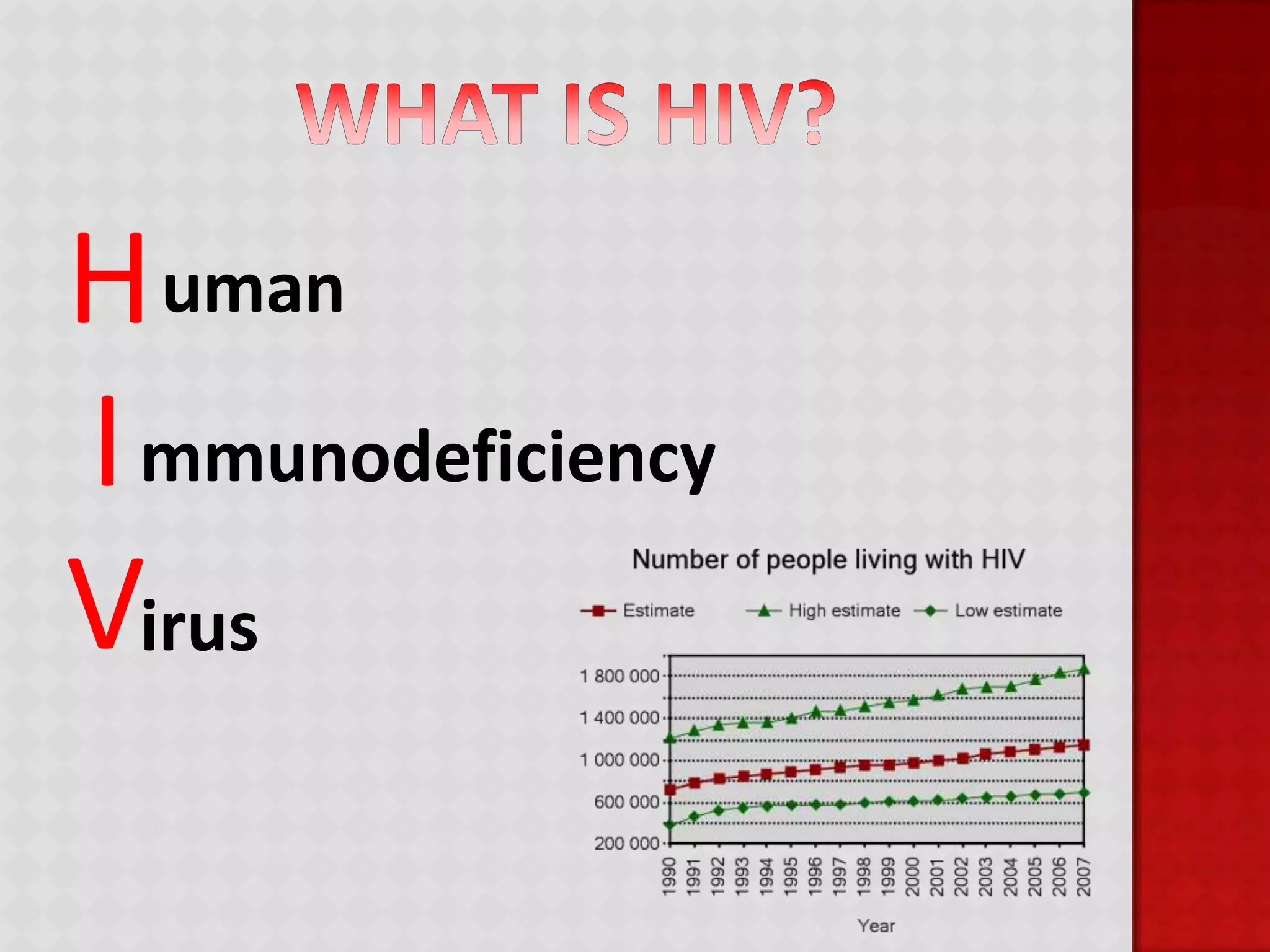
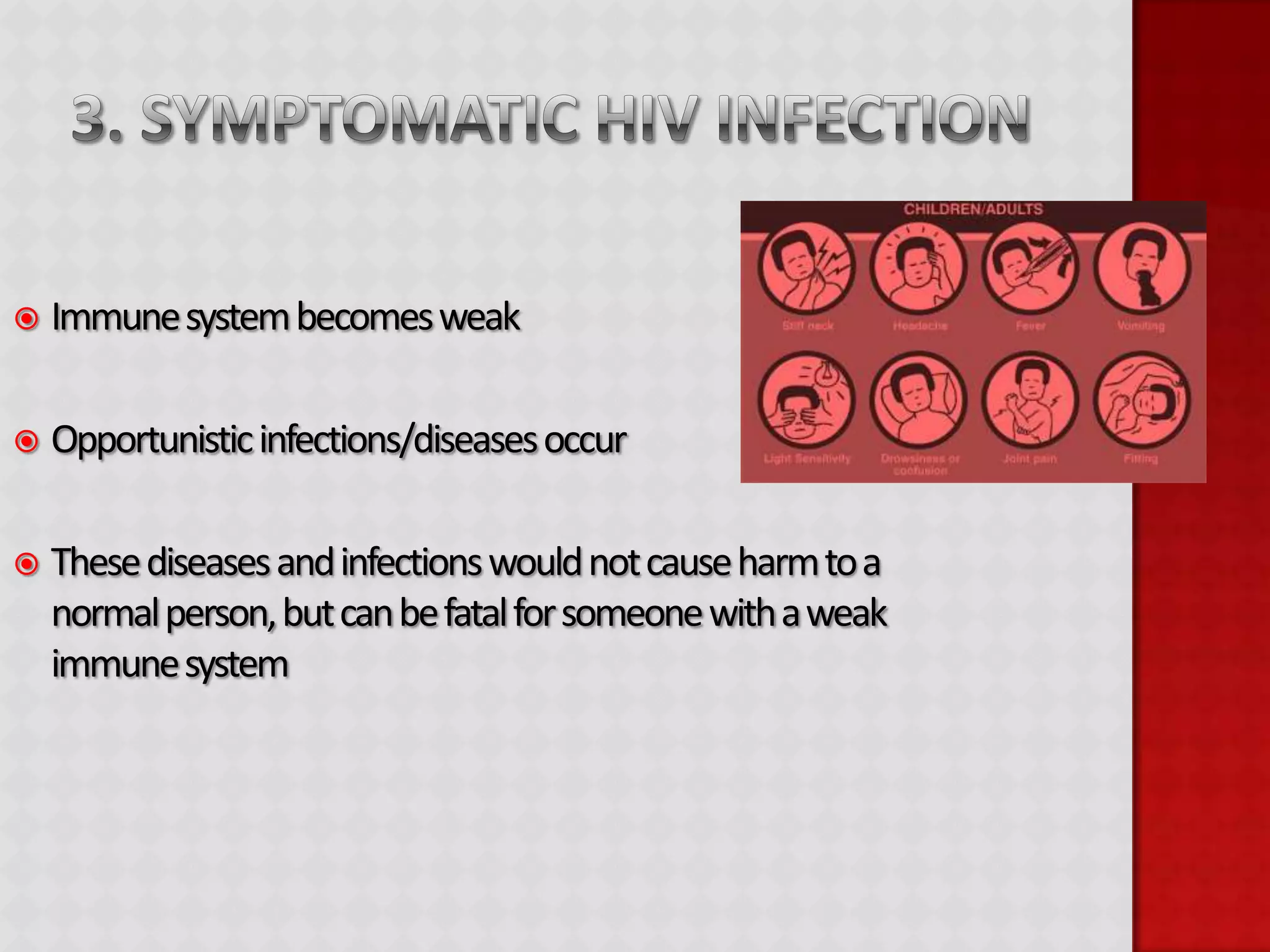
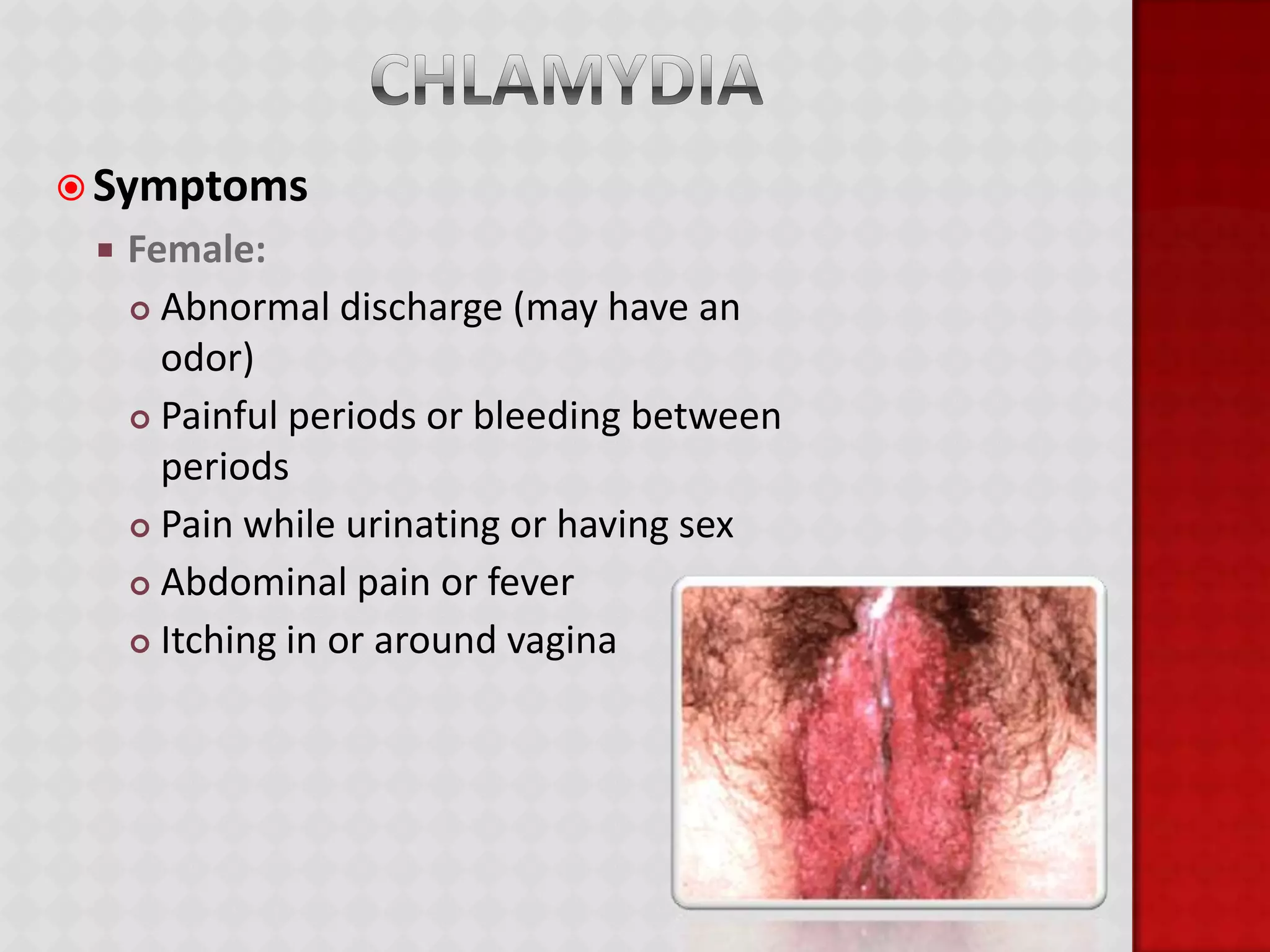
