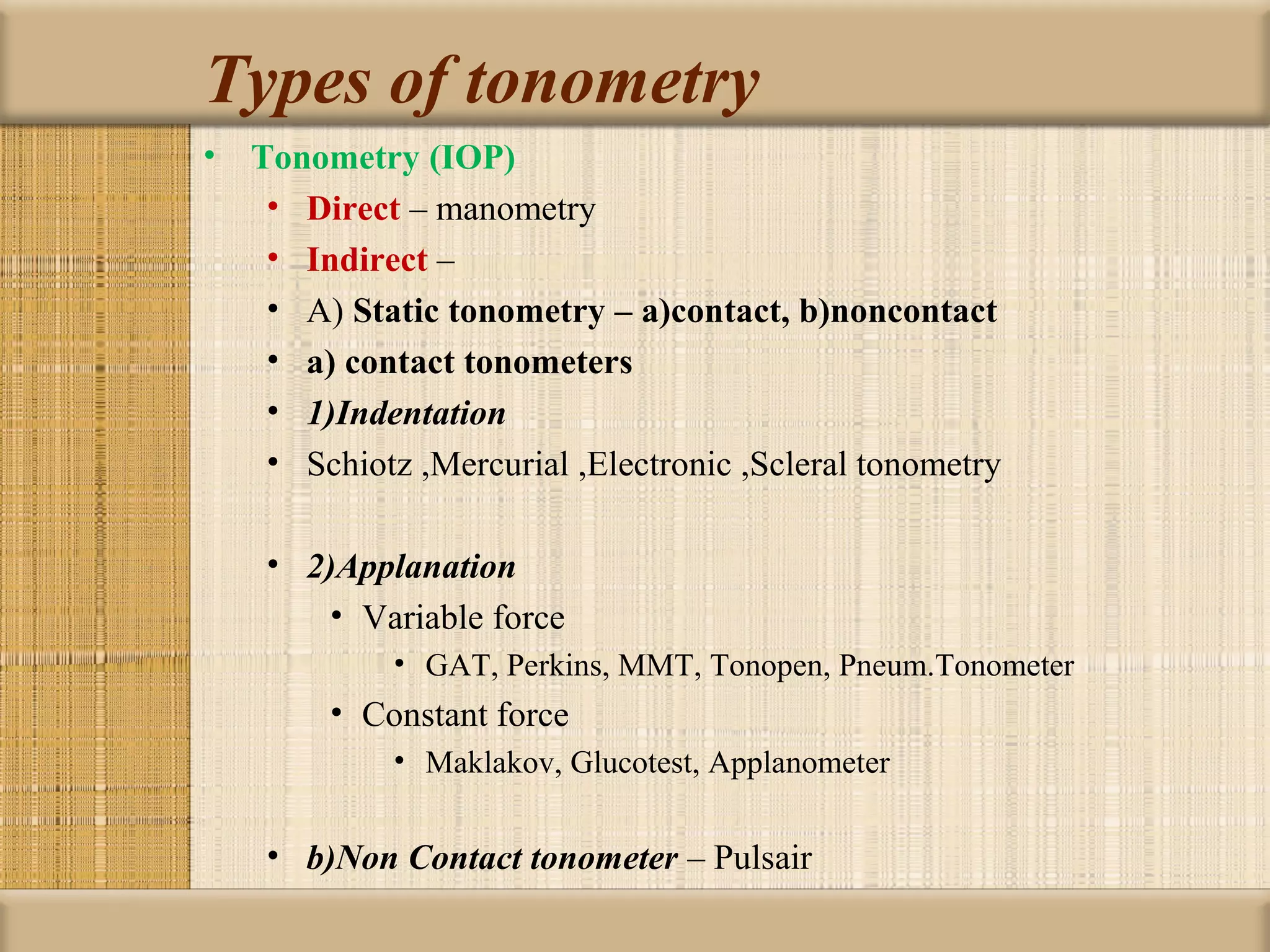
