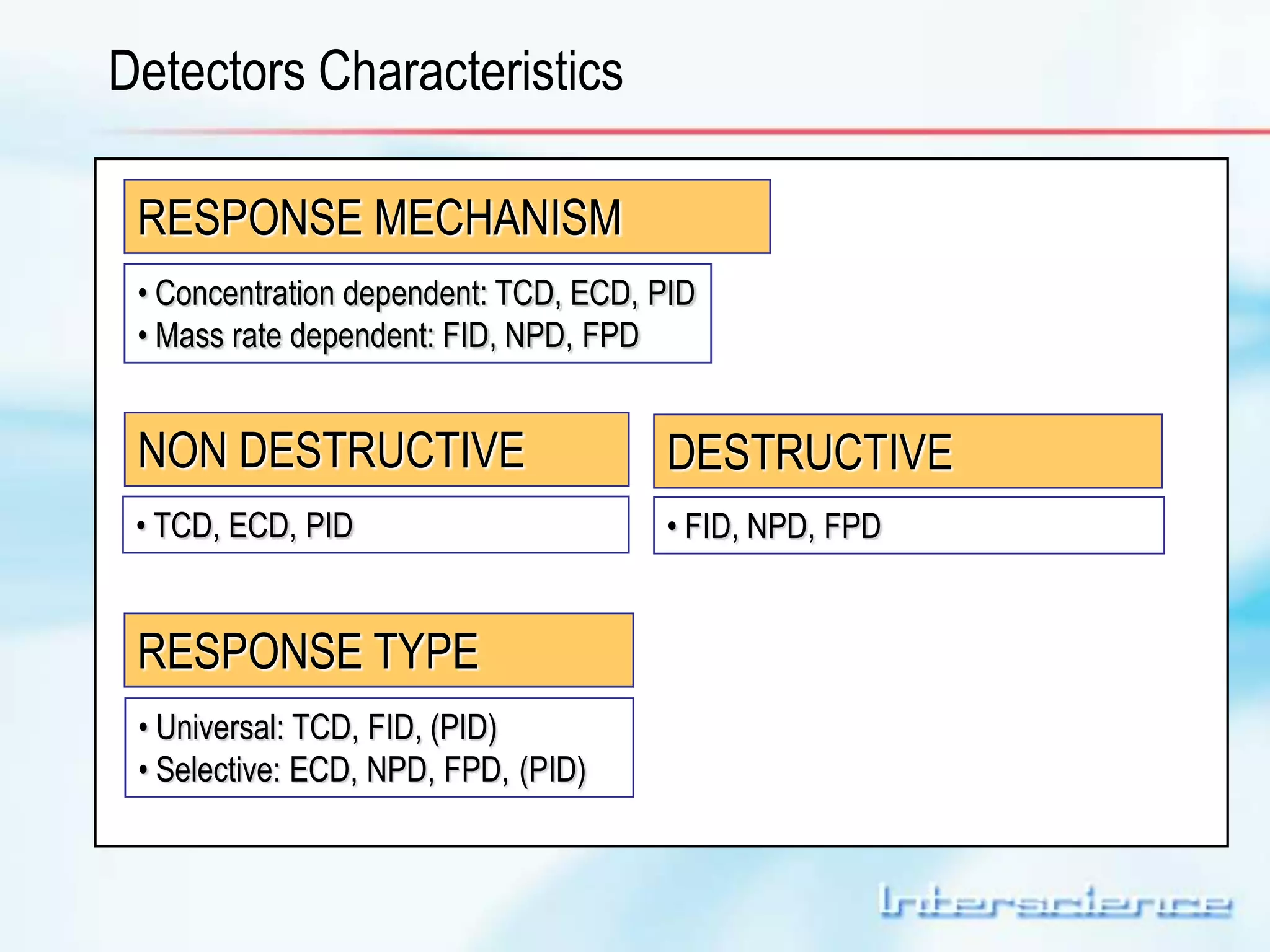
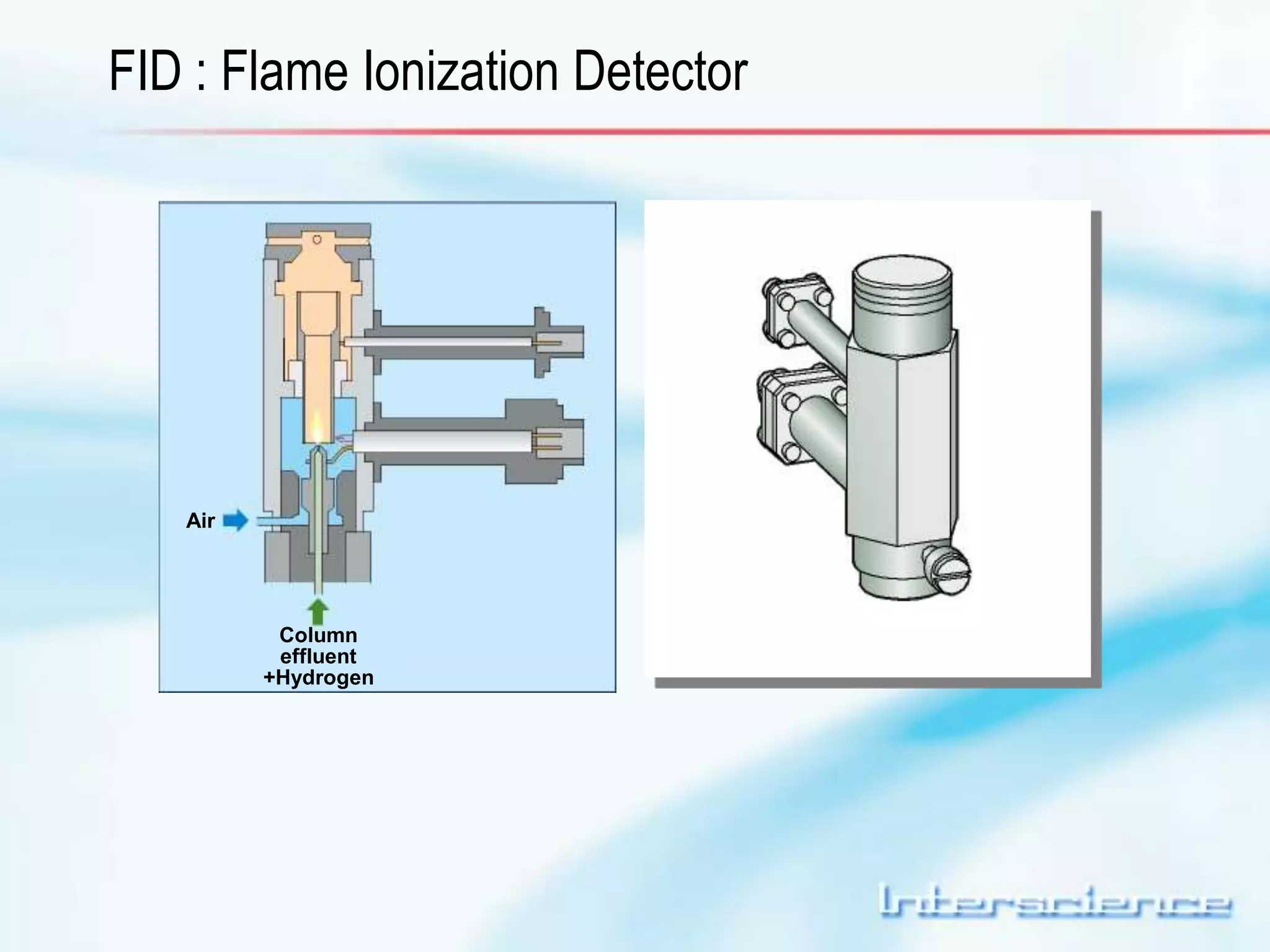
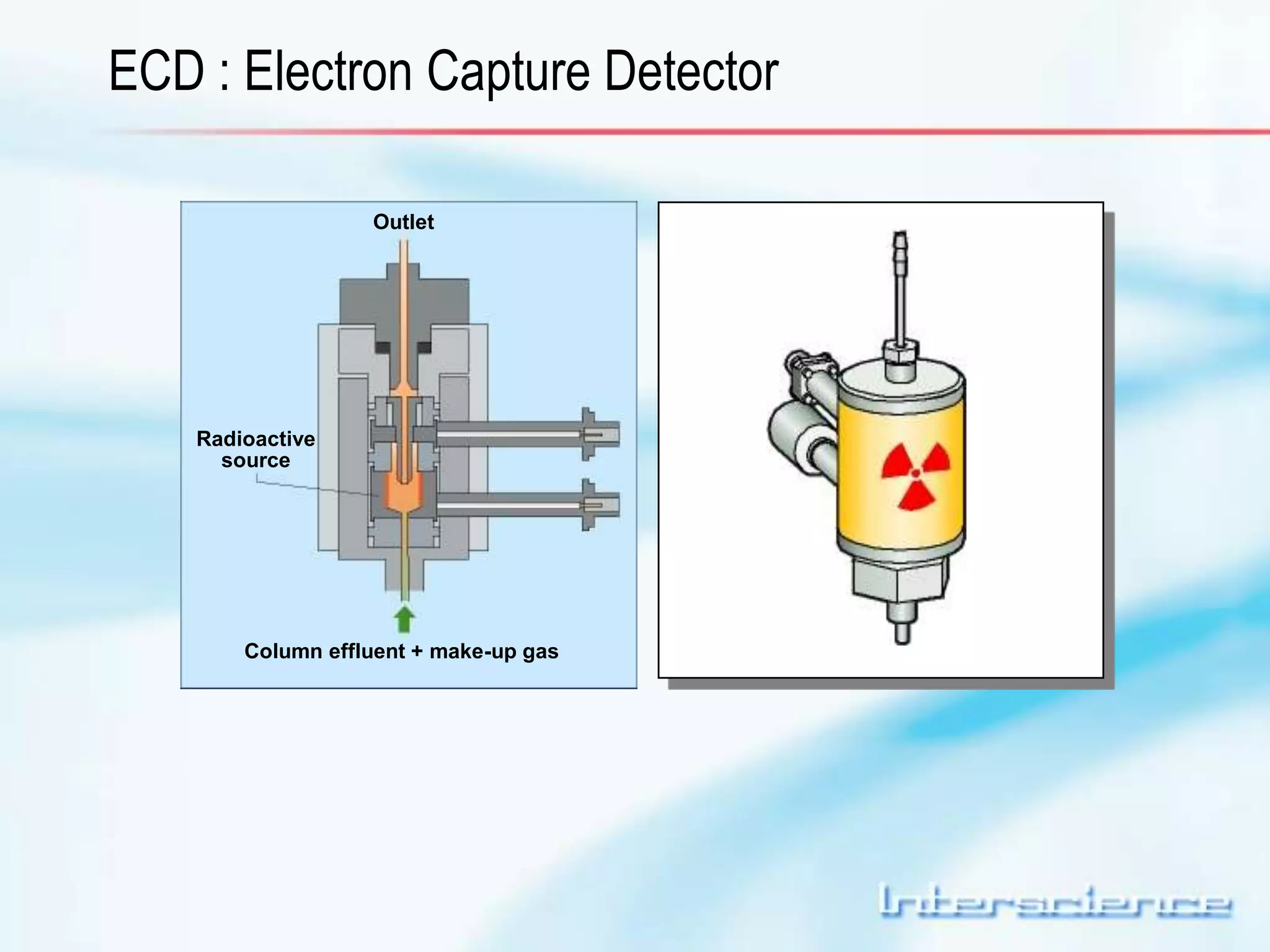
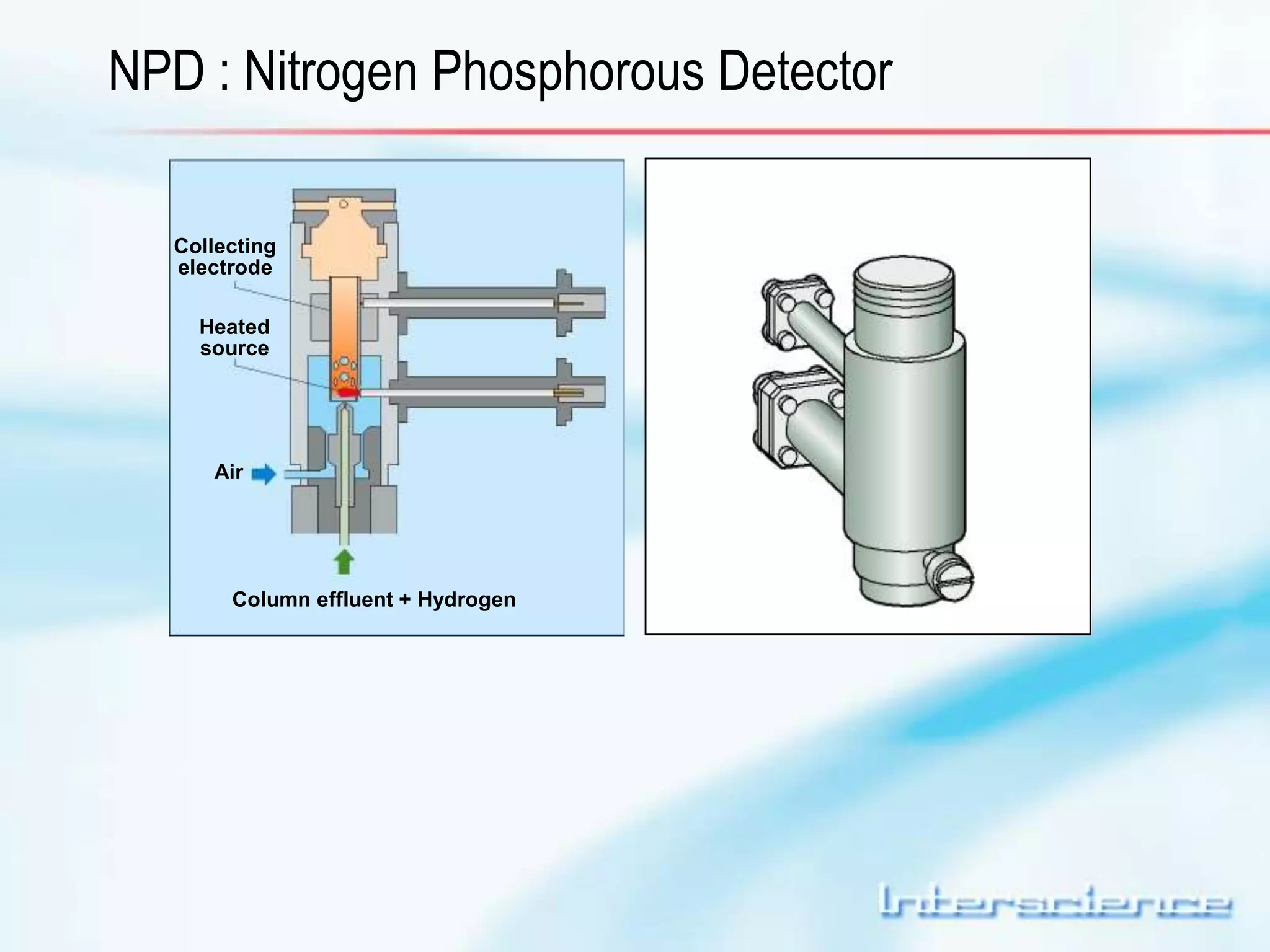
