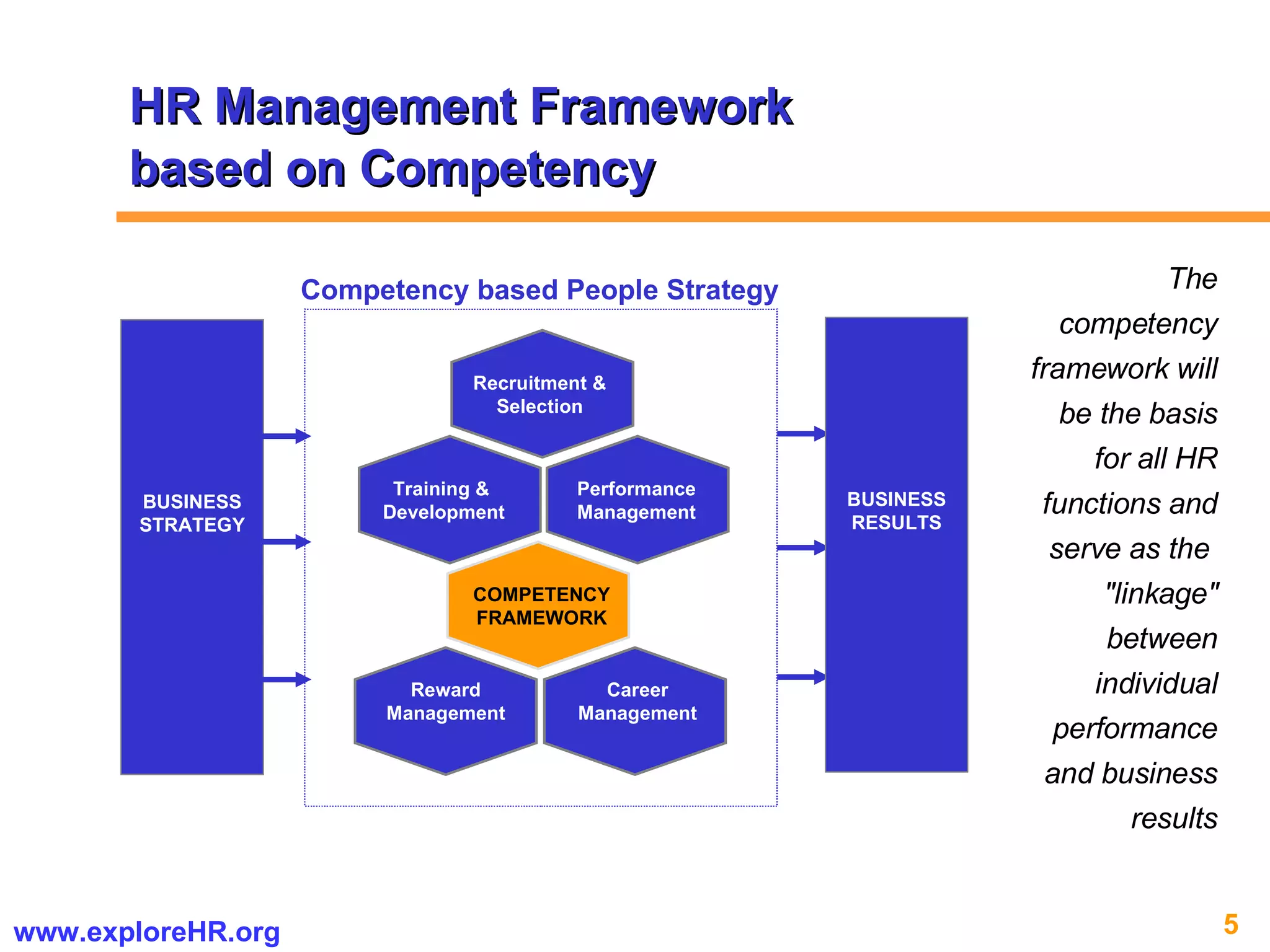
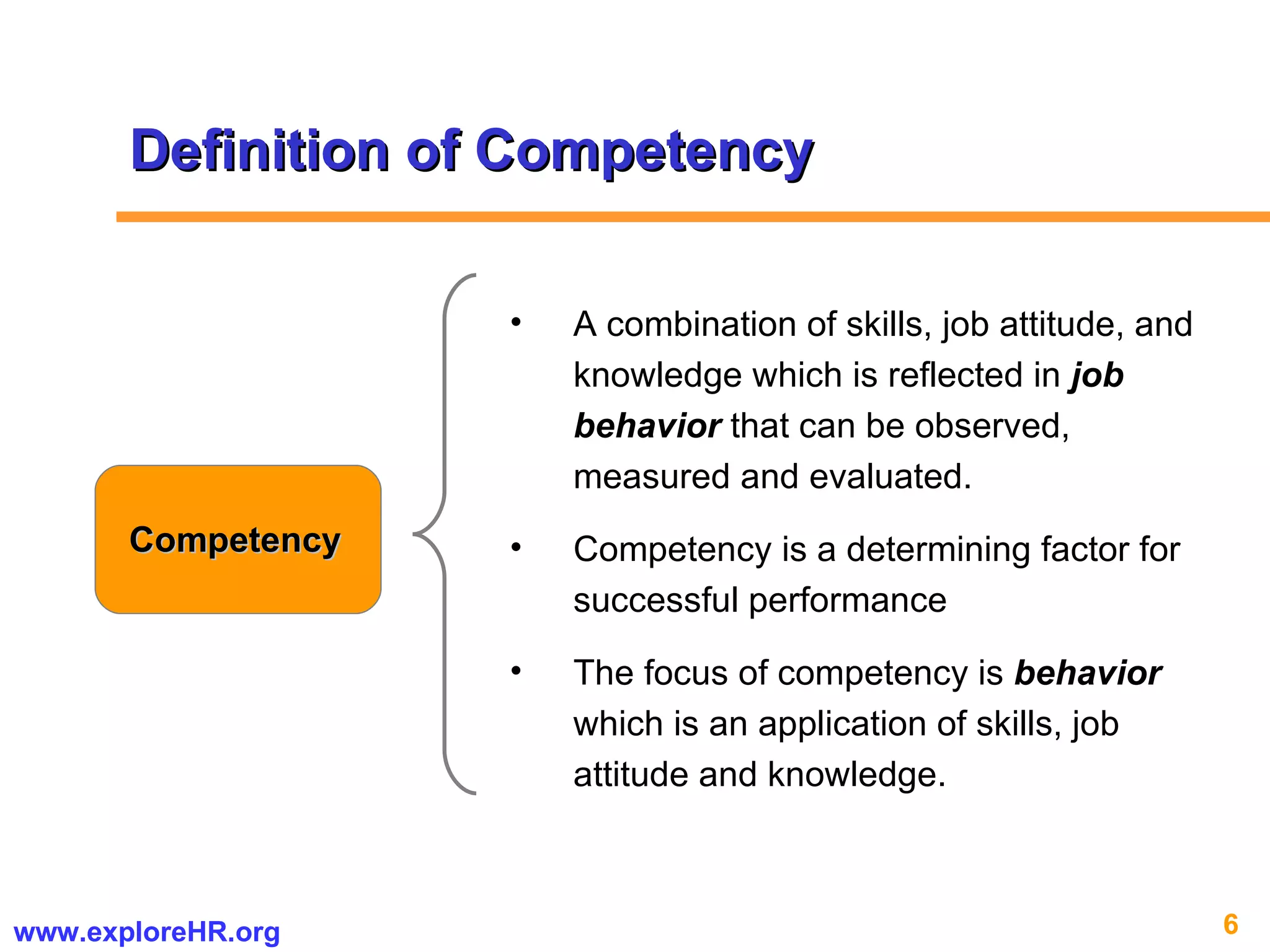
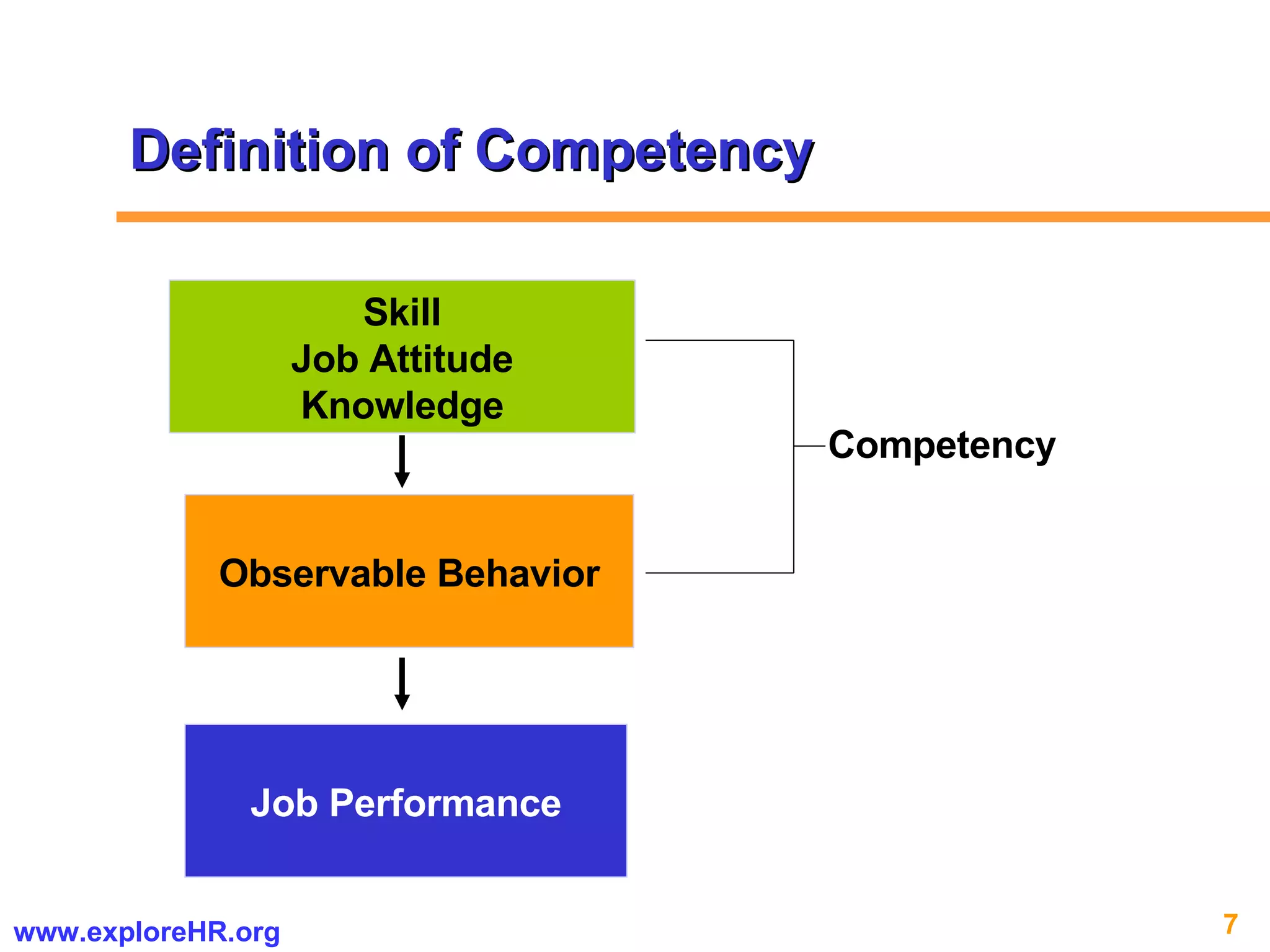
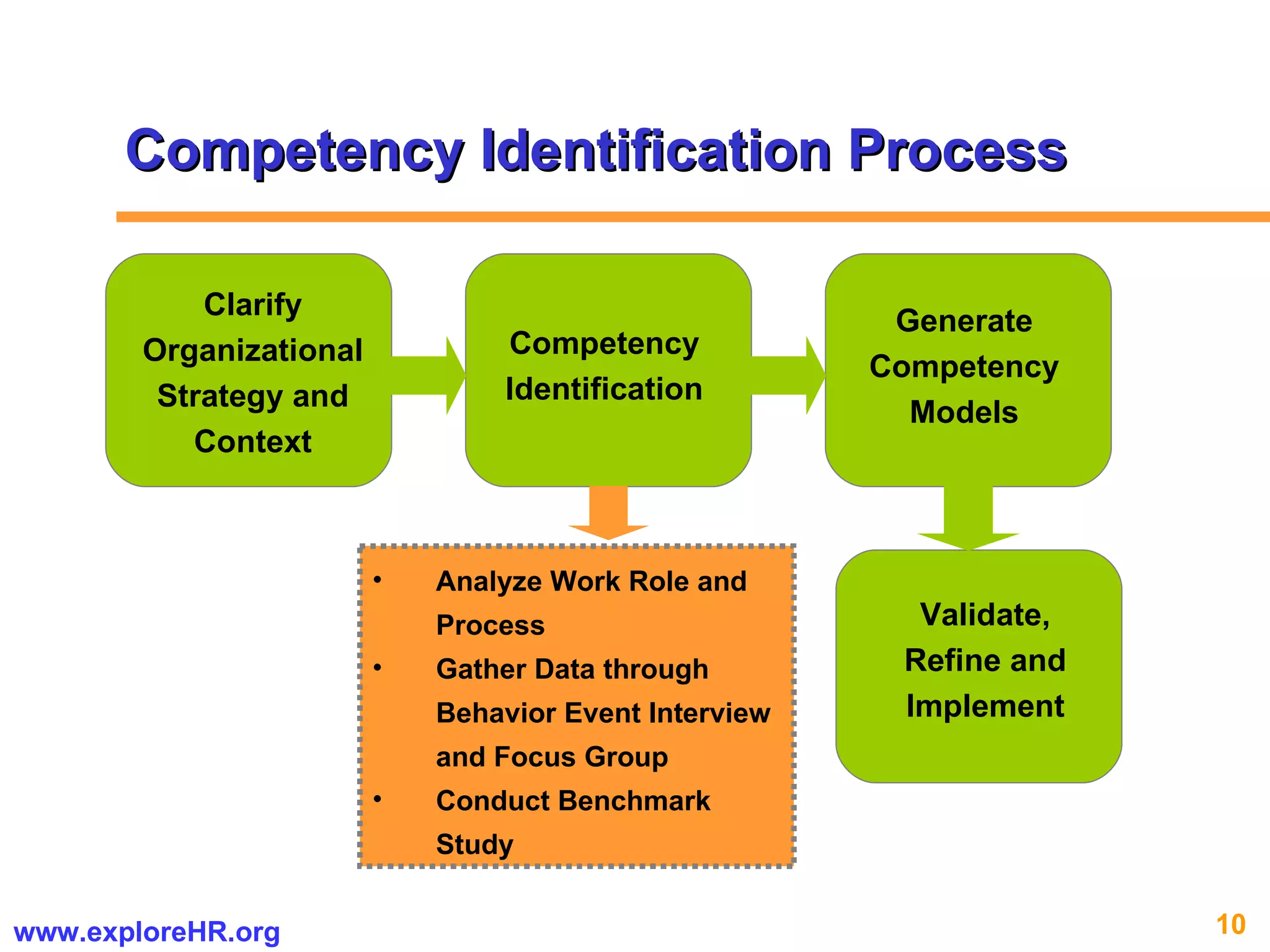