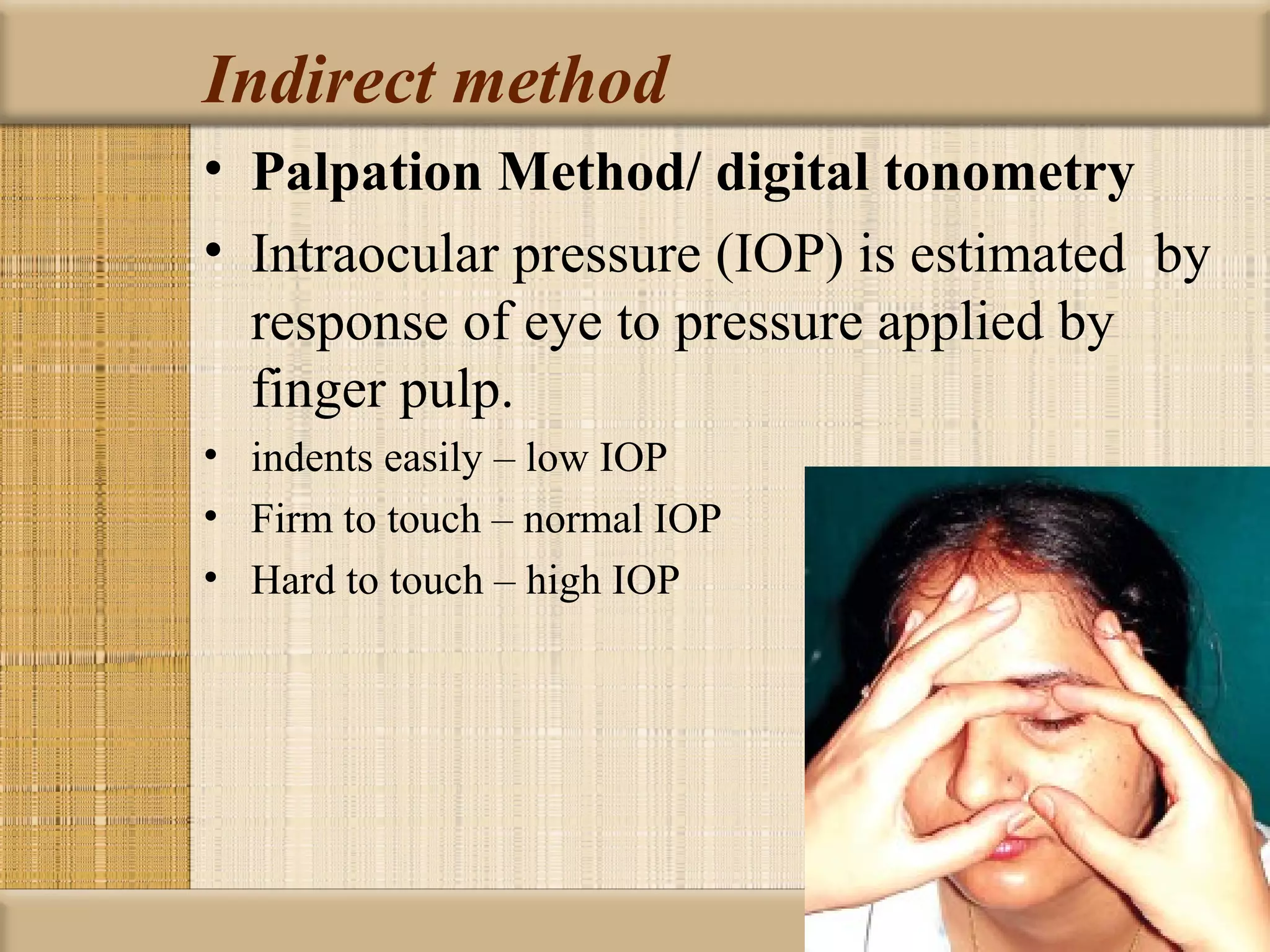
