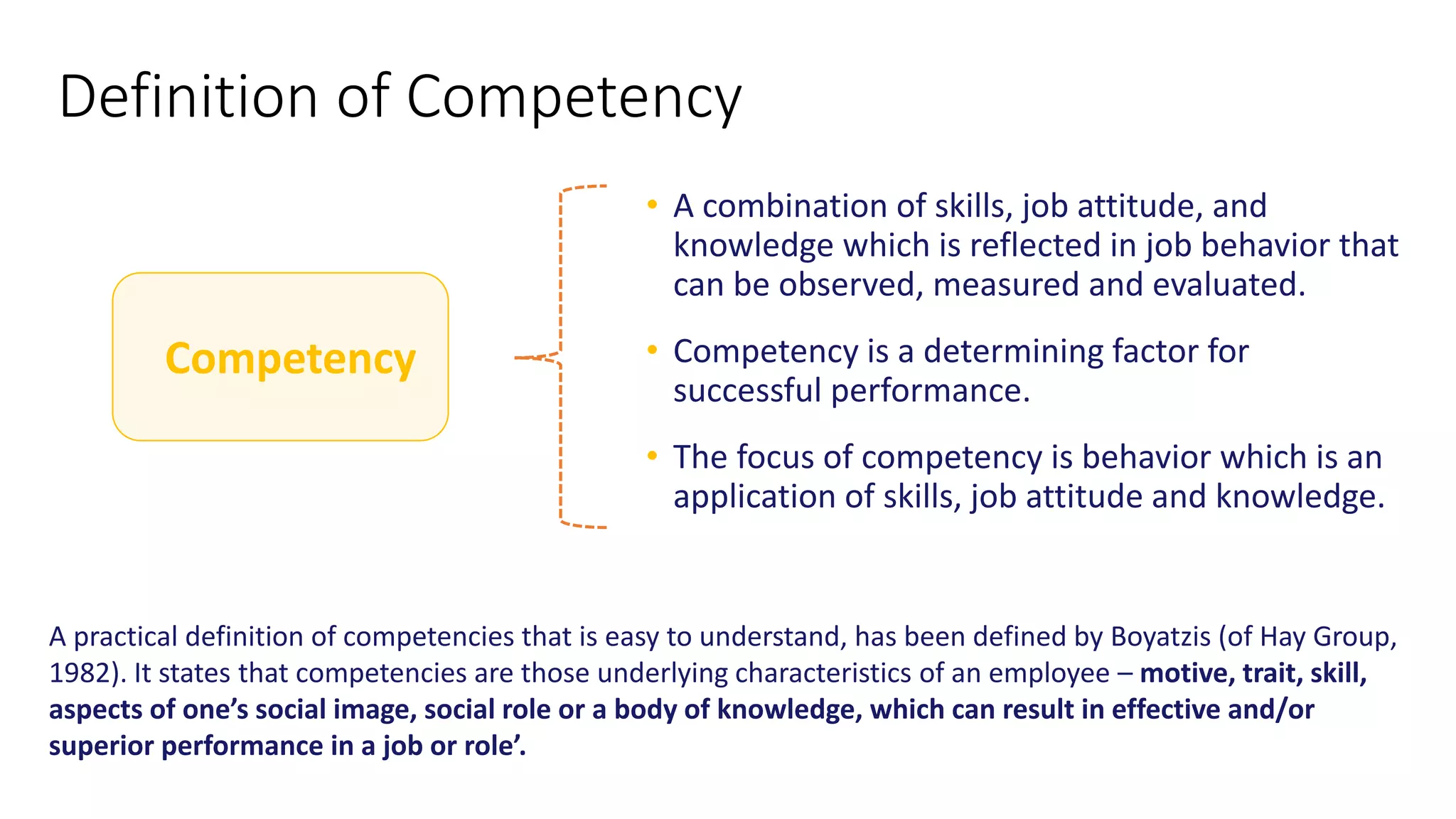
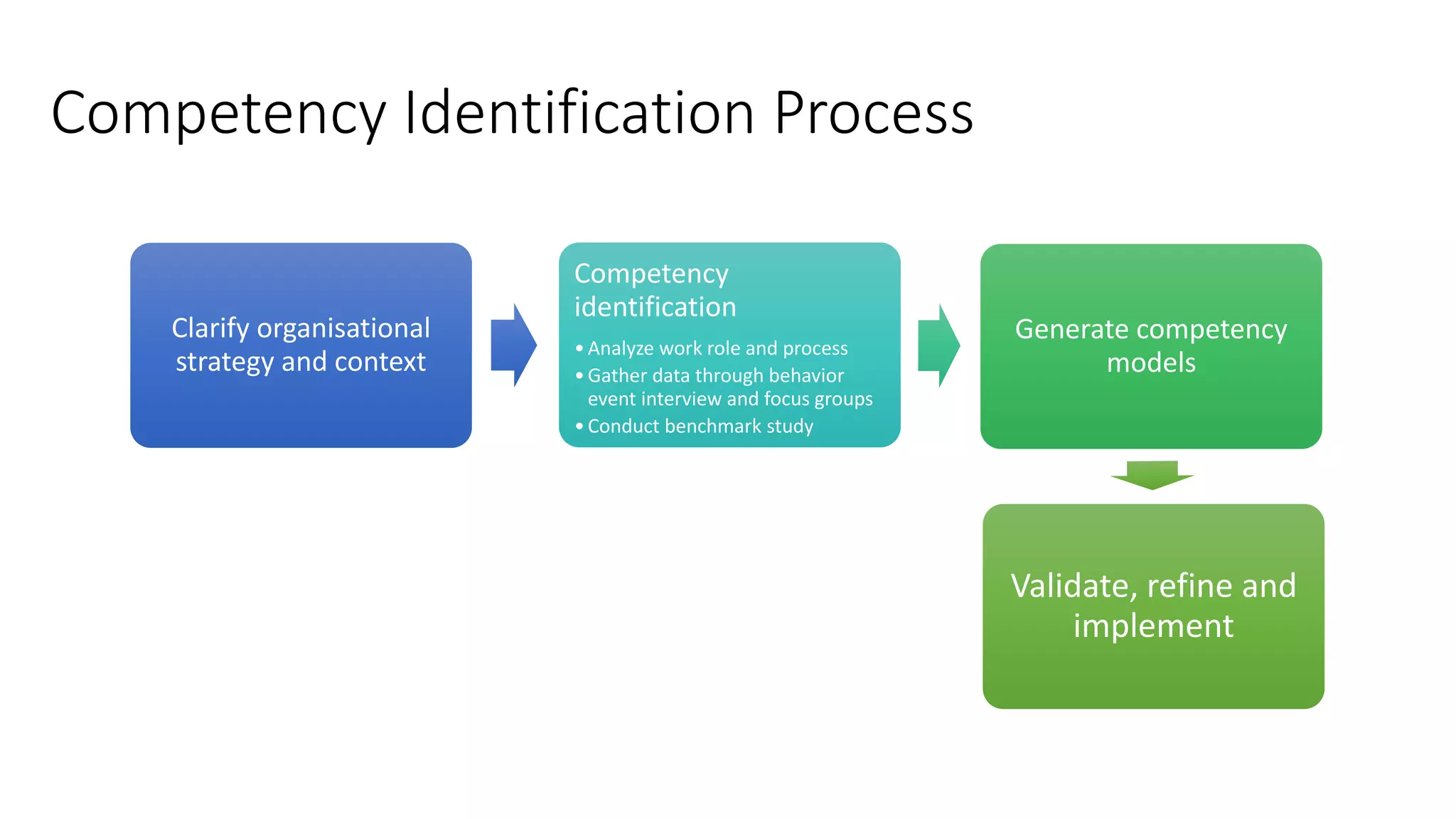
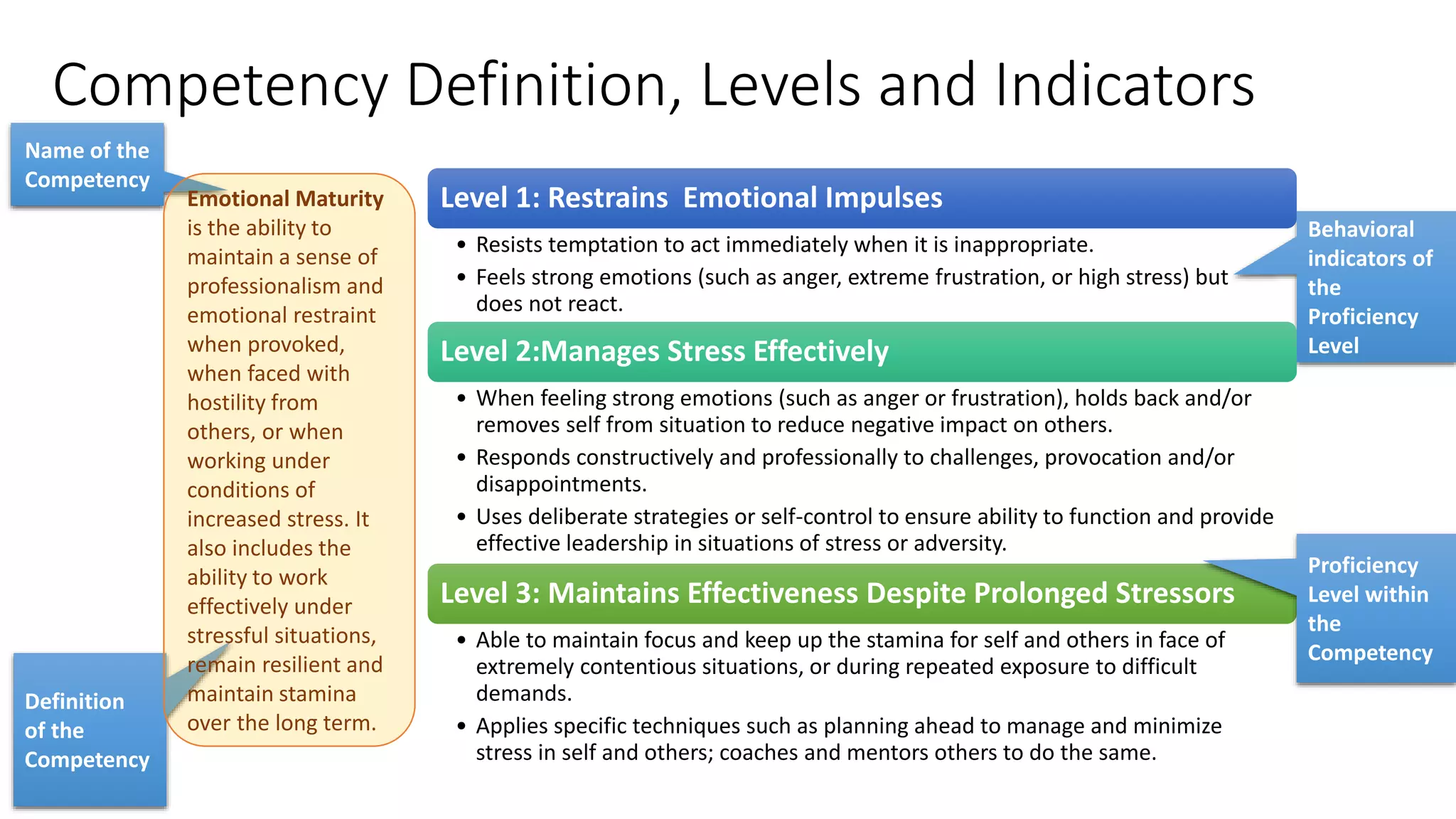
