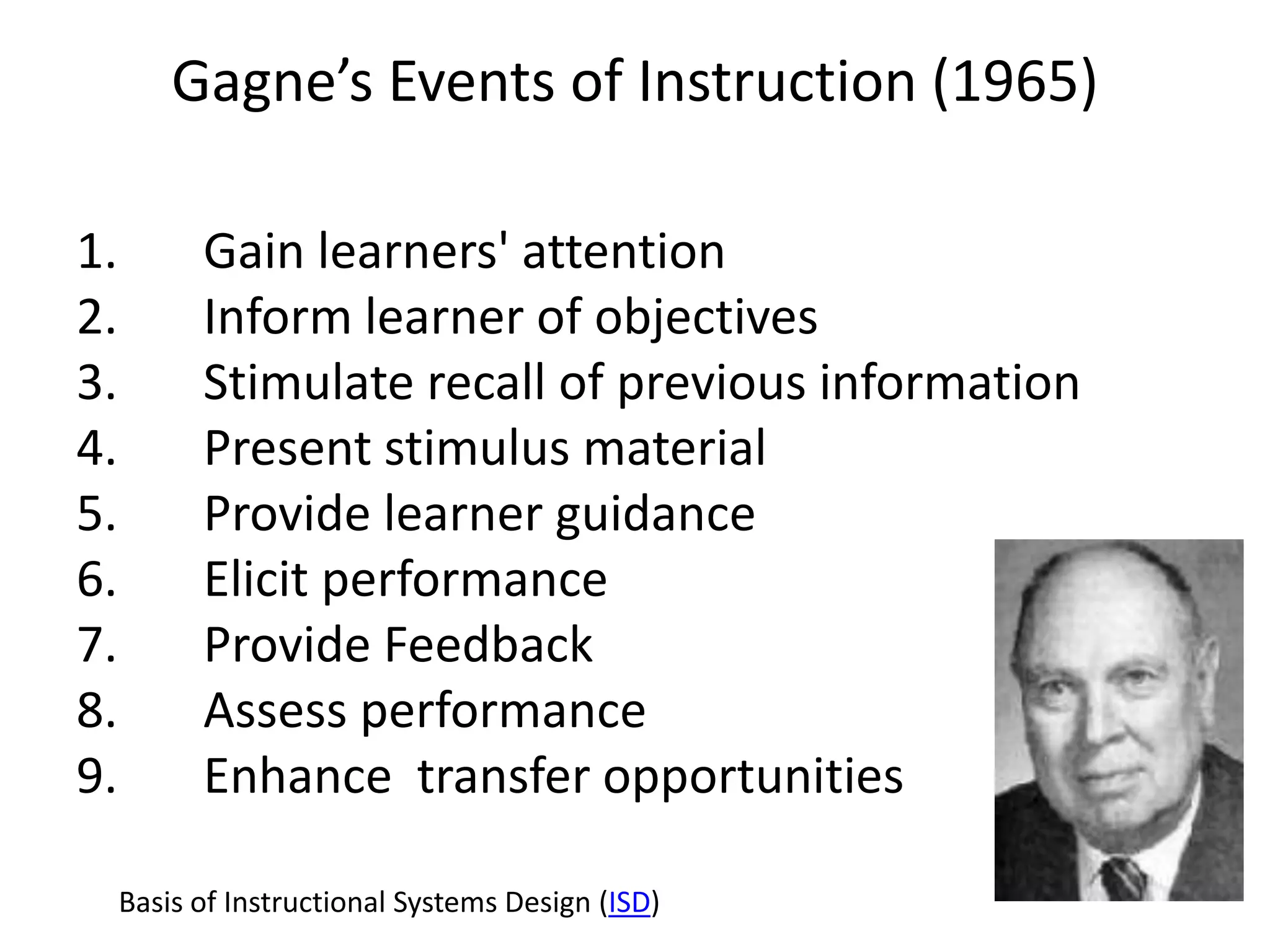
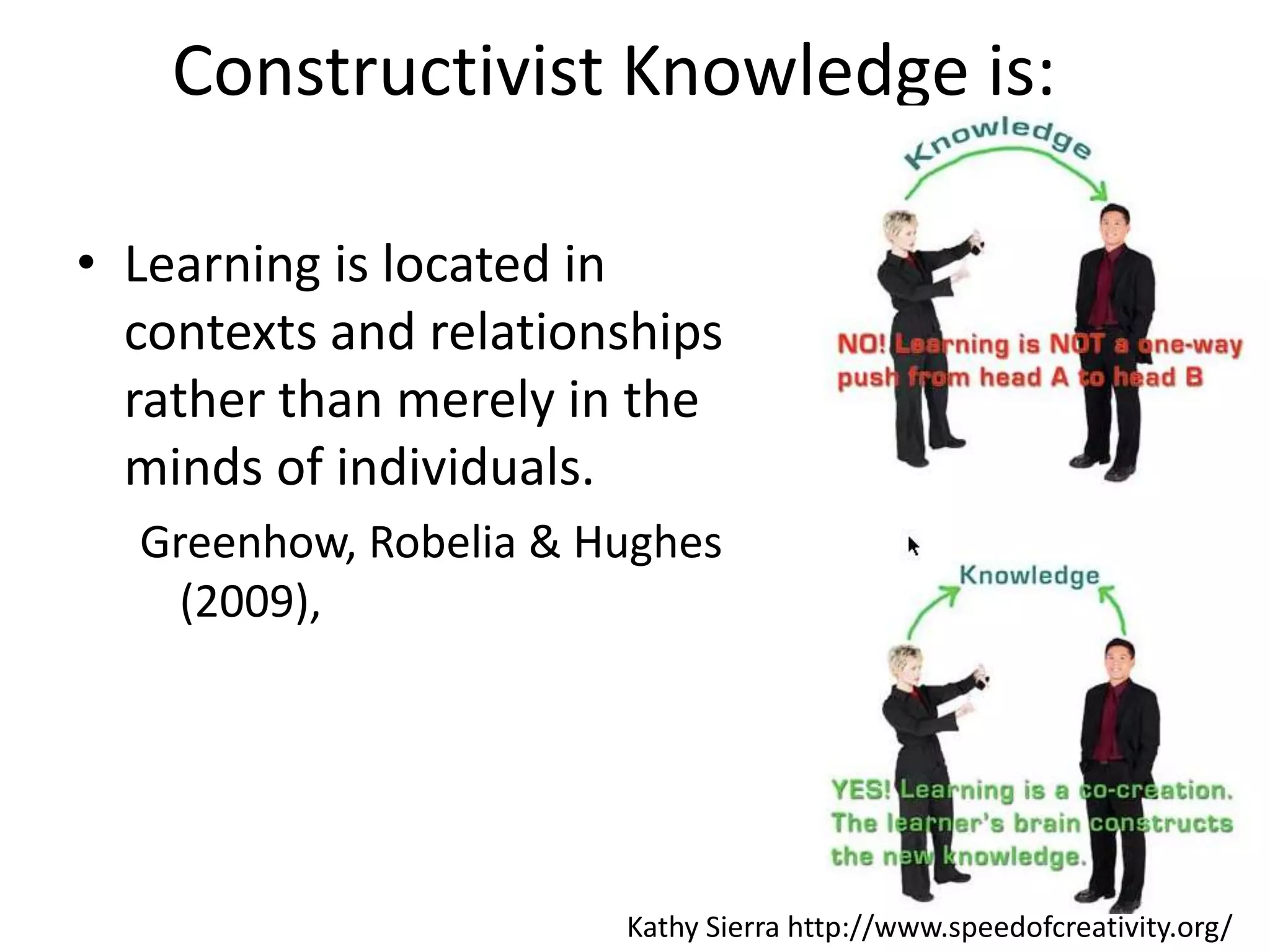
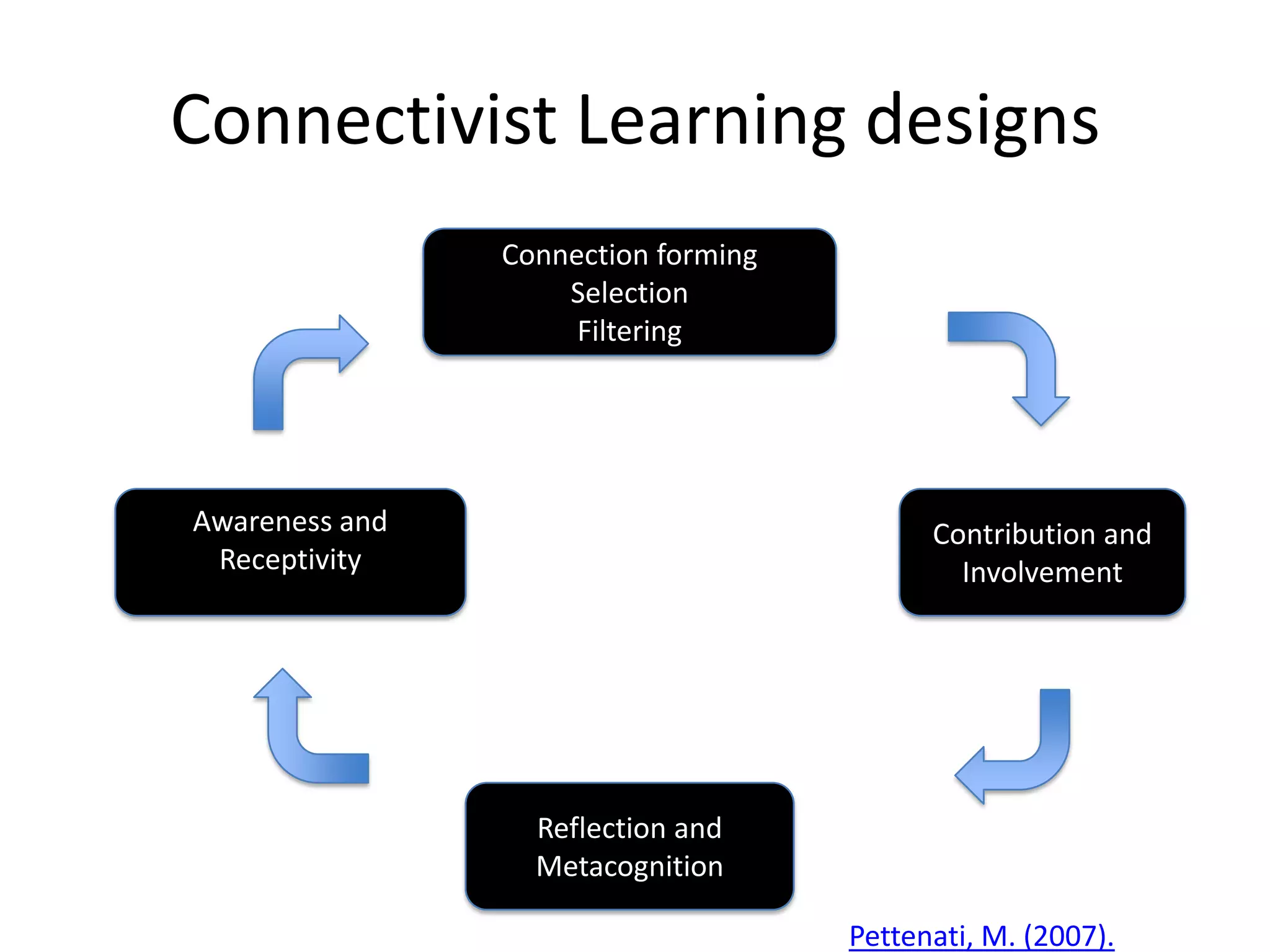
