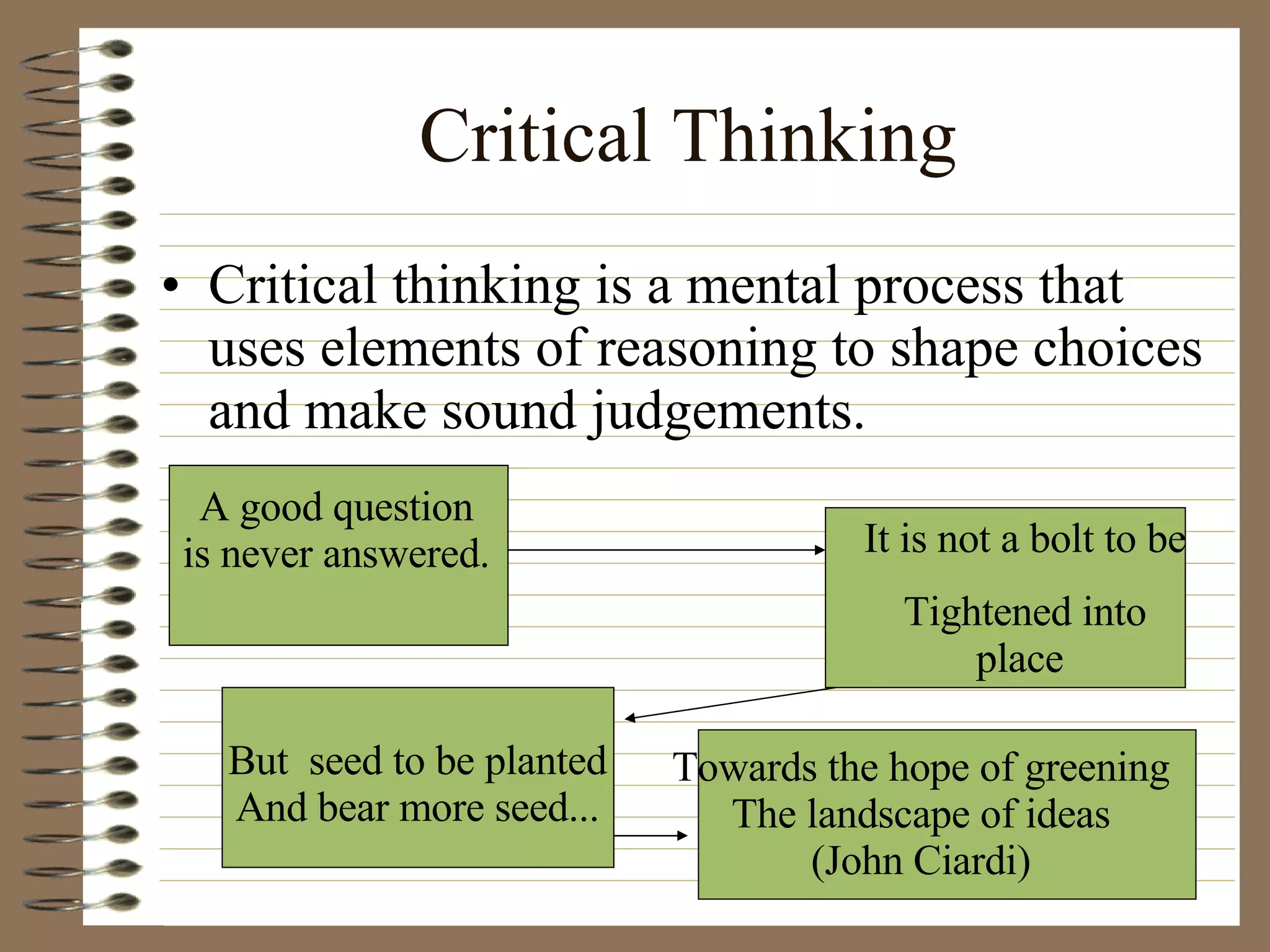
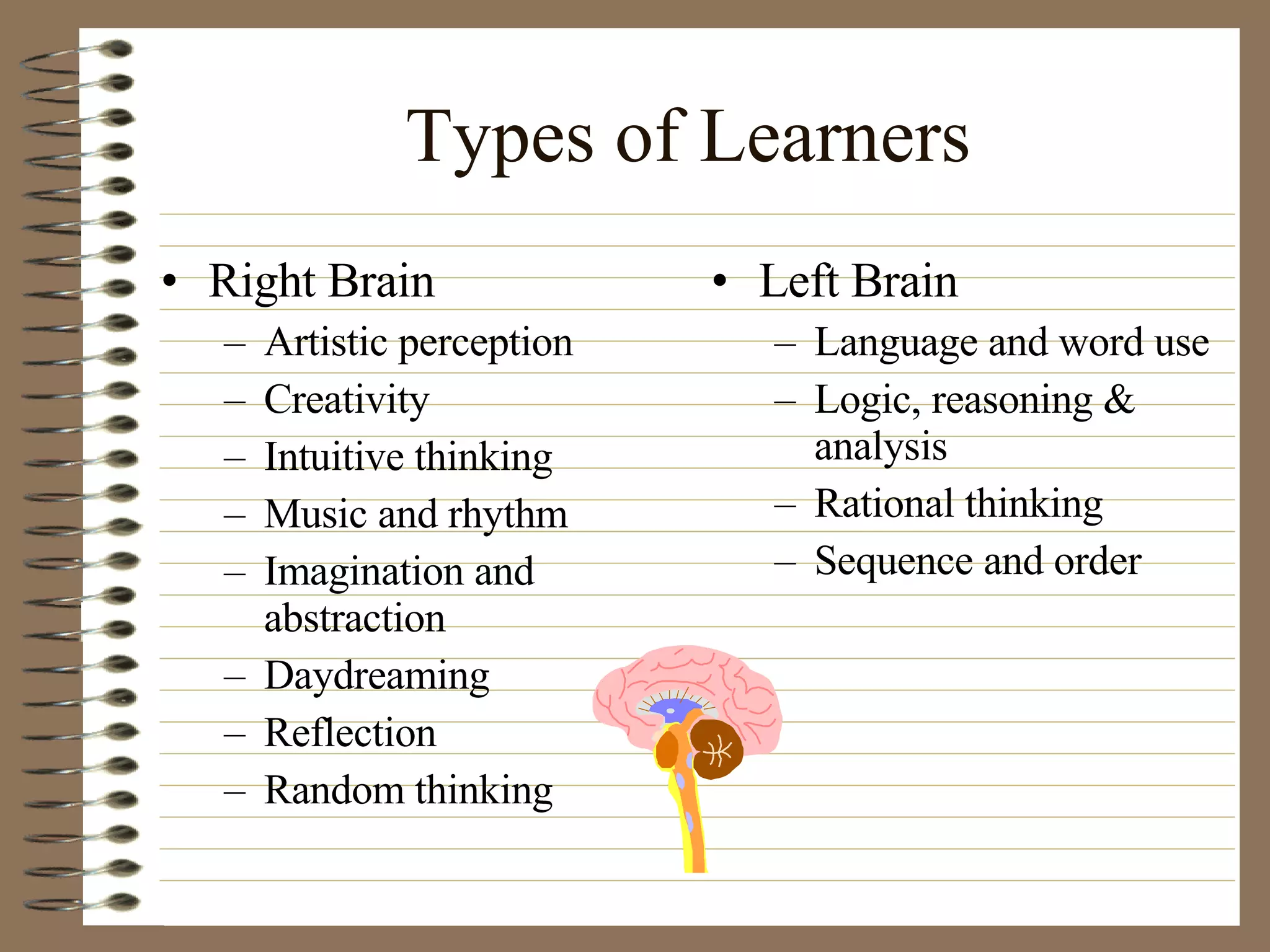
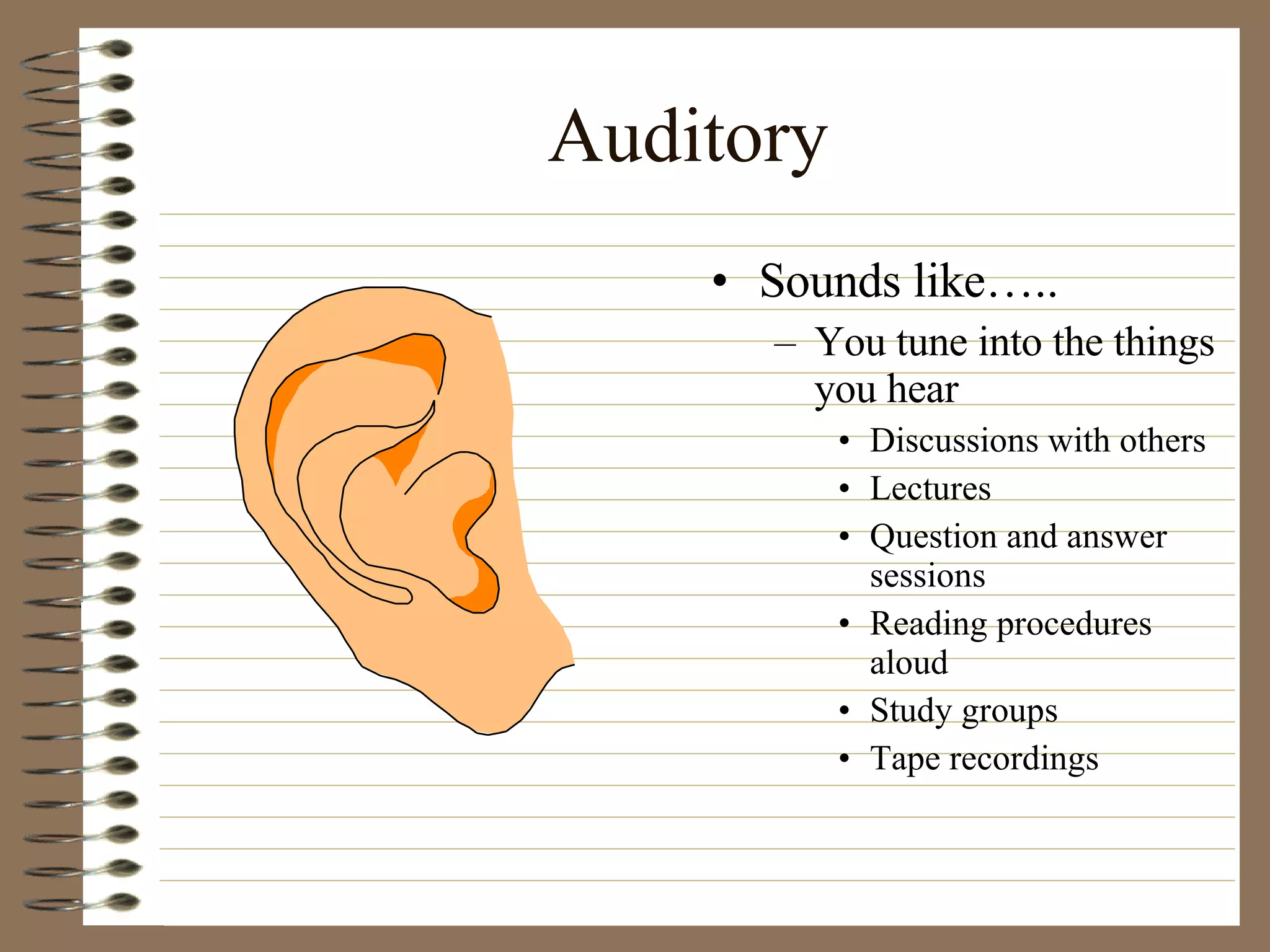
