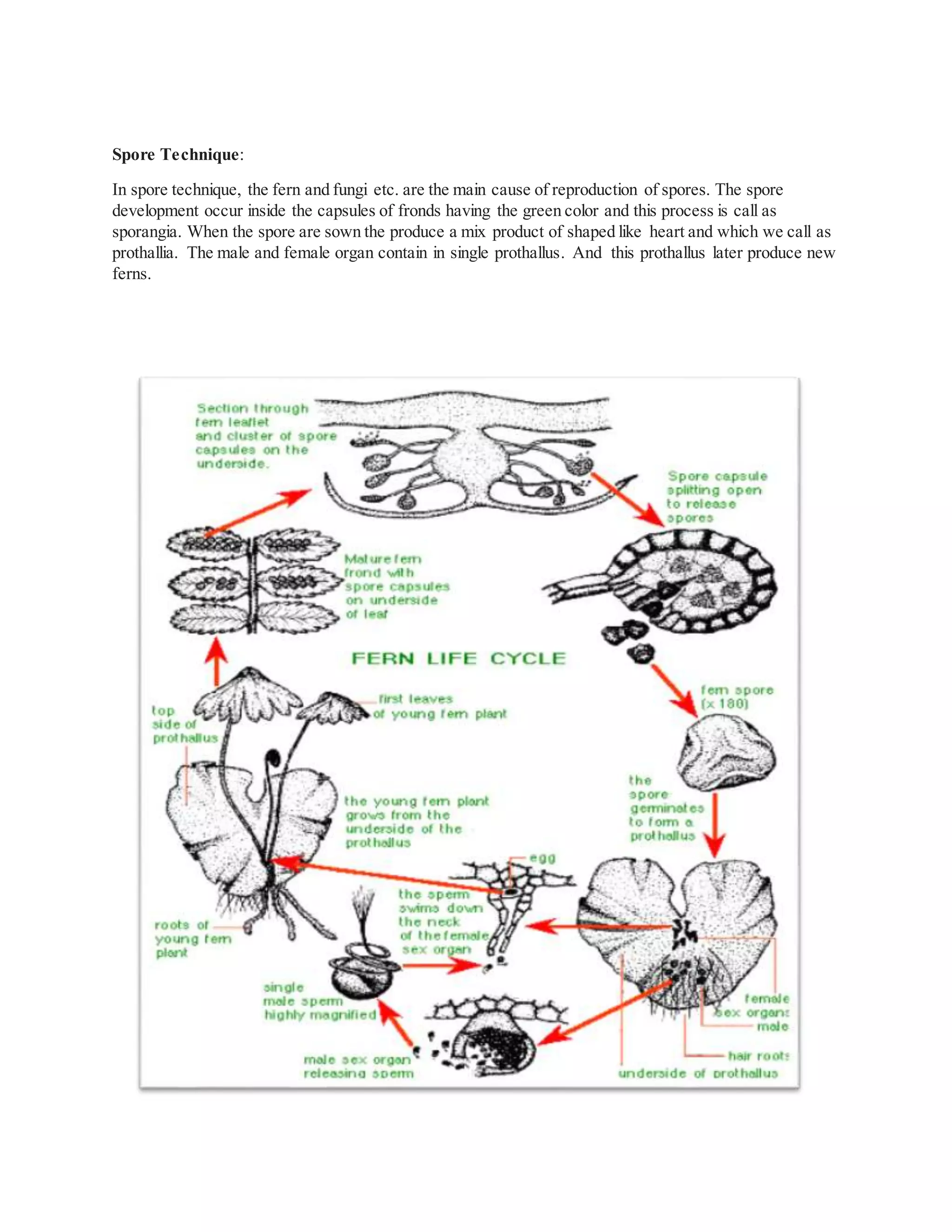
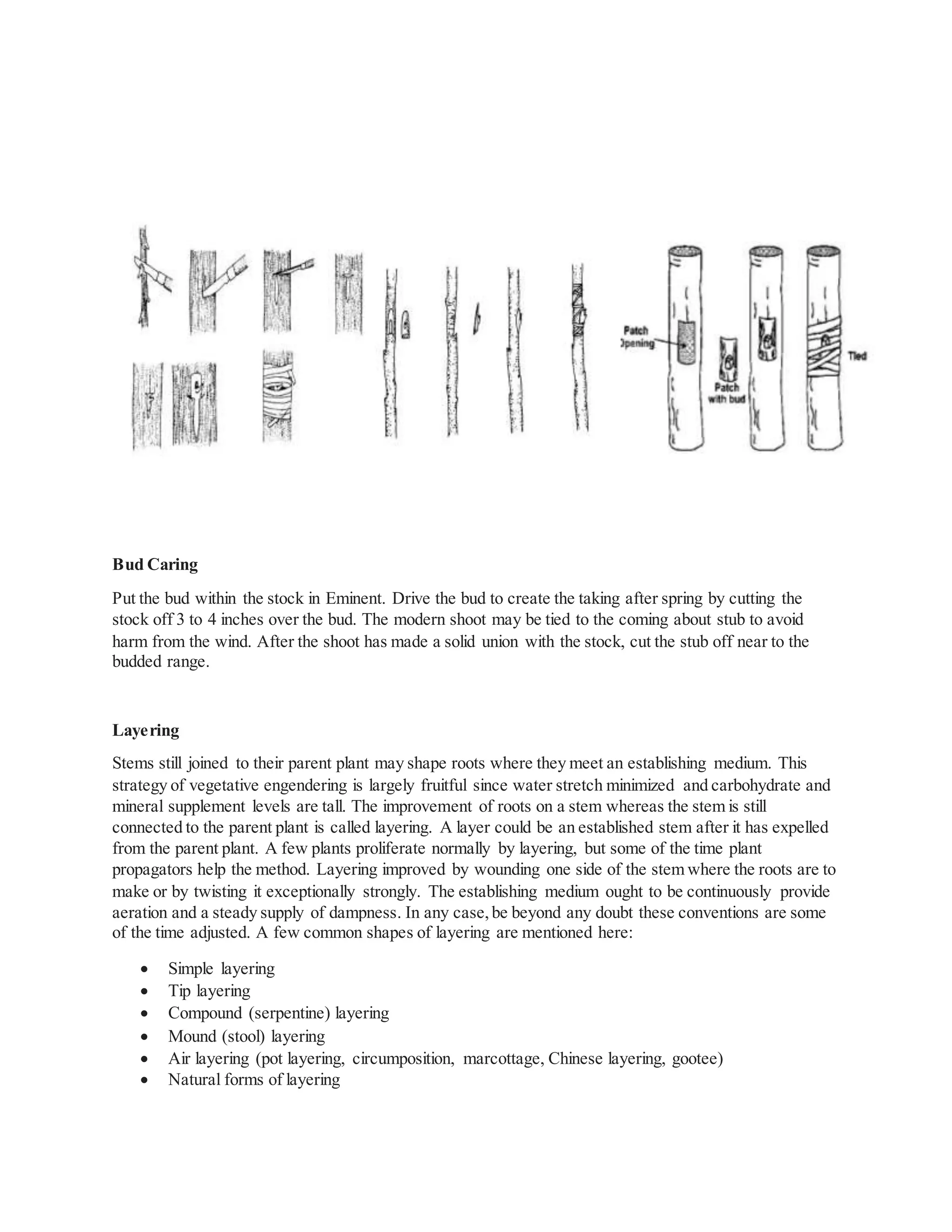
Plant propagation can occur sexually through seeds or asexually through various vegetative methods. Sexual propagation involves the fertilization of egg and pollen to produce seeds, while asexual propagation involves propagating a new plant from a part of the parent plant other than seeds, such as stems, leaves, or roots. Common asexual propagation techniques include grafting, budding, layering, cuttings, division, and micropropagation or tissue culture. Each technique has specific steps and conditions required for successful propagation of a new plant that is genetically identical to the parent plant.