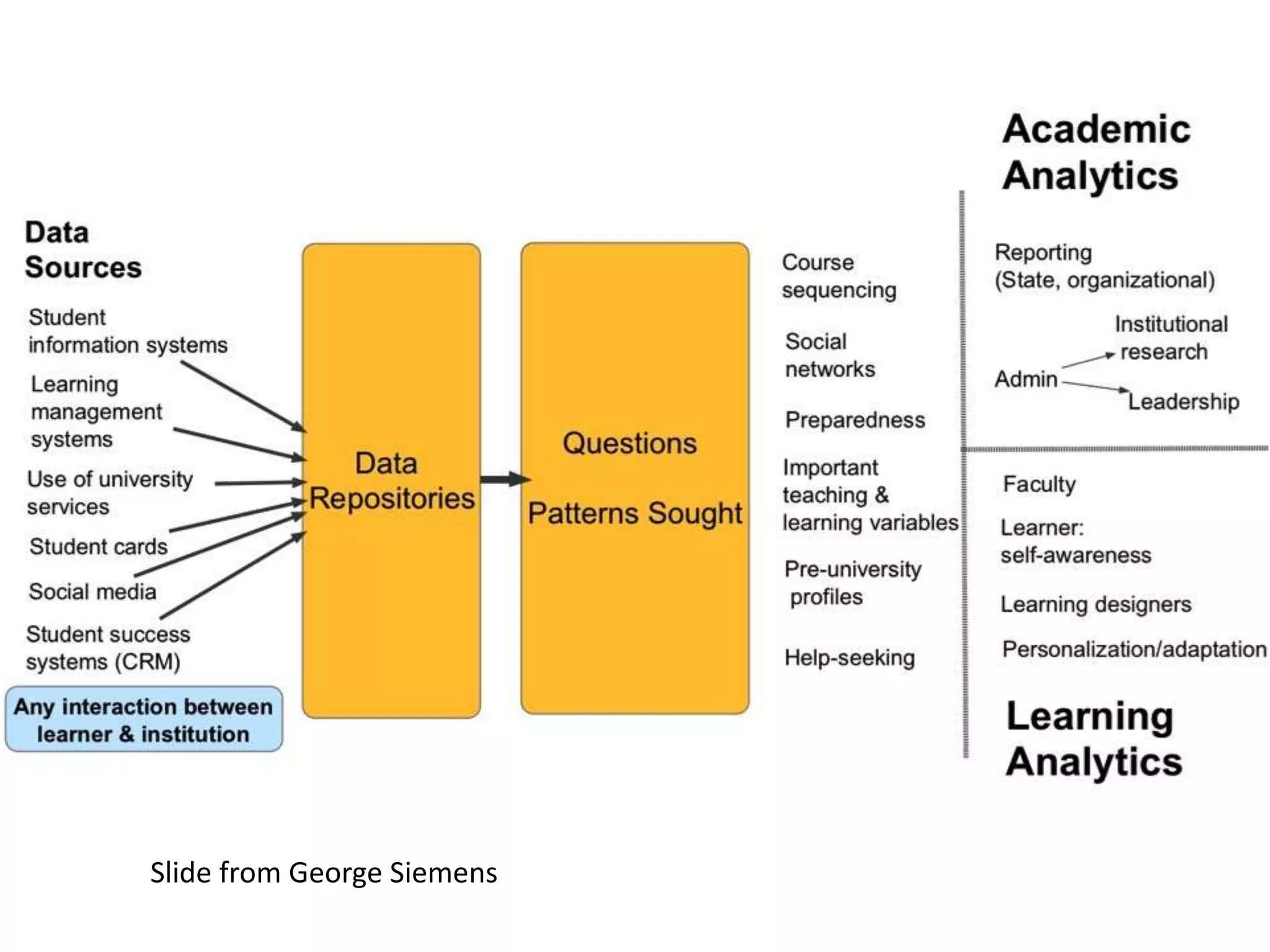
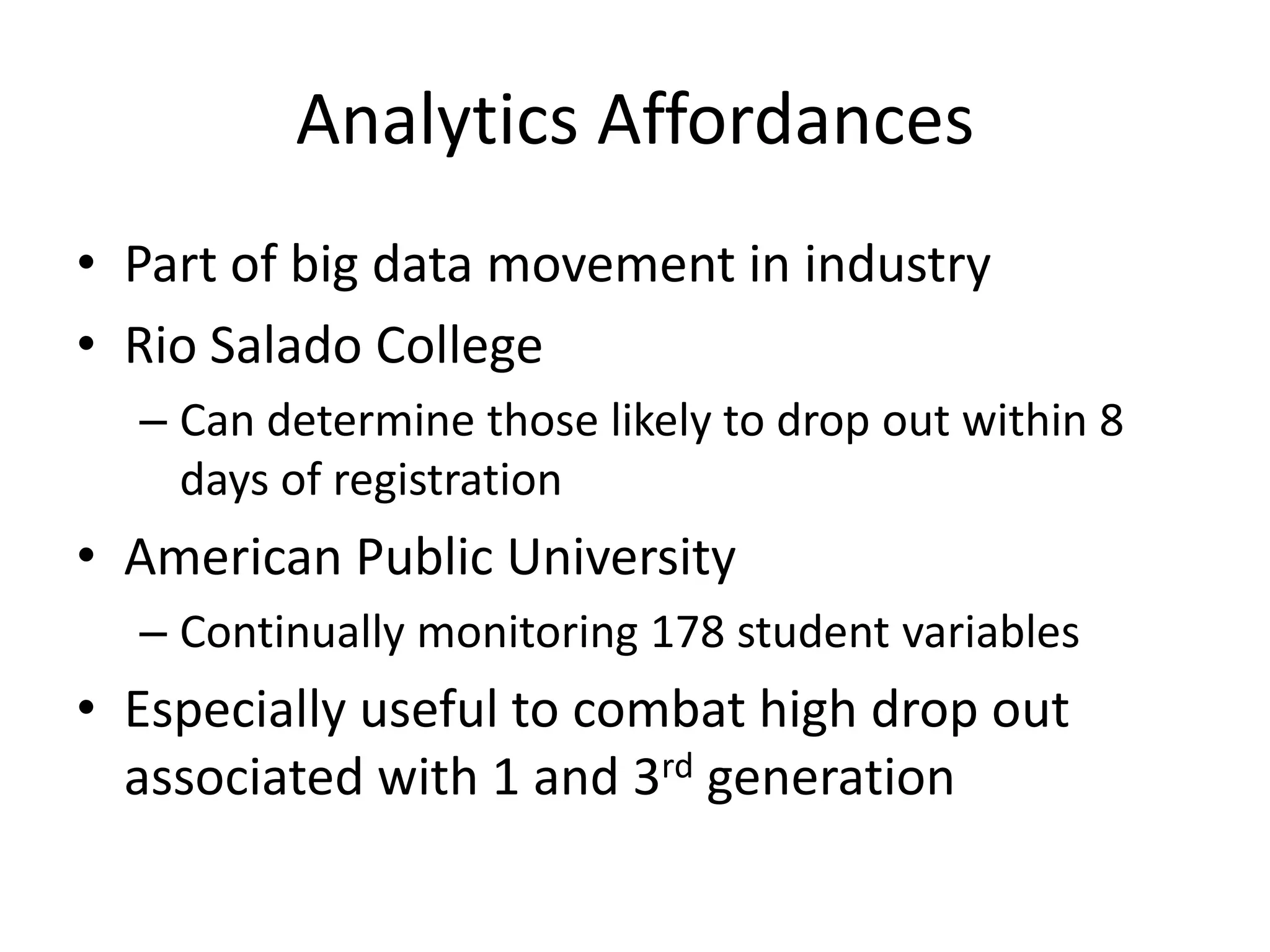
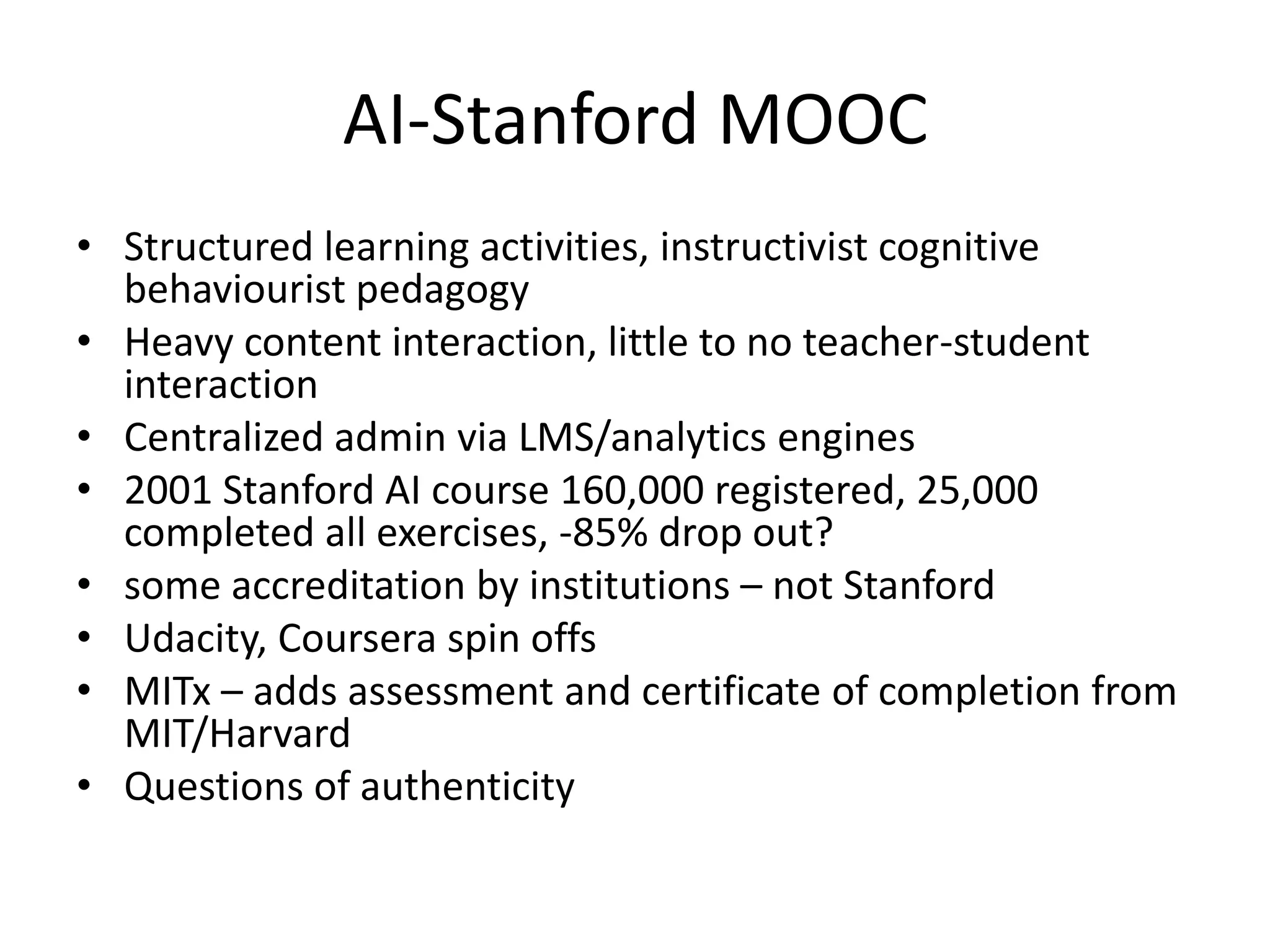