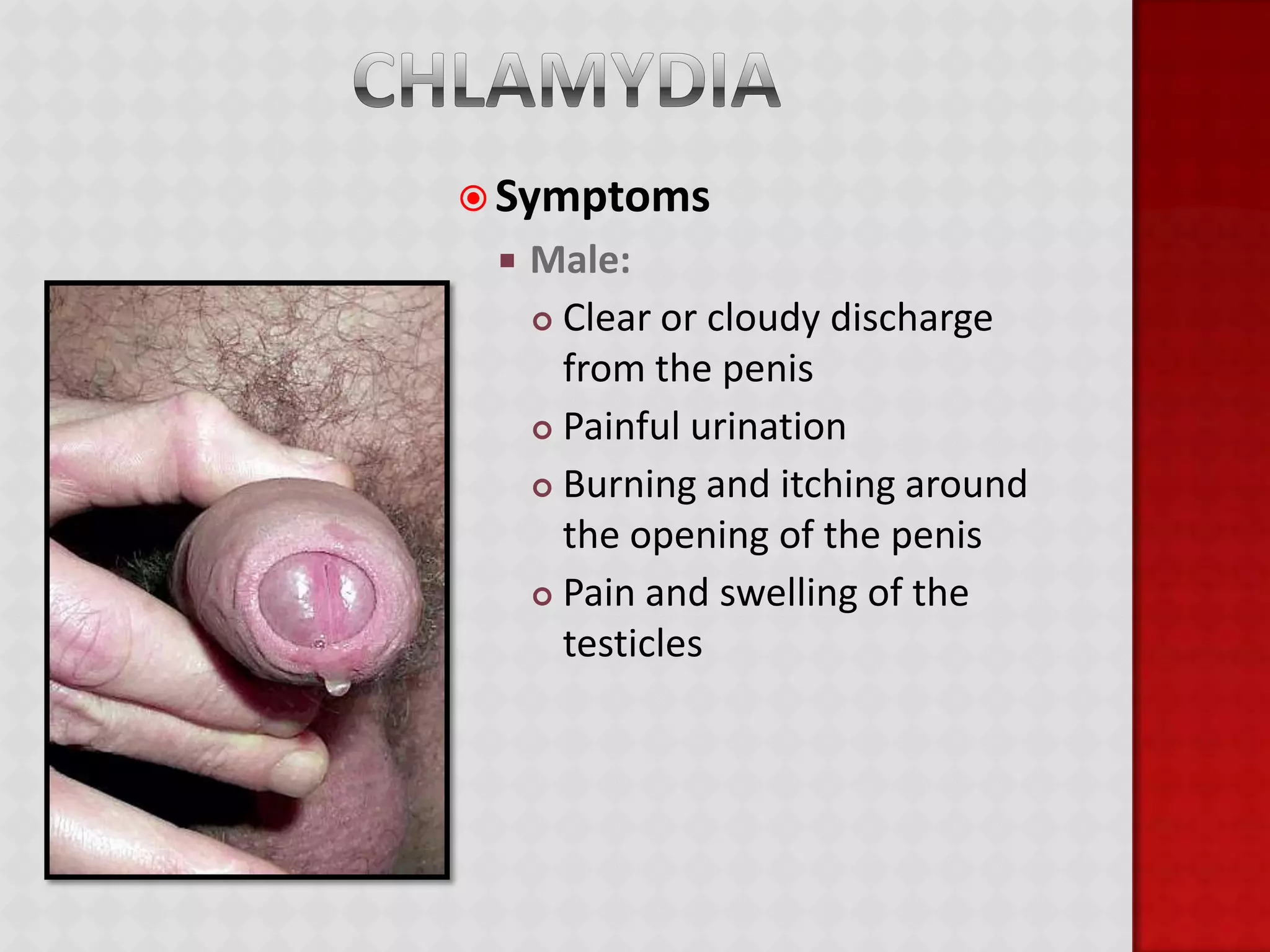
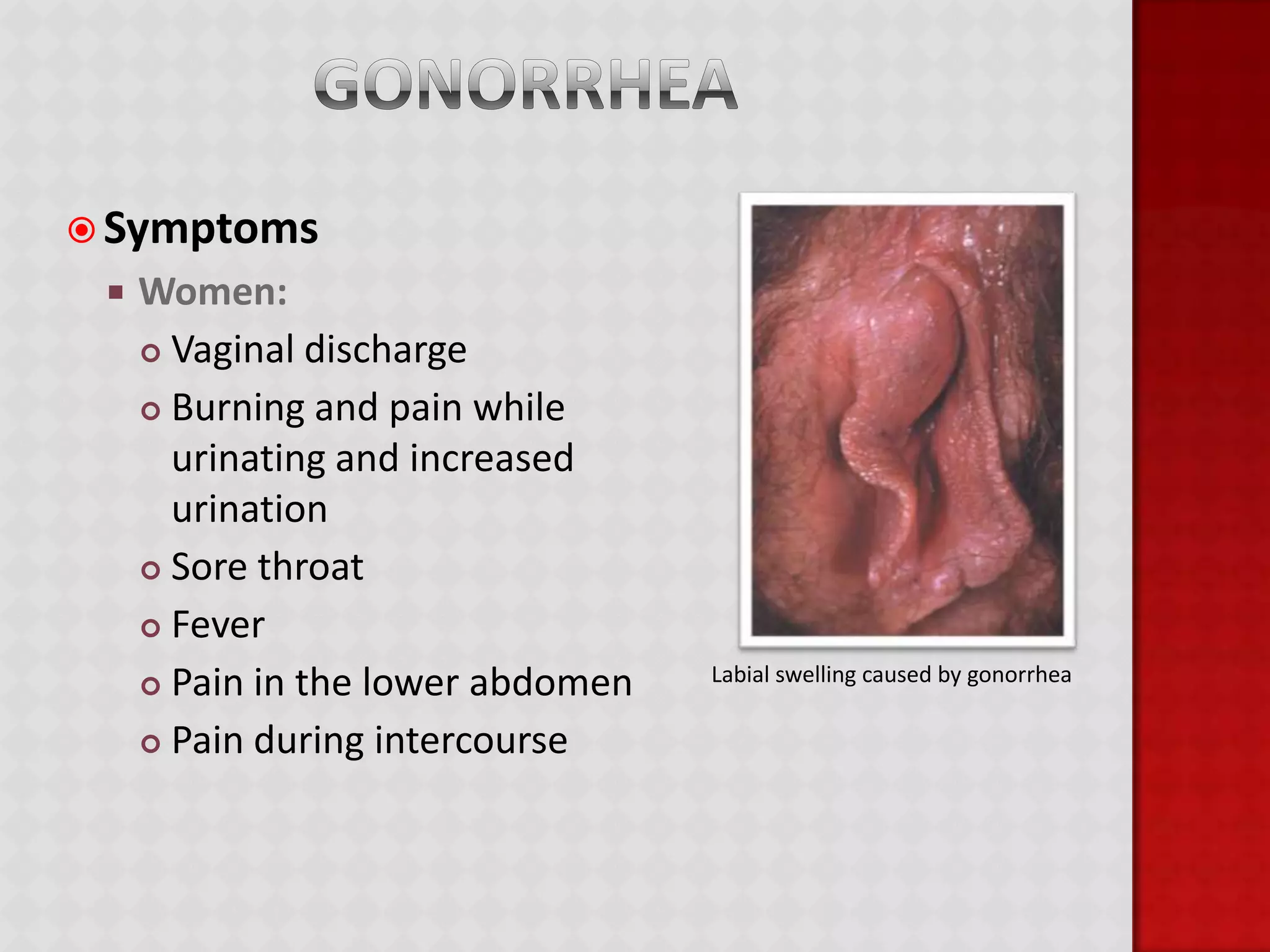
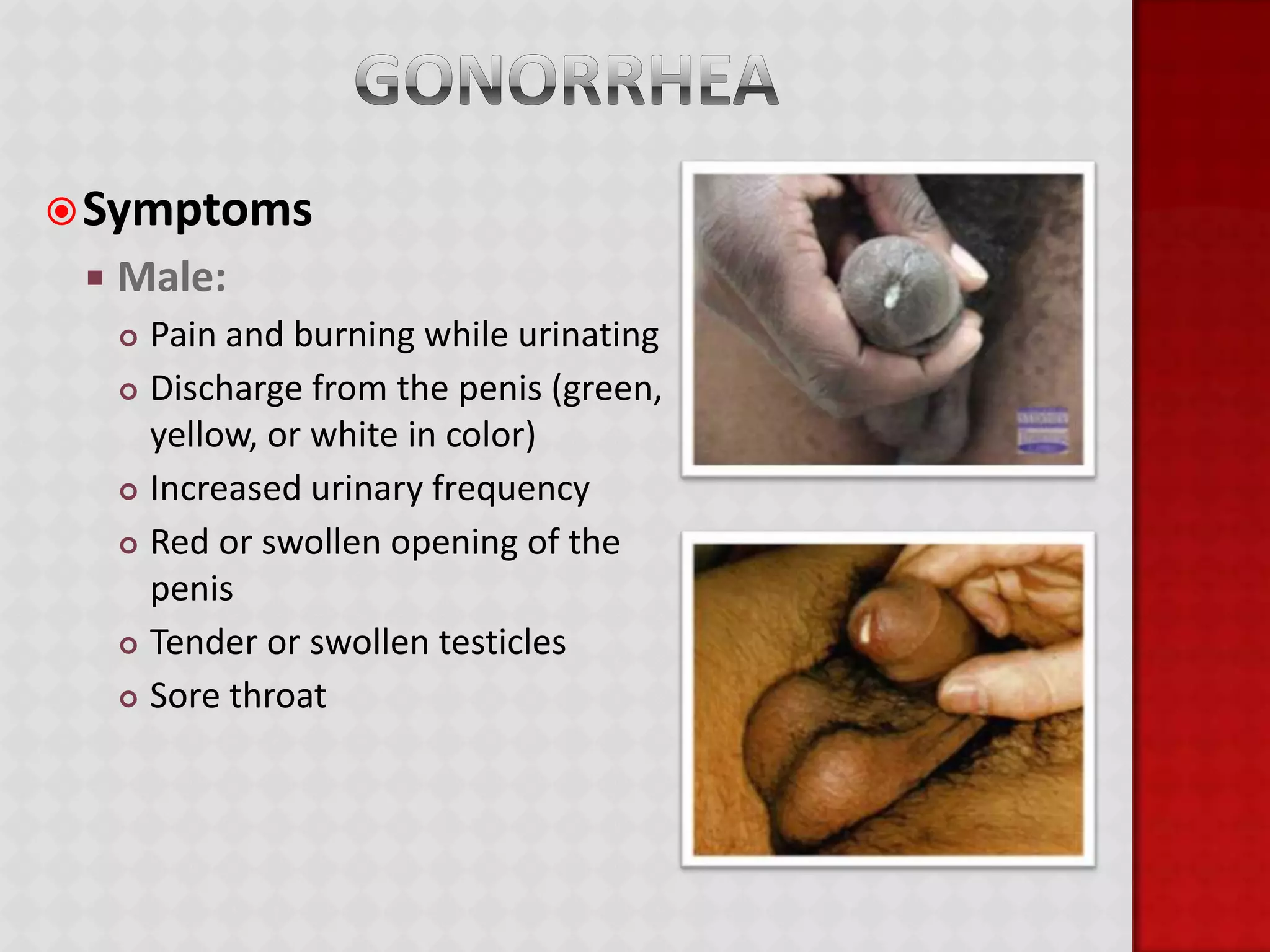
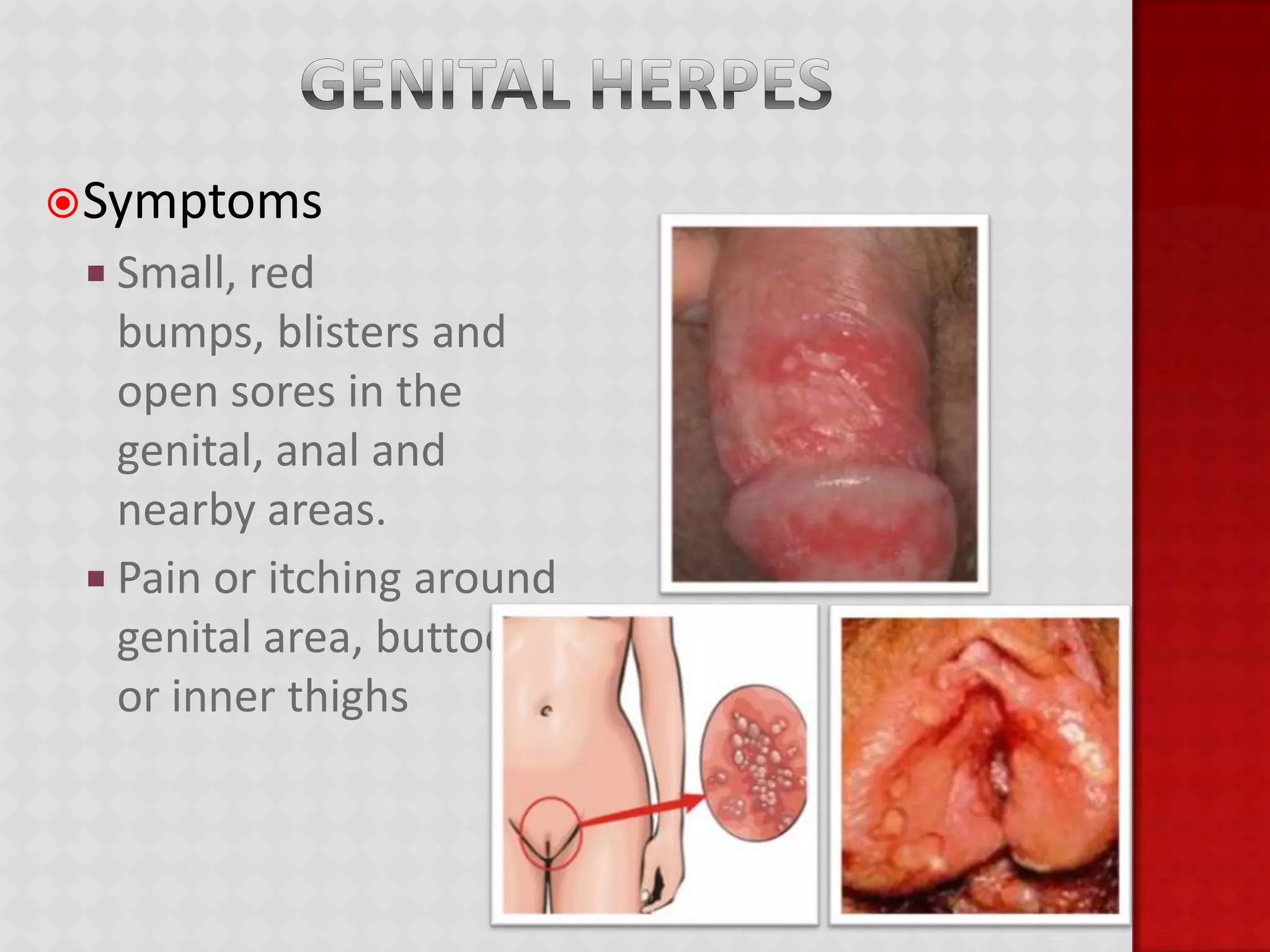