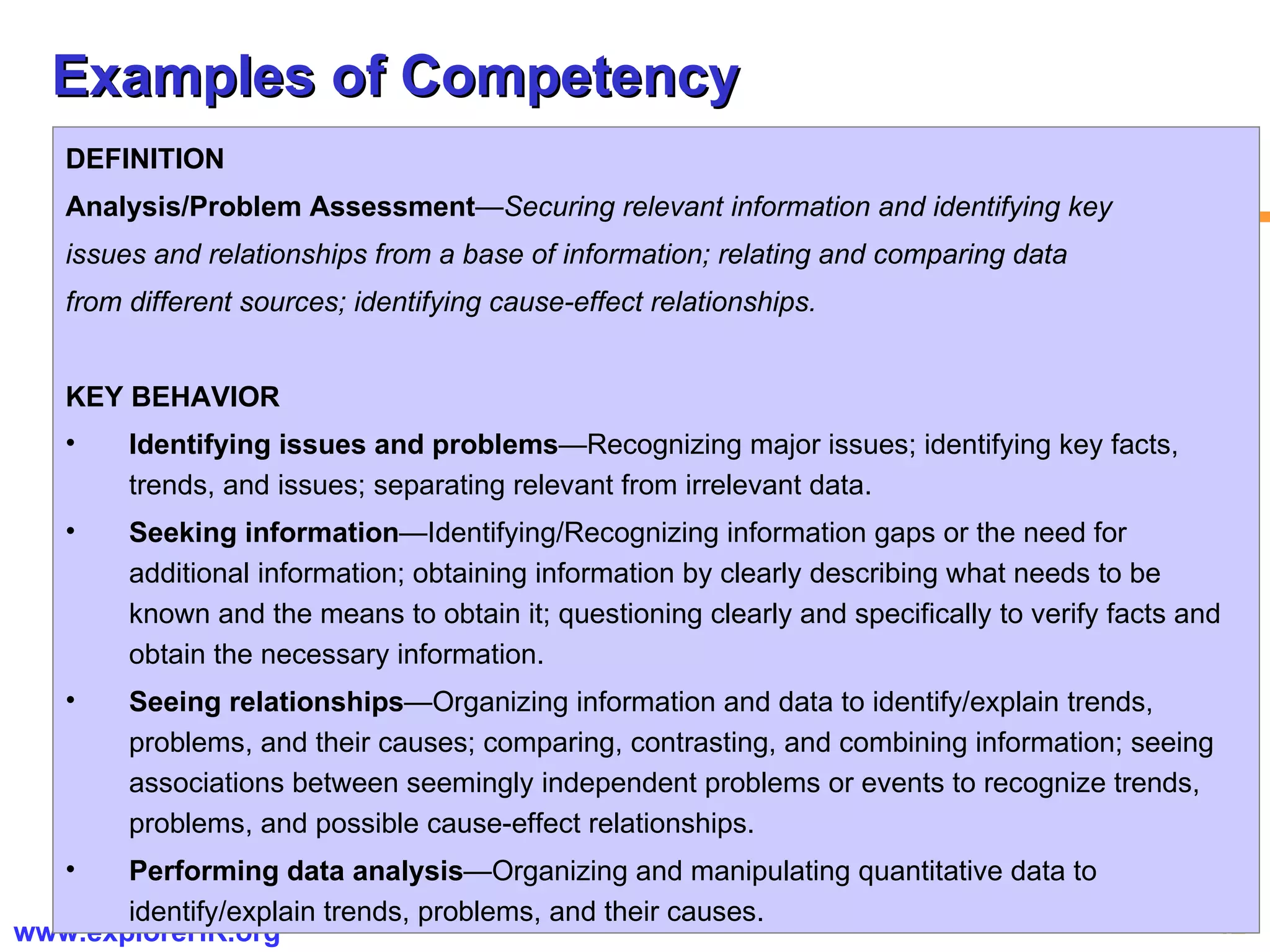
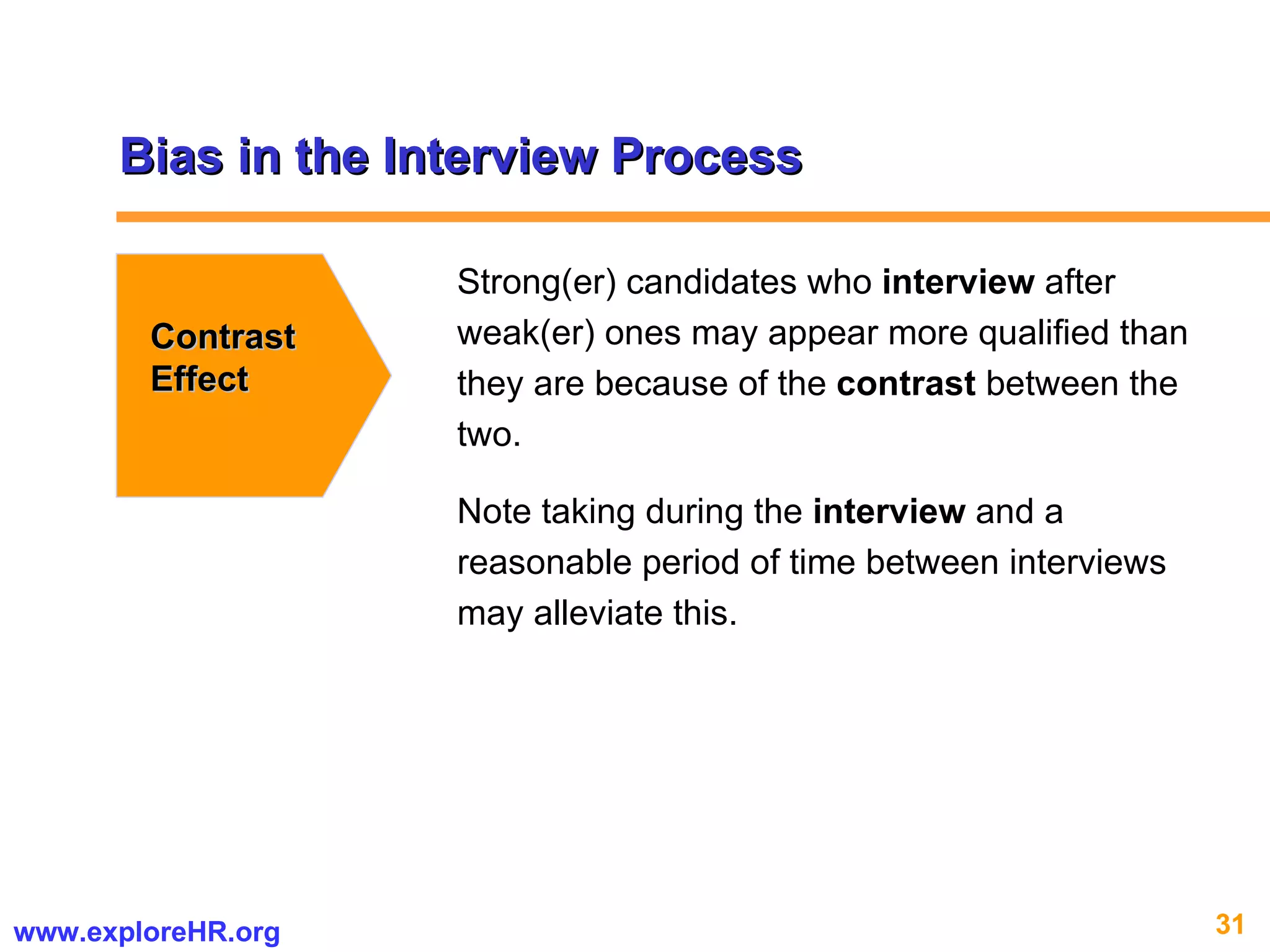
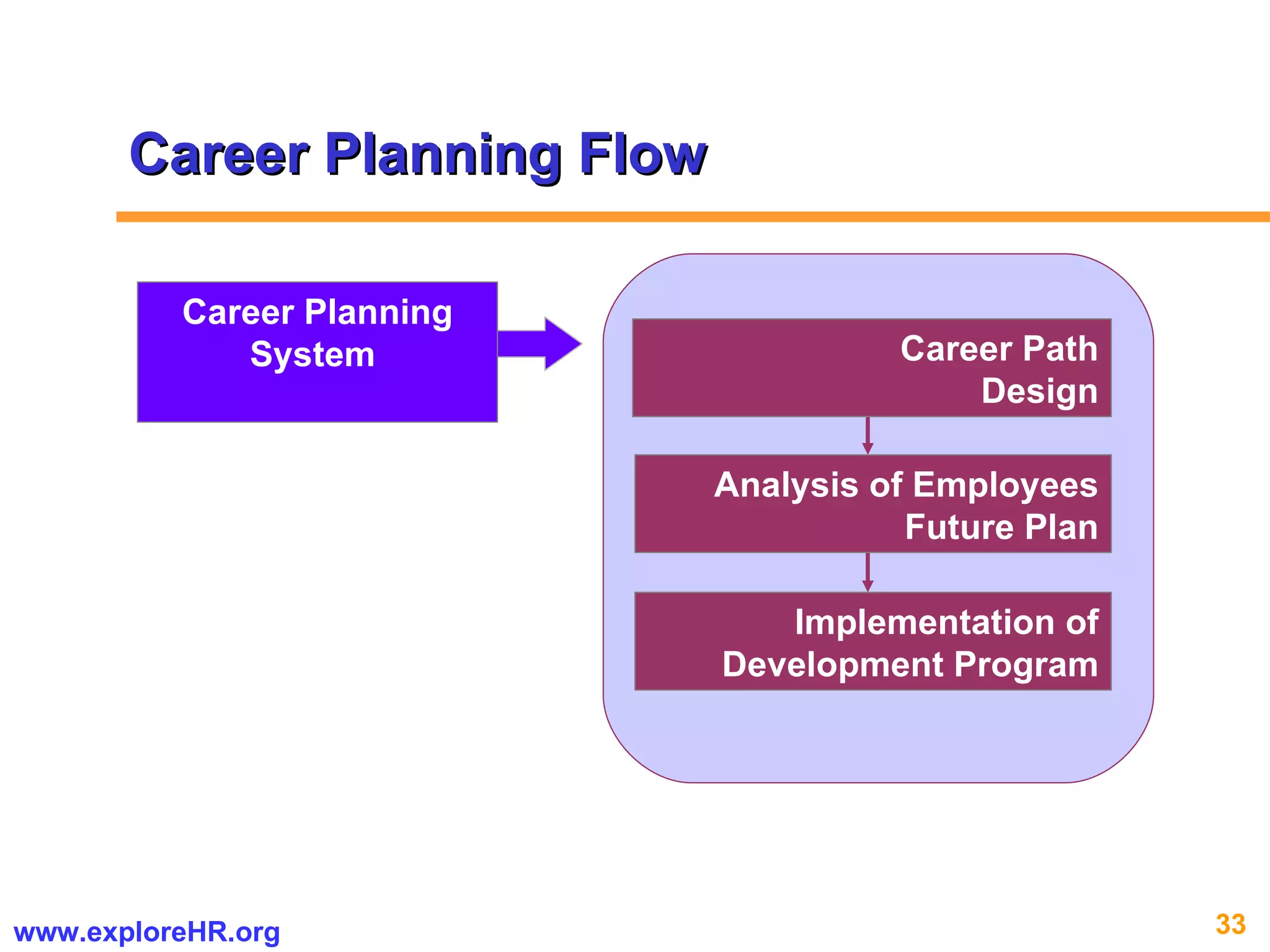