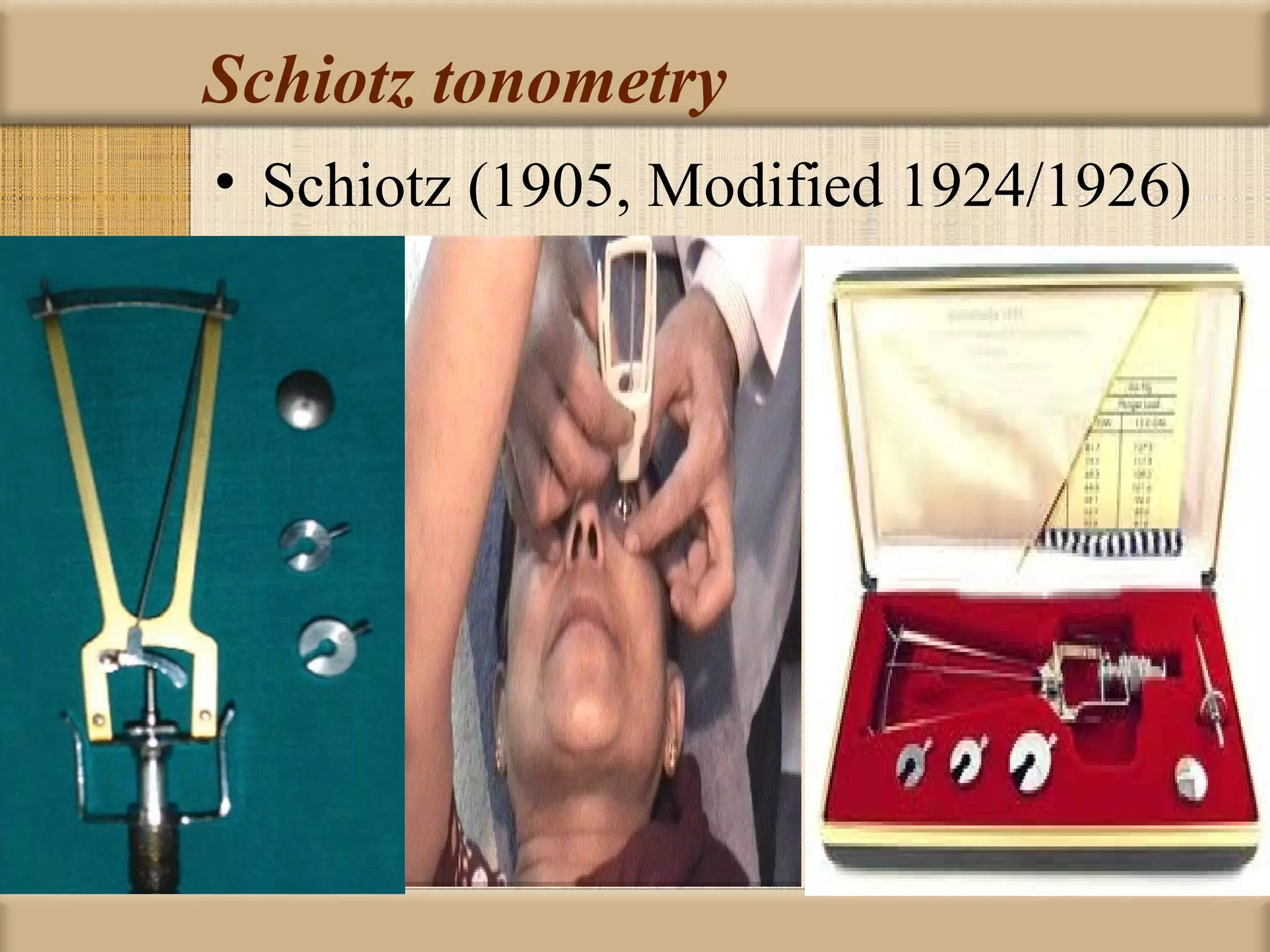