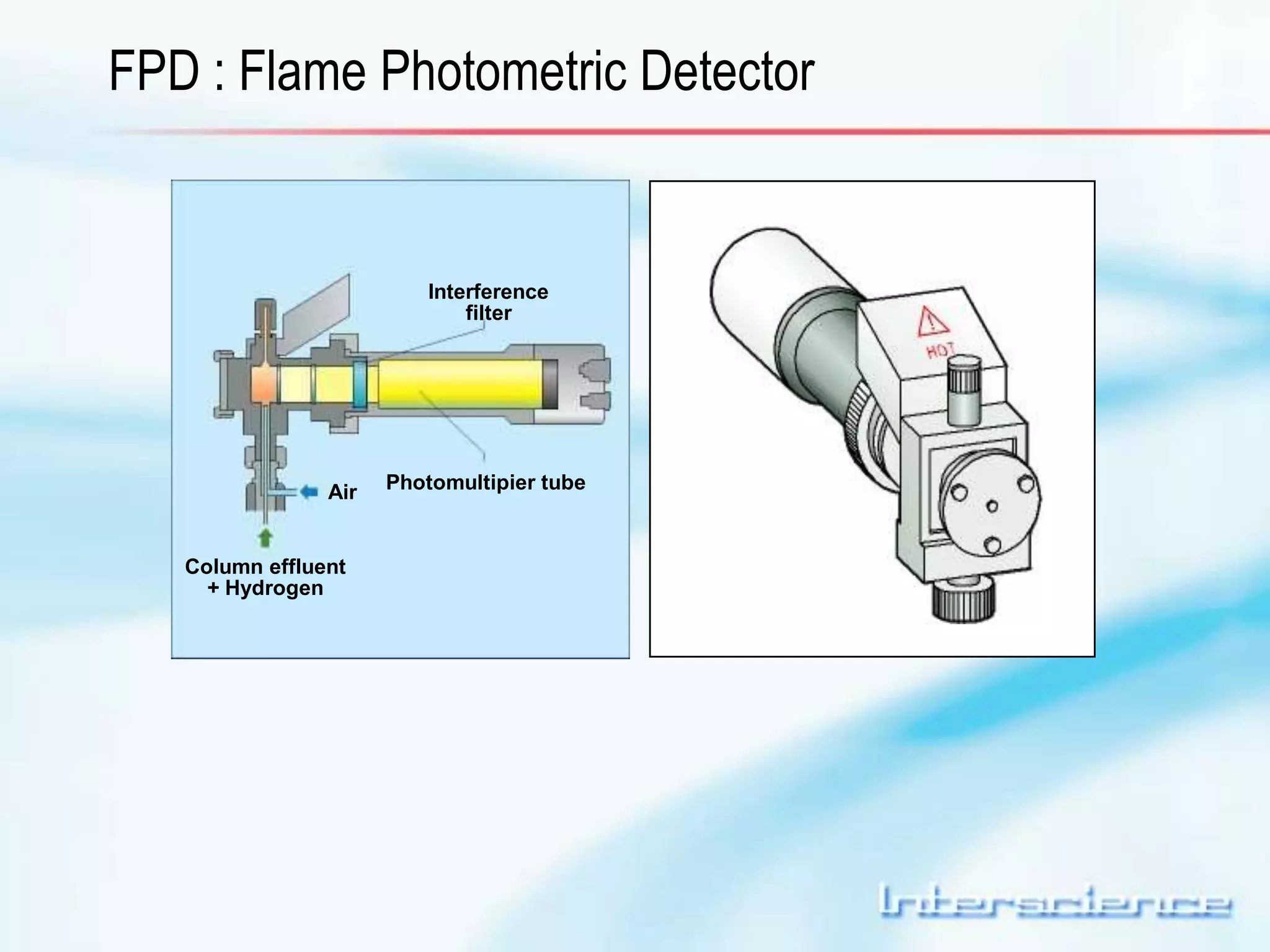
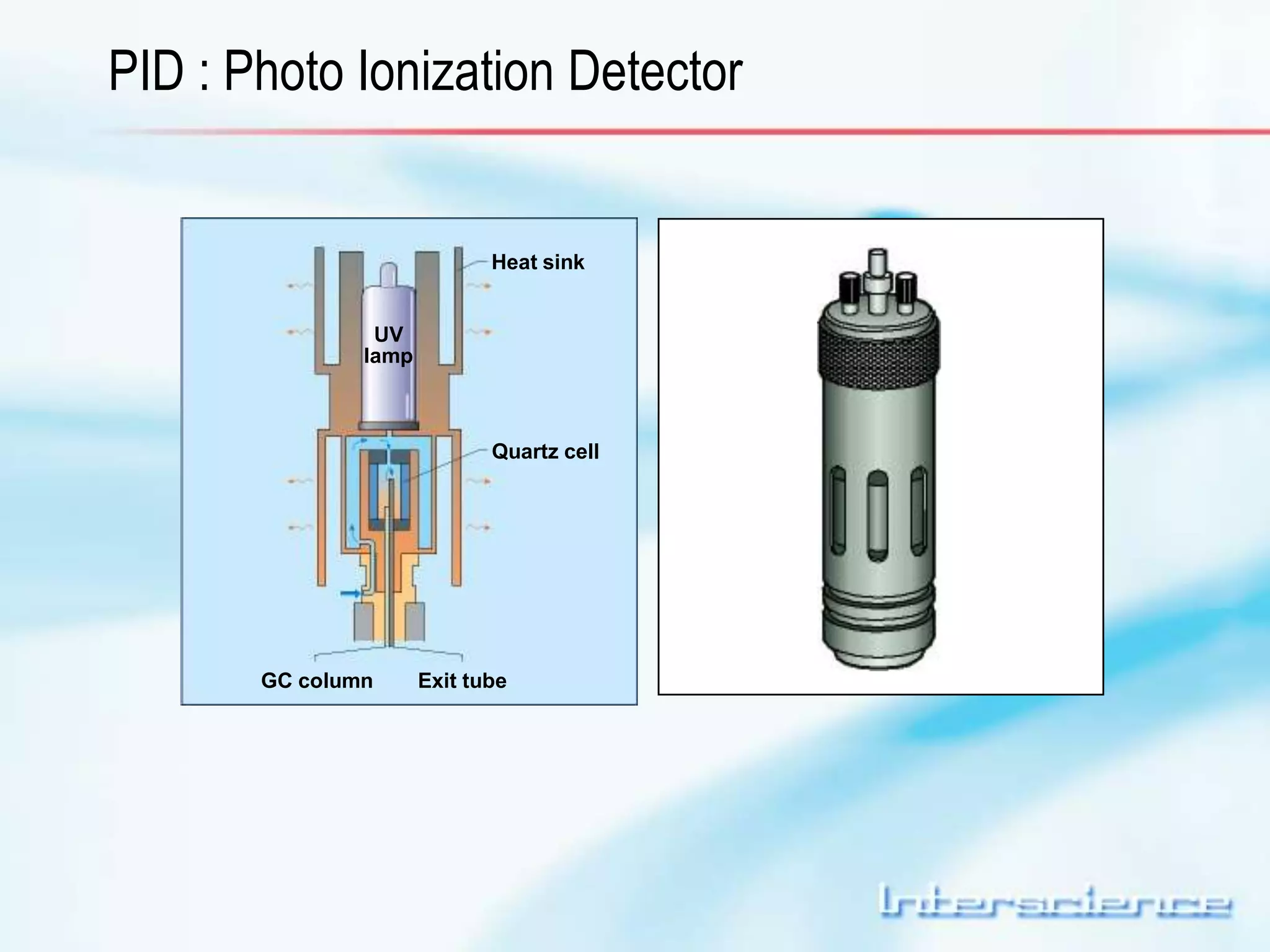
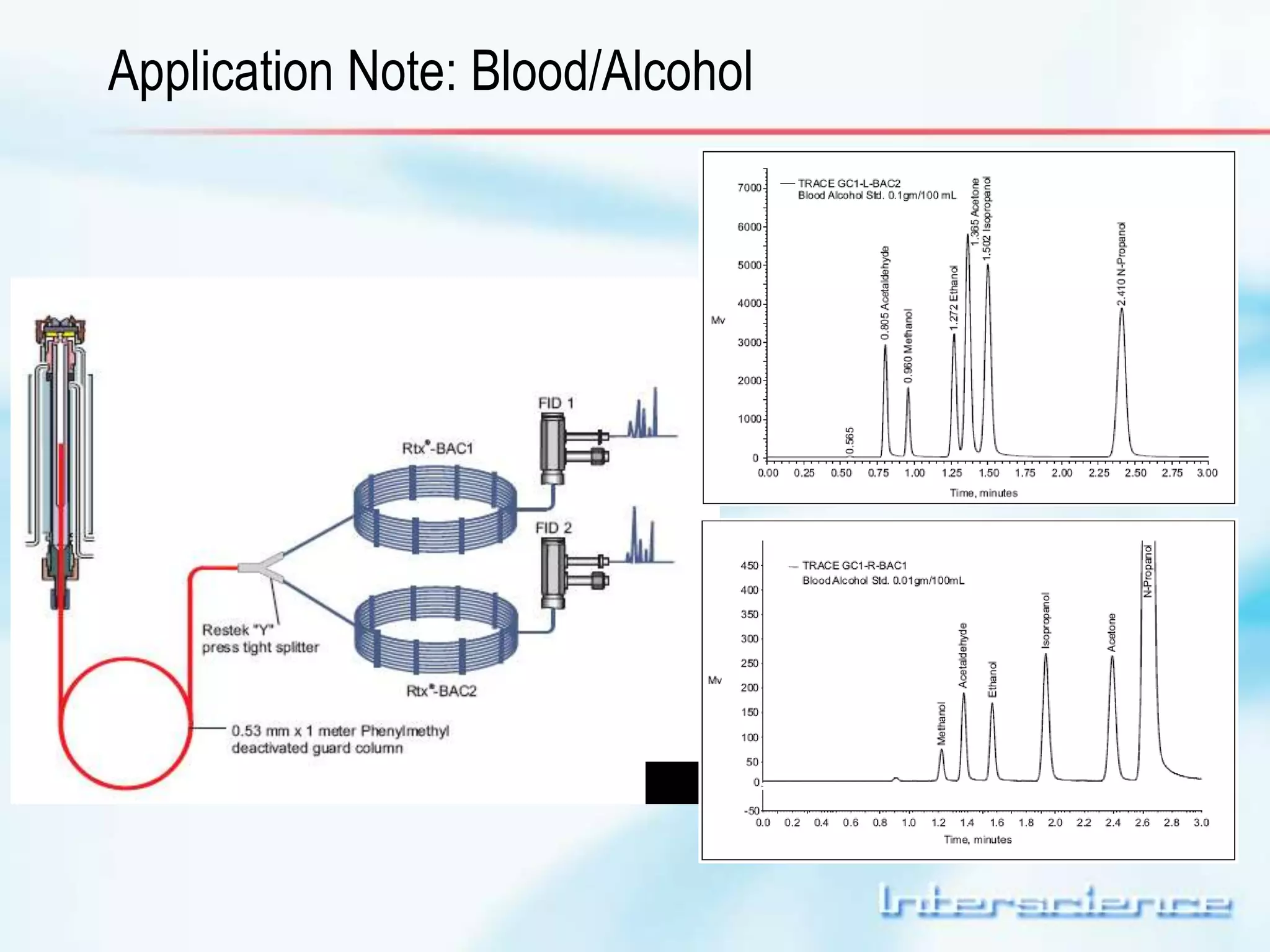