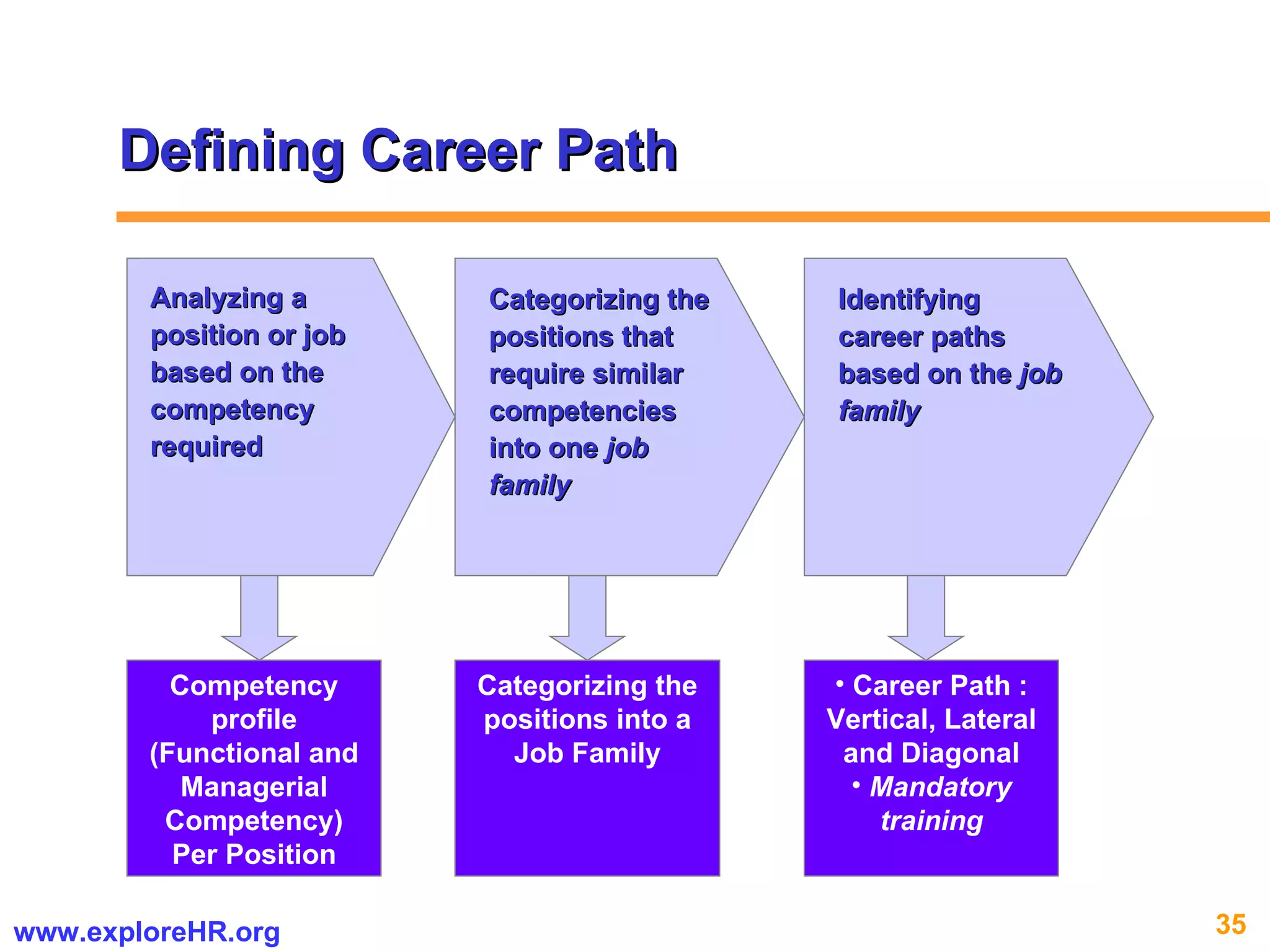
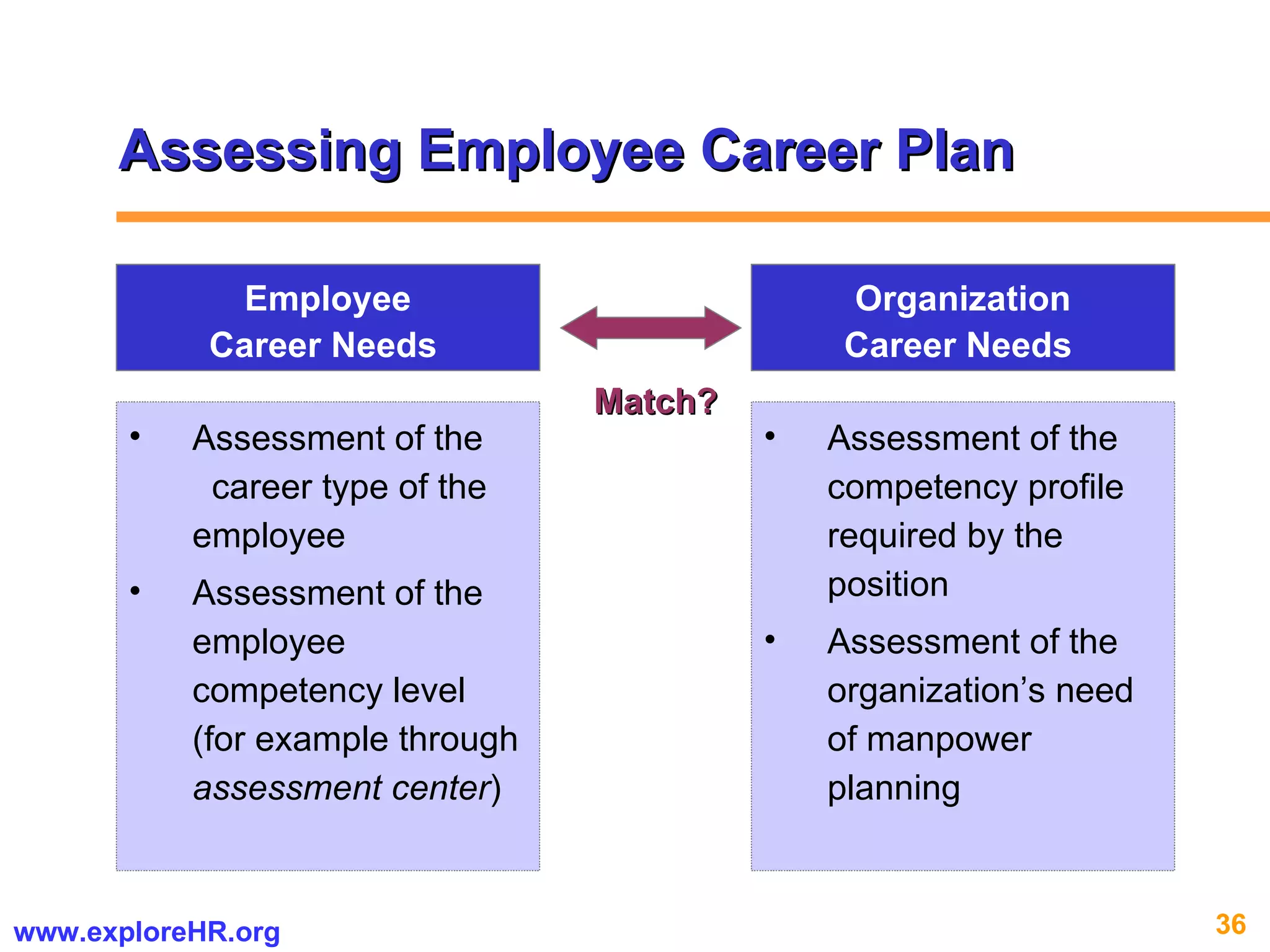
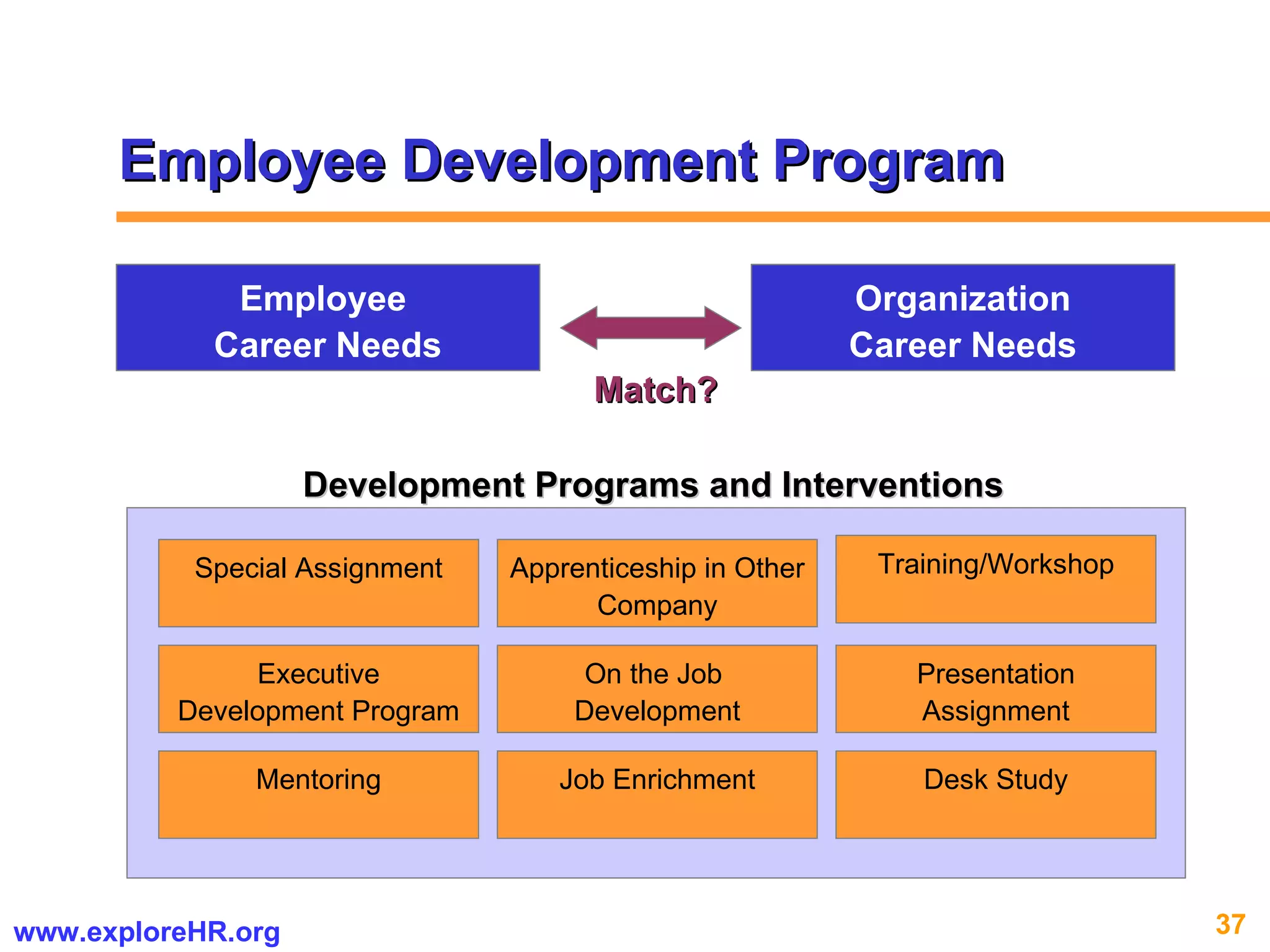
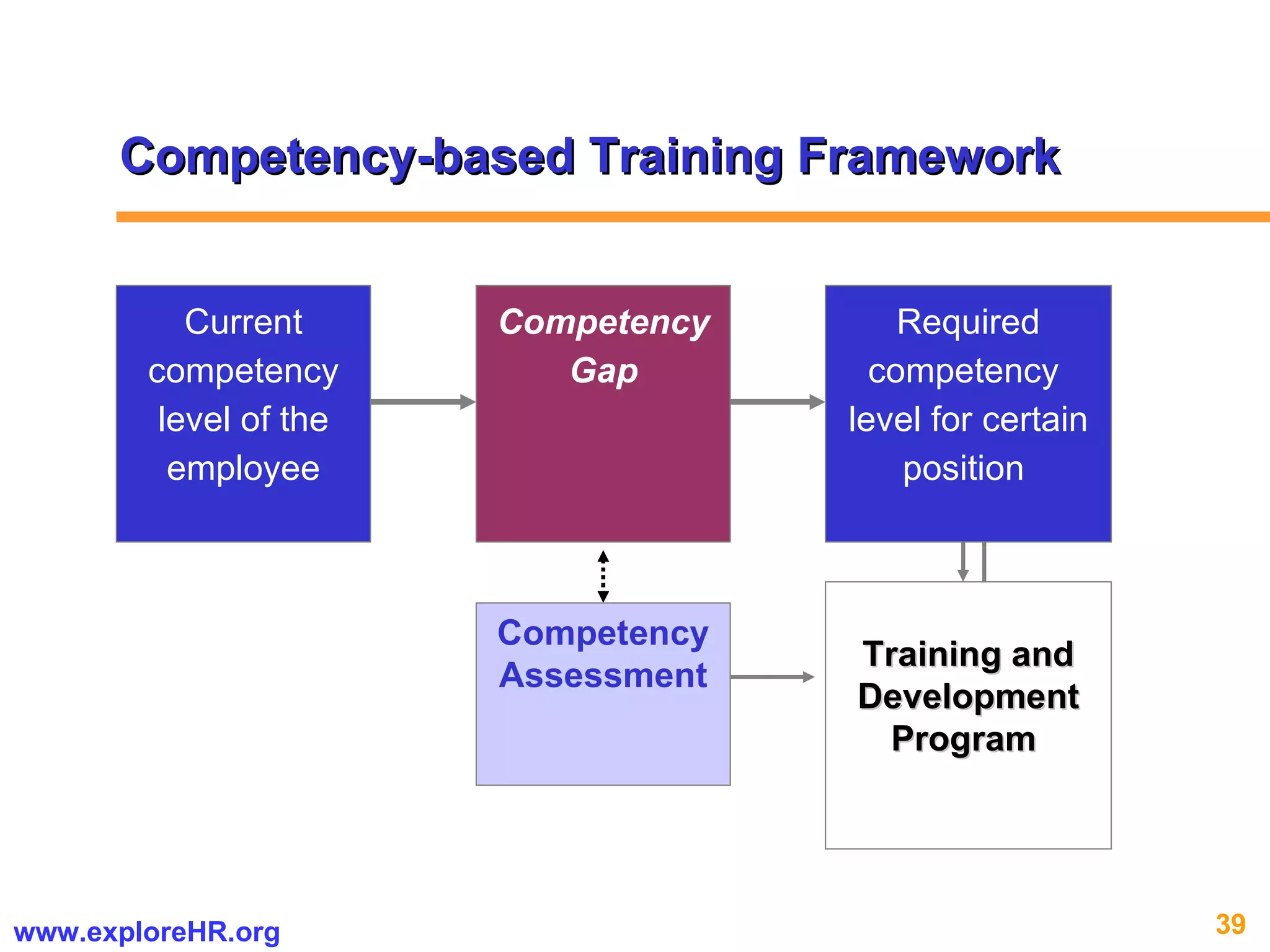
