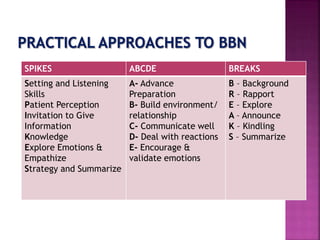
This document discusses effective communication of bad news in healthcare settings. It provides guidelines and frameworks for delivering difficult information to patients in a compassionate manner. The SPIKES protocol recommends six steps: setting up the interaction, assessing the patient's perception, obtaining permission to share, providing knowledge and information, addressing emotions empathetically, and developing a strategy and summarizing. Other tips include using plain language, conveying news gradually, acknowledging emotions, exploring treatment options, and encouraging questions. The overall goal is to inform patients while also supporting them emotionally.