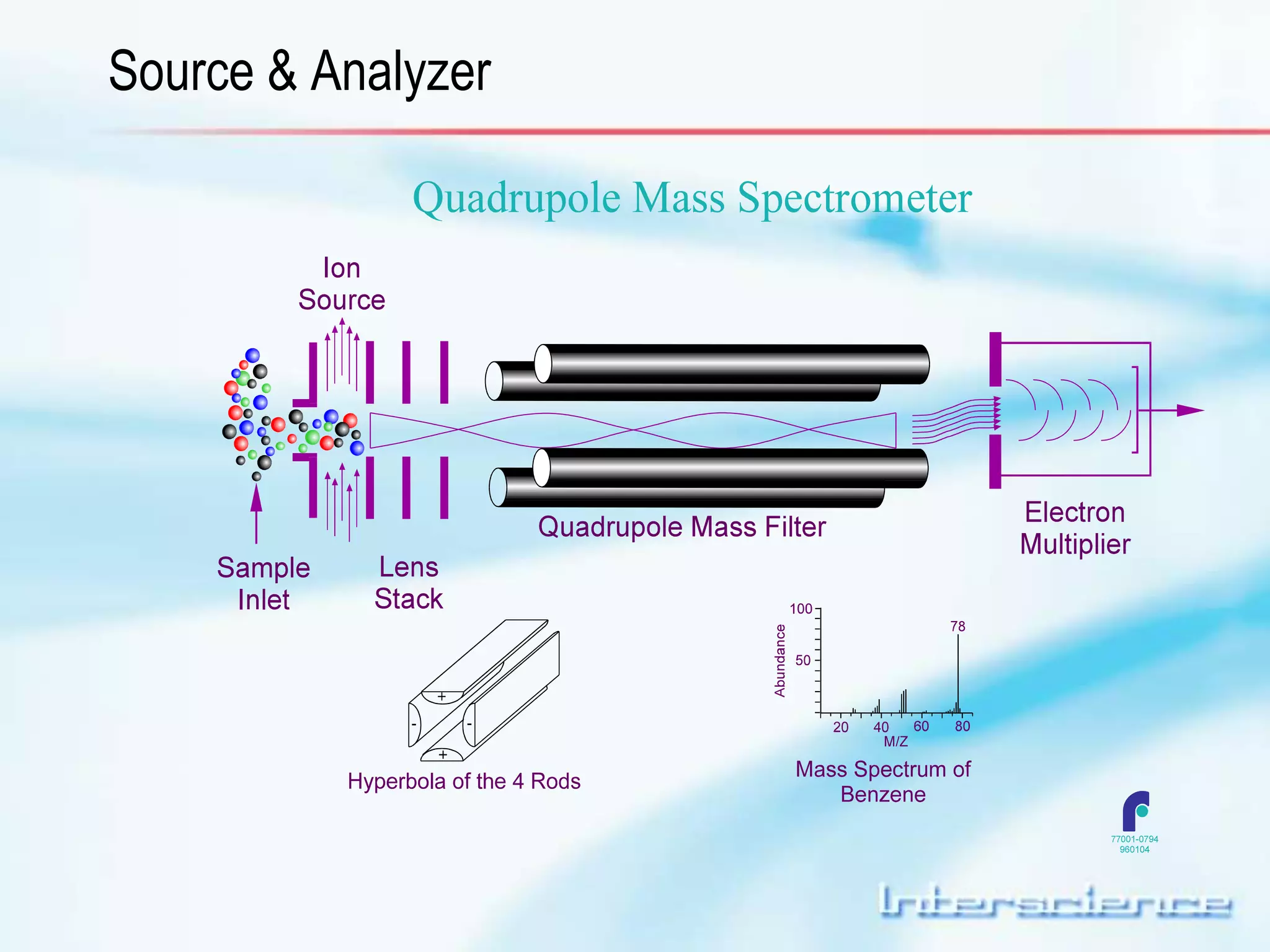
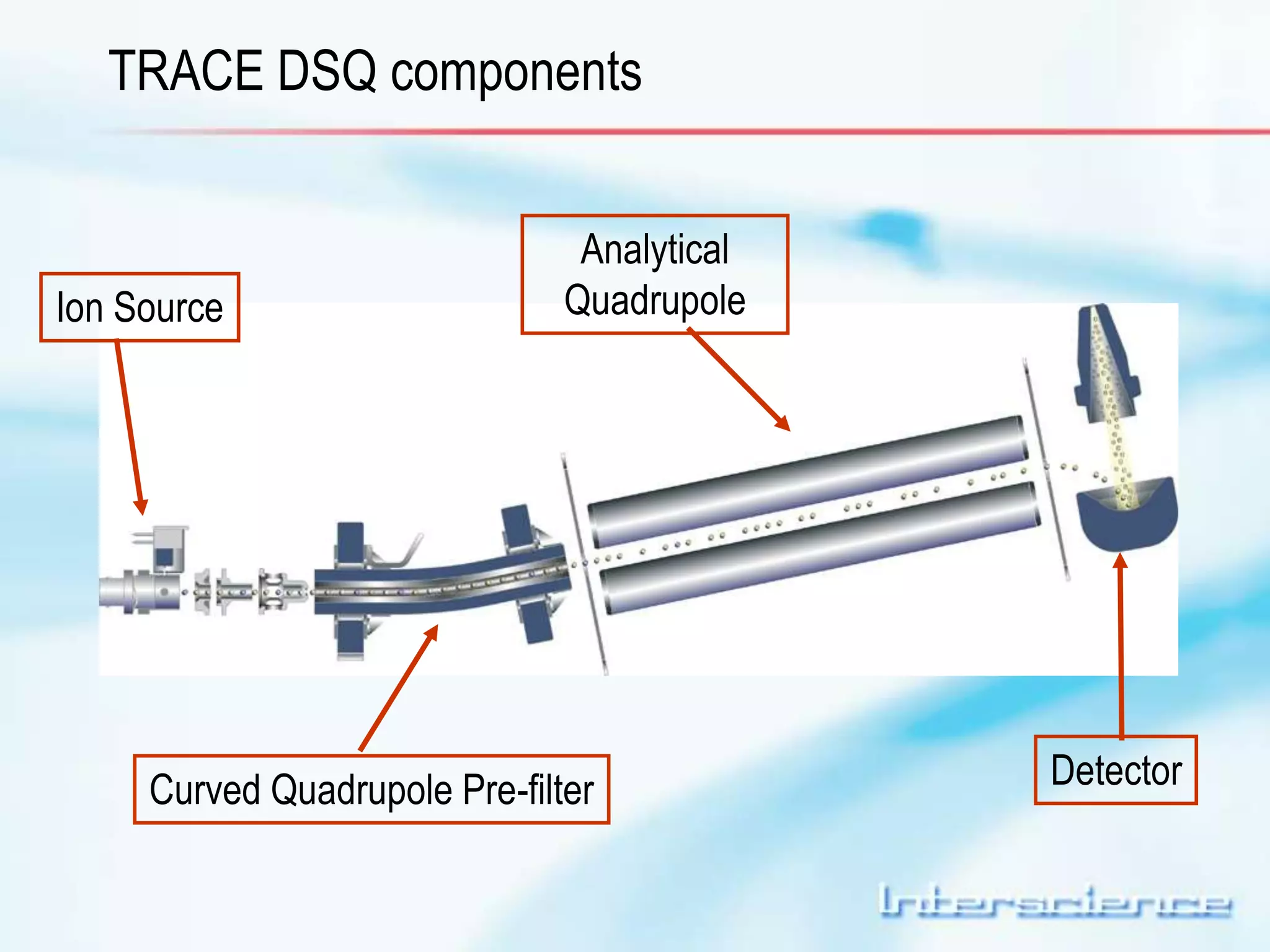
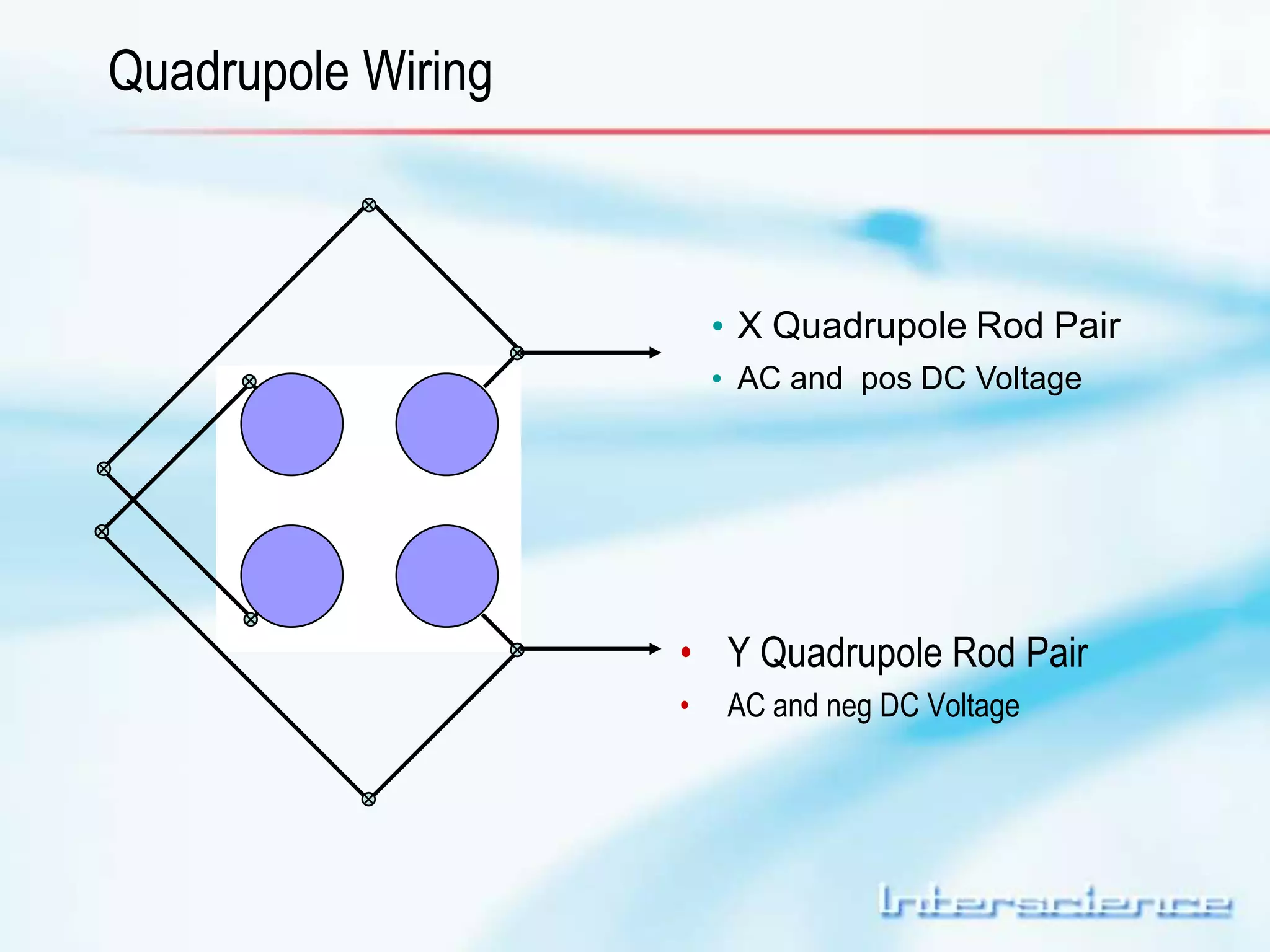
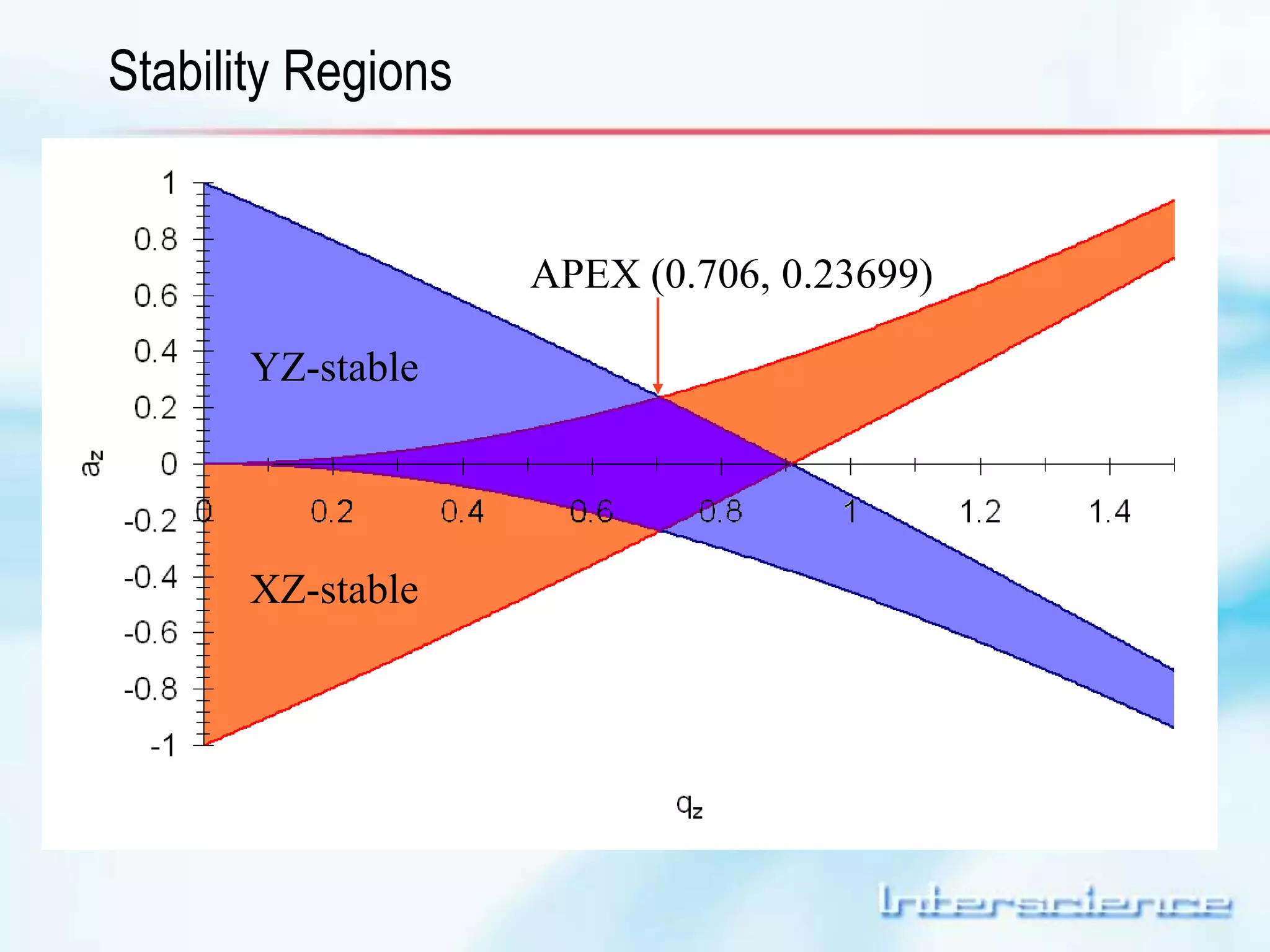