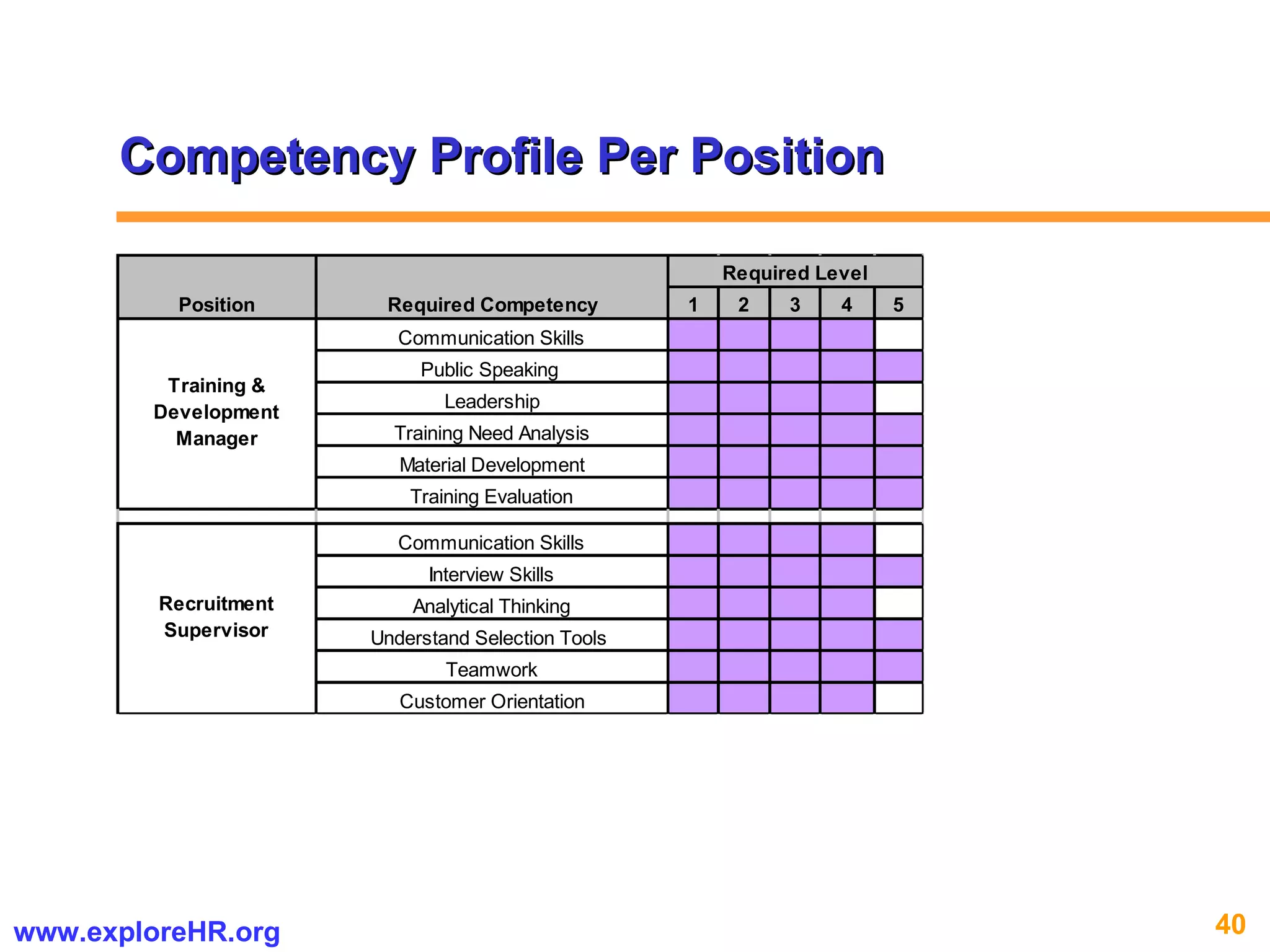
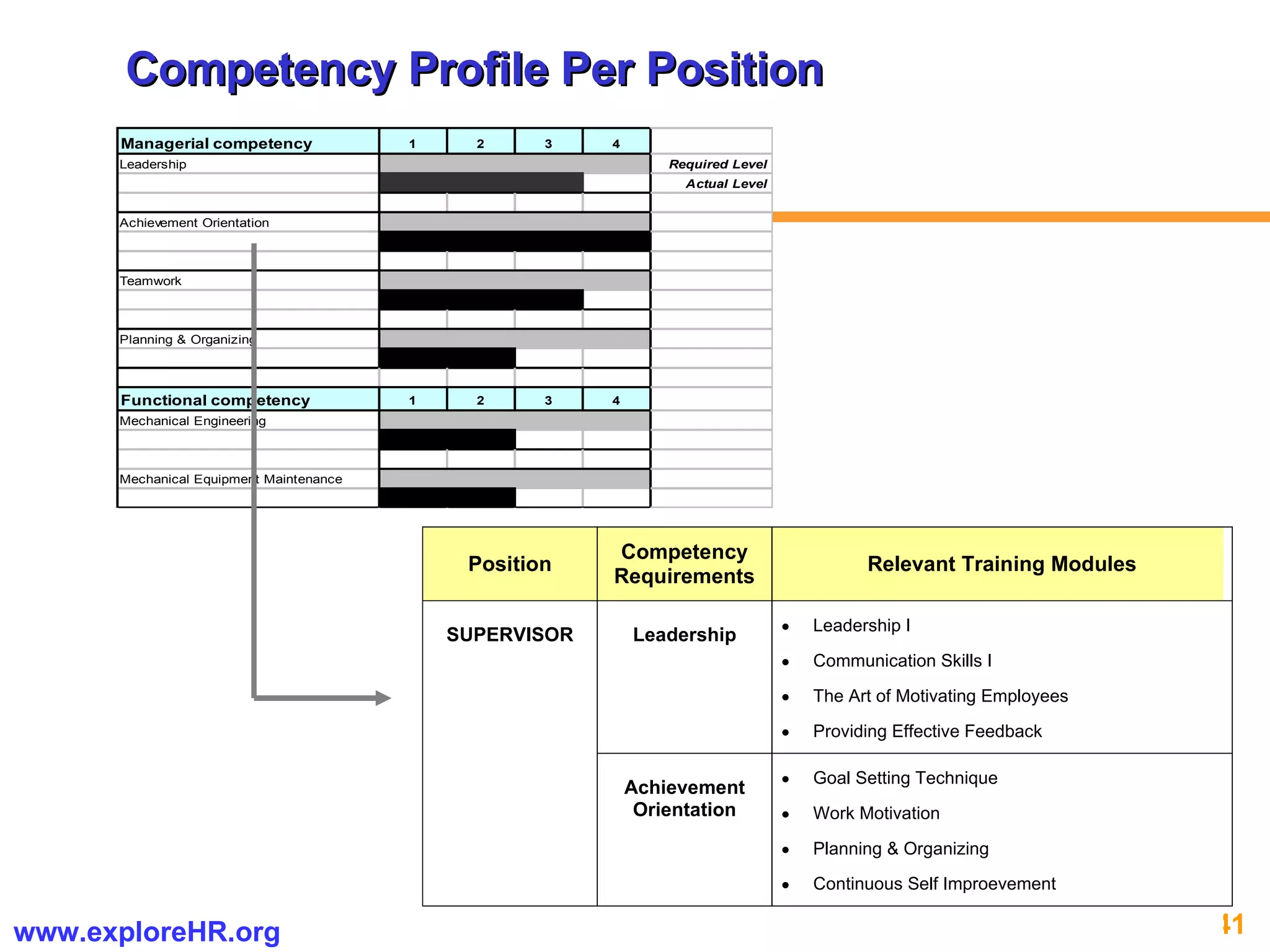
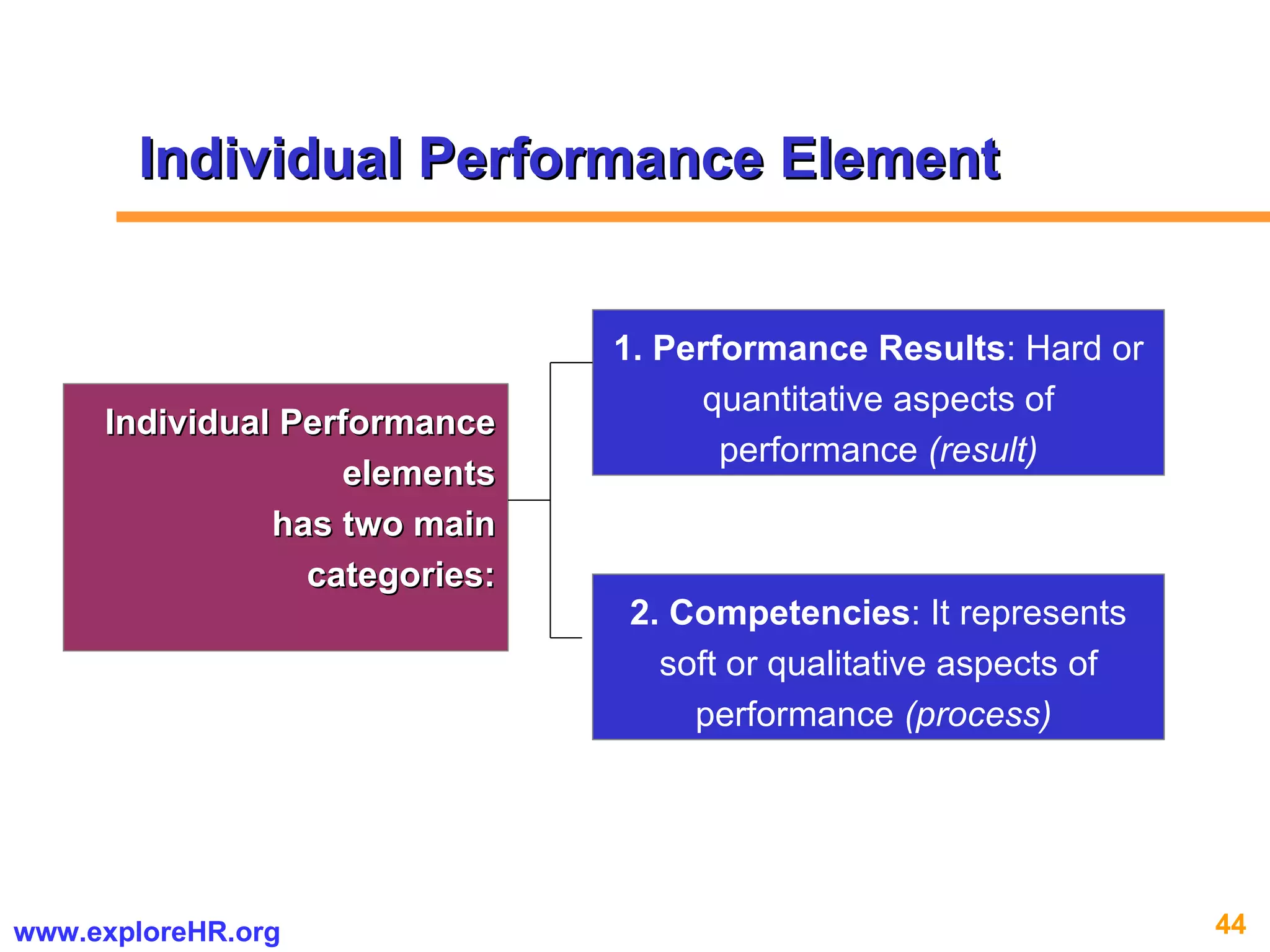
