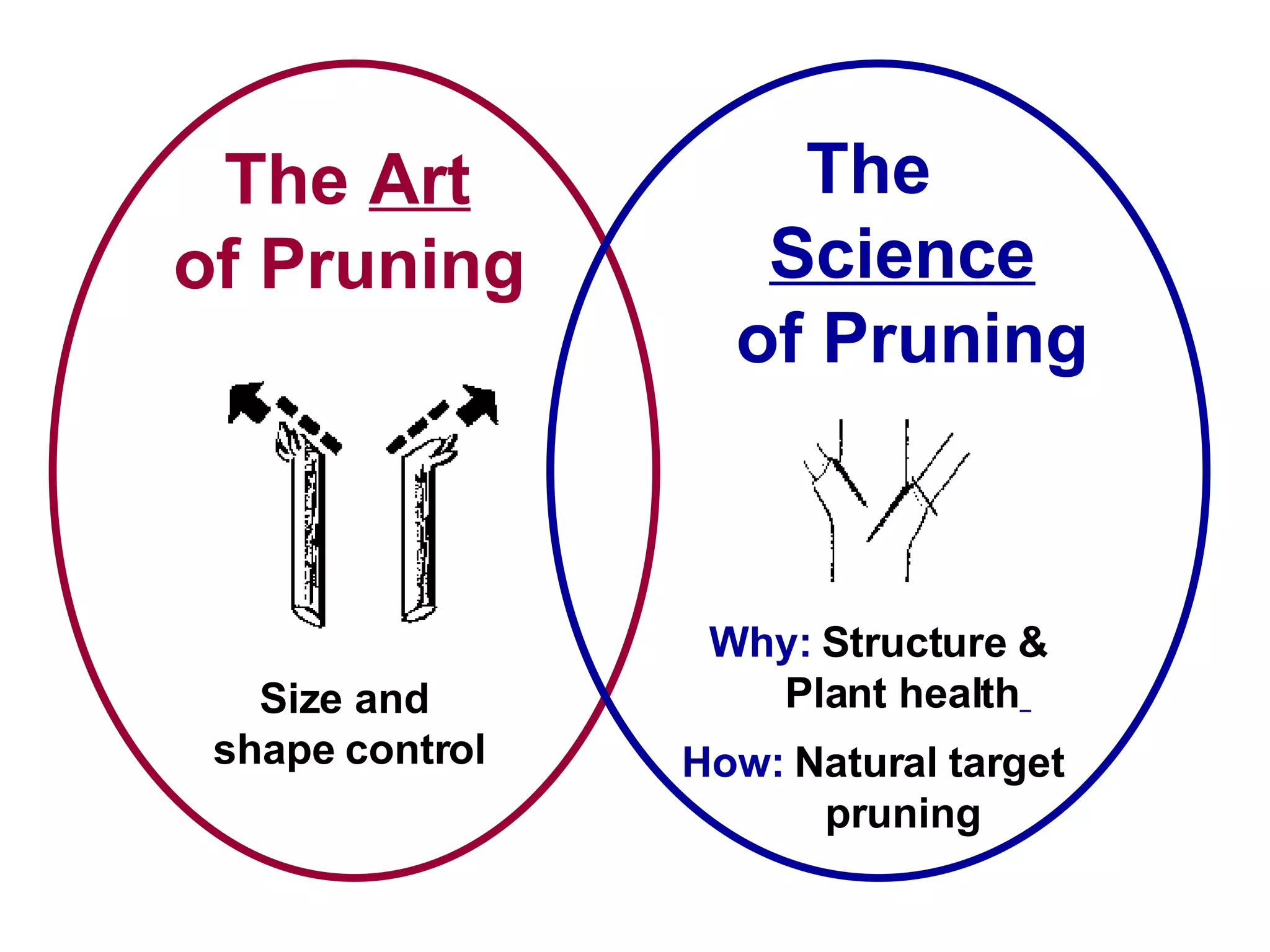
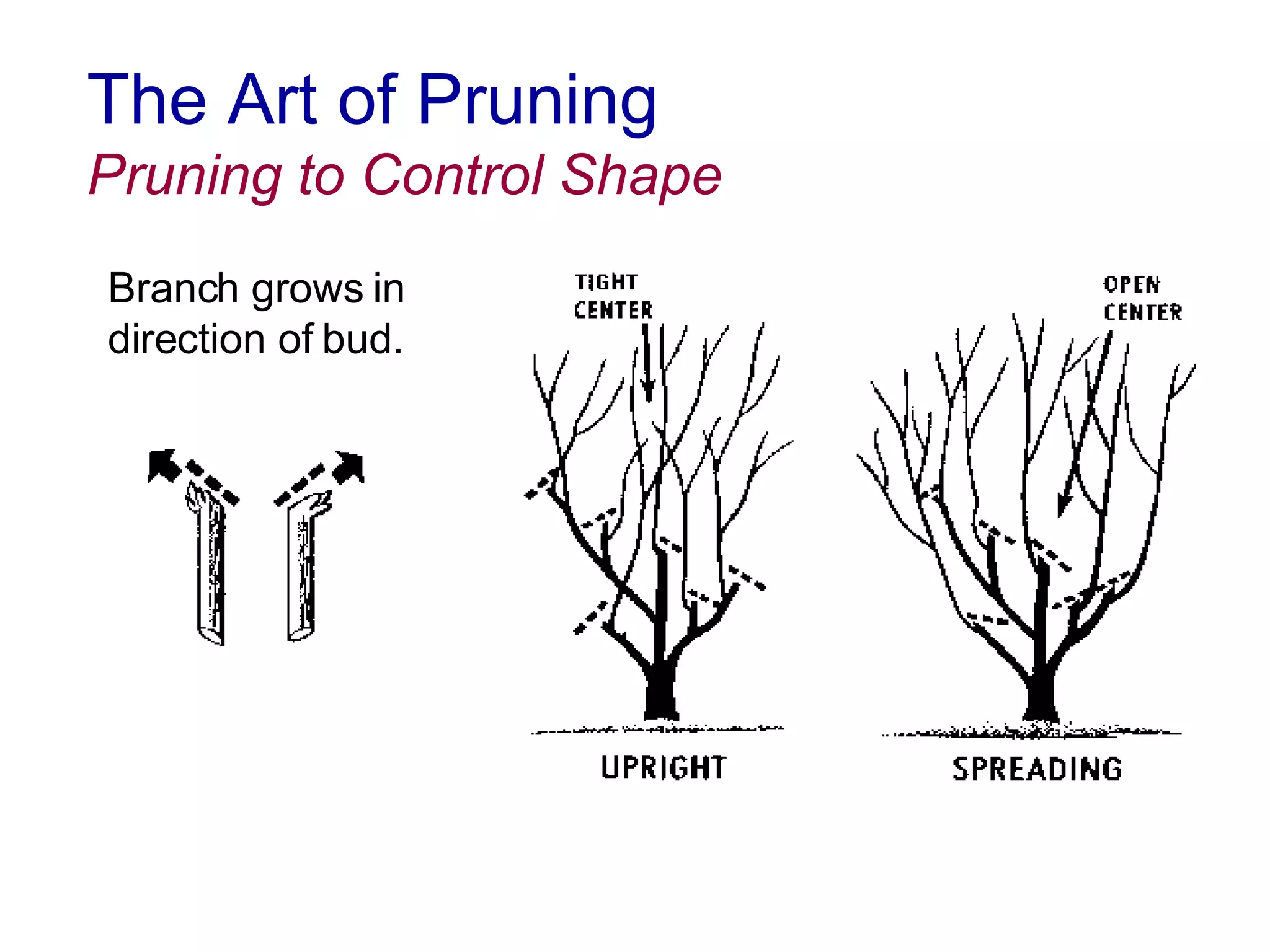
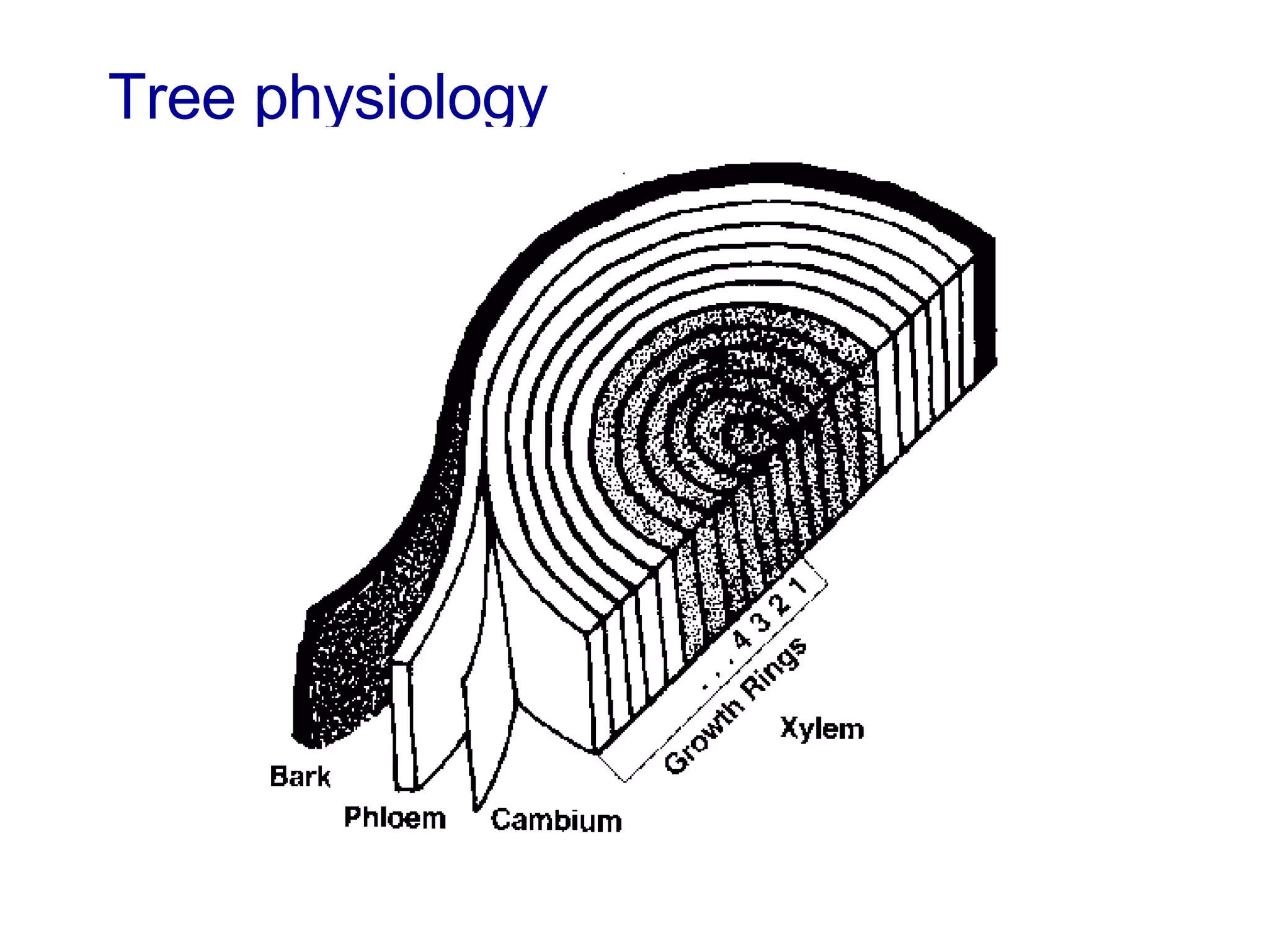
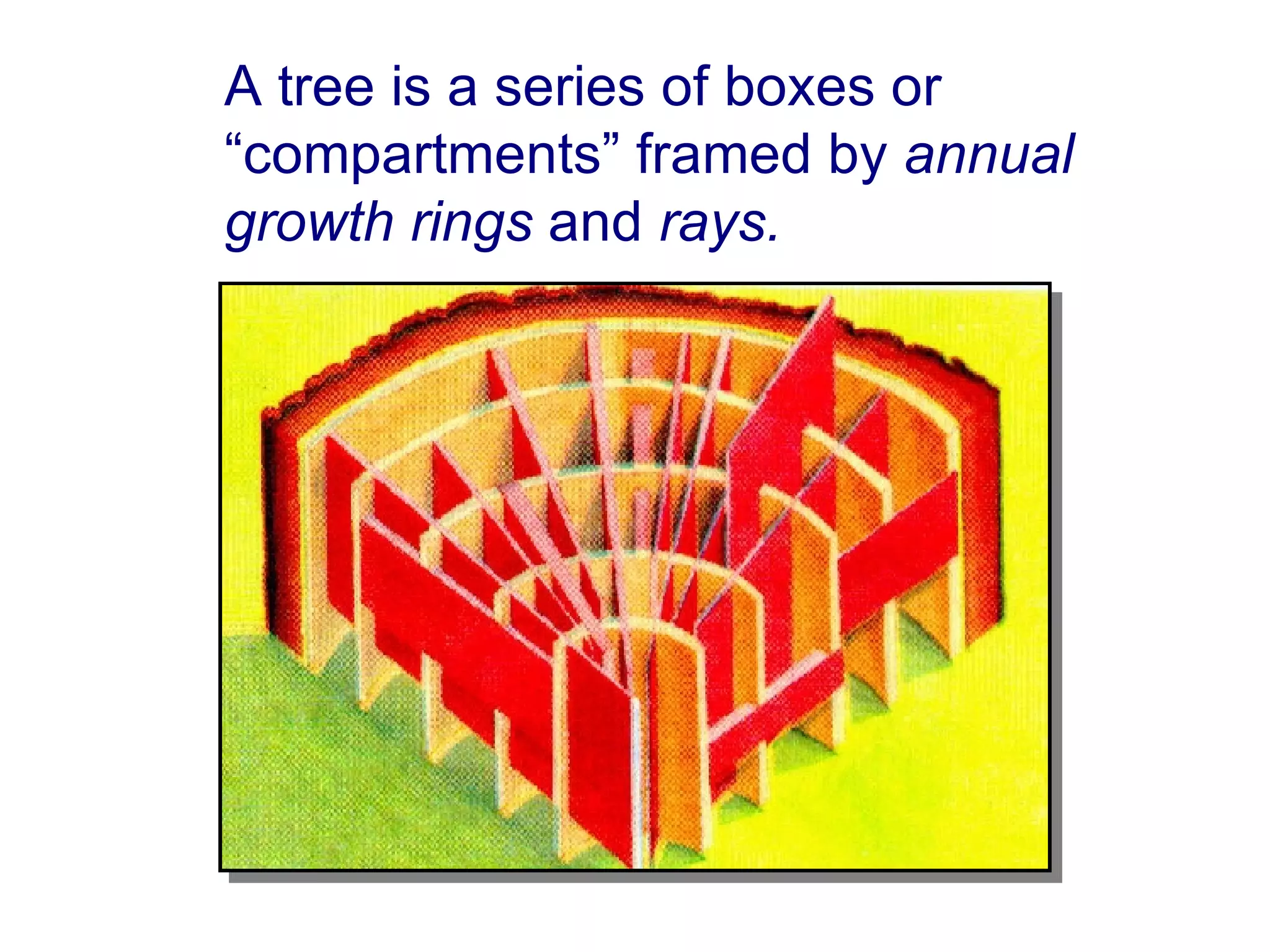