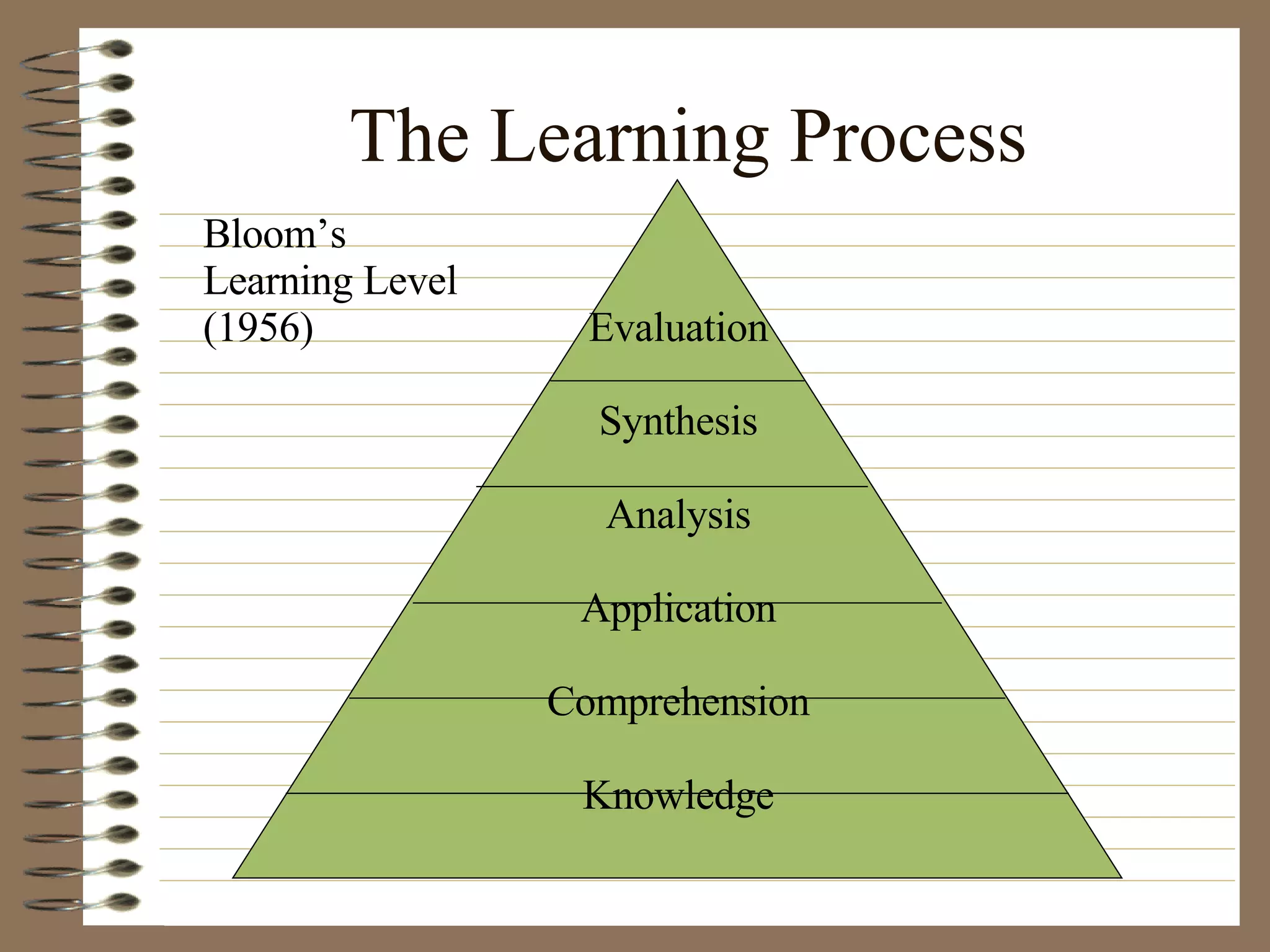
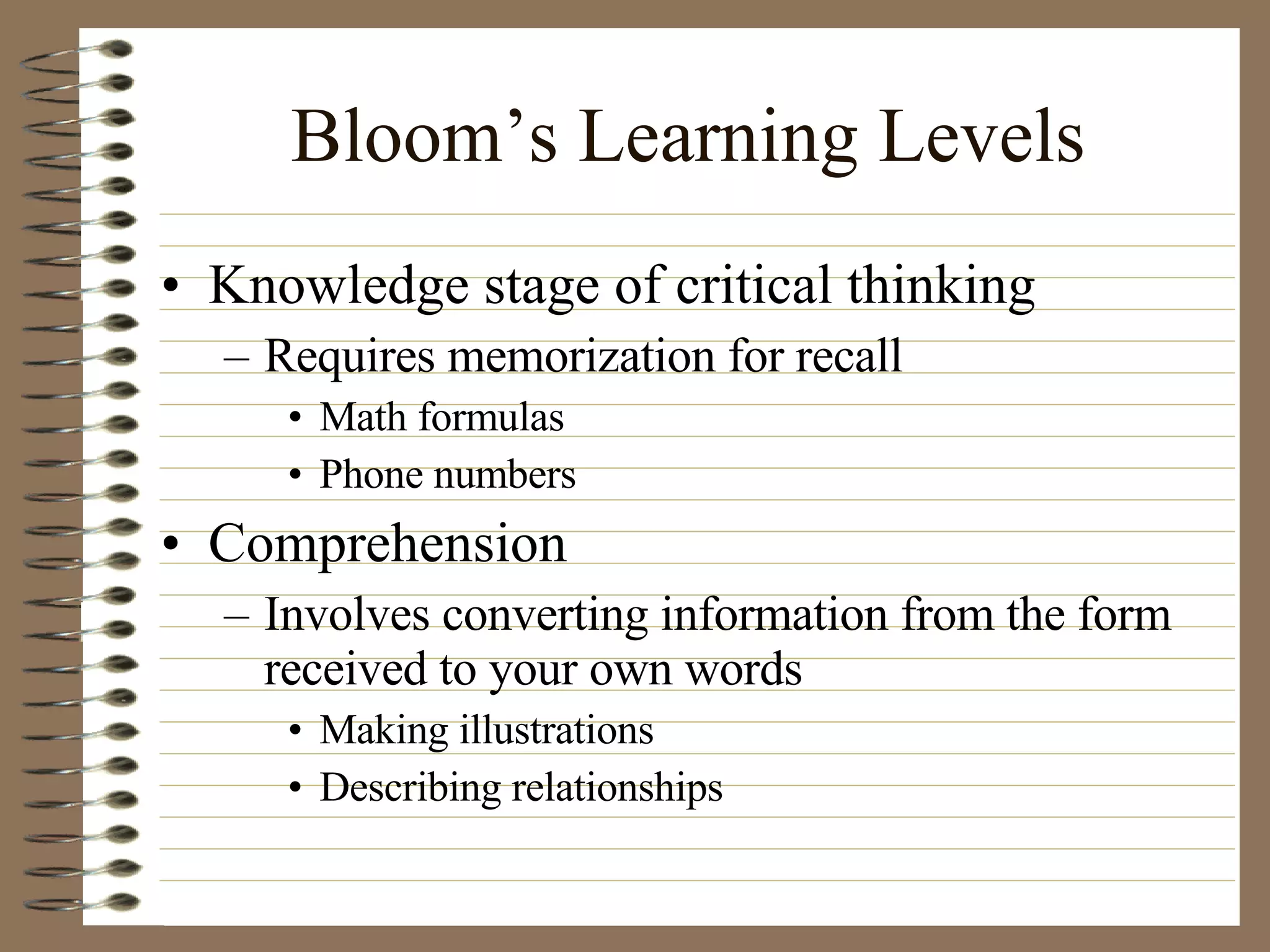
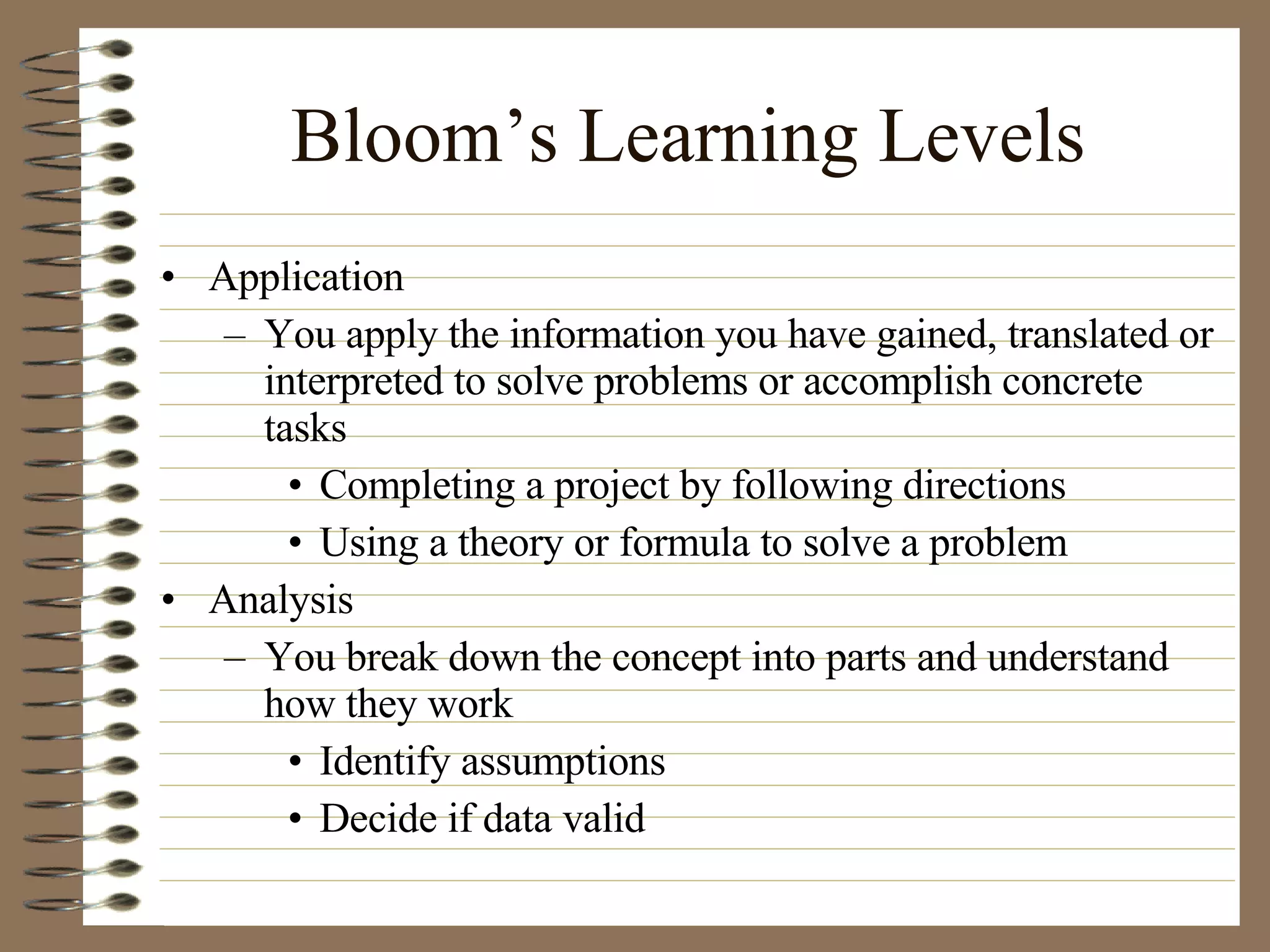
