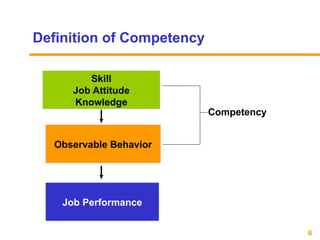
The document outlines a framework for implementing competency-based human resource management, highlighting the importance of competencies in recruitment, selection, training, and performance management. It distinguishes between managerial and functional competencies, describes the process of competency identification, and discusses the benefits for both managers and employees. Additionally, it emphasizes the significance of structured competency-based interviews to enhance hiring accuracy and reduce biases.