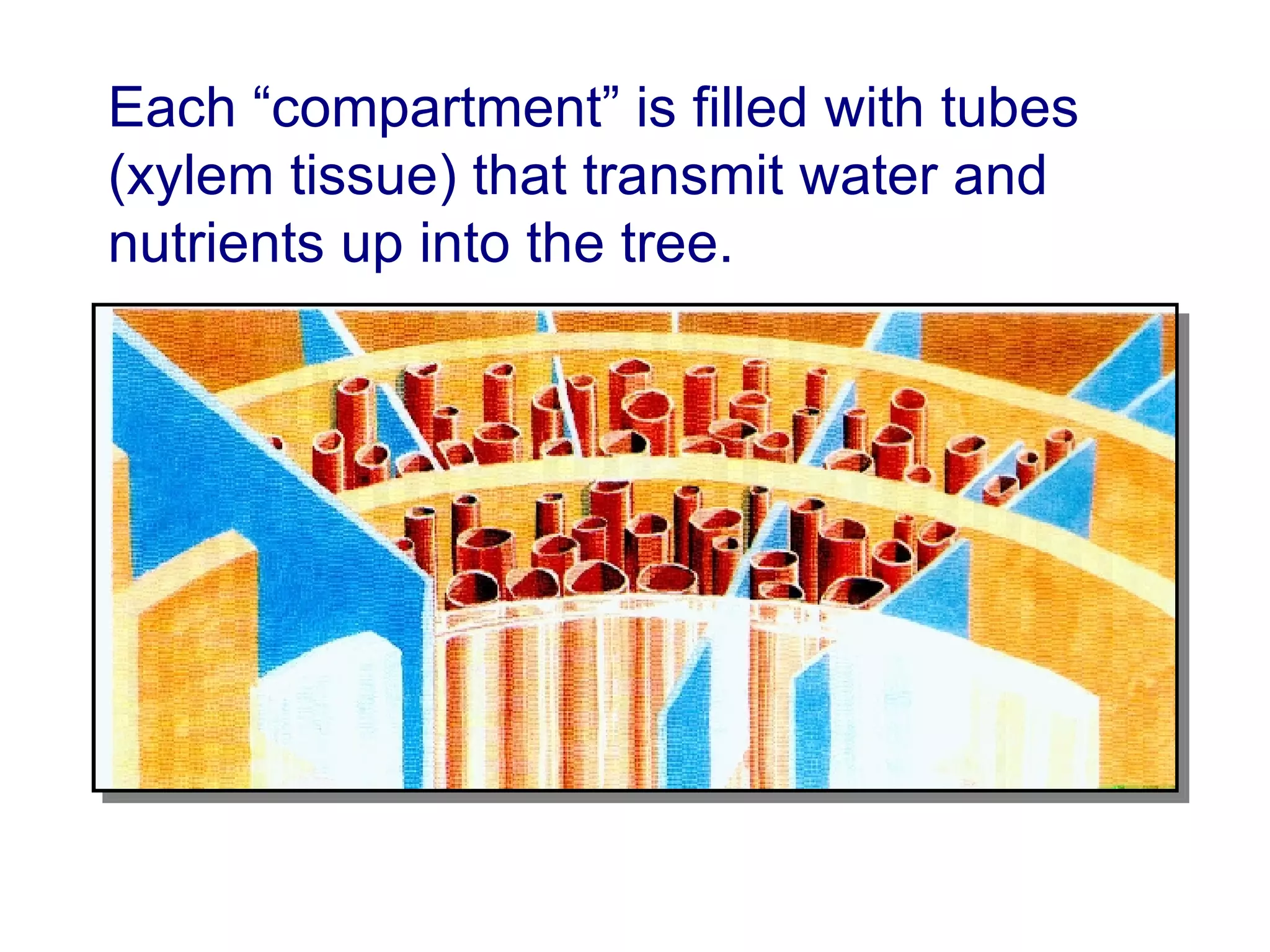
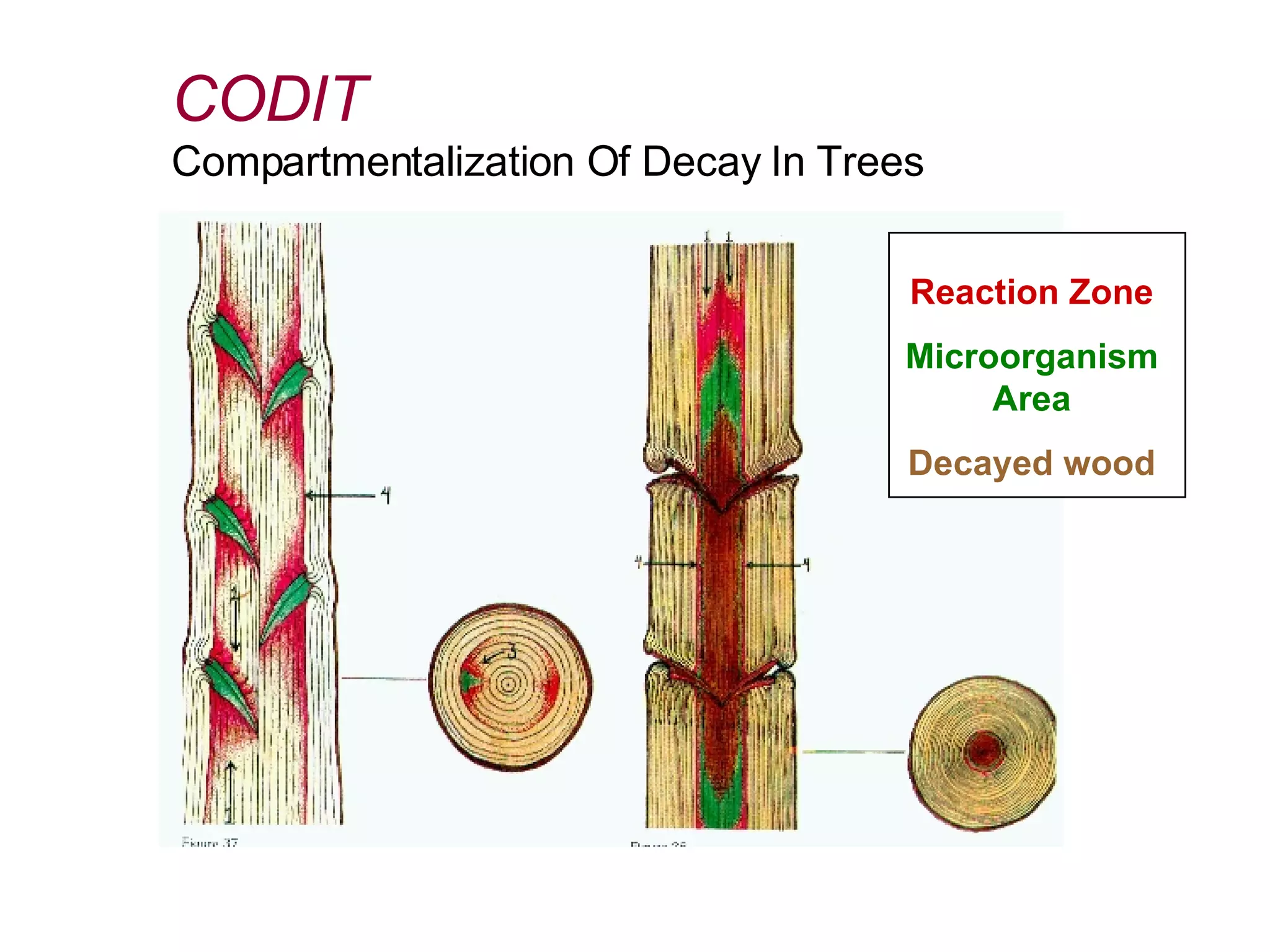
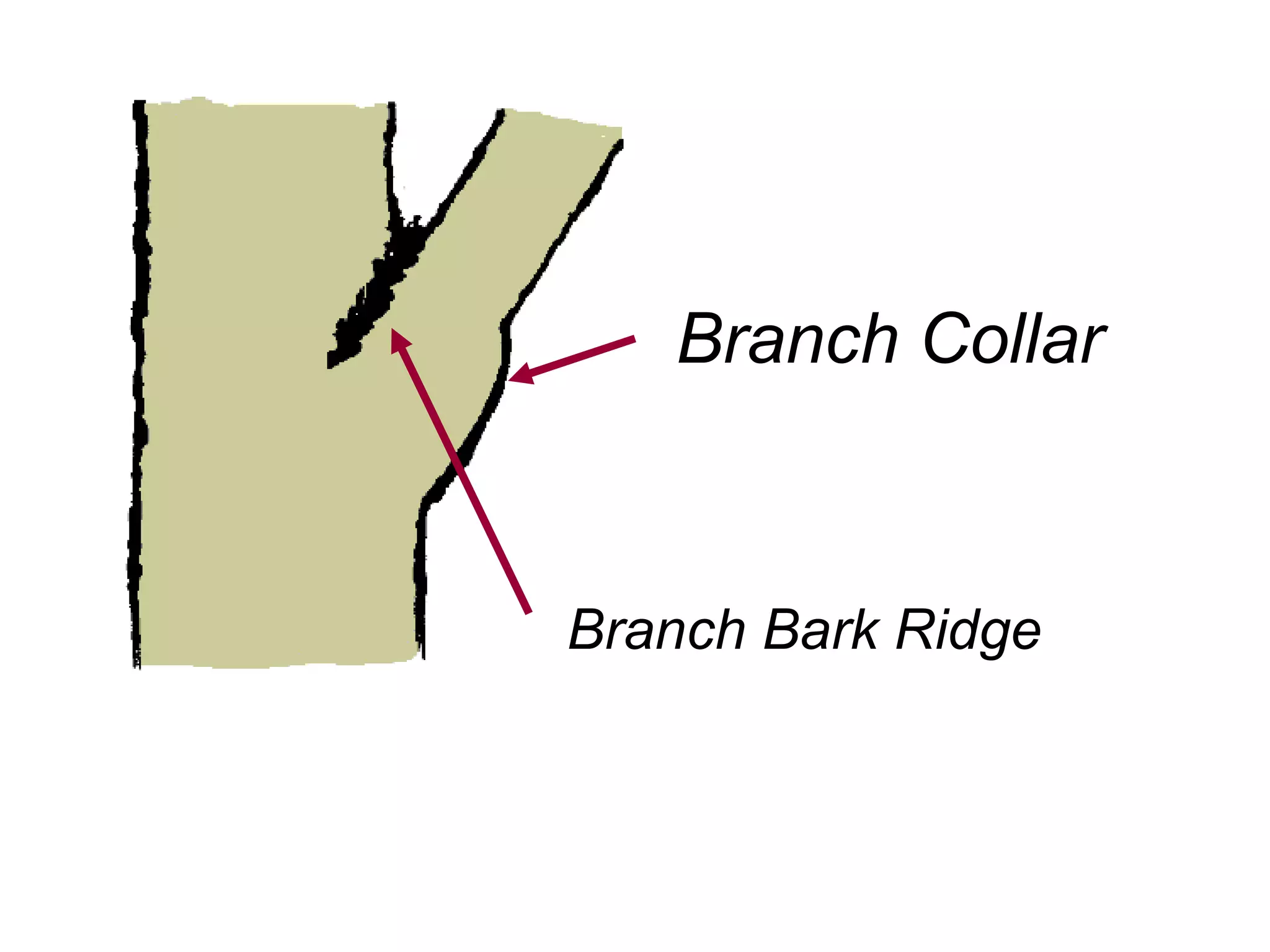
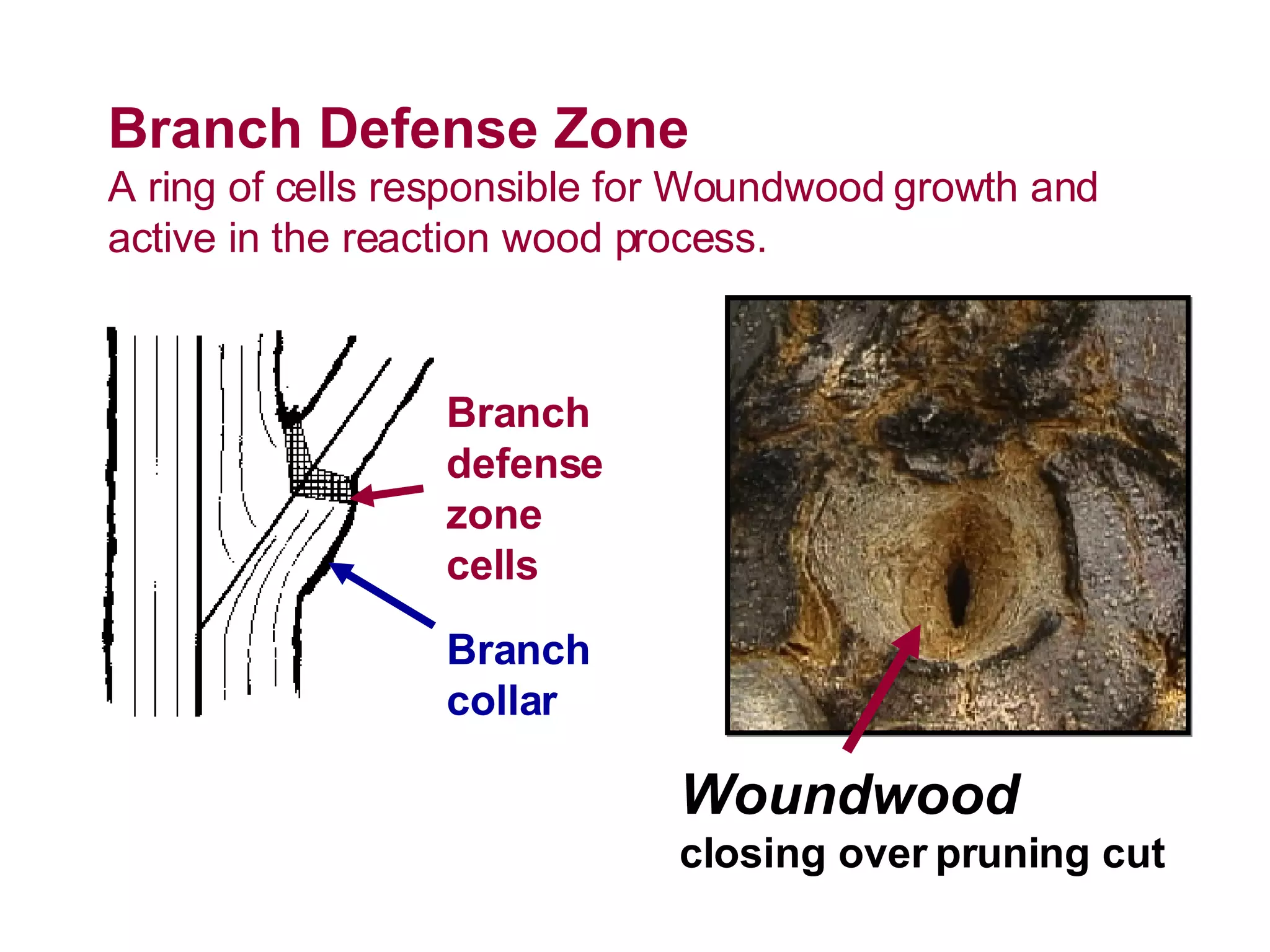