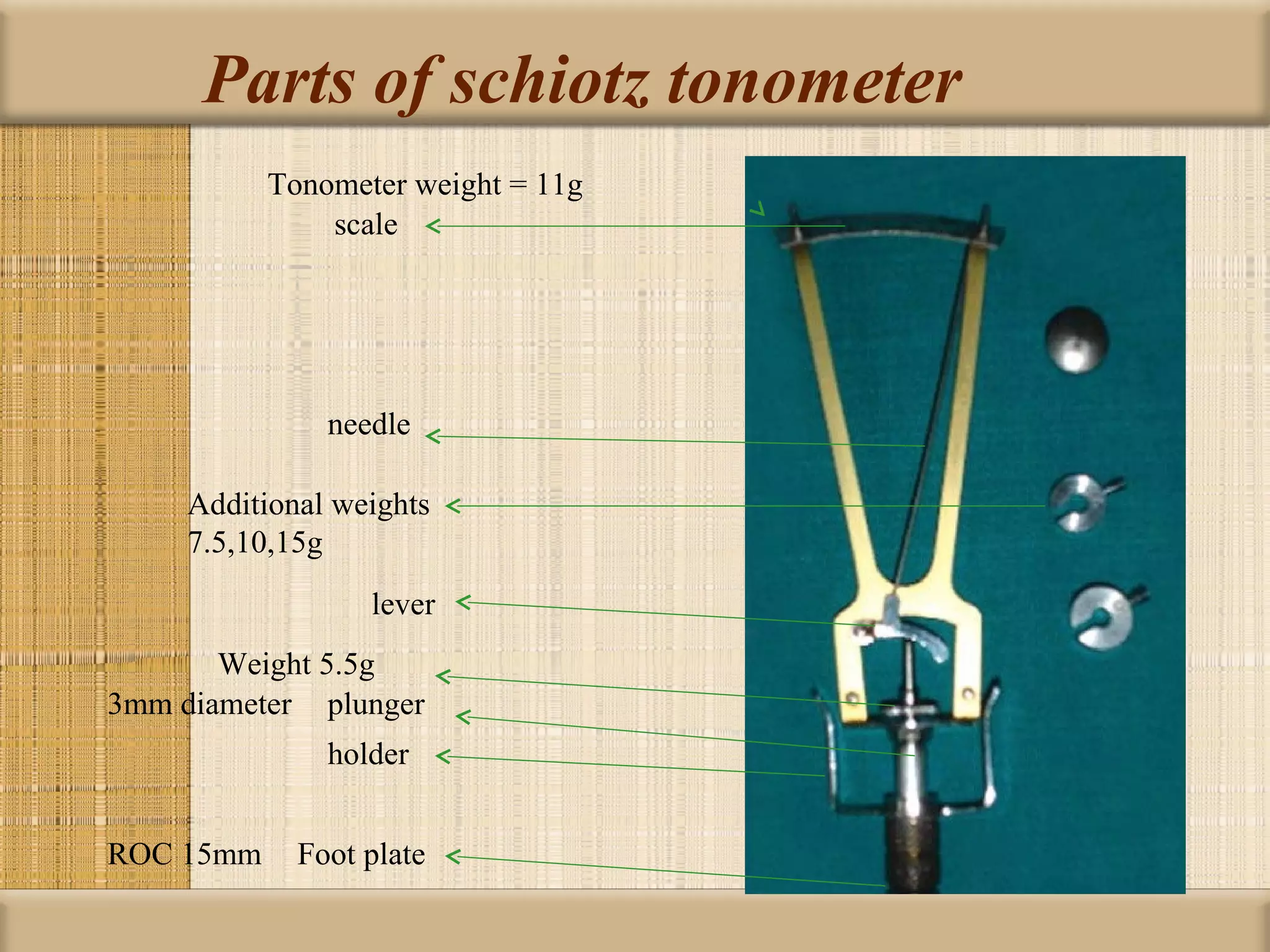
