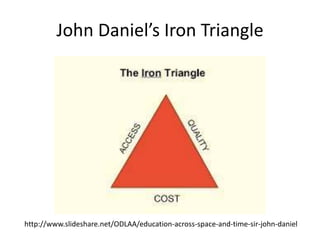
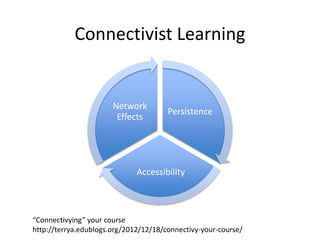
The document discusses the evolution of online teaching and learning compared to traditional campus-based education, emphasizing three pedagogical generations: behaviorist/cognitive, social constructivist, and connectivist. It highlights the importance of quality indicators in different pedagogies, including content clarity, collaboration, and network effects. The author advocates for a shift in education quality control that aligns with modern expectations and the complexities of online learning environments.