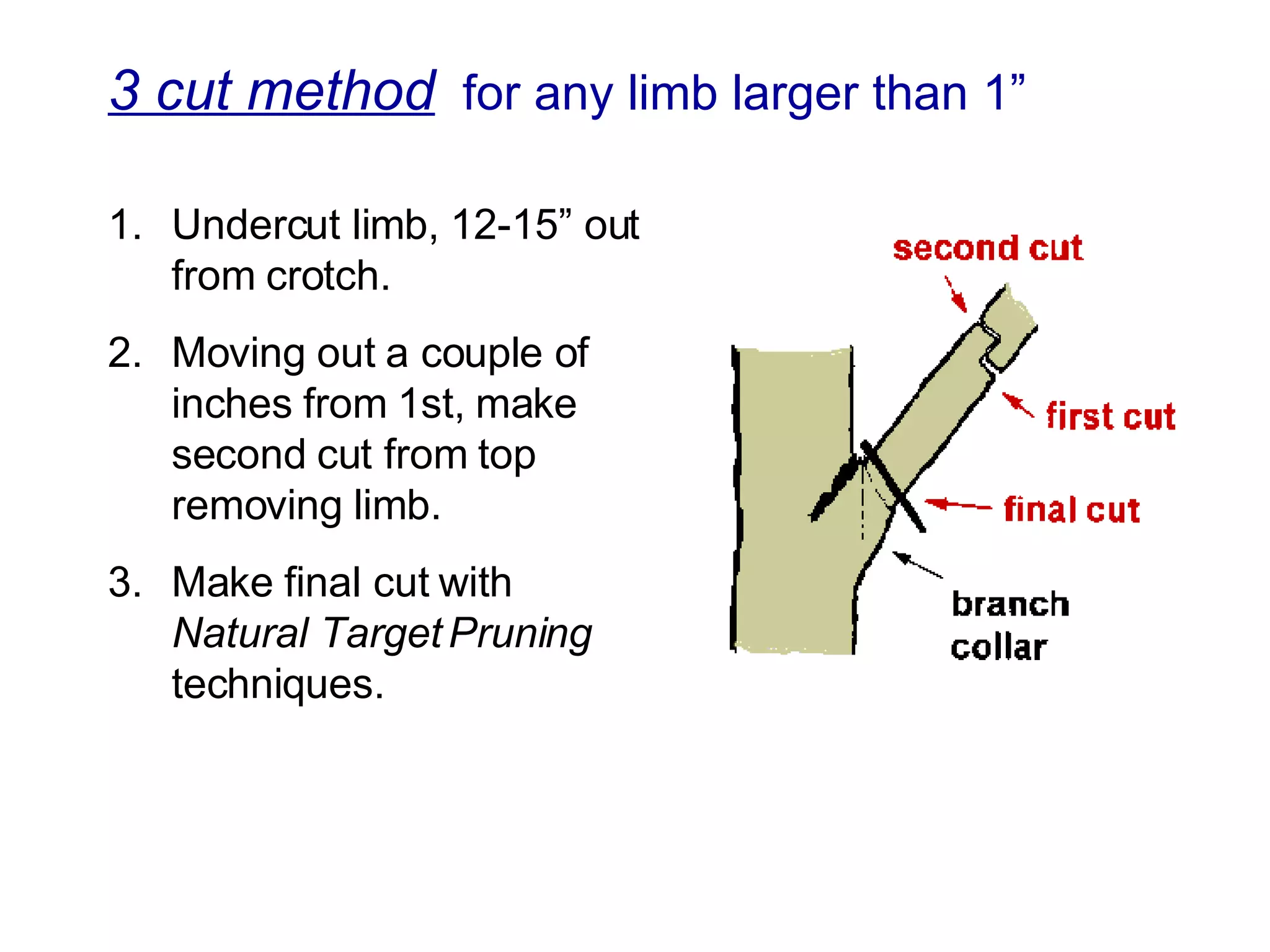
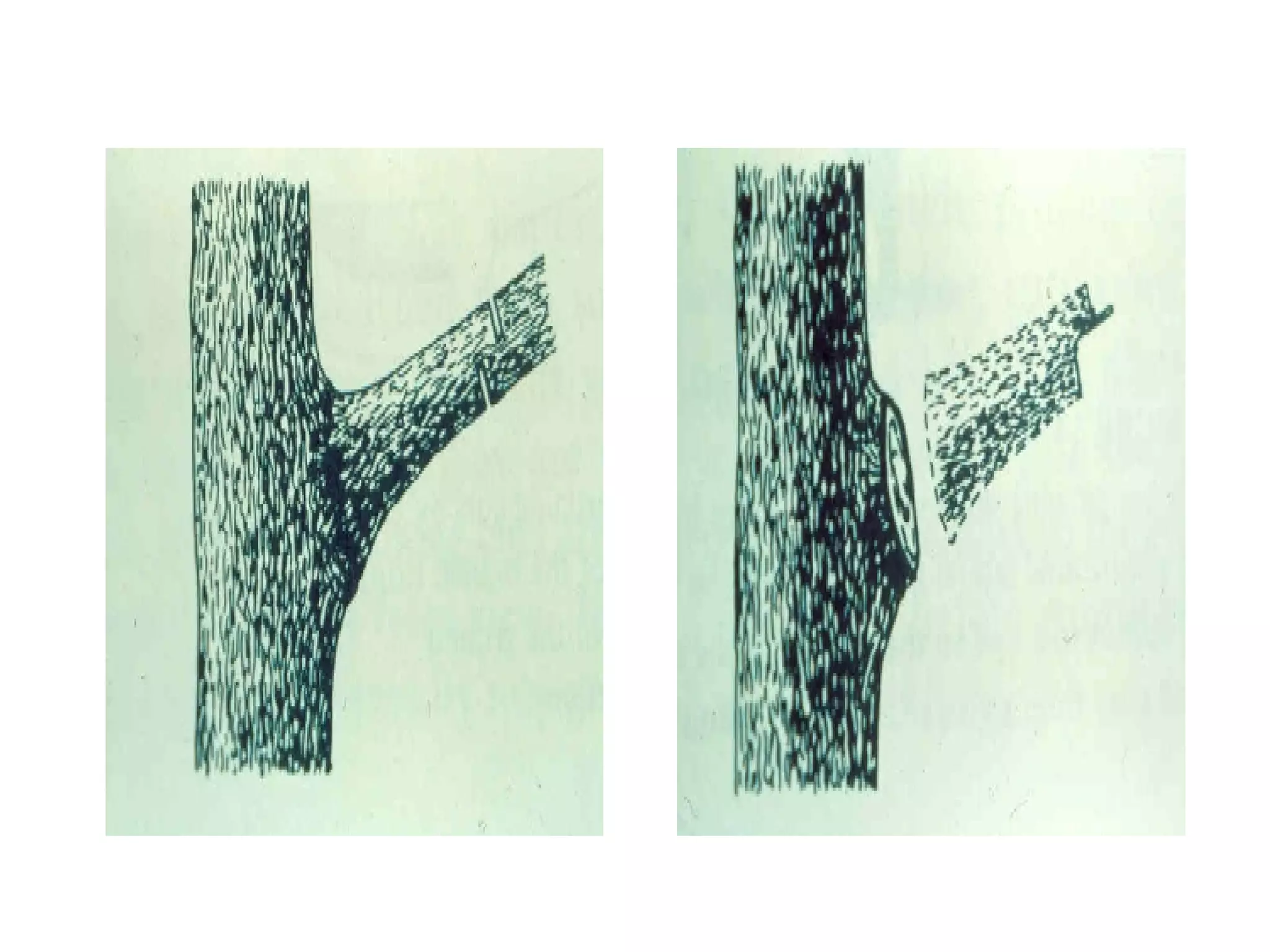
1. The document discusses different types of pruning cuts including