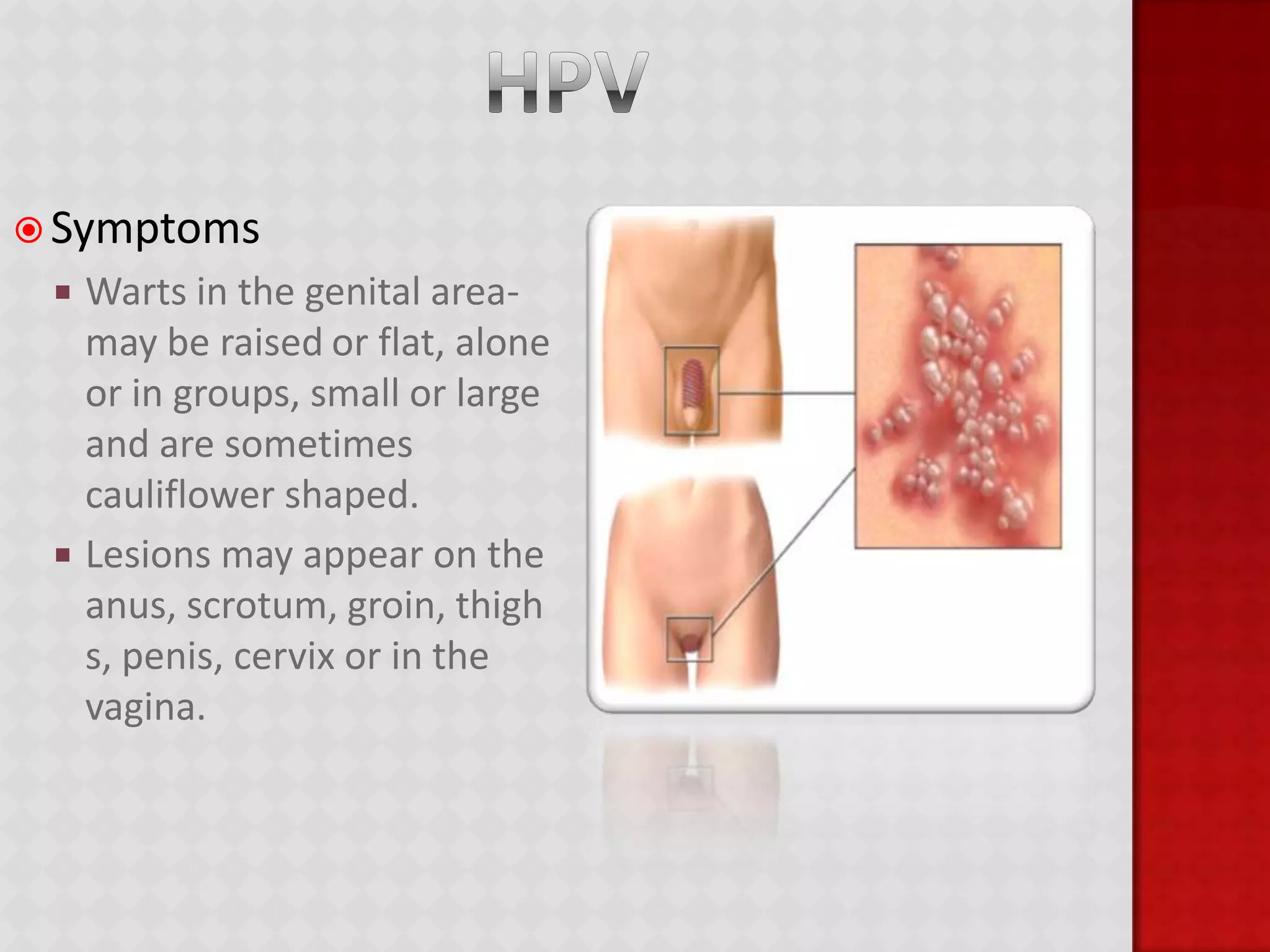
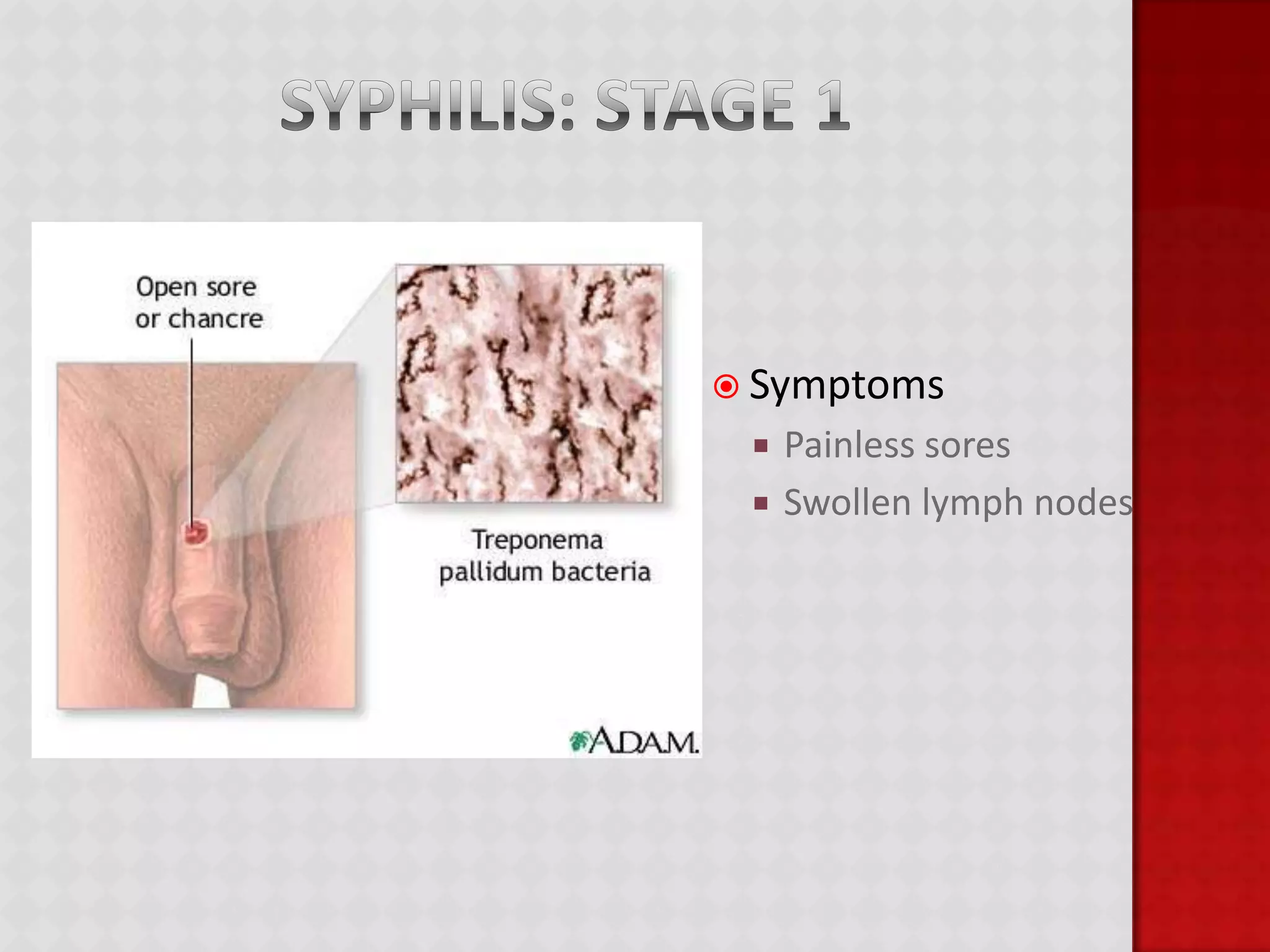
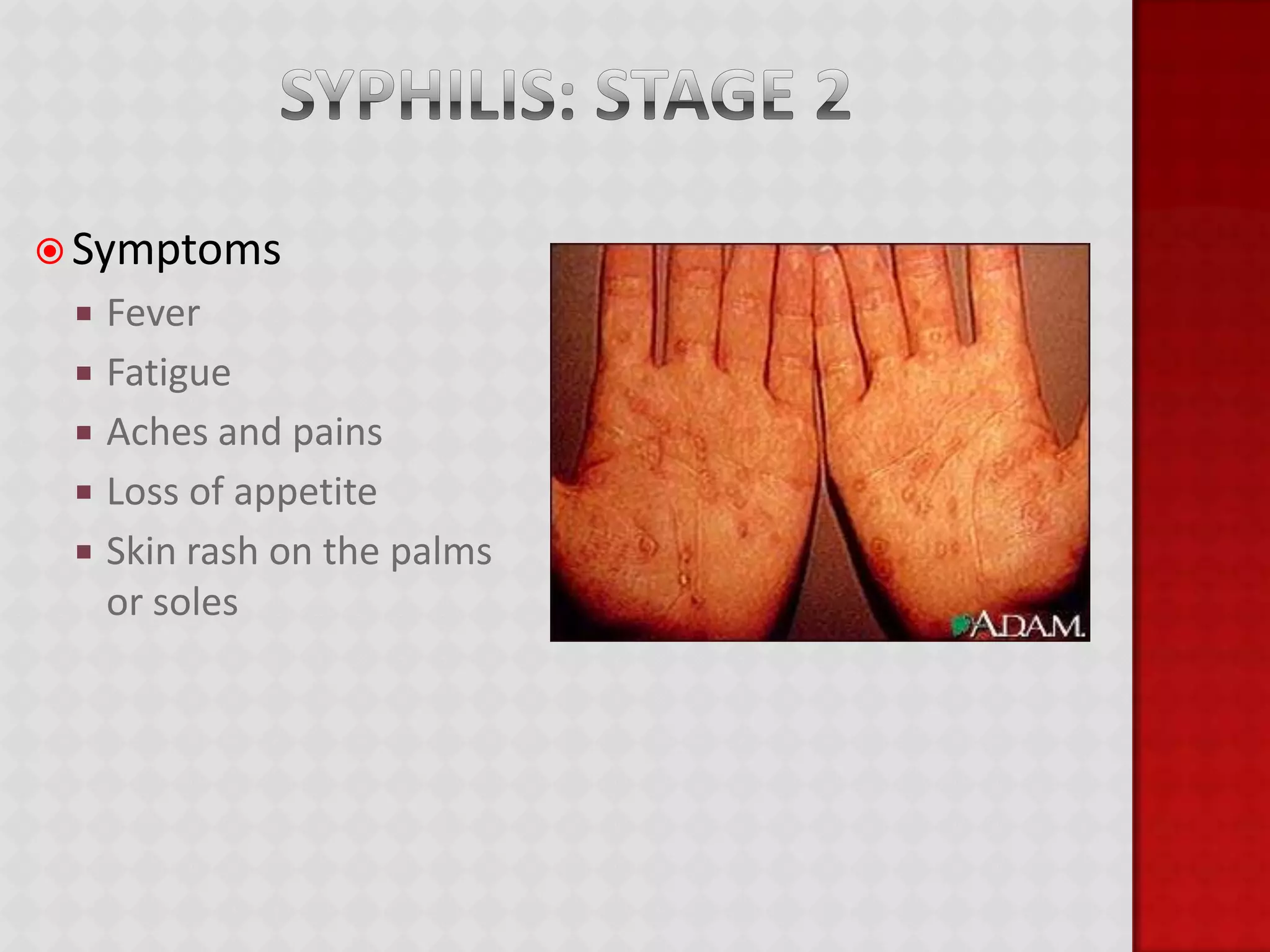
