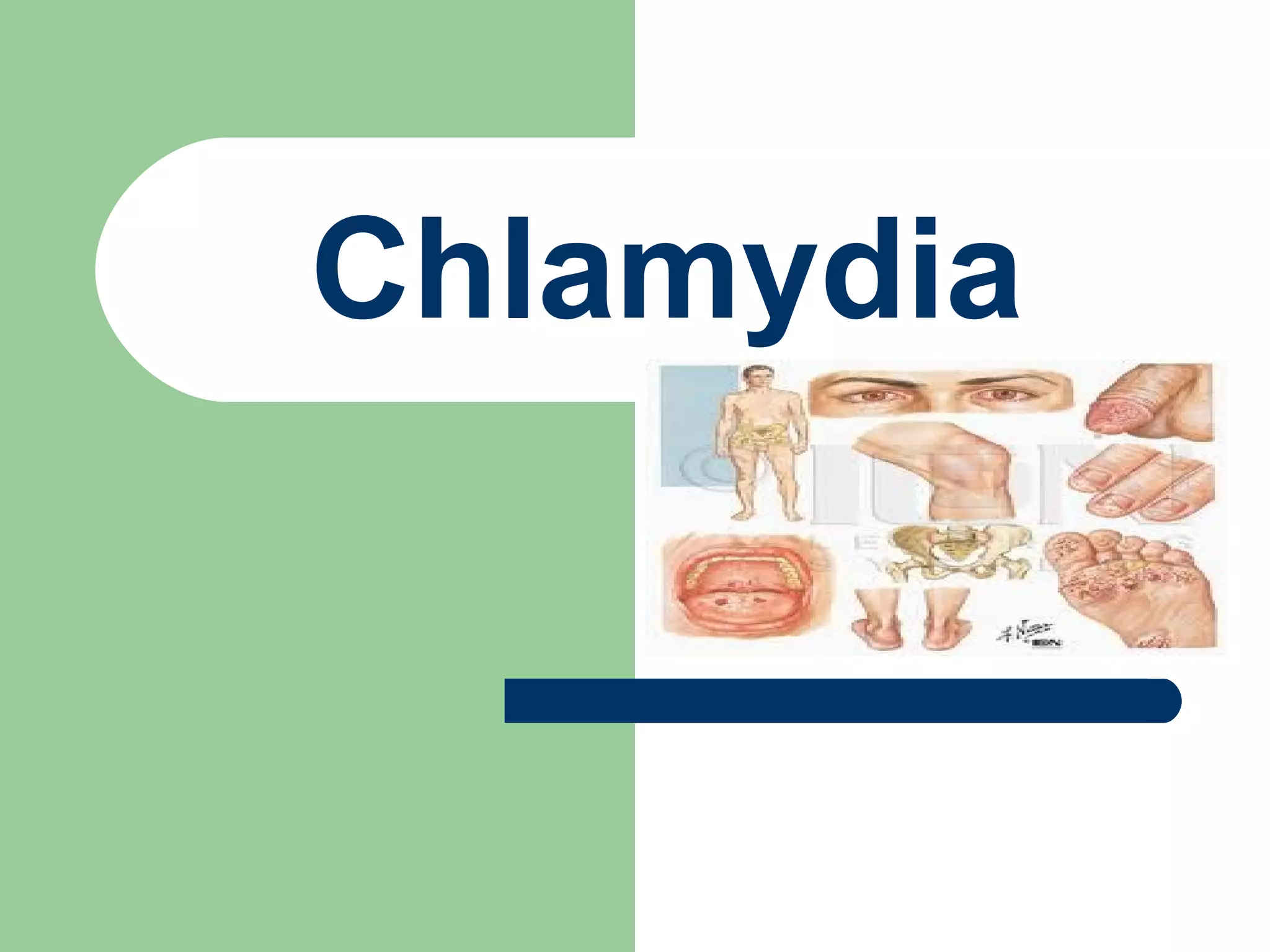
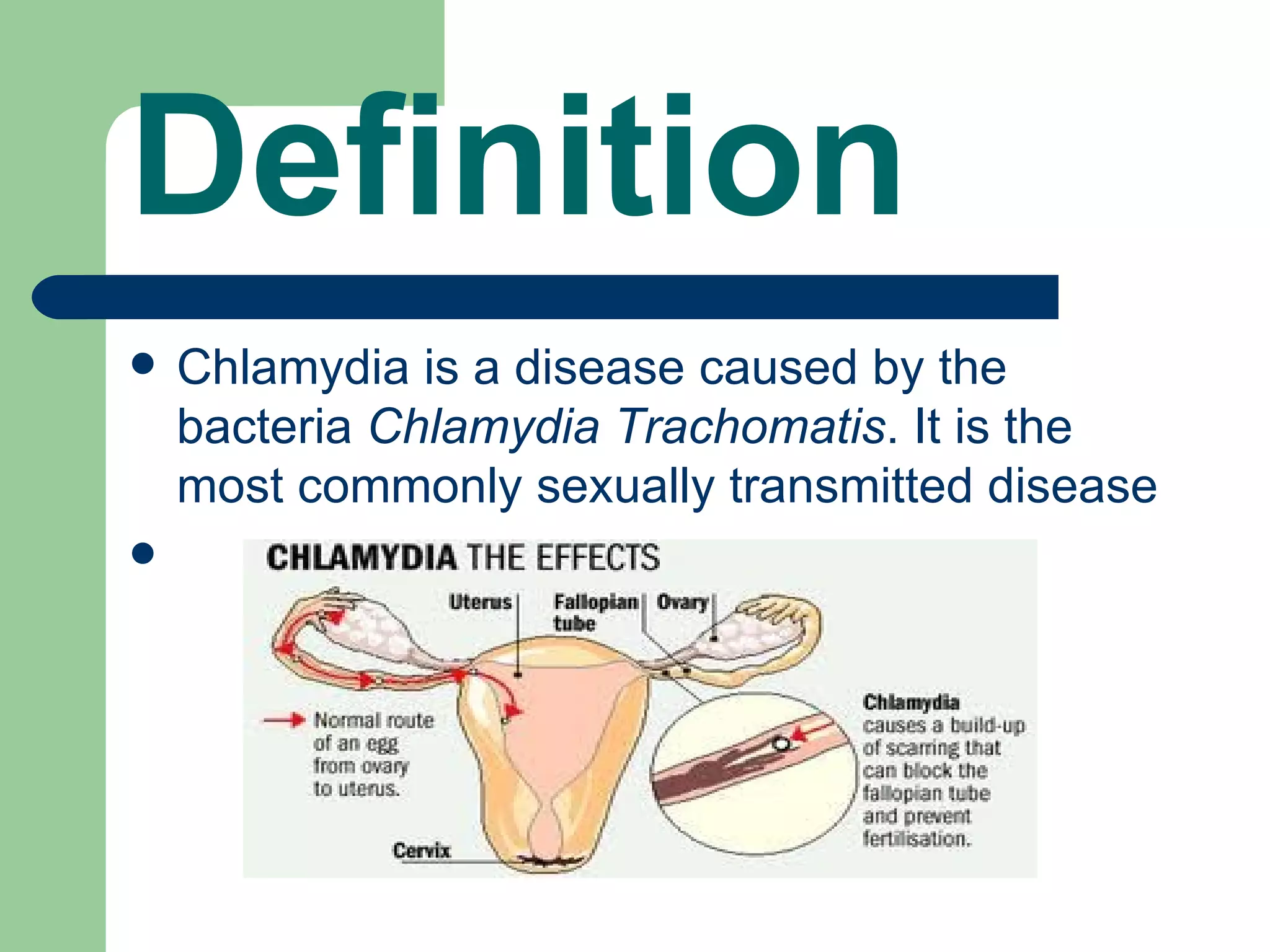
Chlamydia is a common sexually transmitted bacterial infection caused by Chlamydia trachomatis. While many infected individuals show no symptoms, symptoms can include burning during urination and abnormal discharge. Chlamydia is easily spread during unprotected sex and untreated infections can lead to pelvic inflammatory disease in women. Chlamydia is treated with antibiotics and screening is recommended for sexually active individuals under 26.