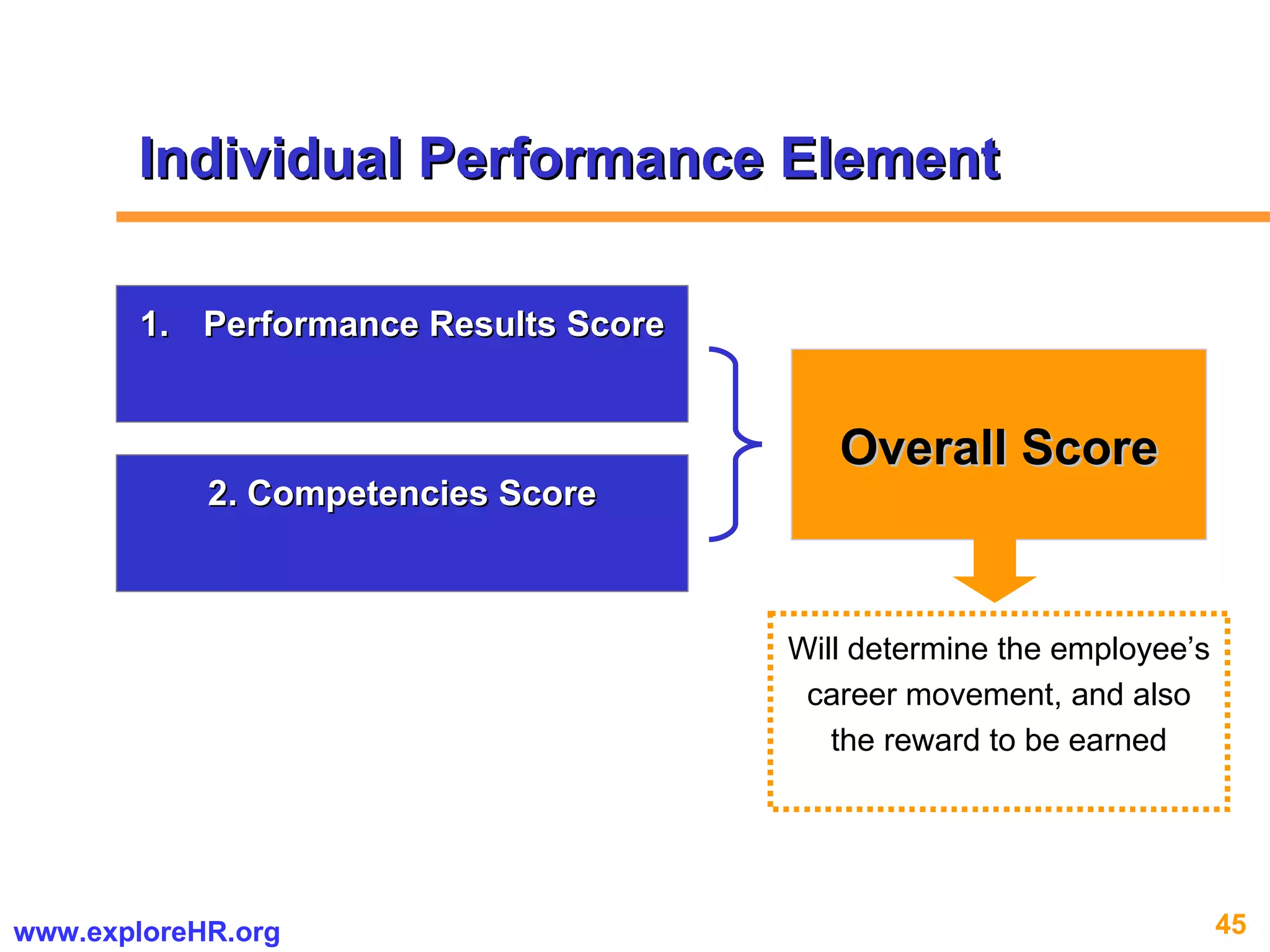
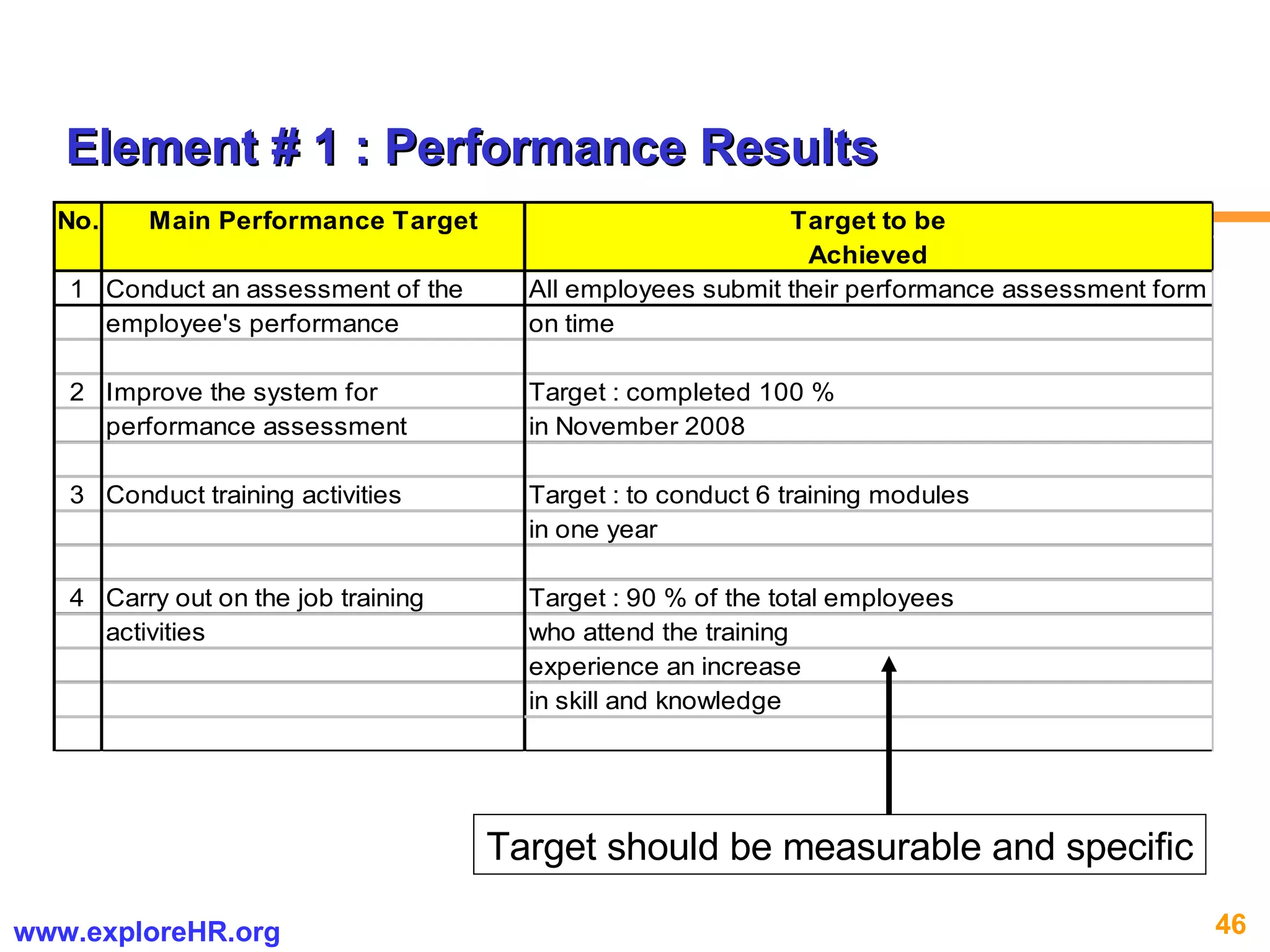
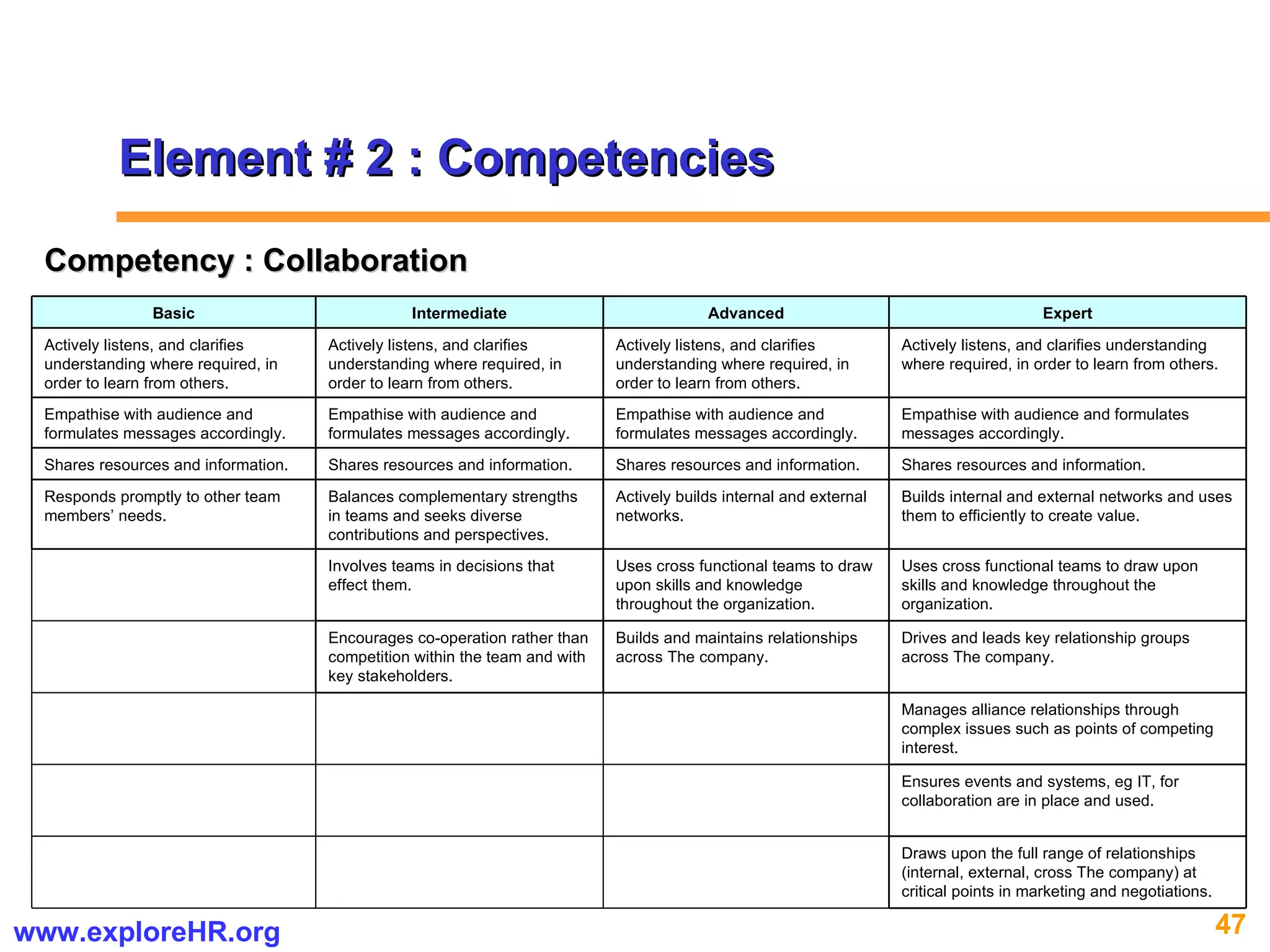
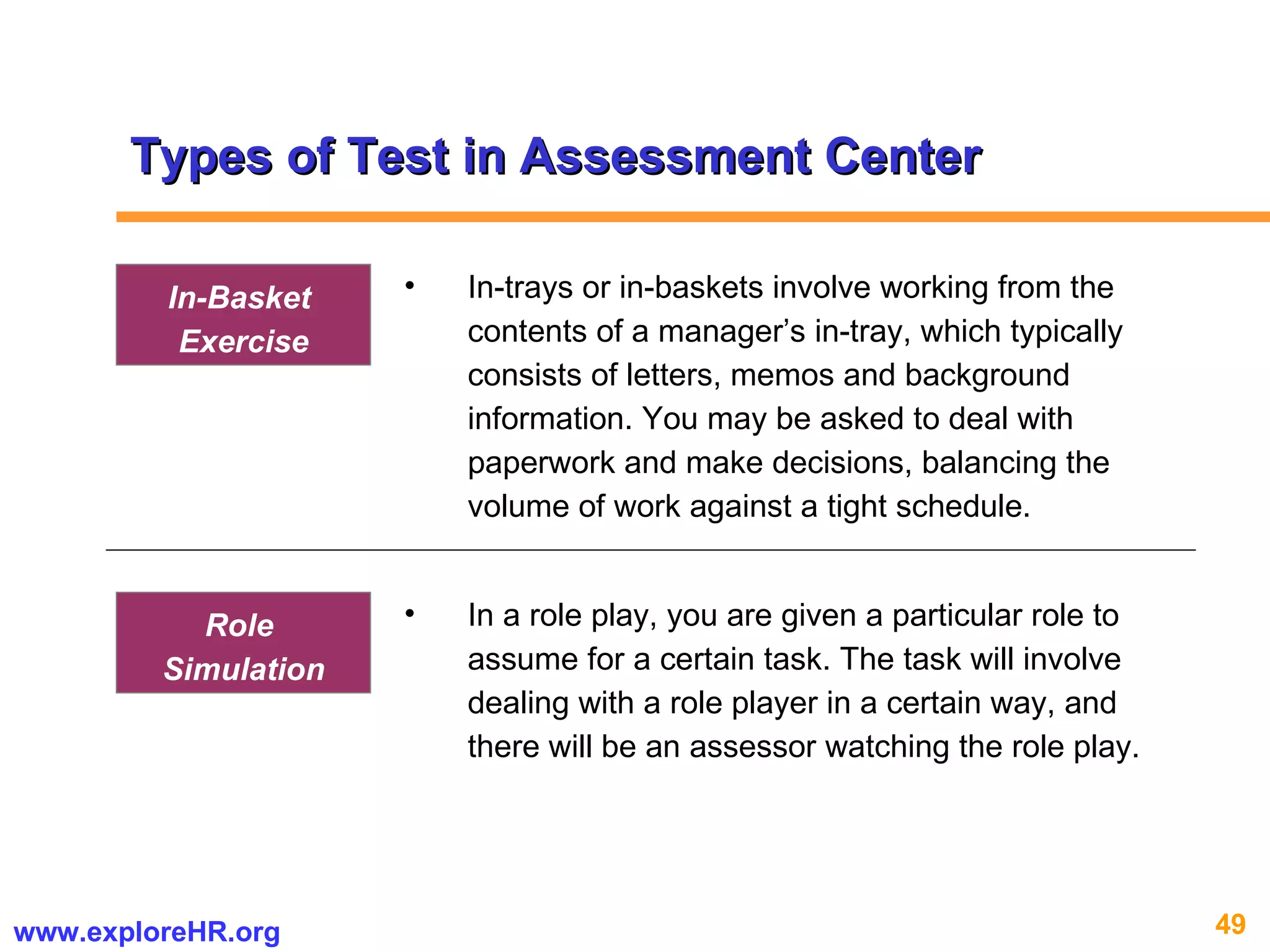
The document provides an overview of competency-based human resource (HR) management. It discusses developing a competency model and framework, competency-based interviewing, career planning, training and development, and performance management. The benefits of using competency models for both managers and employees are highlighted. Assessment centers and various assessment exercises are also described as ways to assess competencies.