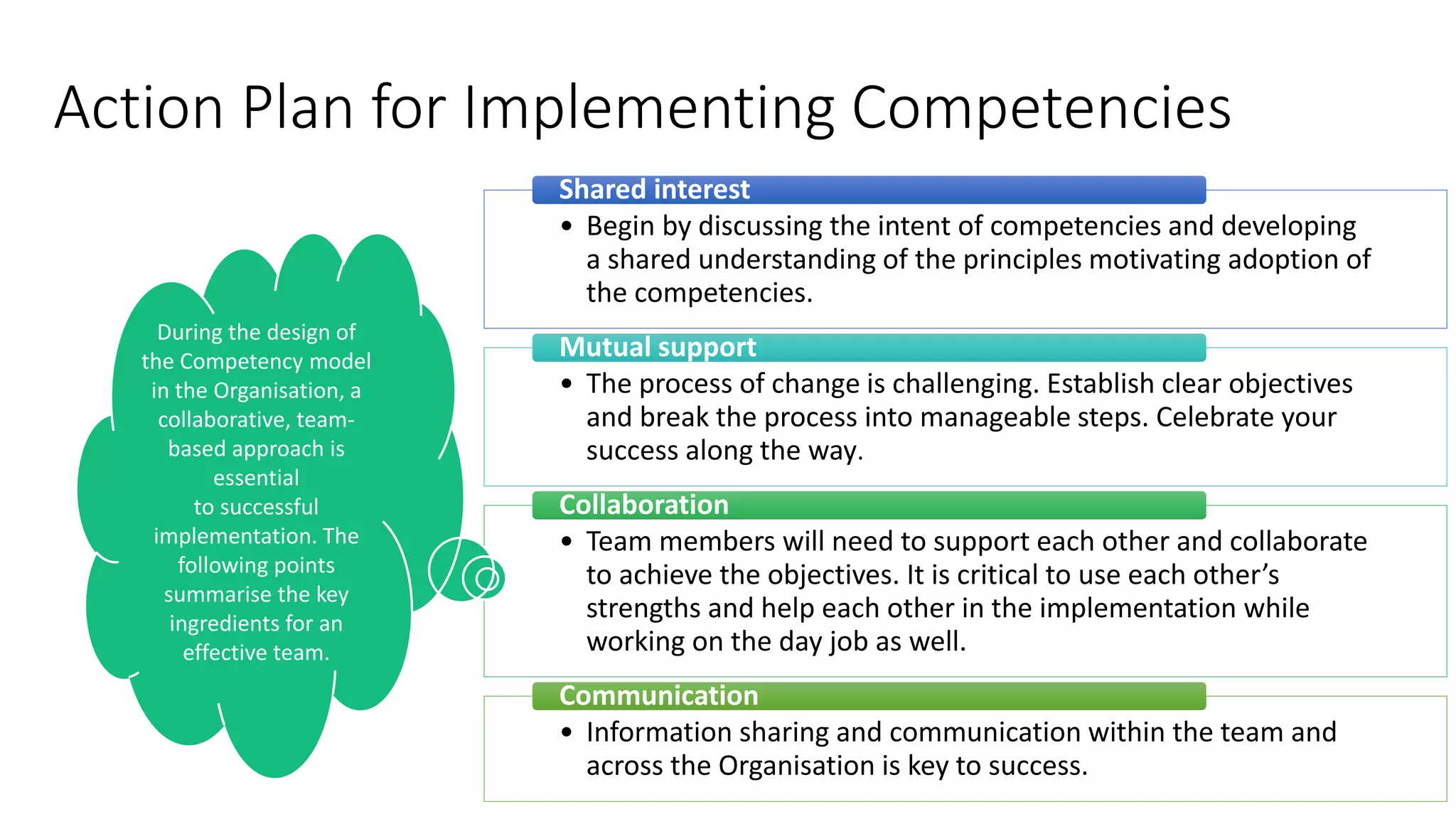
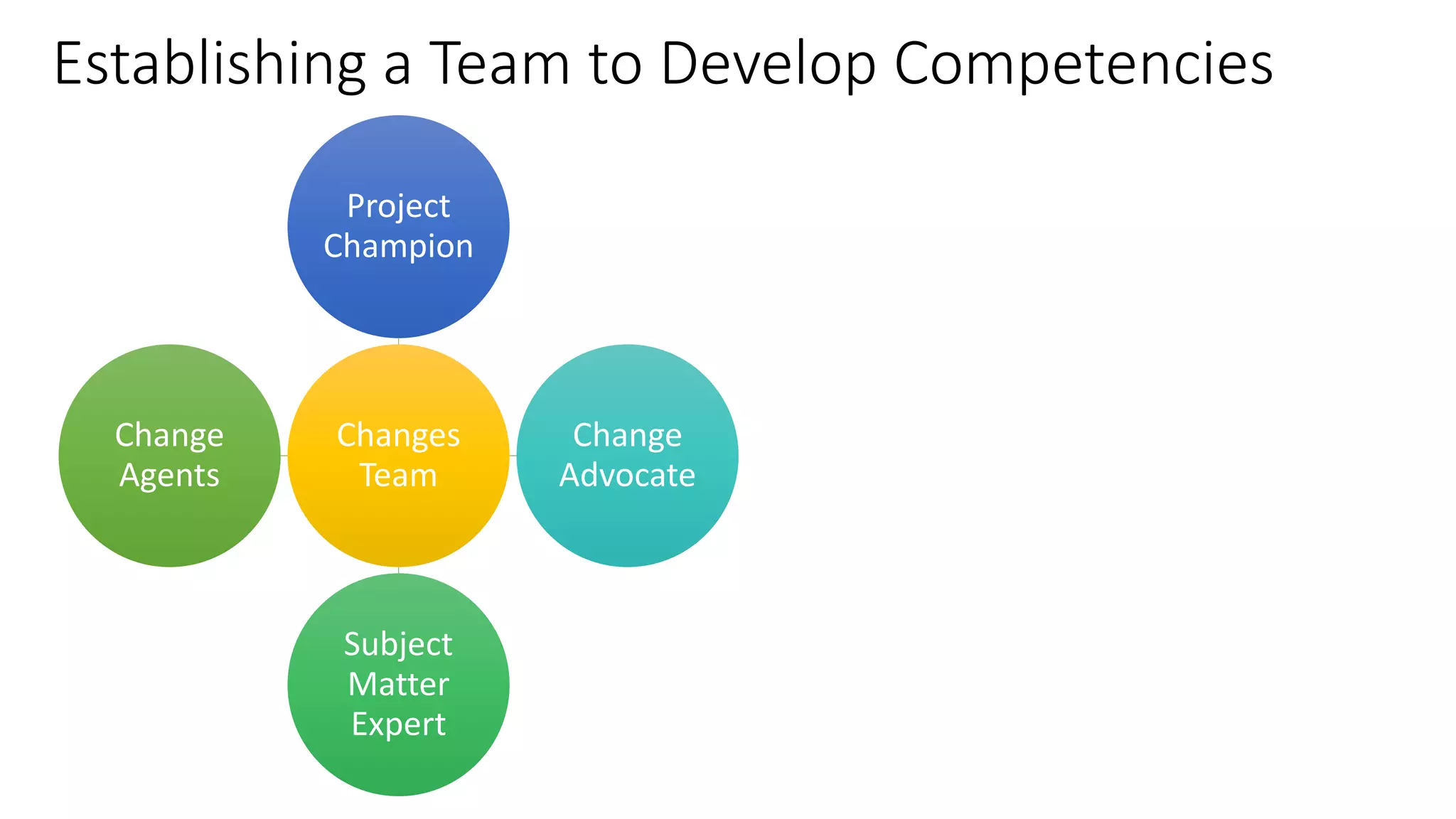
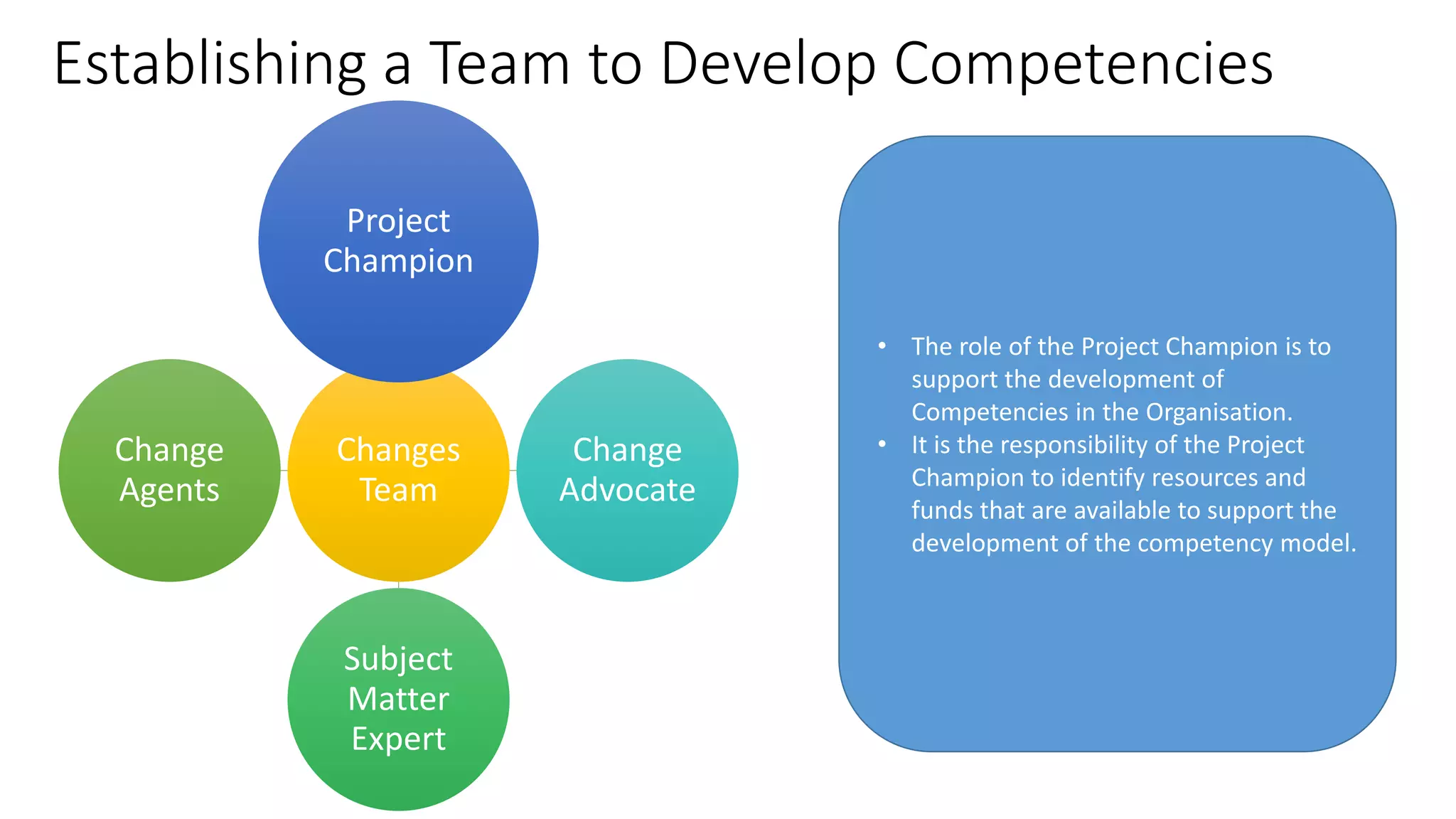
