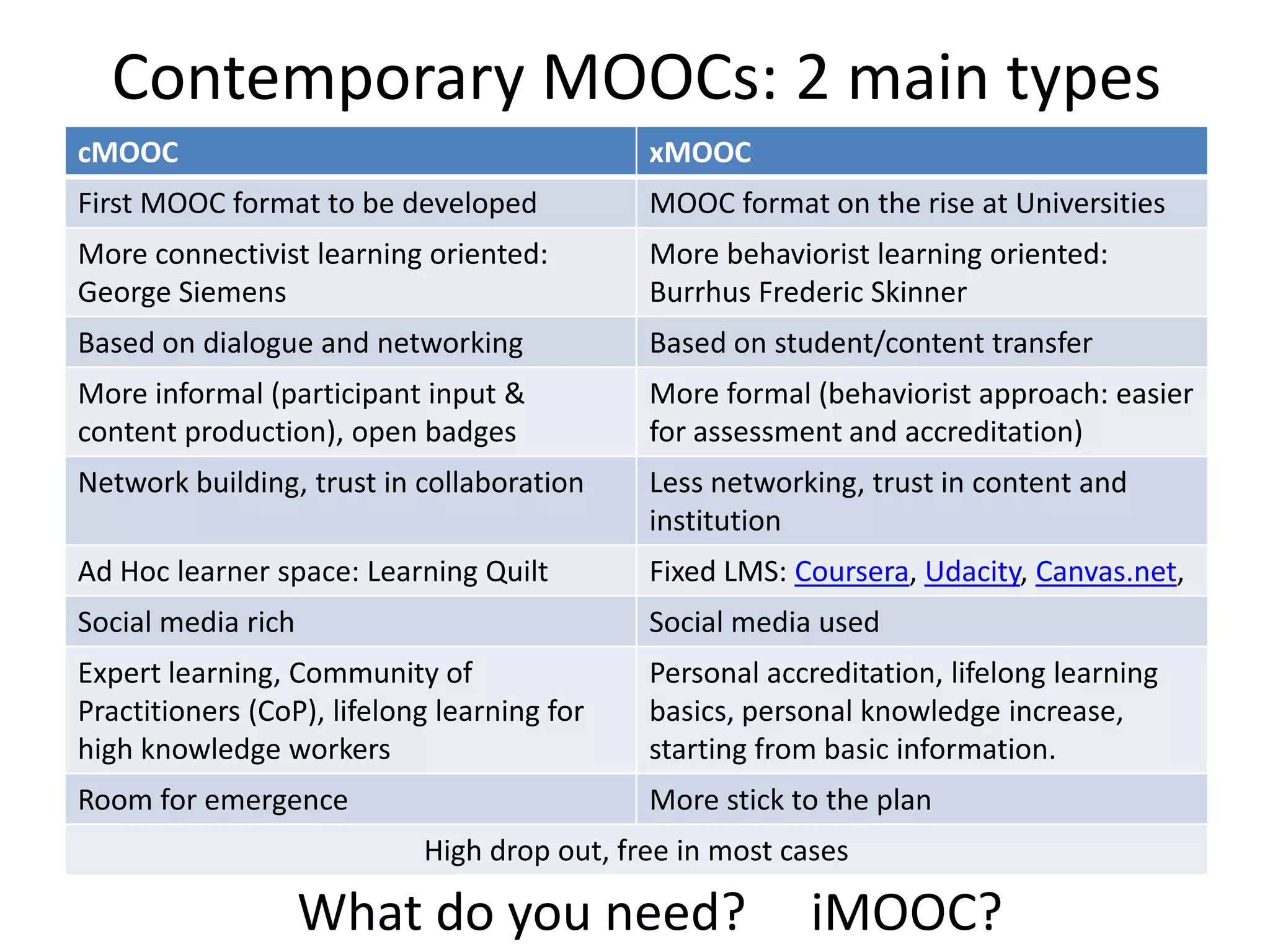
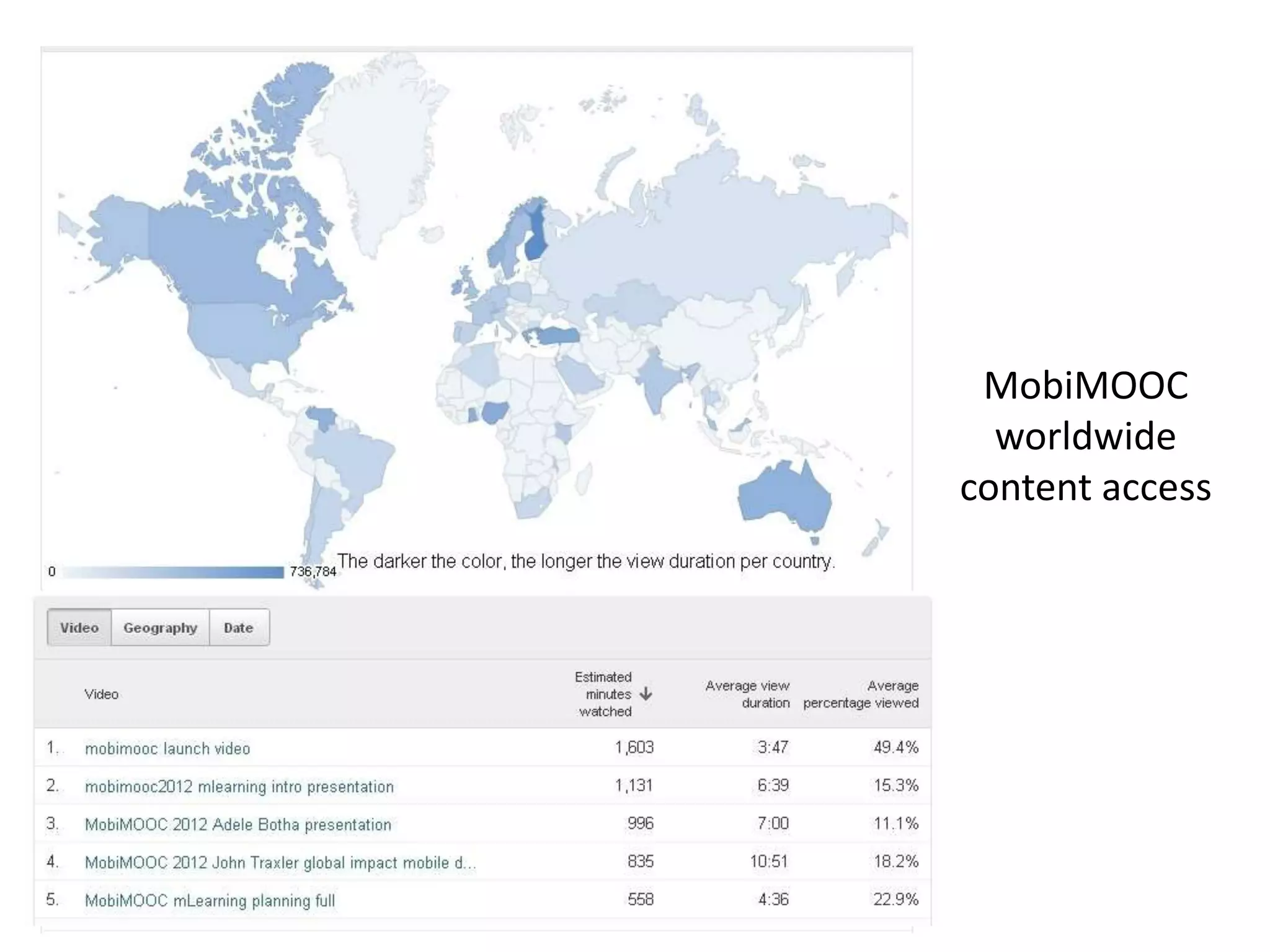
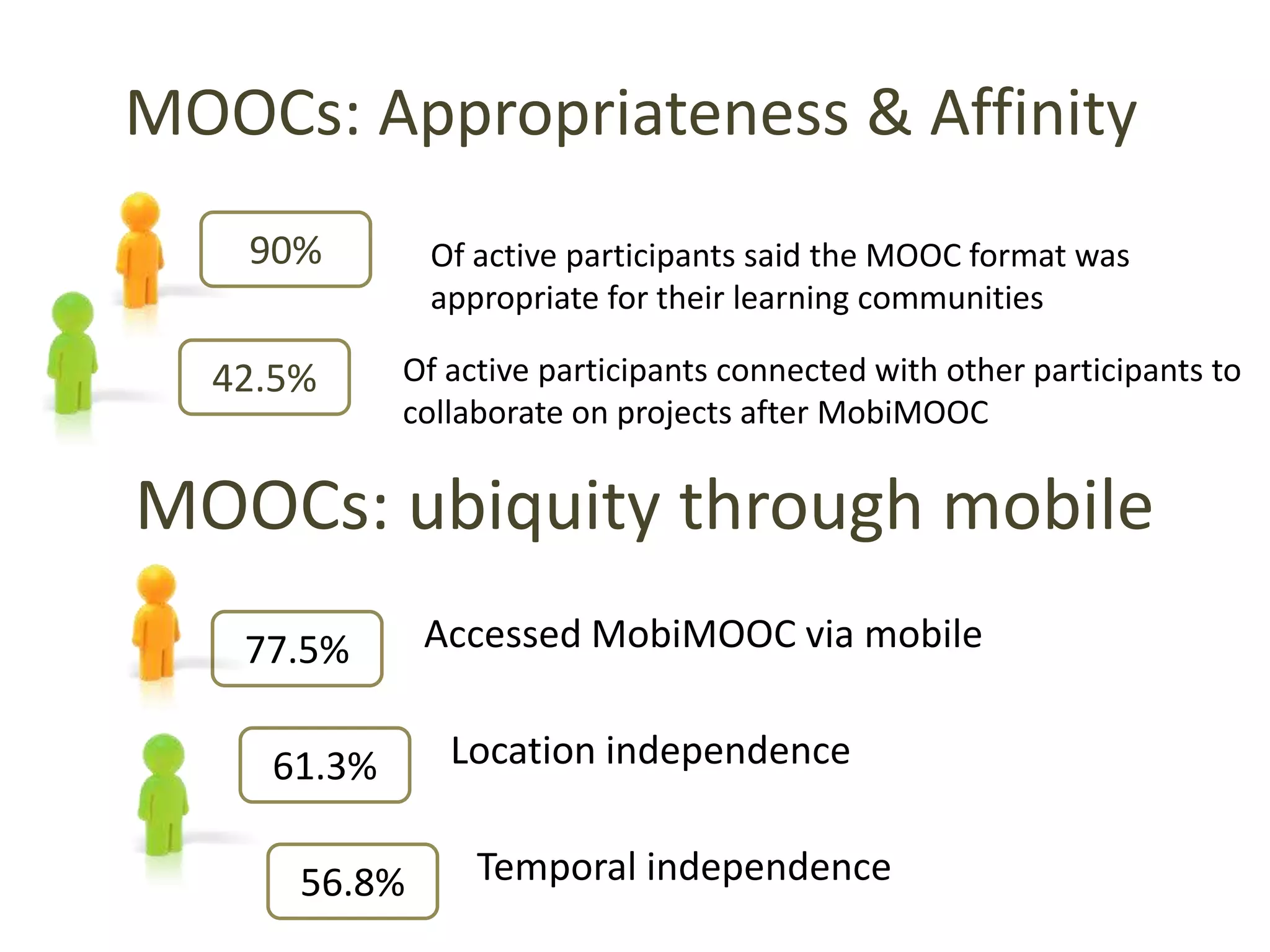
This document discusses the use of mobile devices to increase access to MOOCs through a "MobiMOOC" approach. It summarizes key findings from a MobiMOOC course that had over 1250 learners from around the world. The results showed that mobile access led to more learner interactions and reflections. Some challenges included ensuring digital literacy and a user-friendly mobile learning environment. Core factors for success included clear timelines, communication guidelines, and motivating facilitators. The document provides contact information for the author to discuss MOOC designs further.