natural target pruning cuts, reduction cuts, and heading cuts.
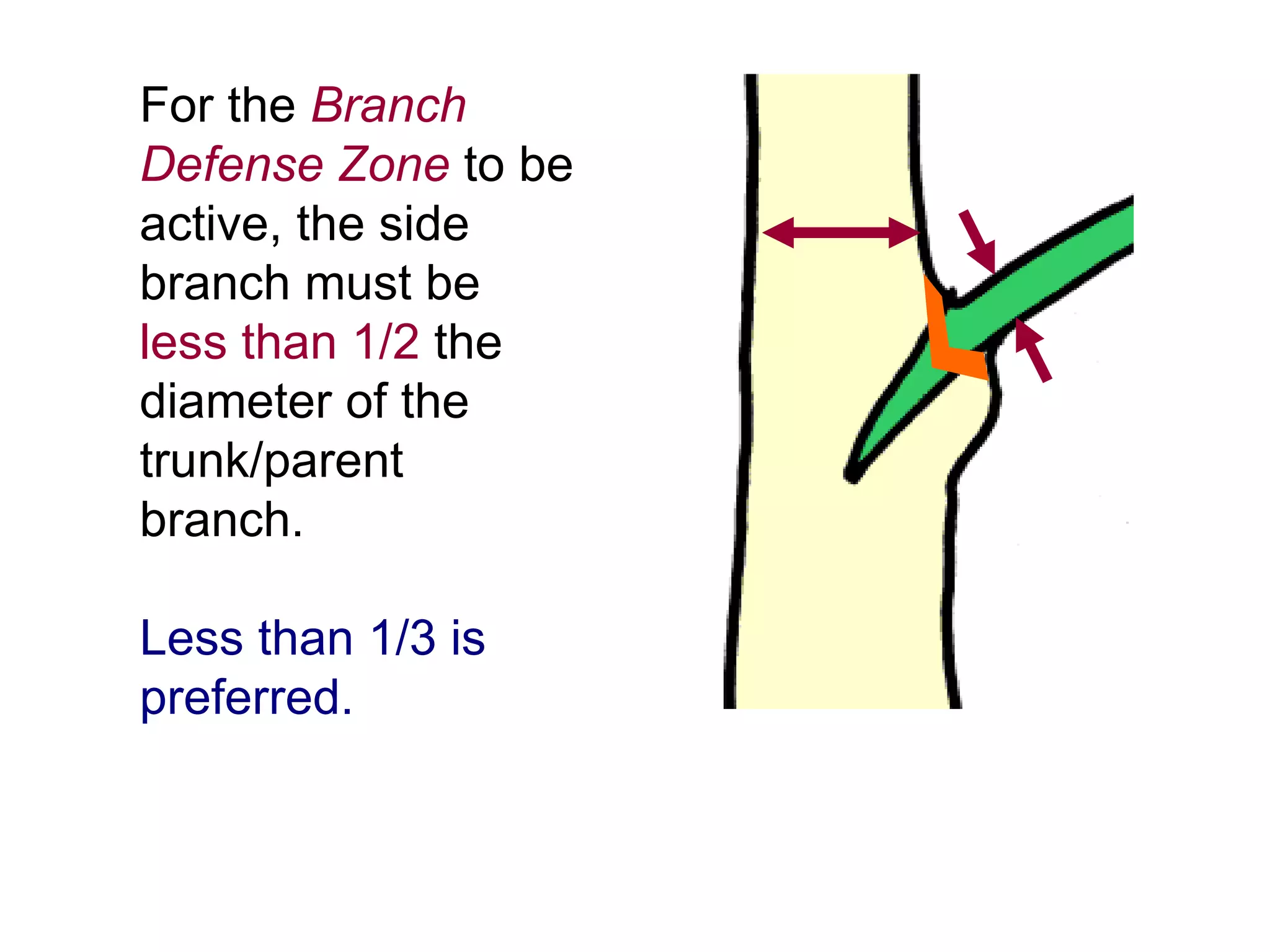
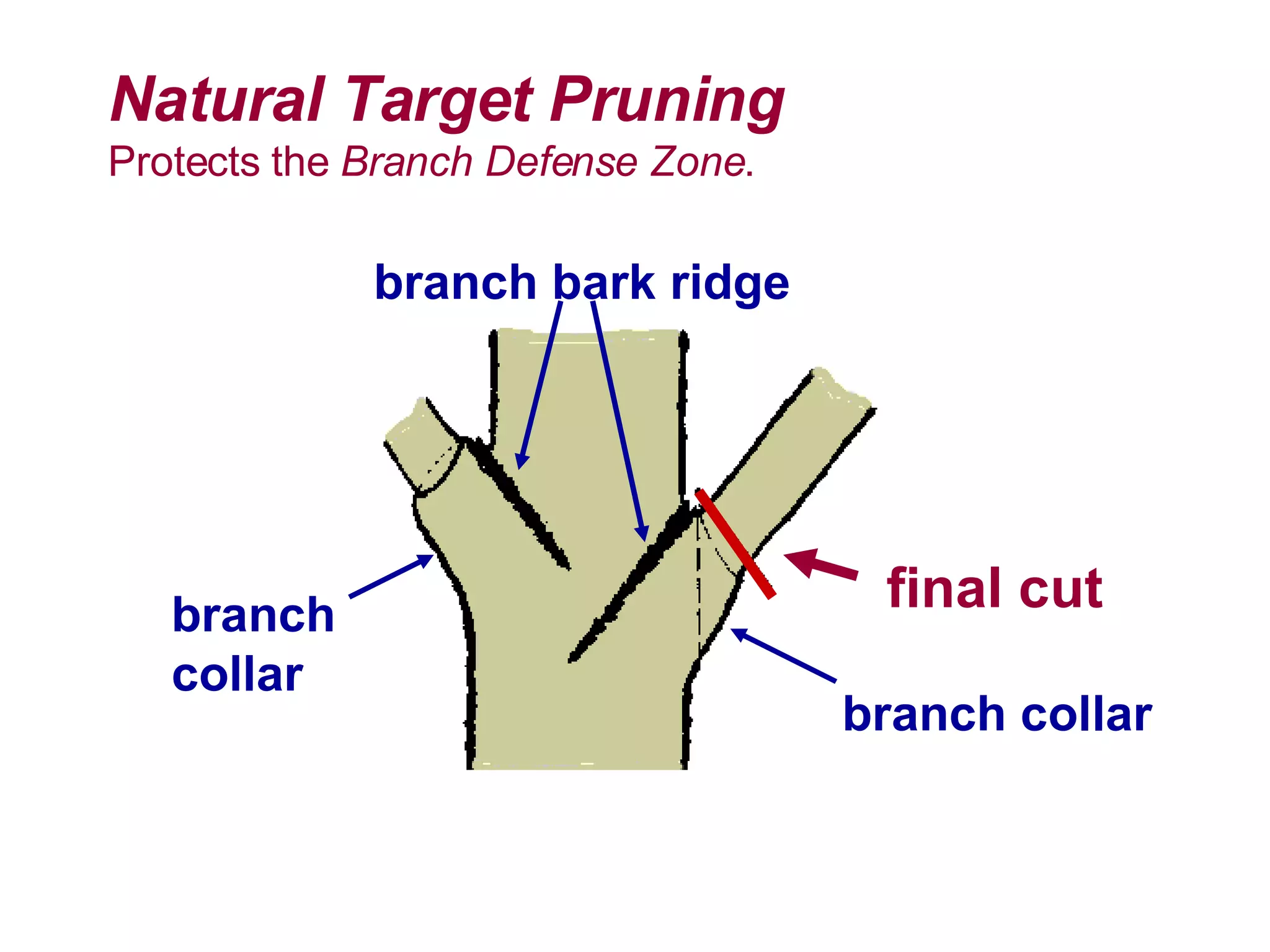
