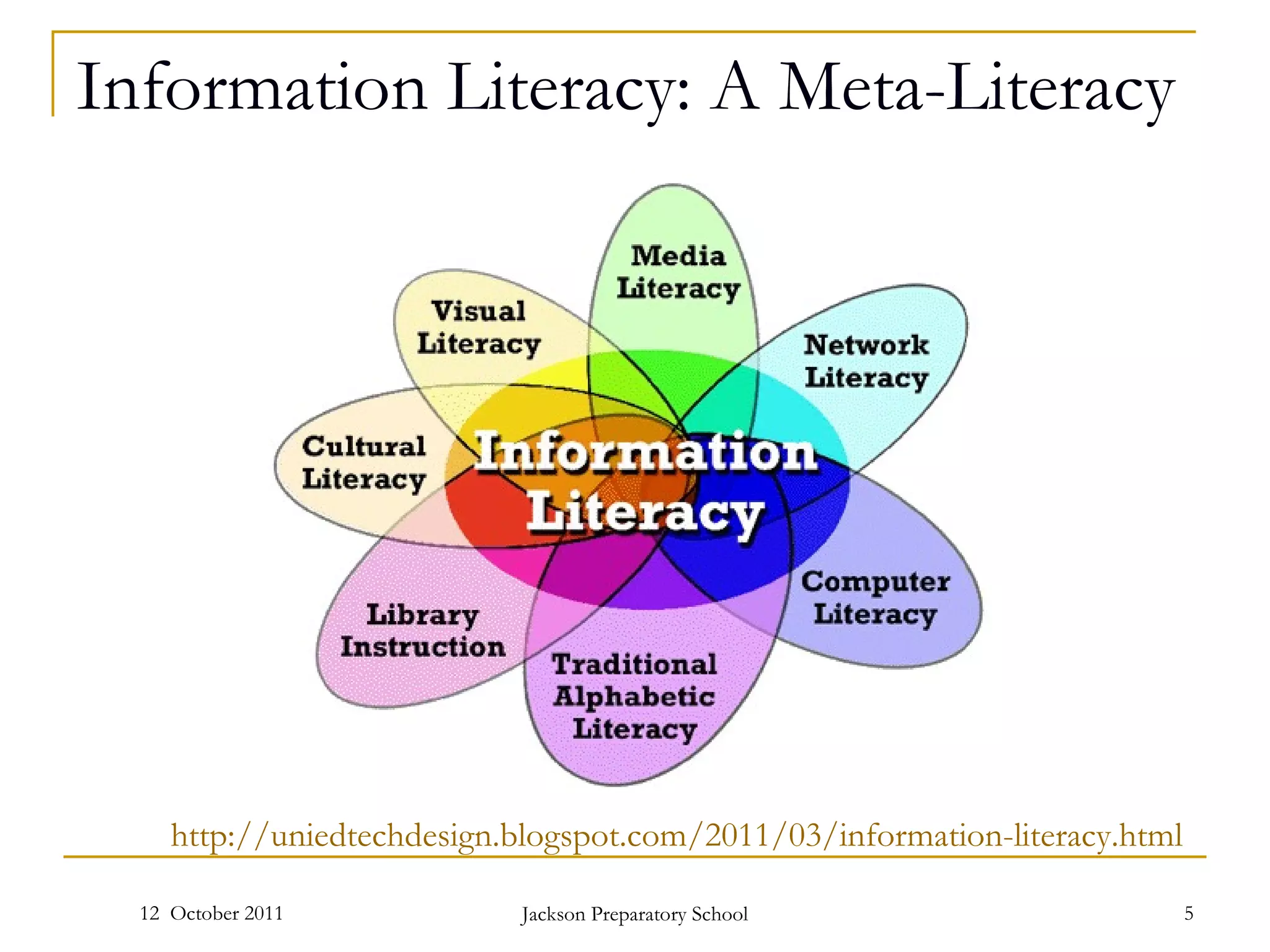
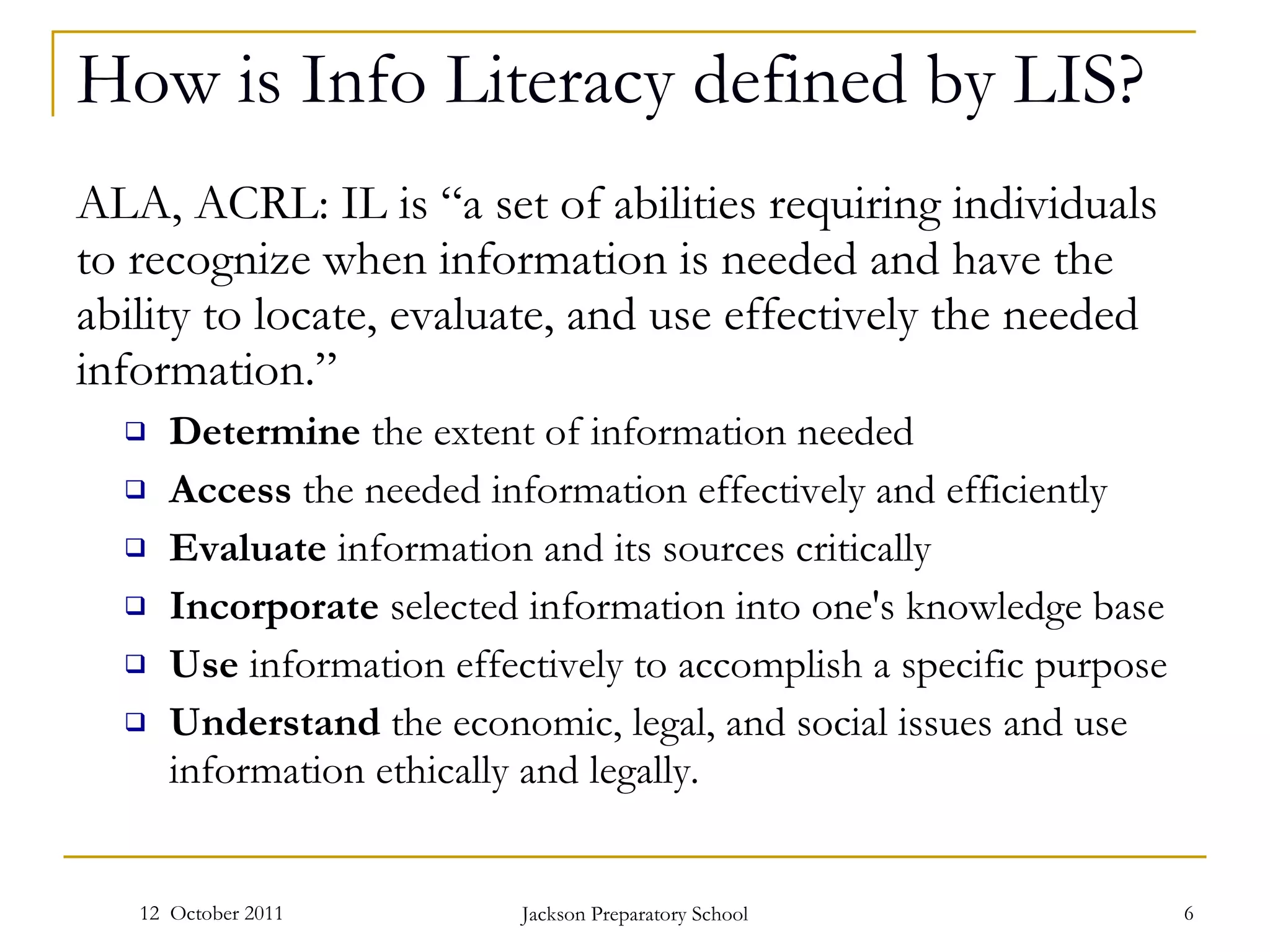
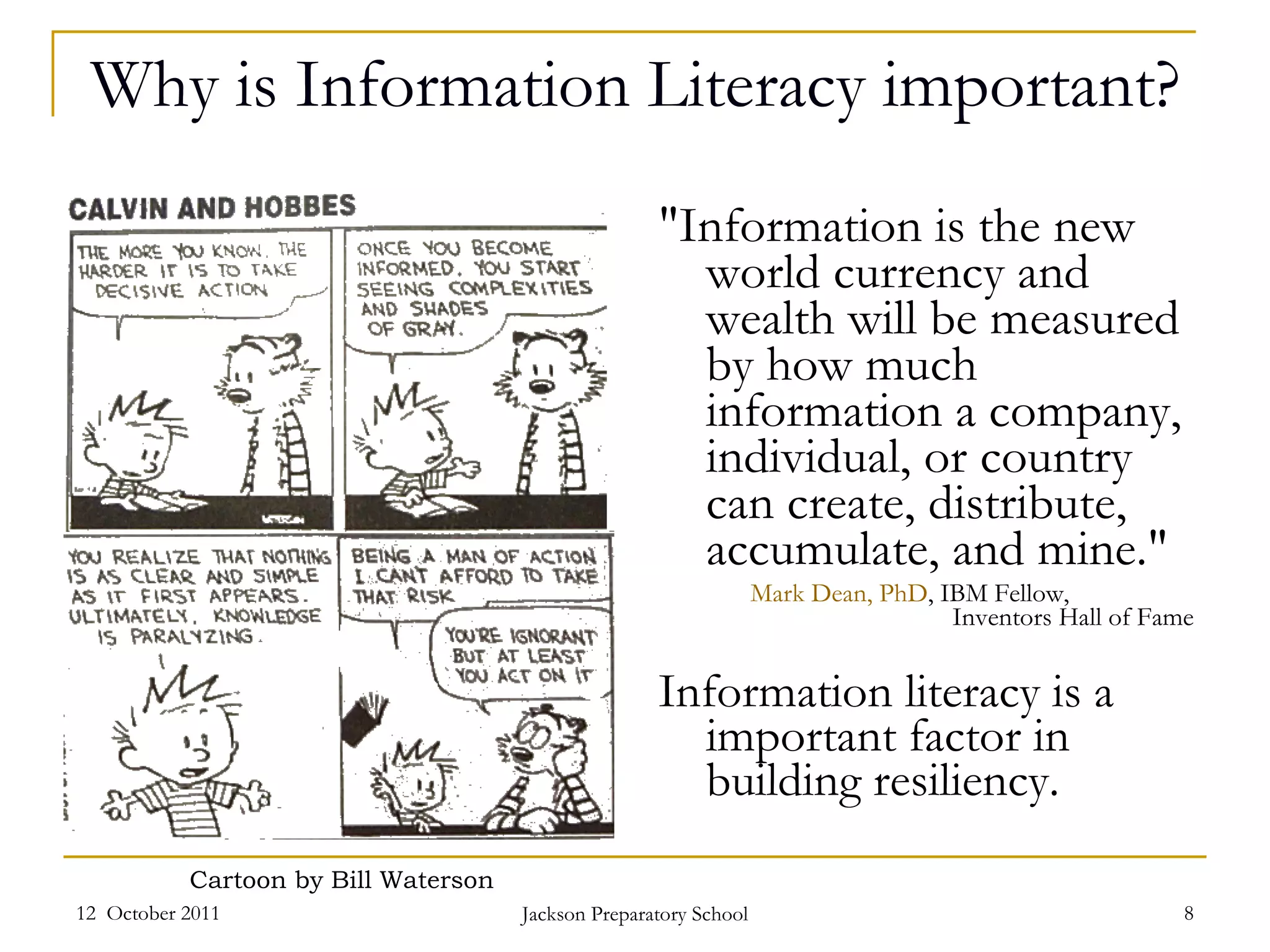
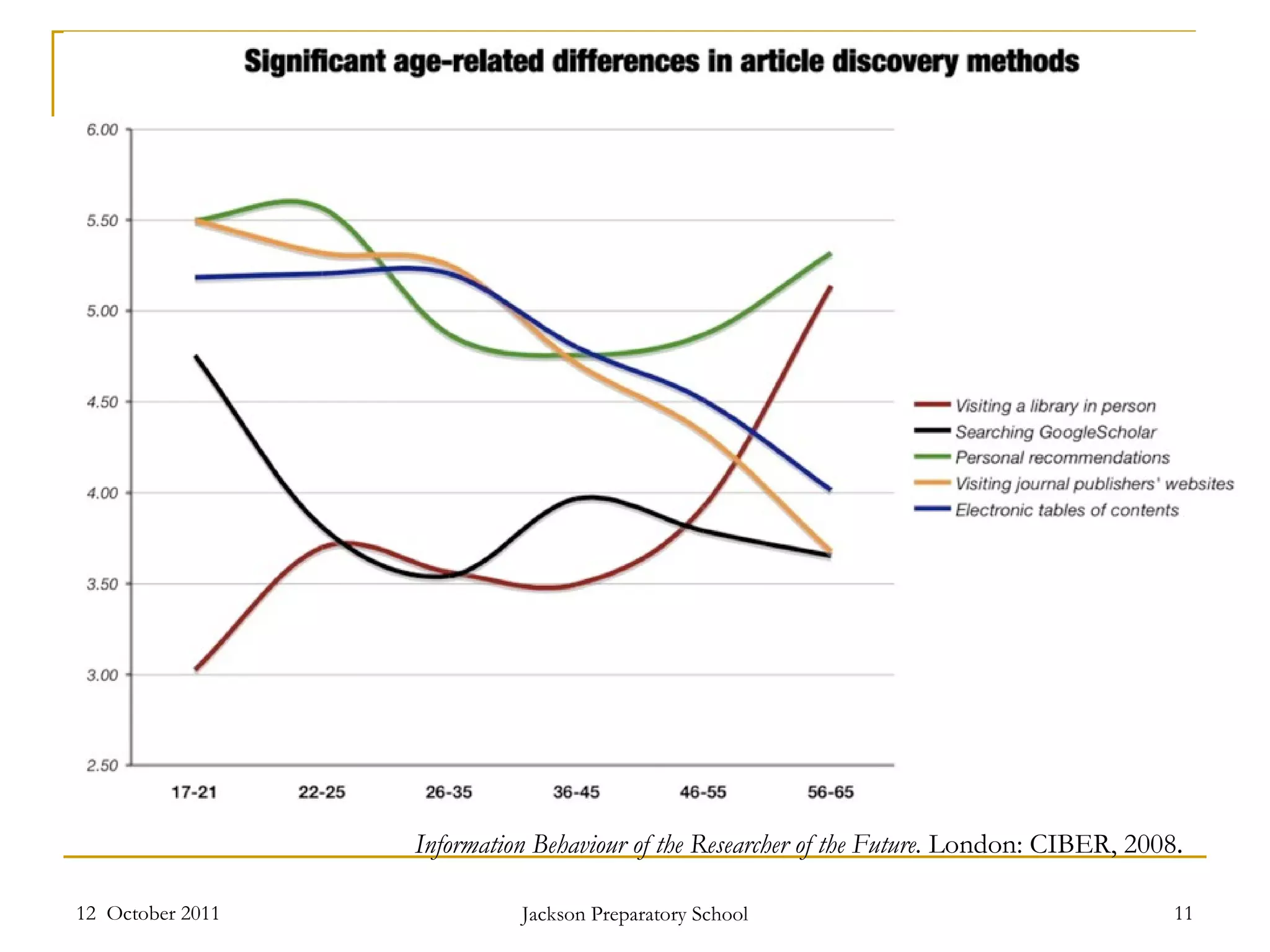
The document discusses information literacy and its importance. It defines information literacy as a set of abilities requiring individuals to recognize needed information and locate, evaluate, and effectively use it. Information literacy is important because information is the new currency and builds resiliency. Research shows the Google Generation prefers quick information over in-depth searching. Various frameworks are discussed for teaching and assessing information literacy skills.
![Information Literacy for the Google Generation Teresa S. Welsh, Ph.D. [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/welshjps11-111012080628-phpapp02/75/Information-Literacy-for-the-Google-Generation-1-2048.jpg)
















![Thank you for your attention. Please email me at: [email_address] 12 October 2011 Jackson Preparatory School](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/welshjps11-111012080628-phpapp02/75/Information-Literacy-for-the-Google-Generation-33-2048.jpg)