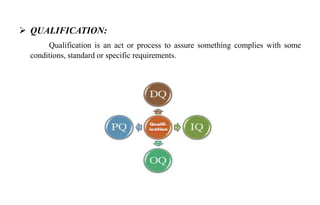
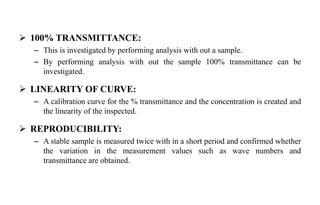
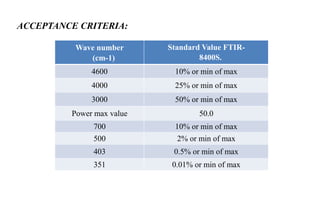
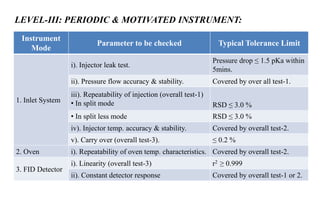
The document provides details on qualification and validation procedures for gas chromatography (GC) and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) systems used in pharmaceutical analysis. It describes calibration tests for both instruments, including tests to check wave number precision and reproducibility, linearity, and temperature accuracy and stability. Validation tests are also outlined, such as resolution checks and tests to evaluate performance against acceptance criteria over time as specified in guidance documents. The document provides a thorough overview of qualification processes for critical analytical instruments.