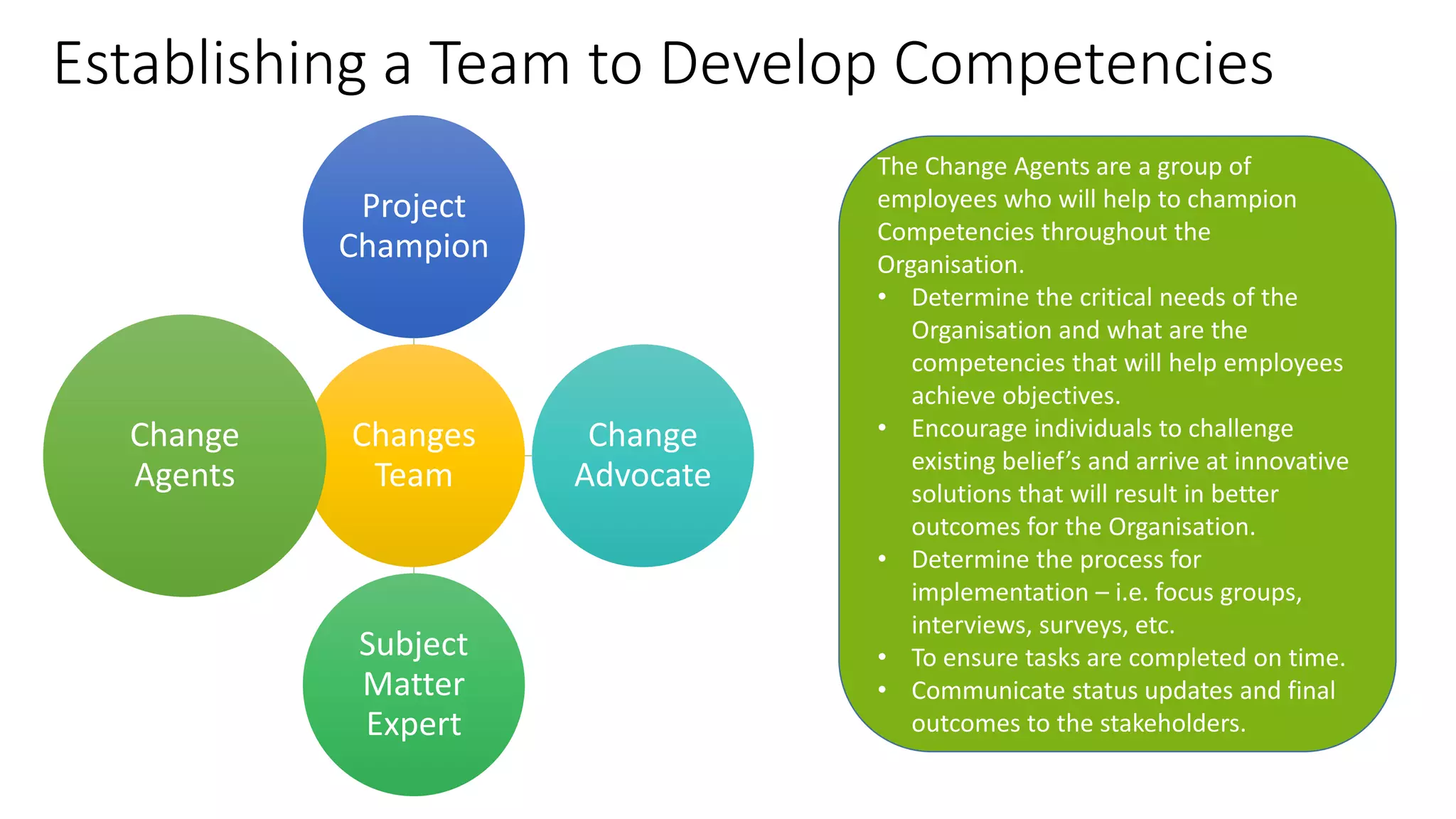
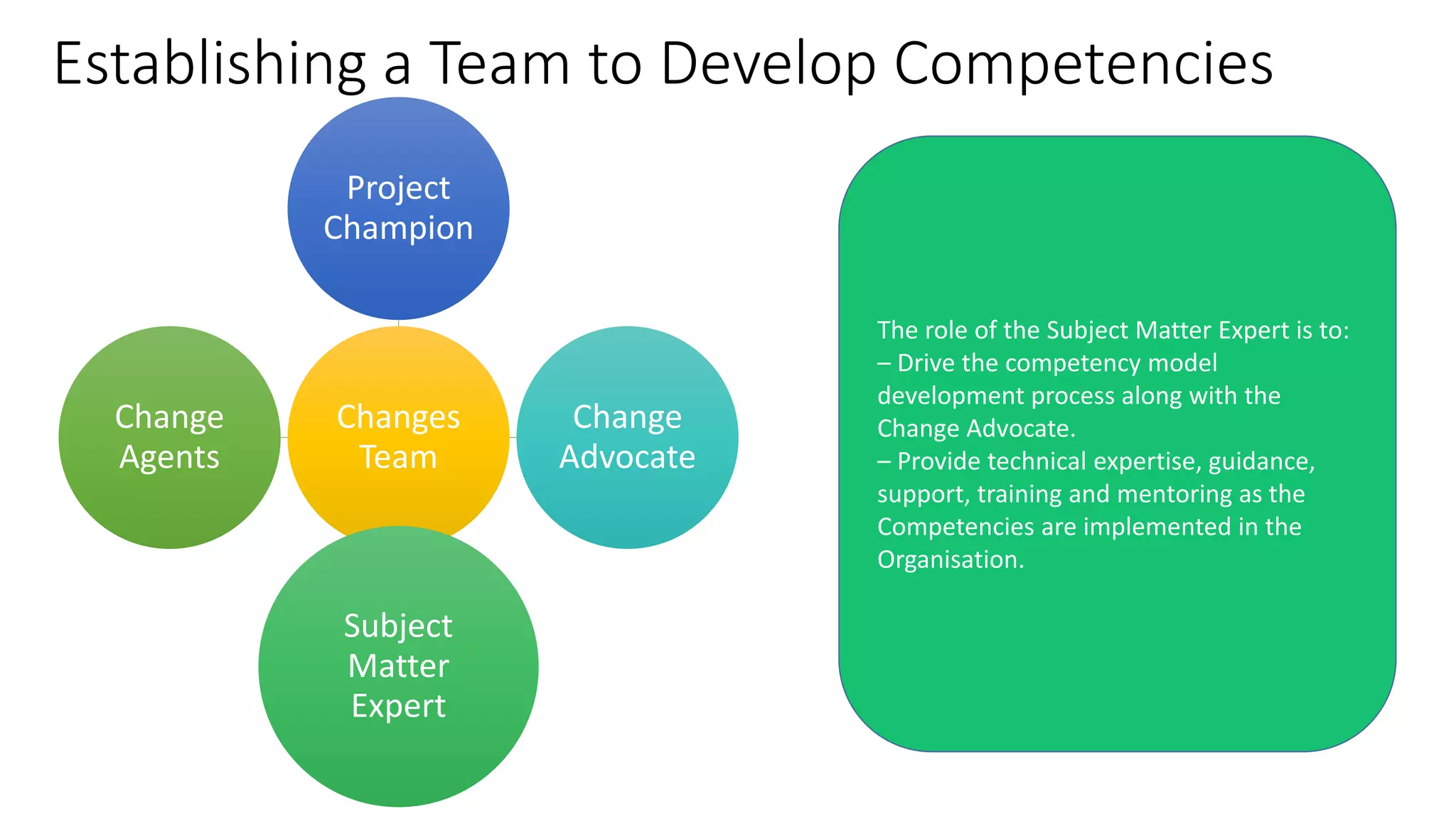
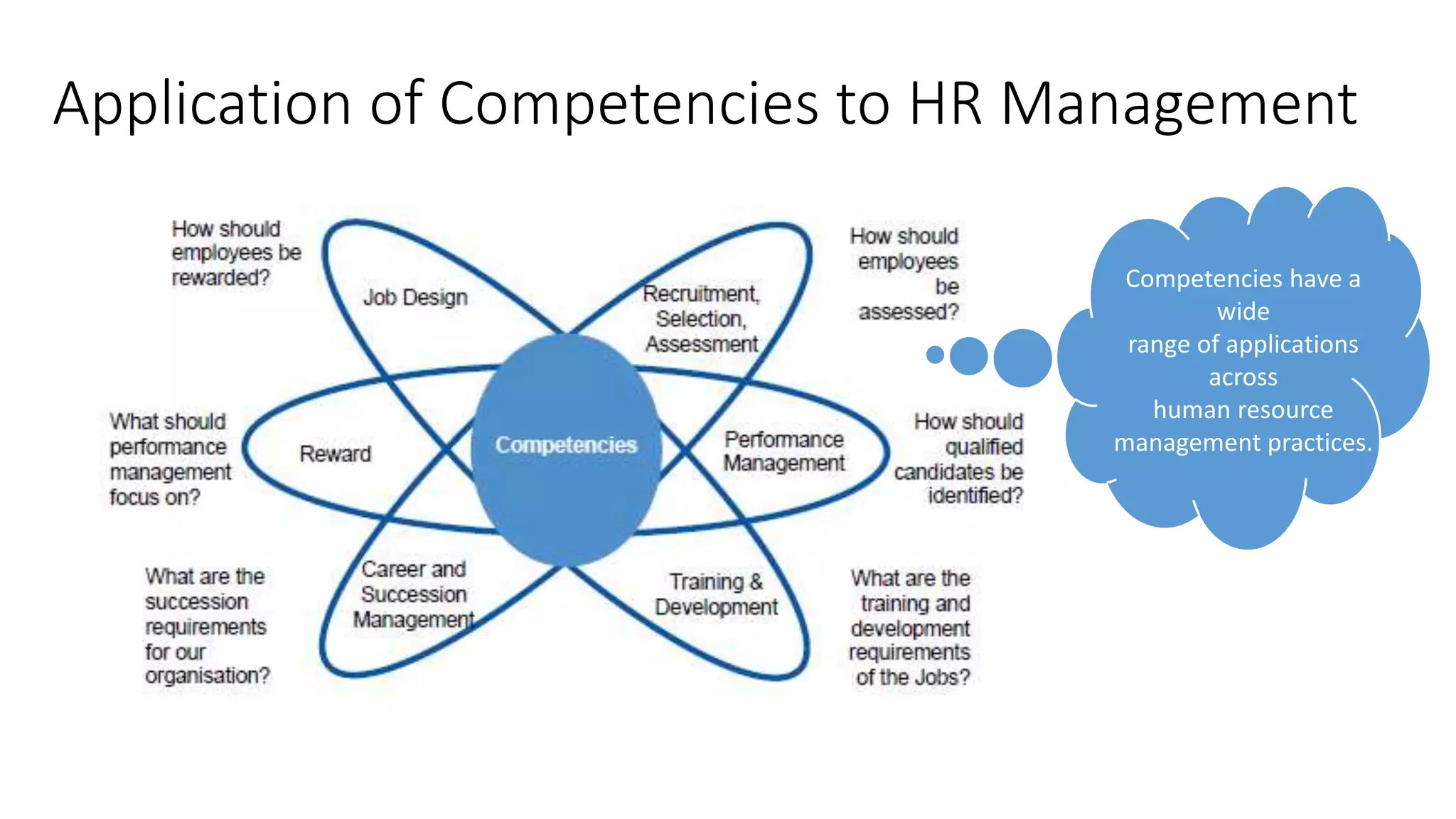
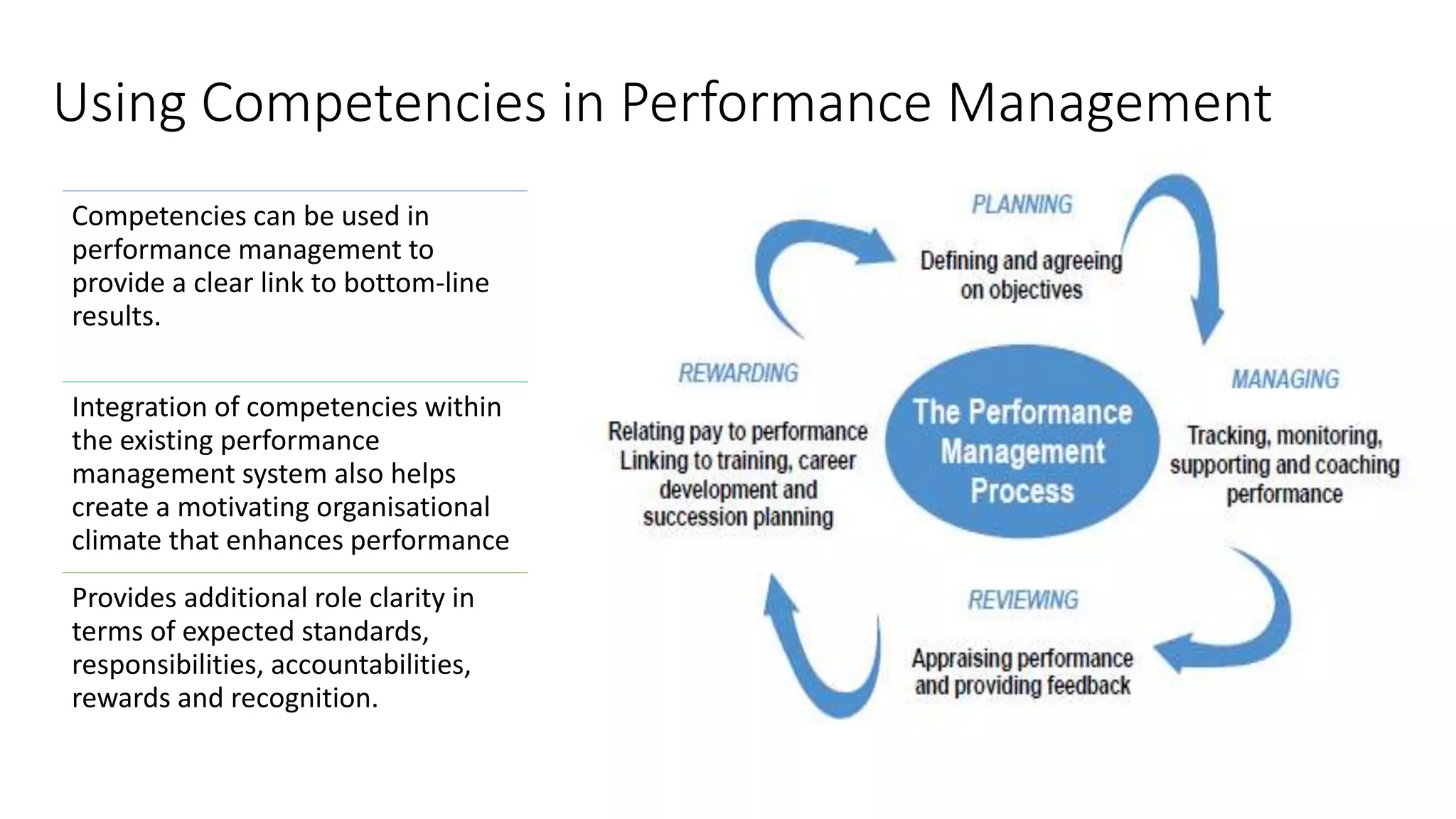