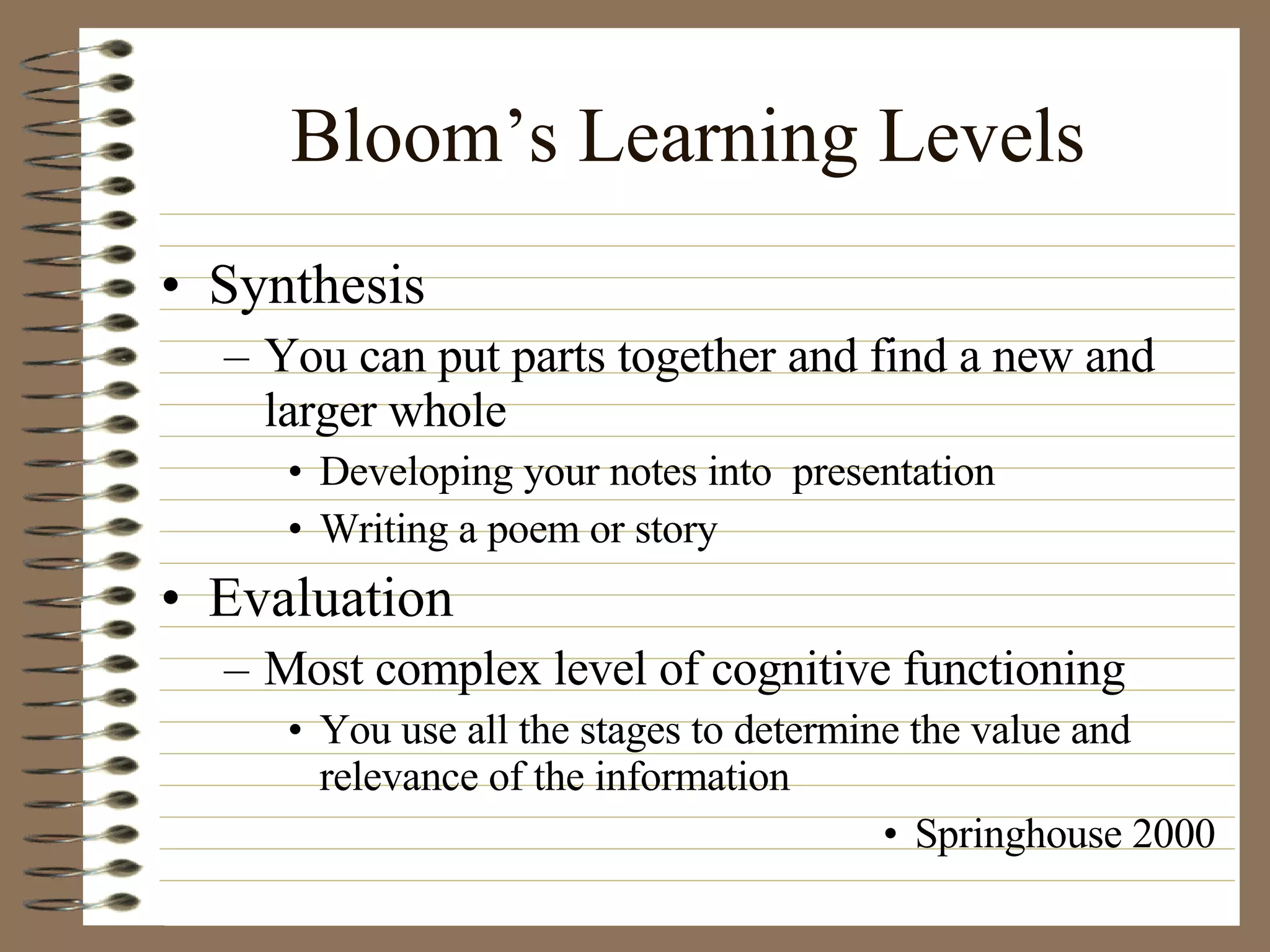
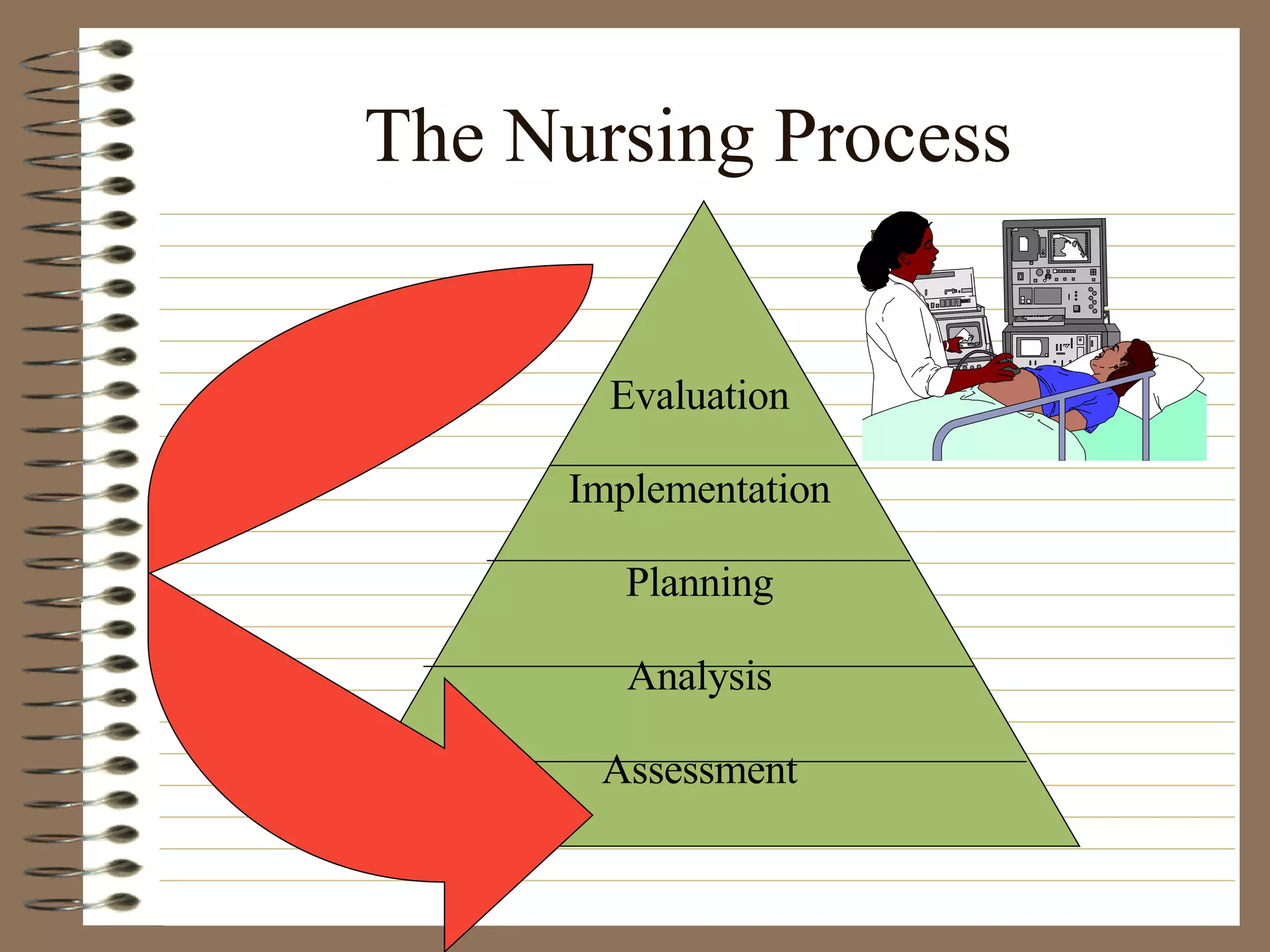