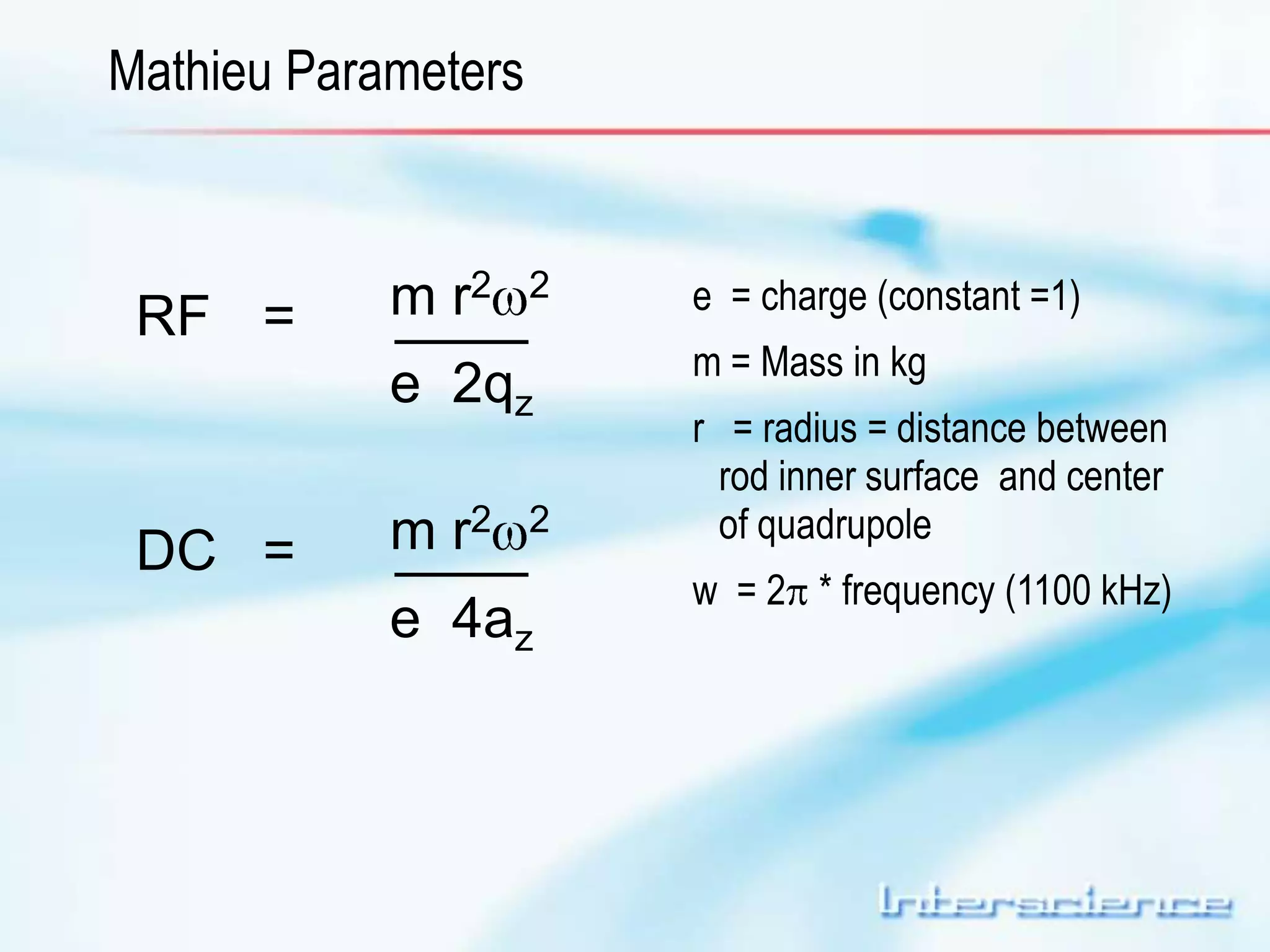
This document provides an overview of gas chromatography (GC) including its basic principles, instrumentation components, and detectors. GC separates molecules via vaporization and movement between a mobile gas phase and a stationary phase. Key components include the injector which introduces samples, the column for separation, the oven which houses the column, and various detectors for identifying molecules. Common detectors measure molecules via concentration-dependent or mass-dependent responses and can have universal or selective responses. The document also discusses GC-mass spectrometry which couples separation with identification capabilities.