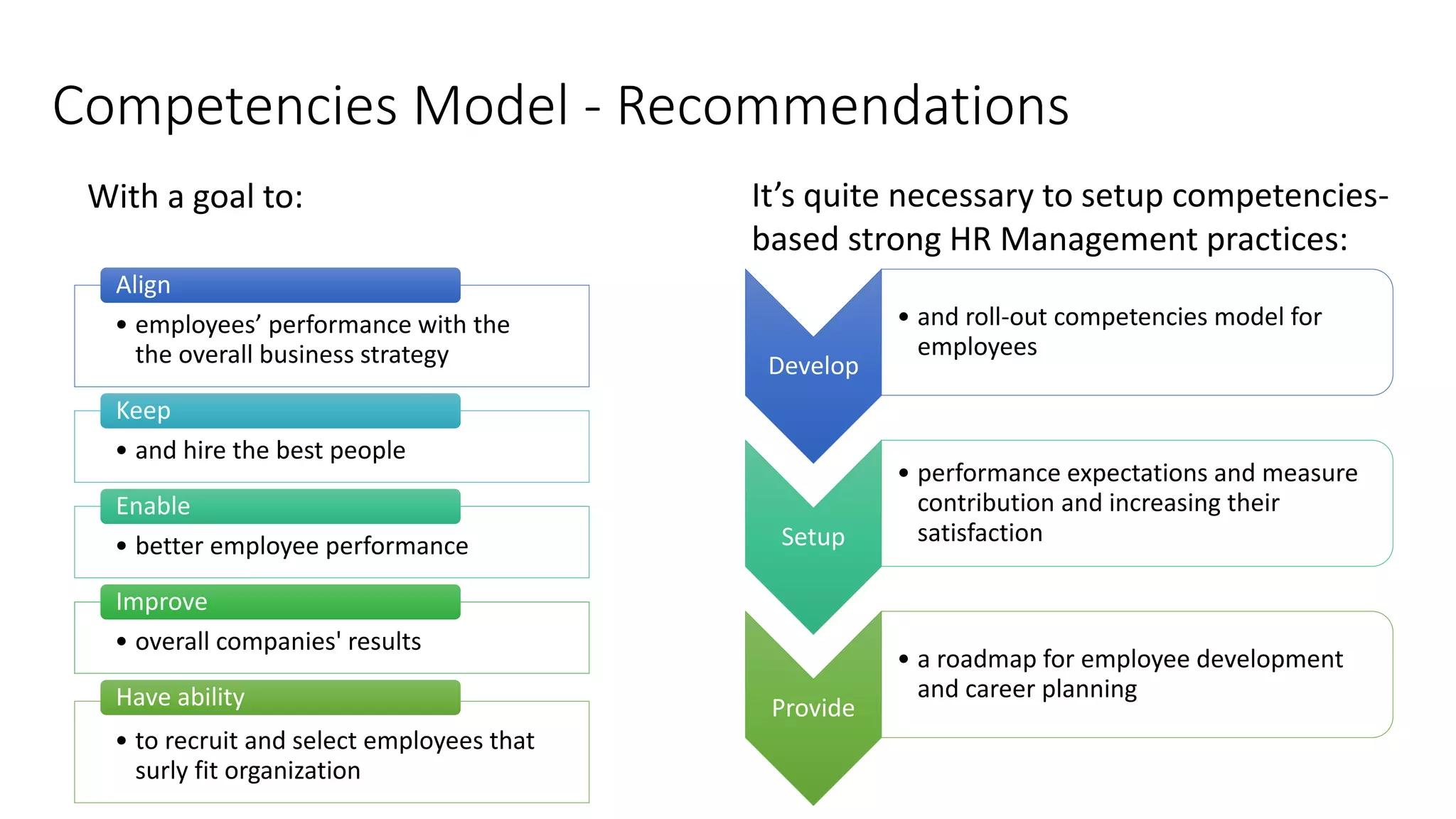
The document outlines a competency-based approach to human resource management, defining competencies as a combination of skills, knowledge, and job attitudes that contribute to successful performance. It differentiates between traditional job descriptions and competency models, emphasizing the benefits for both managers and employees in terms of performance clarity, assessment, and development. The implementation strategy for competency models is highlighted, including the establishment of project champions, change advocates, and subject matter experts to ensure effective application in HR practices.