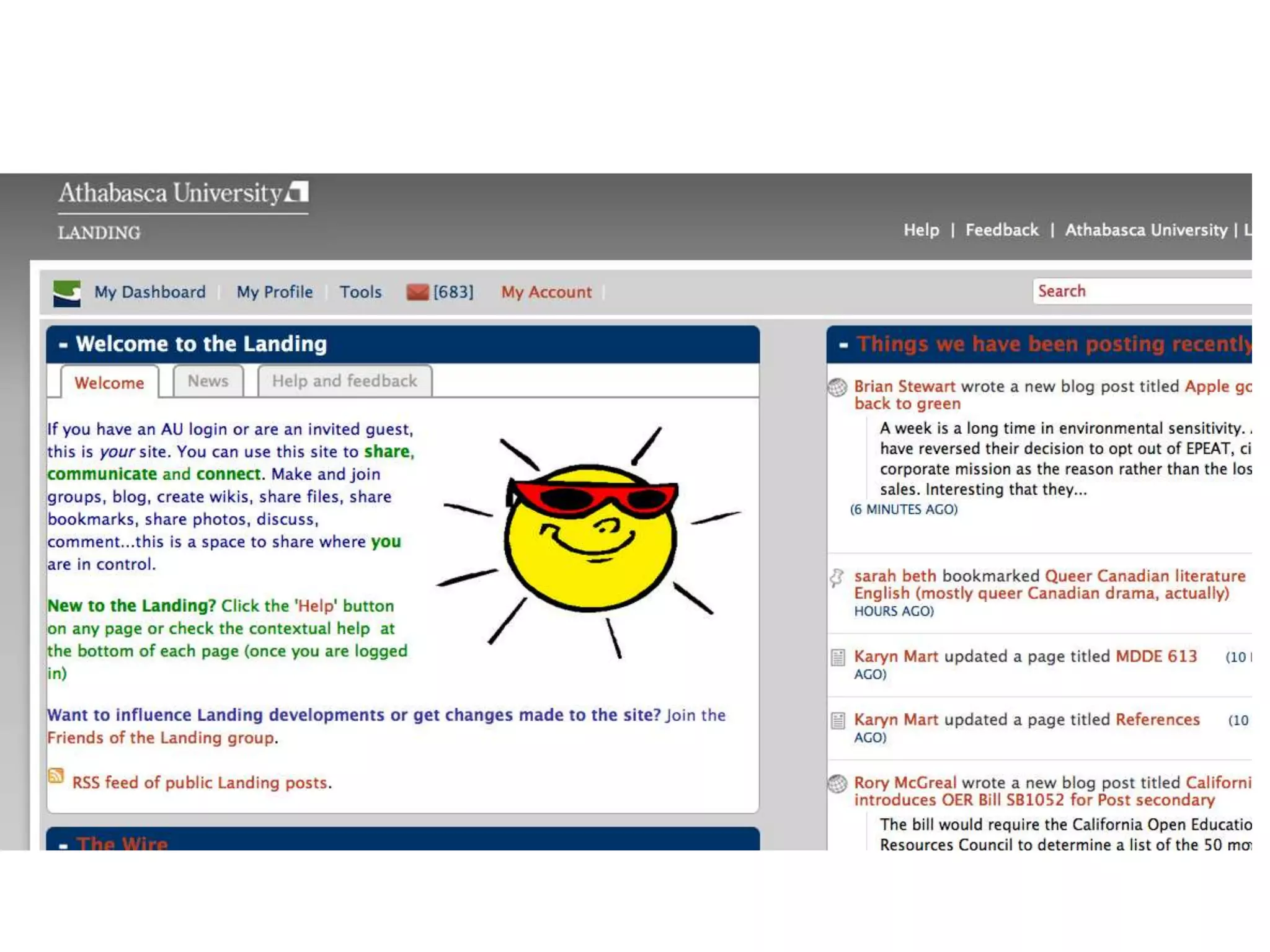
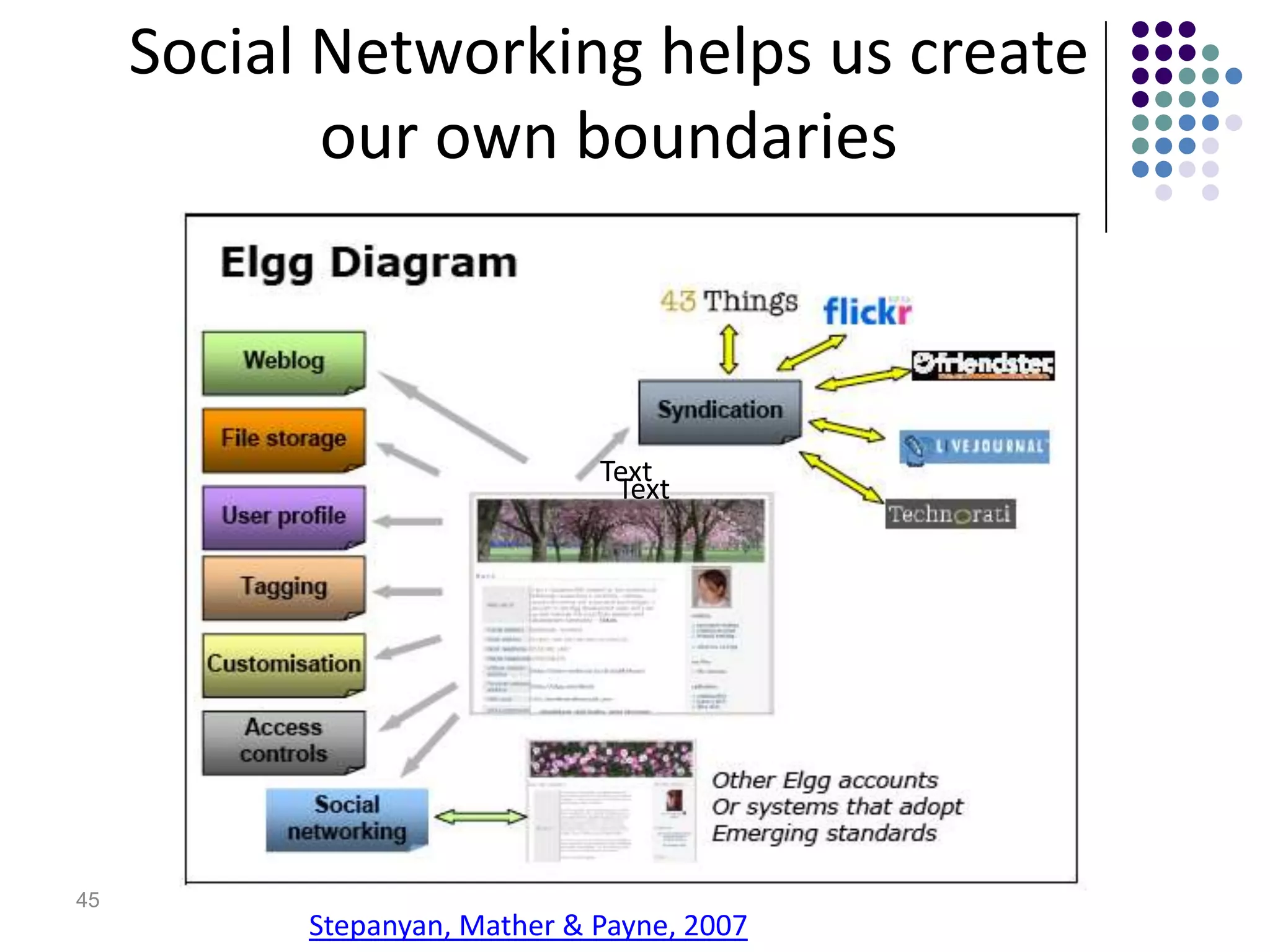
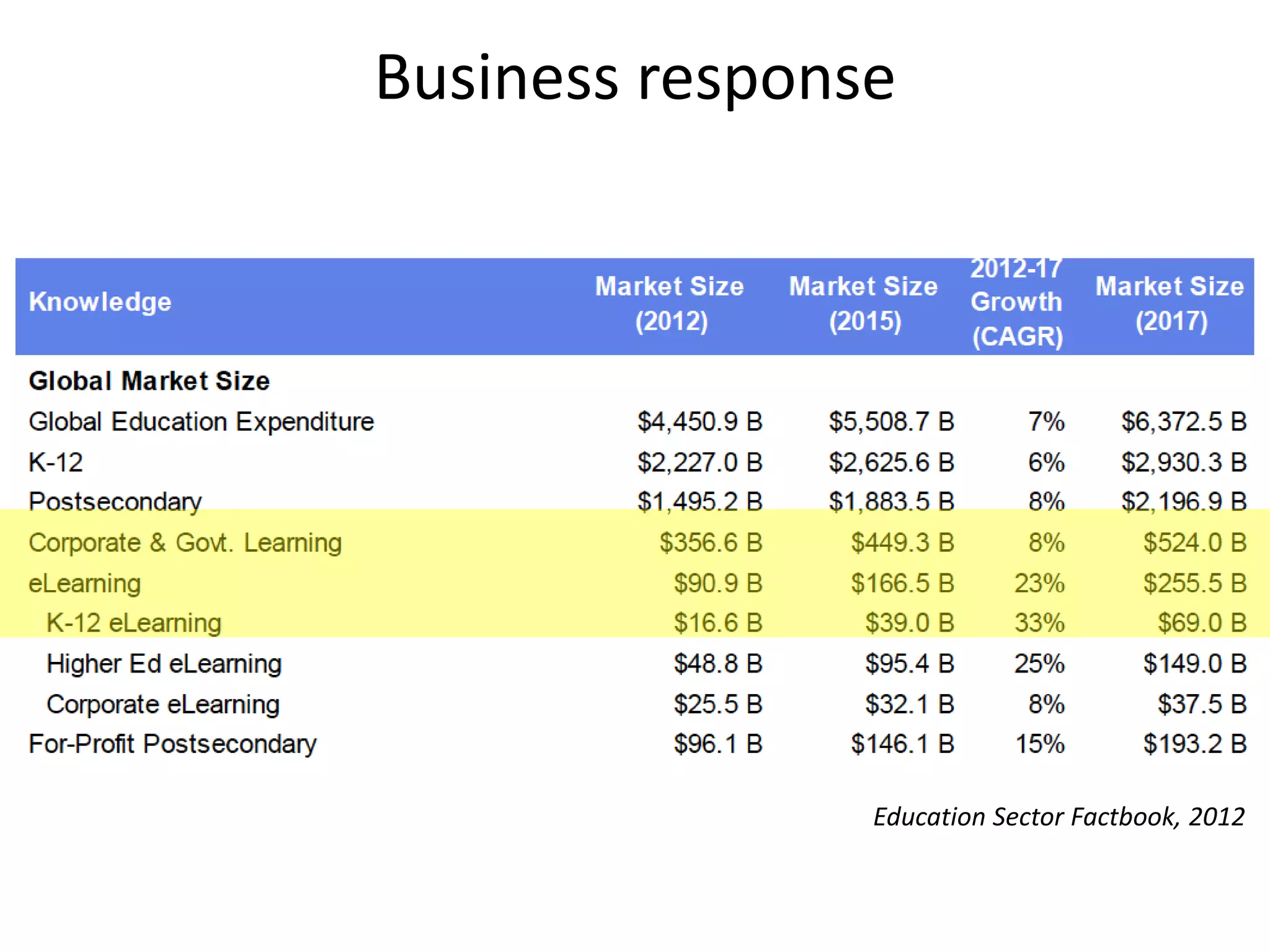
