Embed presentation
Download as PDF, PPTX

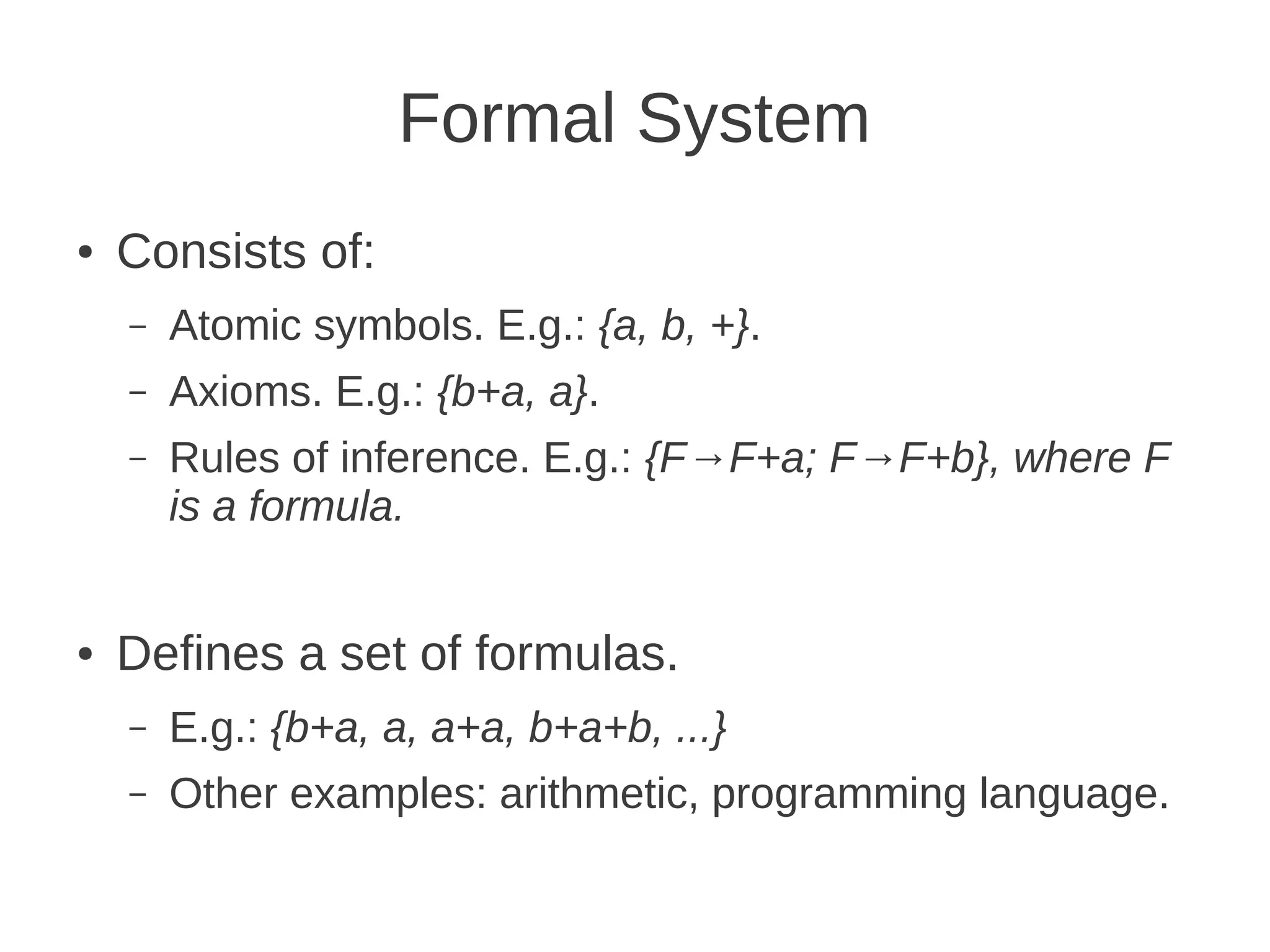
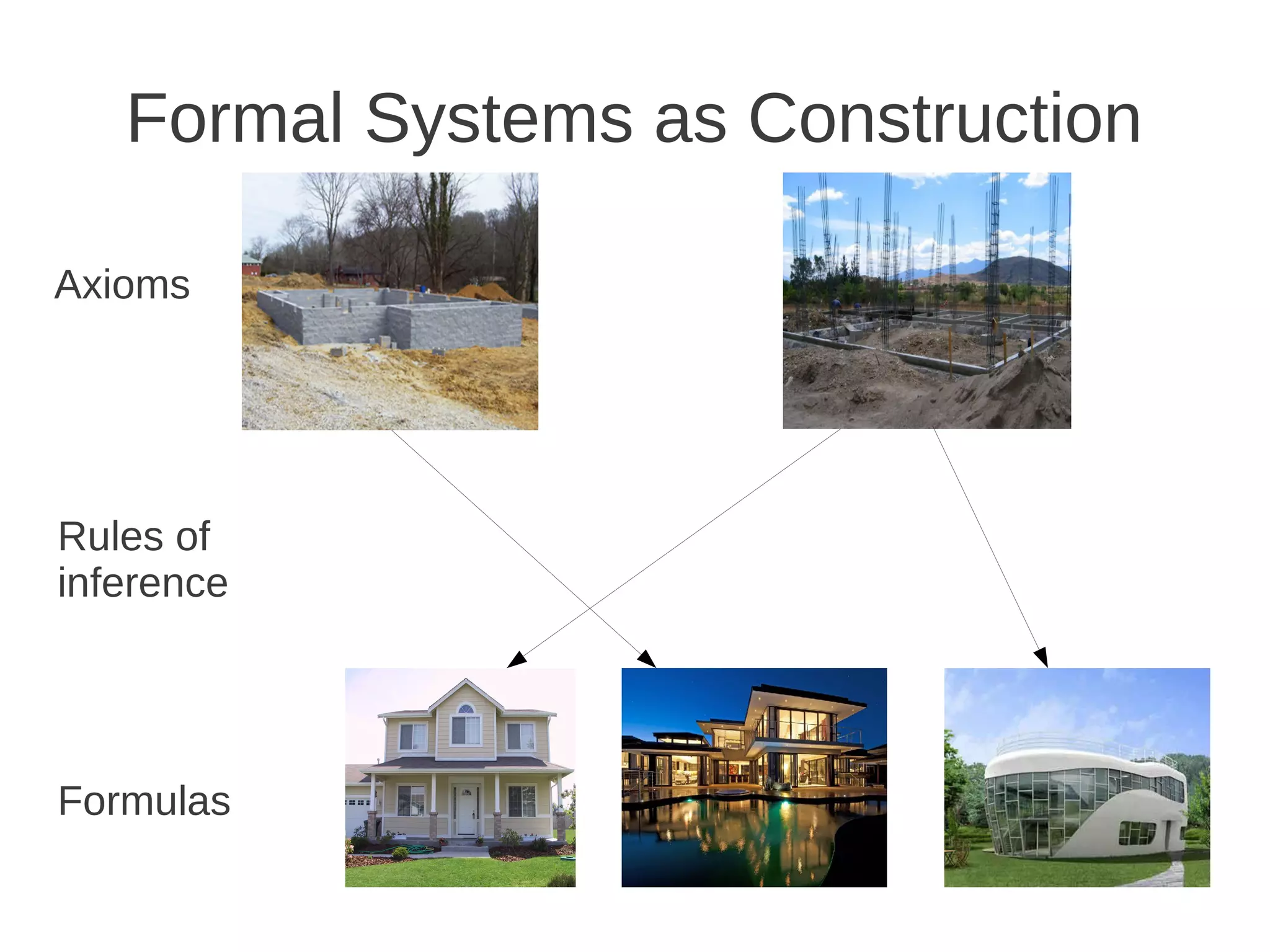

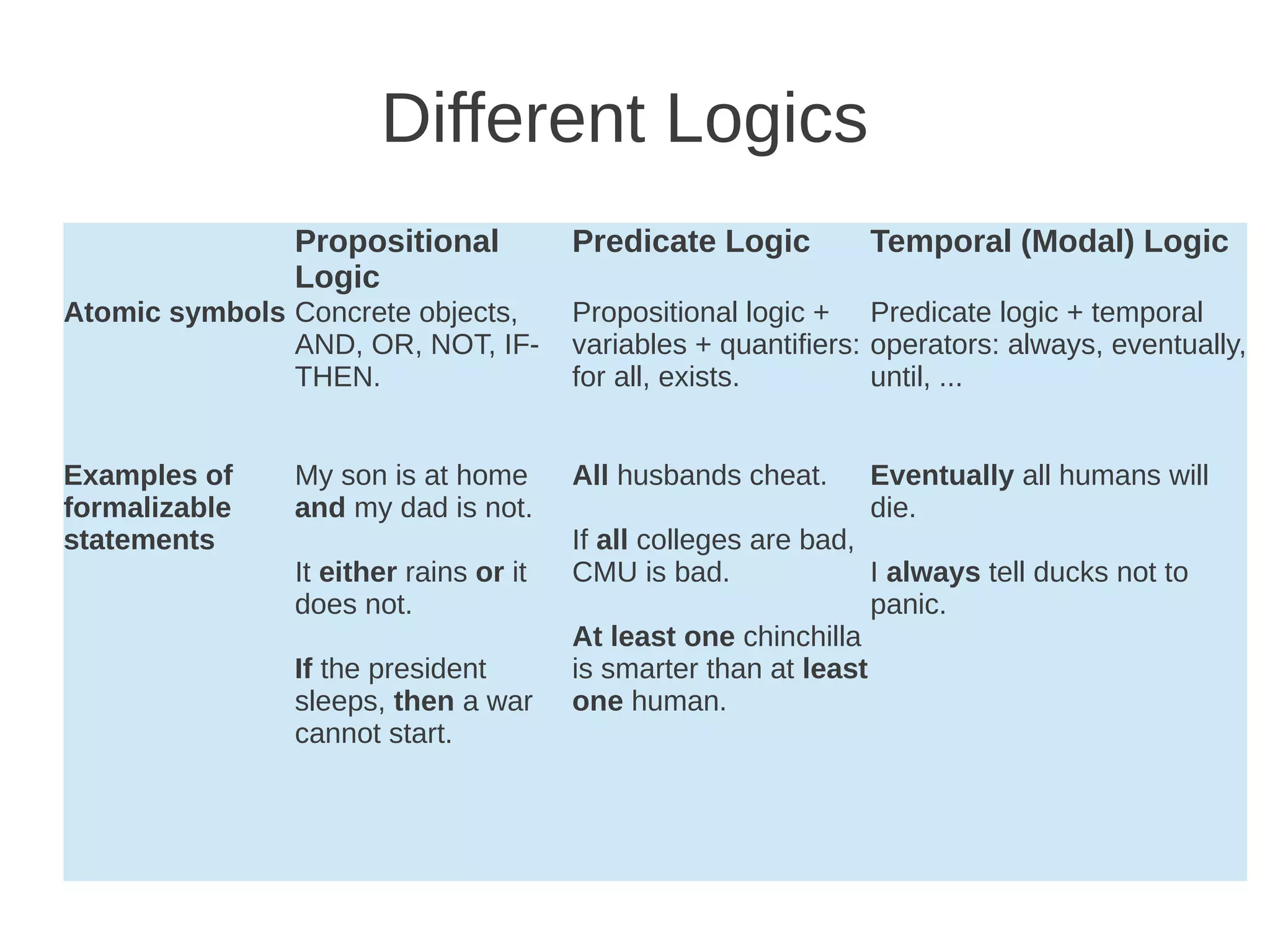


The document discusses formal logic, emphasizing its structure as a formal system with atomic symbols, axioms, and rules of inference. It defines formal logic as a system where formulas can be assigned true or false values, enabling the expression of logical statements. Various types of logic, such as propositional and predicate logic, allow for the formalization of diverse statements.