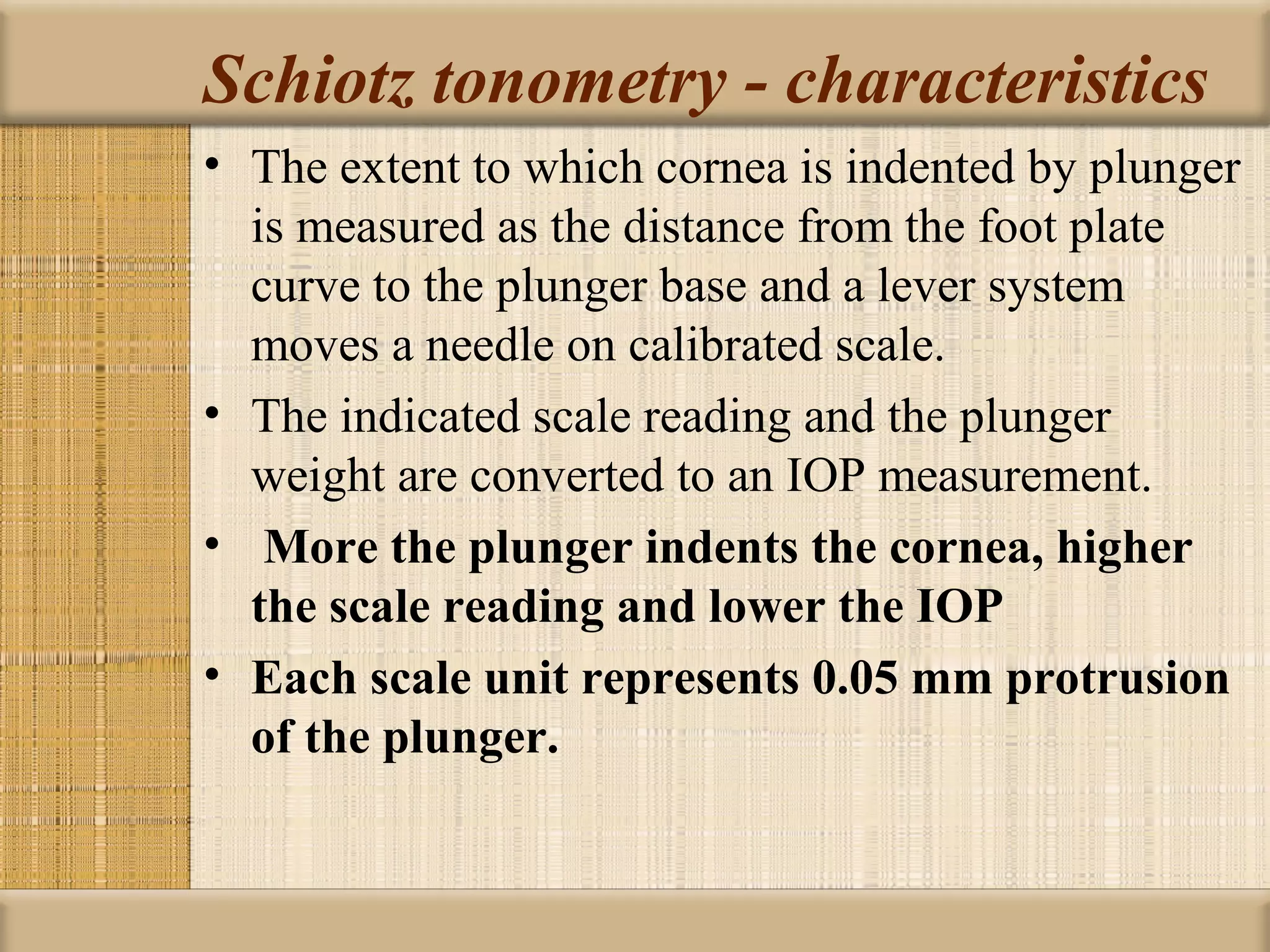