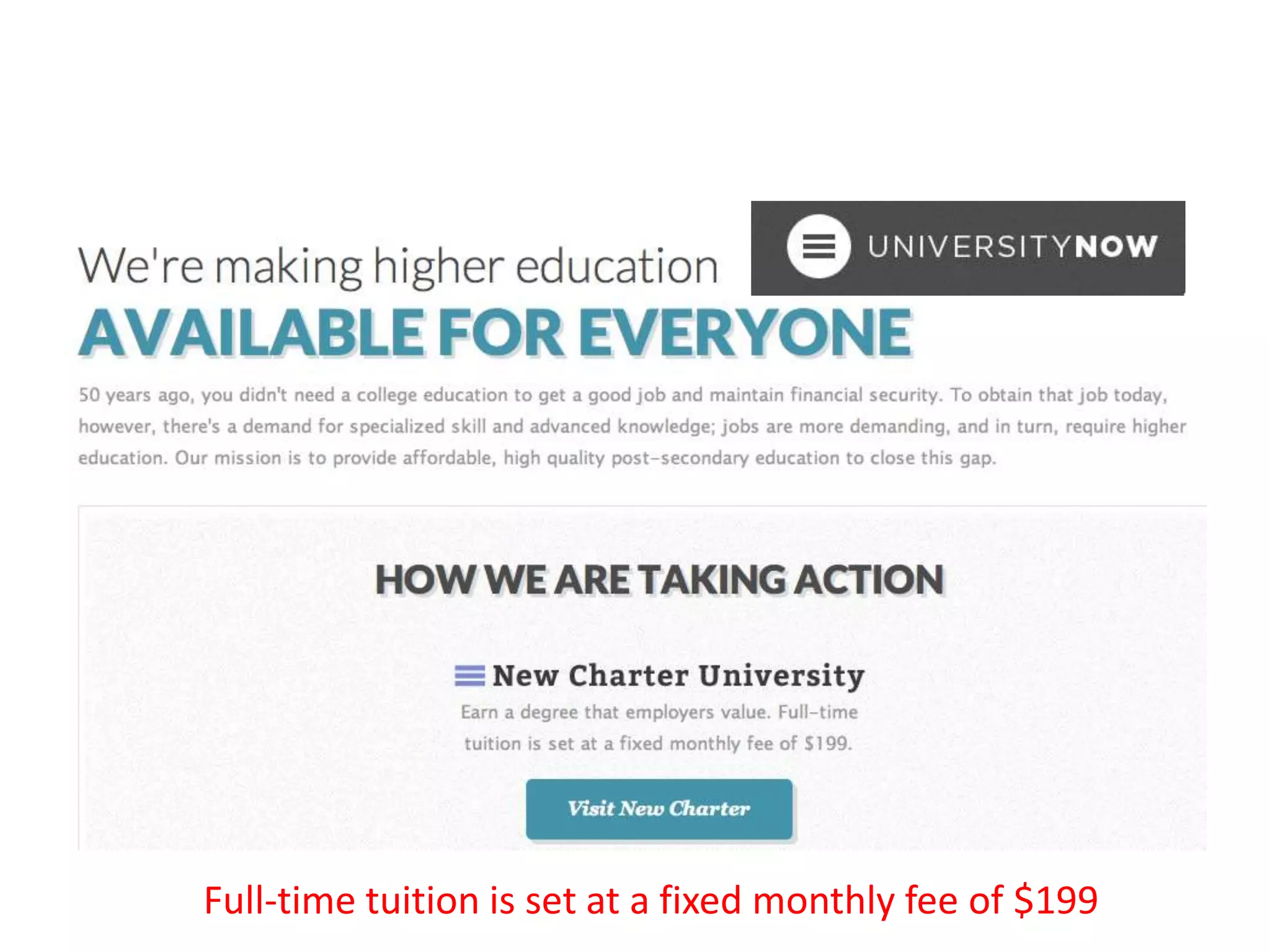
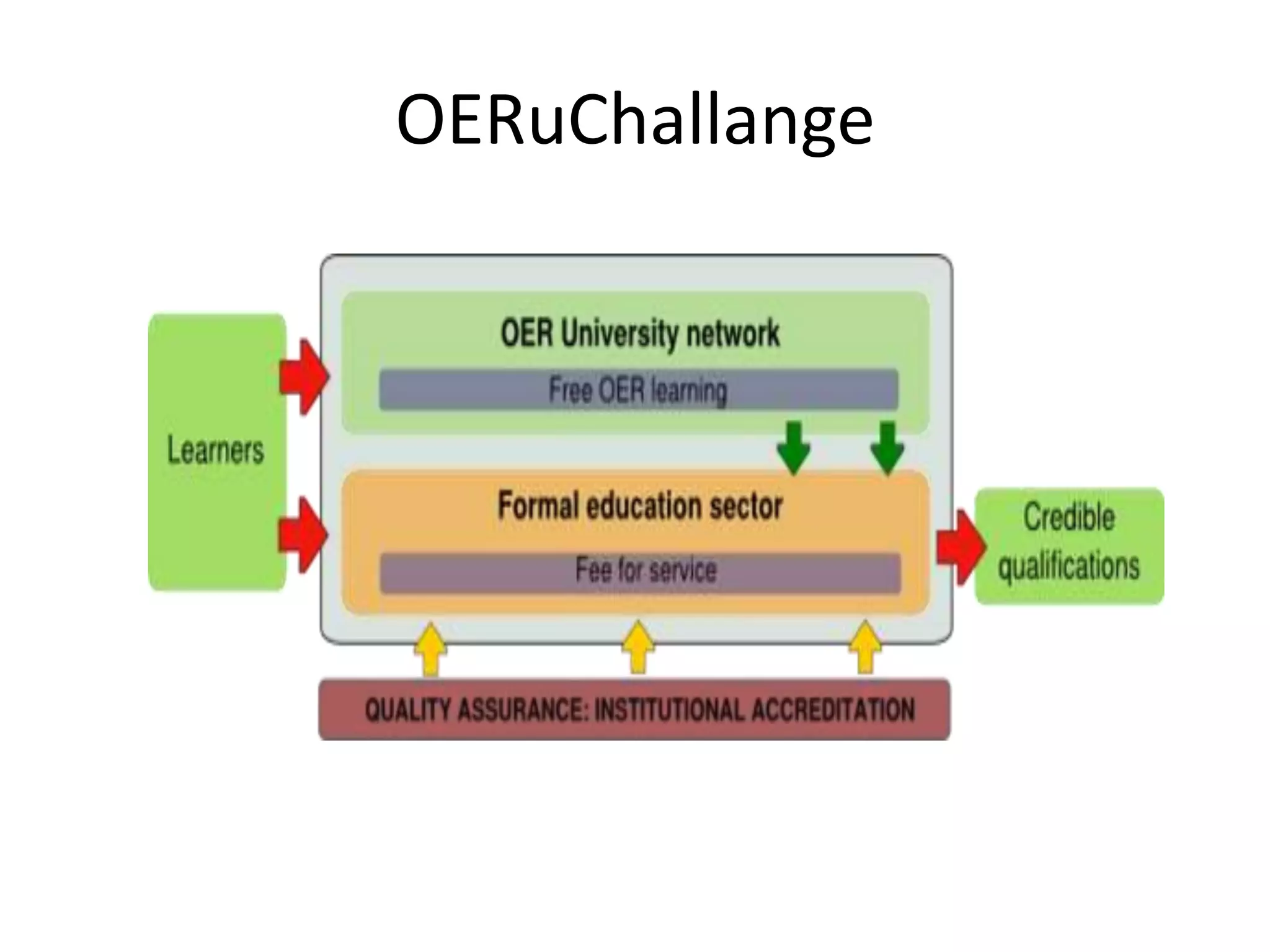
This document summarizes Terry Anderson's presentation on MOOCs, walled gardens, analytics and networks in multi-generation pedagogical innovations. It discusses the three generations of educational technology and pedagogy: 1) behaviorist/cognitive self-paced individual study, 2) constructivist emphasis on groups, and 3) connectivist focus on networks and sets. Recent developments discussed include open educational resources, learning analytics, MOOCs, walled social networks, and the unbundling of higher education services.