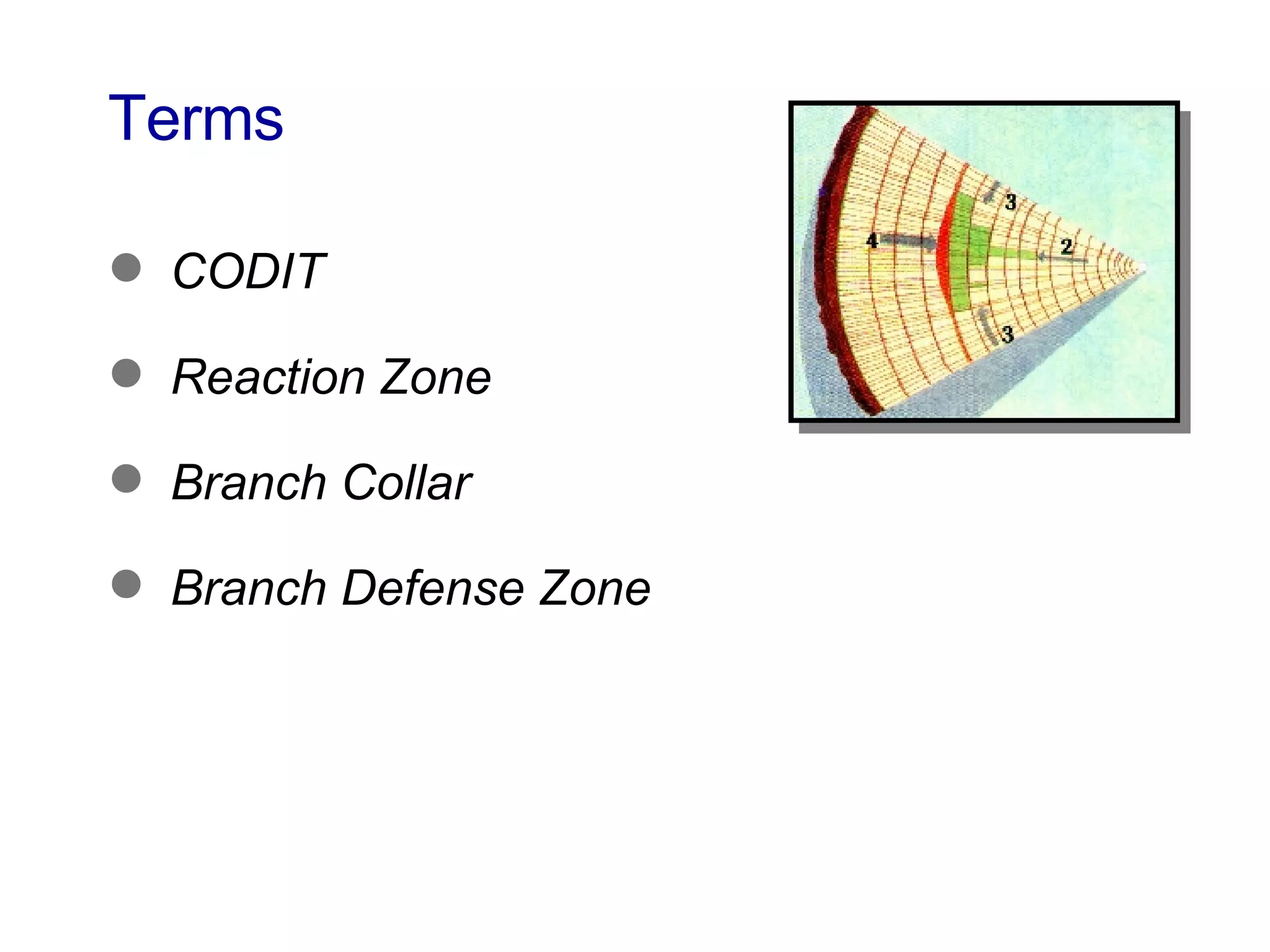
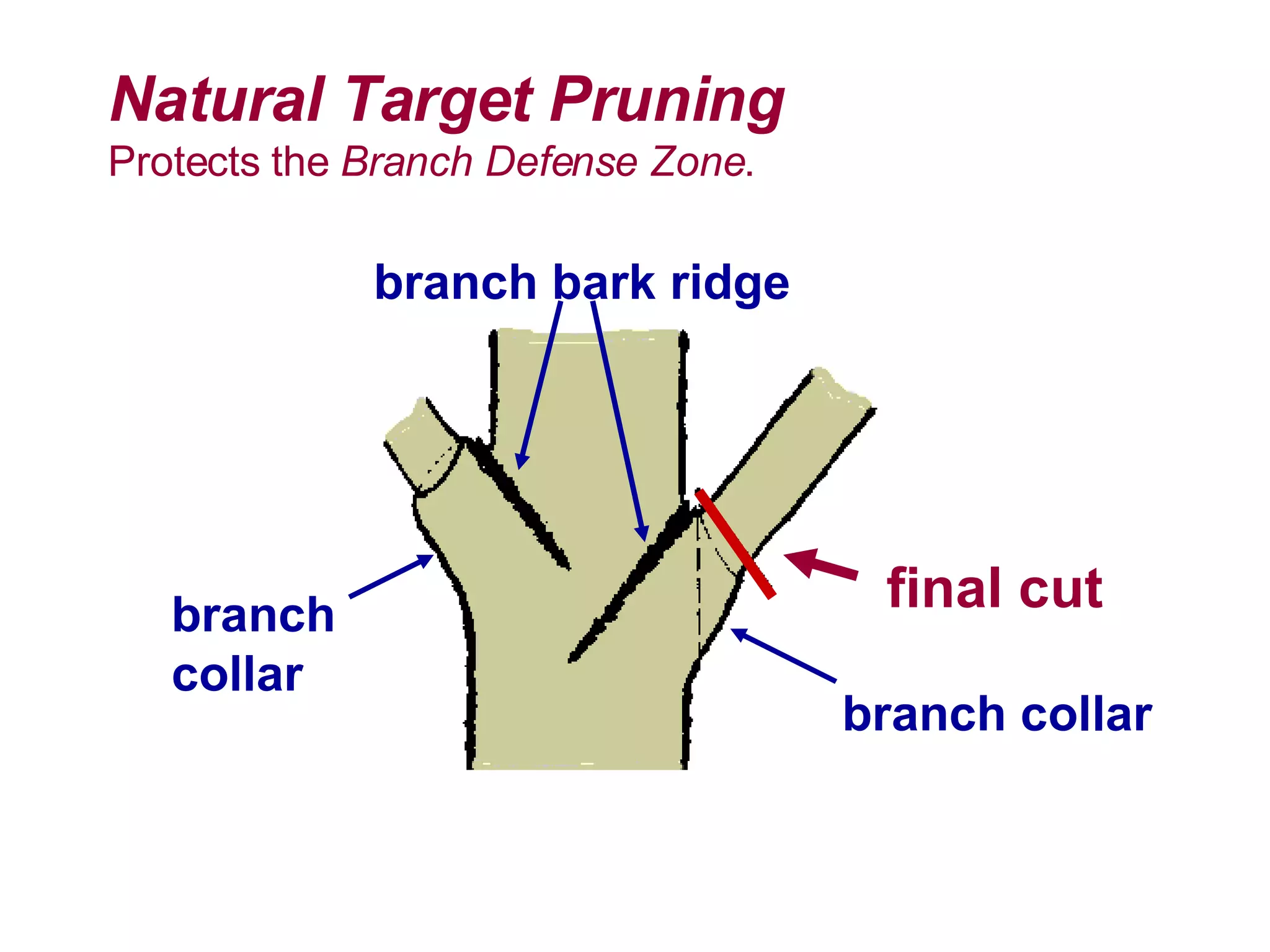
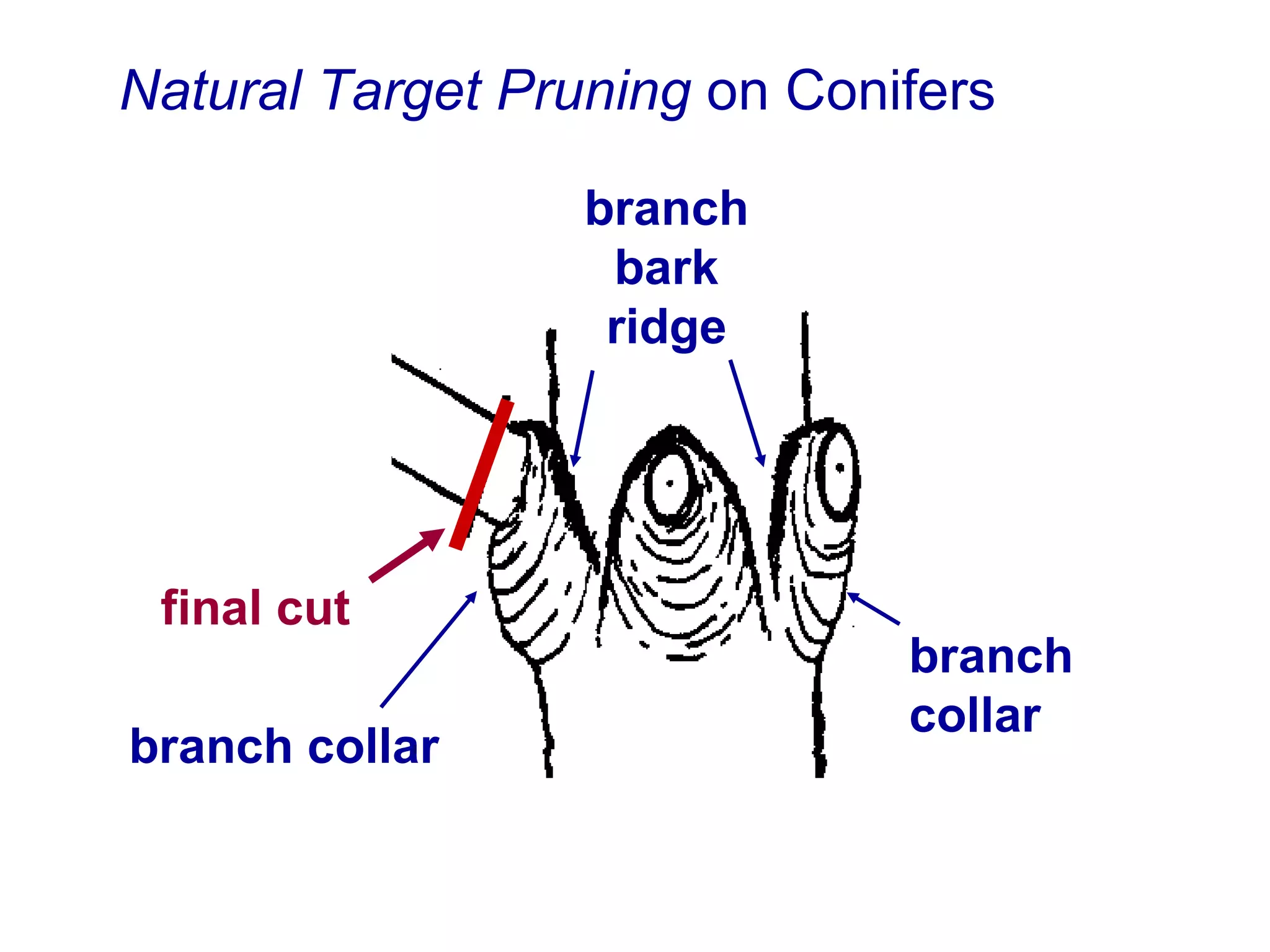
2. Natural target pruning cuts remove a side