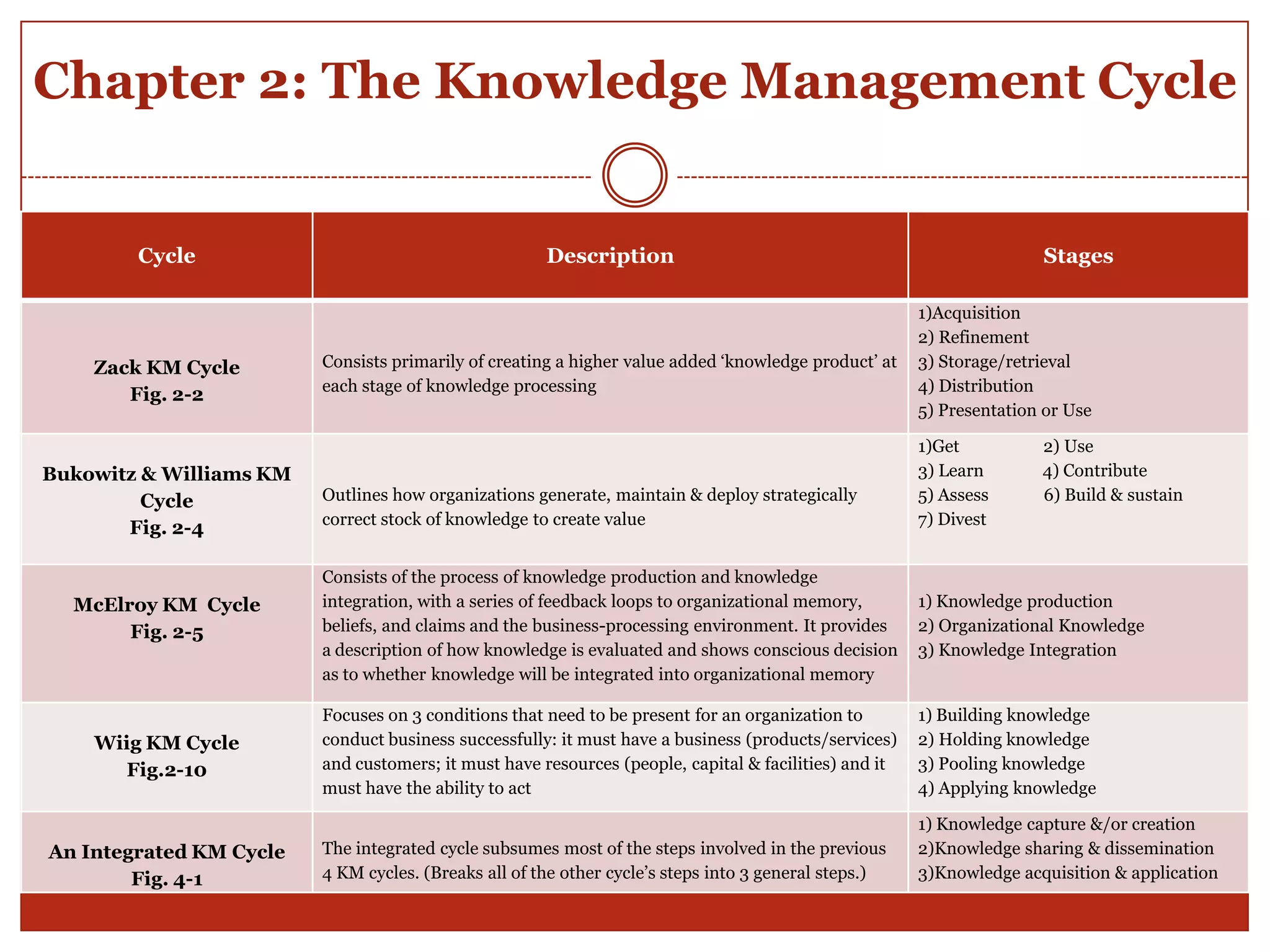
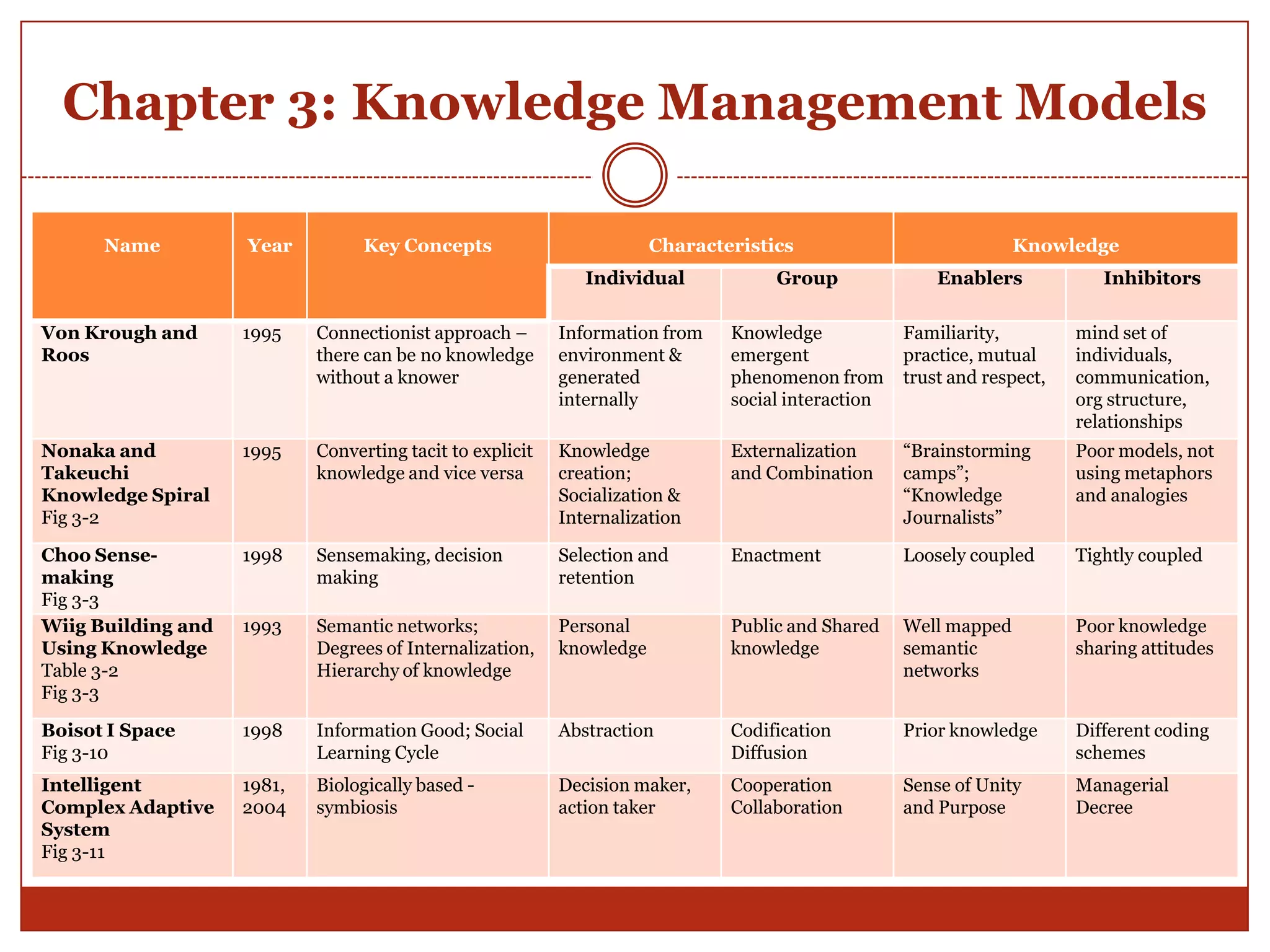
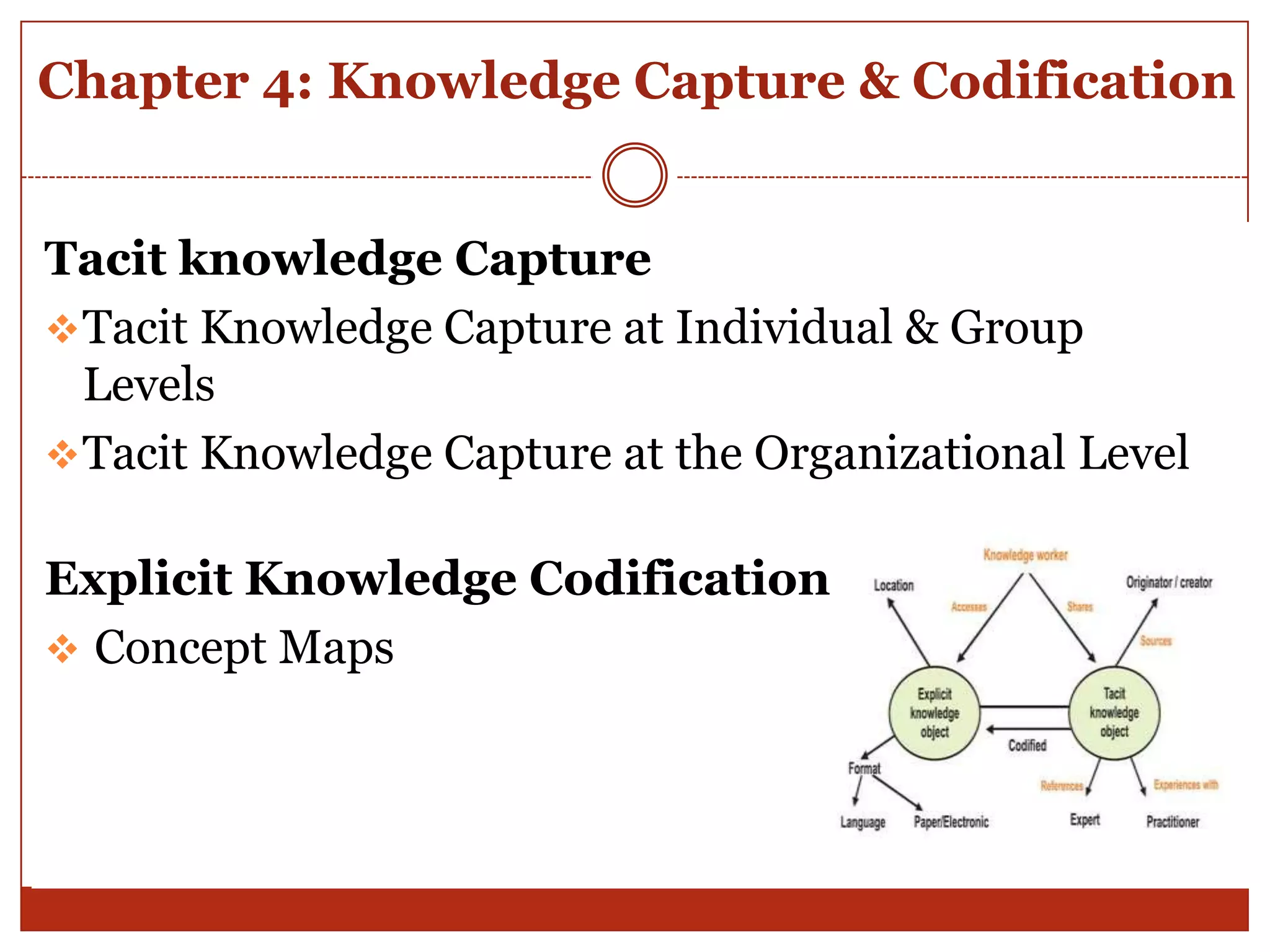
The document provides an overview and summary of the key concepts from the book "Knowledge Management in Theory and Practice" by Kimiz Dalkir. It discusses several knowledge management cycles and models. It also examines topics like knowledge capture and codification, knowledge sharing through communities of practice, knowledge application at individual and group levels, the role of organizational culture, and tools and strategies for knowledge management. The future challenges of knowledge management are also addressed.