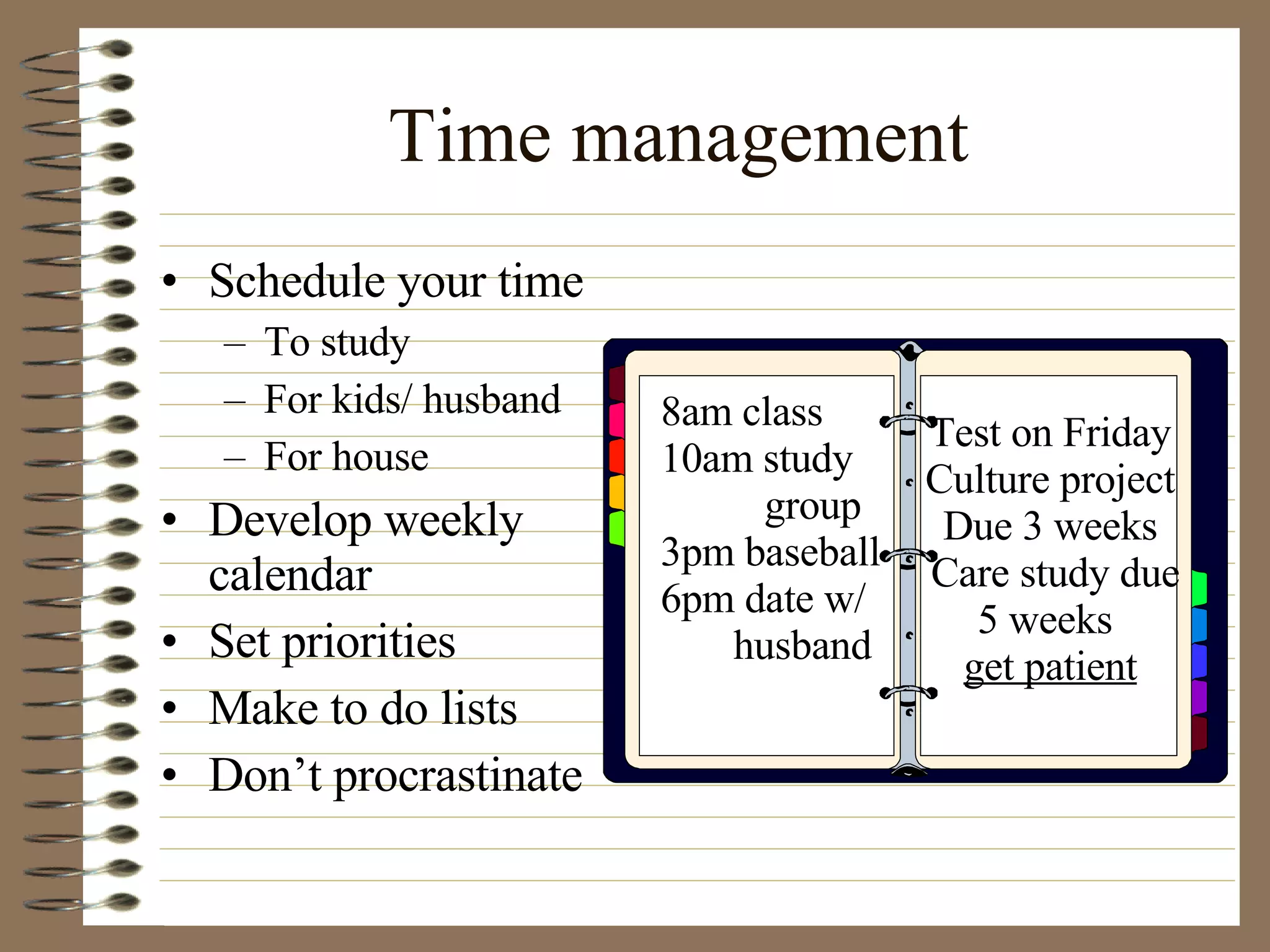
The document provides strategies and tips for nursing students to effectively study, take tests, and manage stress and anxiety around exams. It discusses different learning styles, note-taking techniques, time management, critical thinking, Bloom's taxonomy, and approaches to multiple choice, true/false, essay and open book tests. The key strategies emphasized include developing a study plan, using objectives to guide learning, applying critical thinking and the nursing process to study, and maintaining a positive mindset to overcome test anxiety.