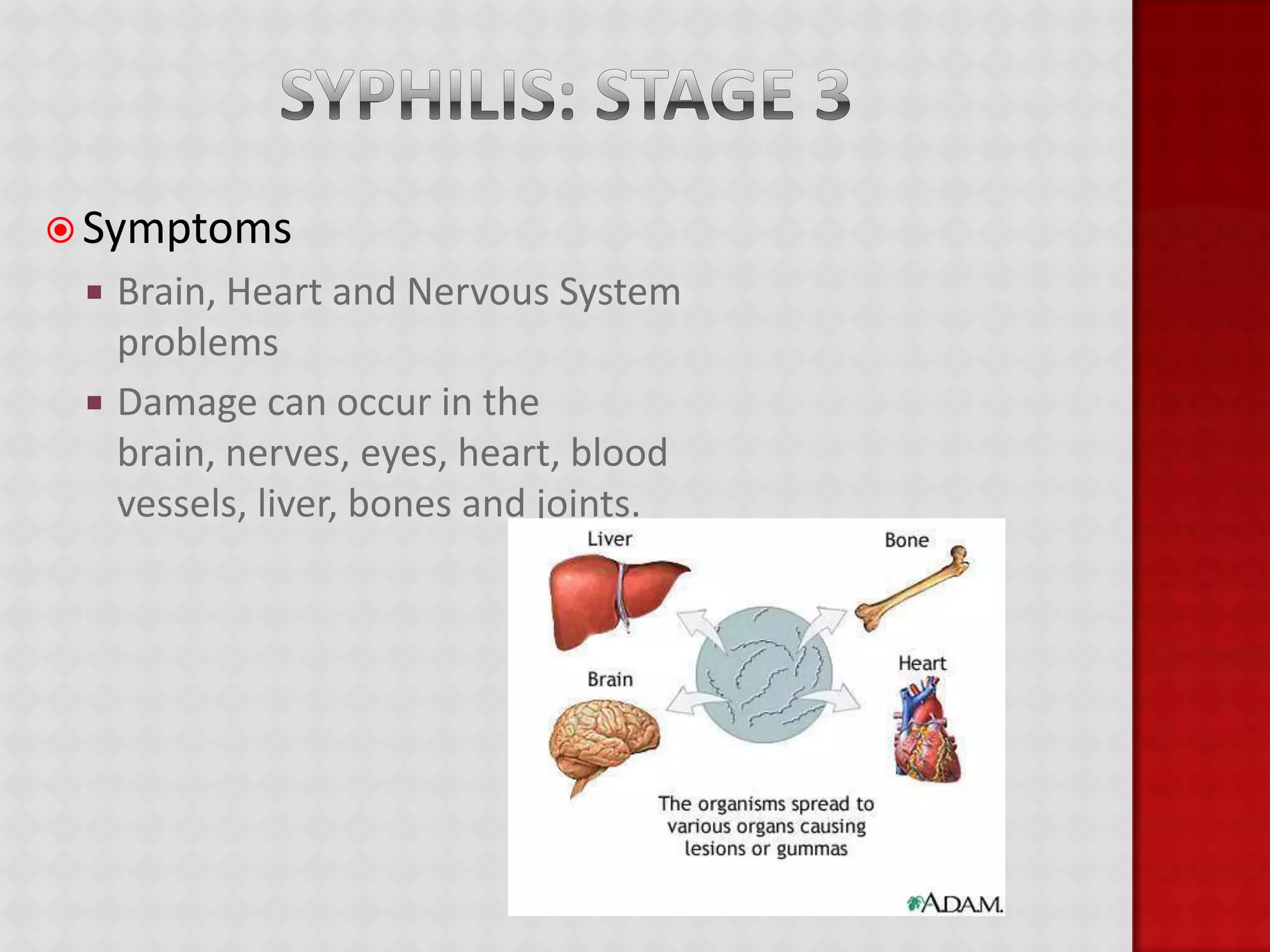
This document provides information about HIV/AIDS including what it is, how it progresses, how it is transmitted, testing procedures, prevention methods, and other sexually transmitted diseases. It defines HIV and AIDS, describes the four stages of HIV from primary infection to AIDS, lists the five bodily fluids through which HIV can be transmitted, and dispels common myths about transmission. The document also outlines home testing, rapid testing, confidential testing, and anonymous testing as well as birth control options and common STDs like chlamydia, gonorrhea, herpes, hepatitis B, and HPV. Prevention methods like abstinence and proper condom use are emphasized.