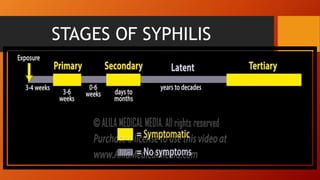
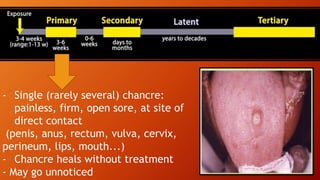
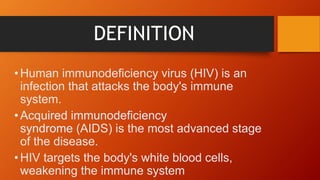
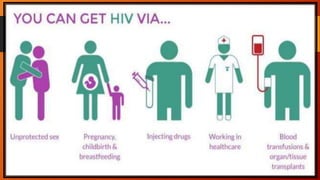
The document provides an overview of sexually transmitted diseases (STDs), their definitions, classifications, and specific examples including syphilis, gonorrhea, and chlamydia. It discusses transmission methods, symptoms, diagnostic evaluations, and treatments for these infections. Additionally, the document covers information about HIV/AIDS and preventive measures to reduce the risk of STDs.