branch back to the larger parent branch/trunk in order to preserve the branch defense zone and allow woundwood to close over the pruning wound.
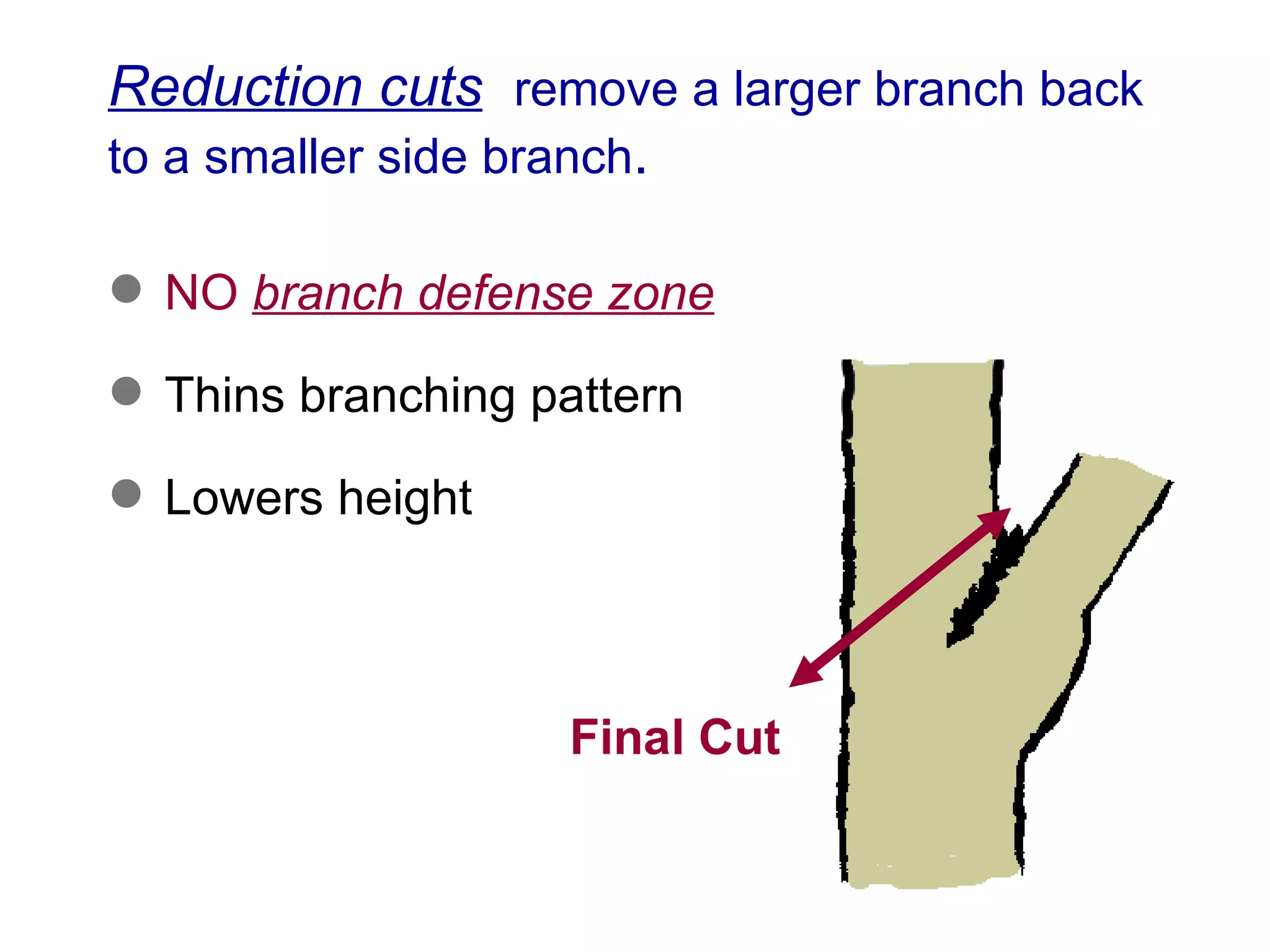
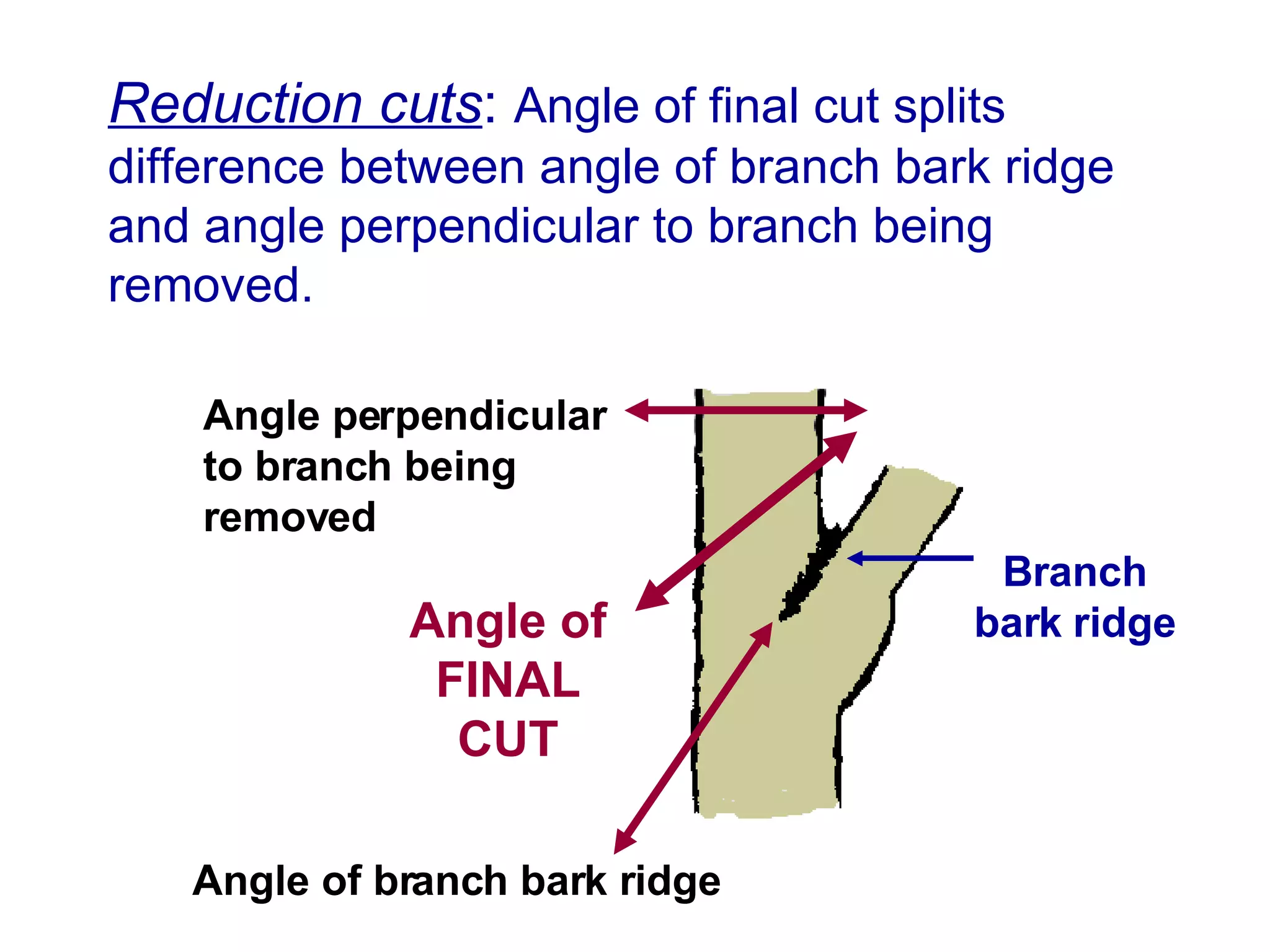
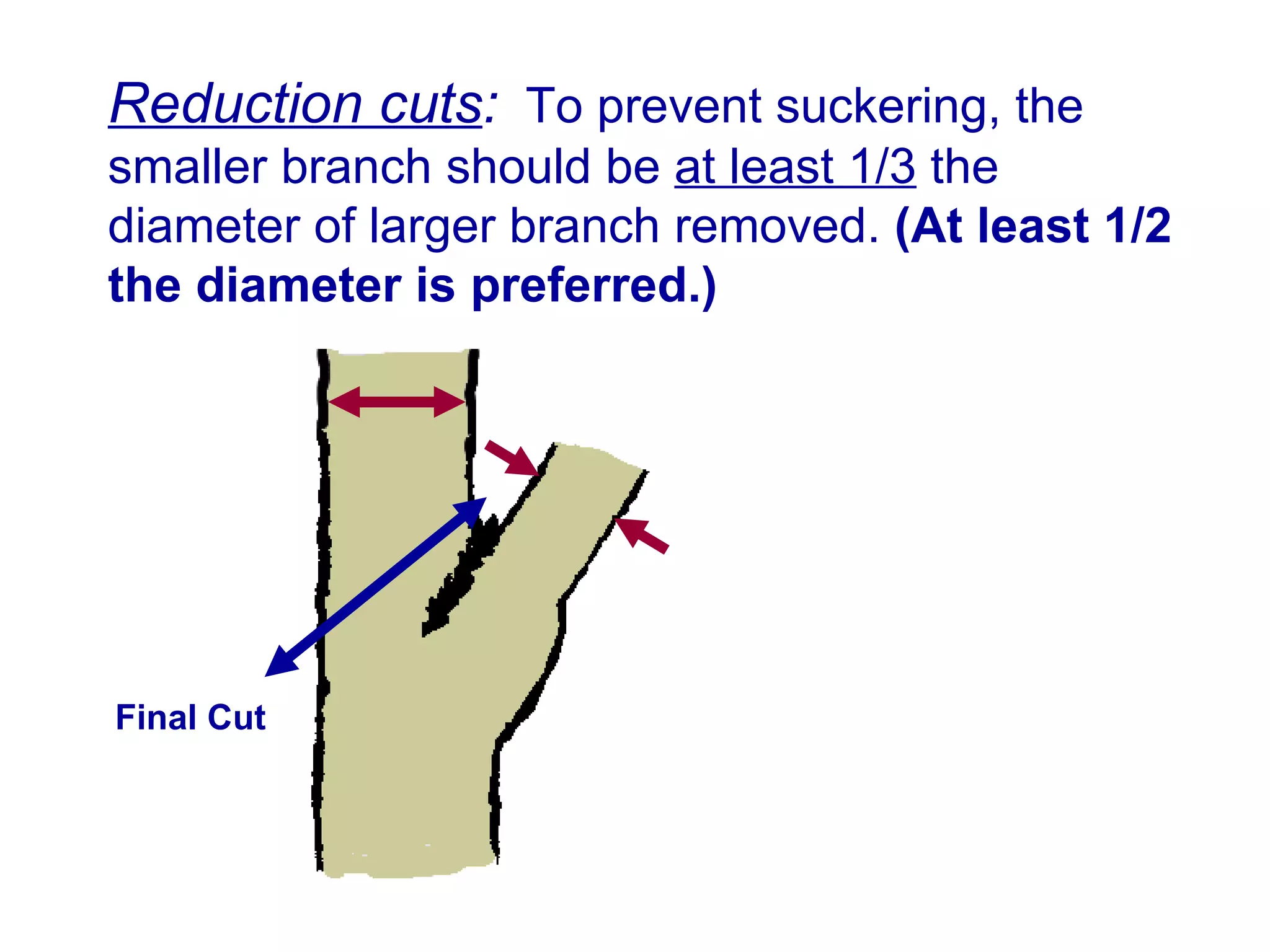
3. Reduction cuts remove a larger branch back to a smaller side branch and should be made at an angle to prevent suckering, with the smaller branch being at least 1/3 the diameter of the larger branch removed.