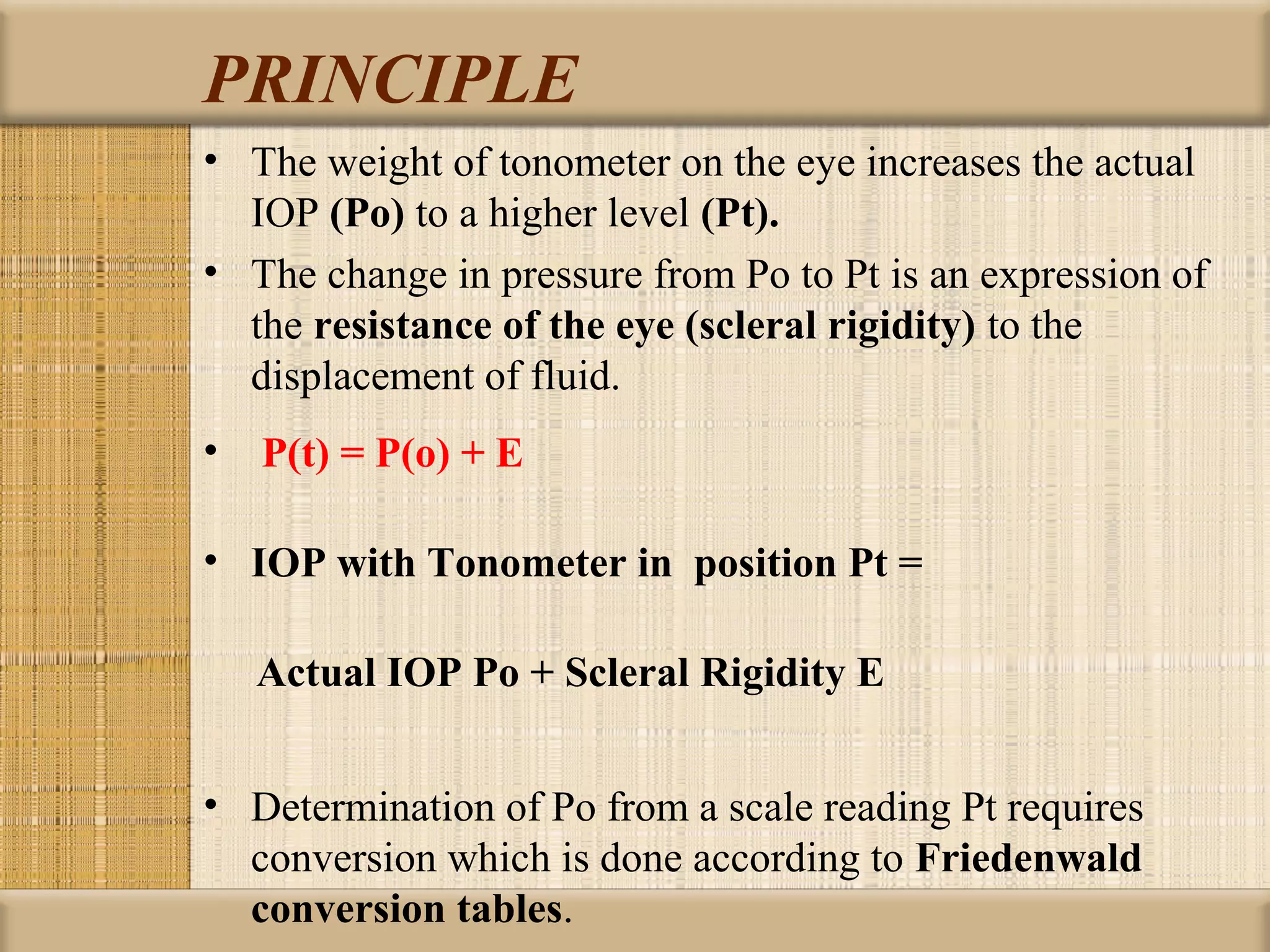
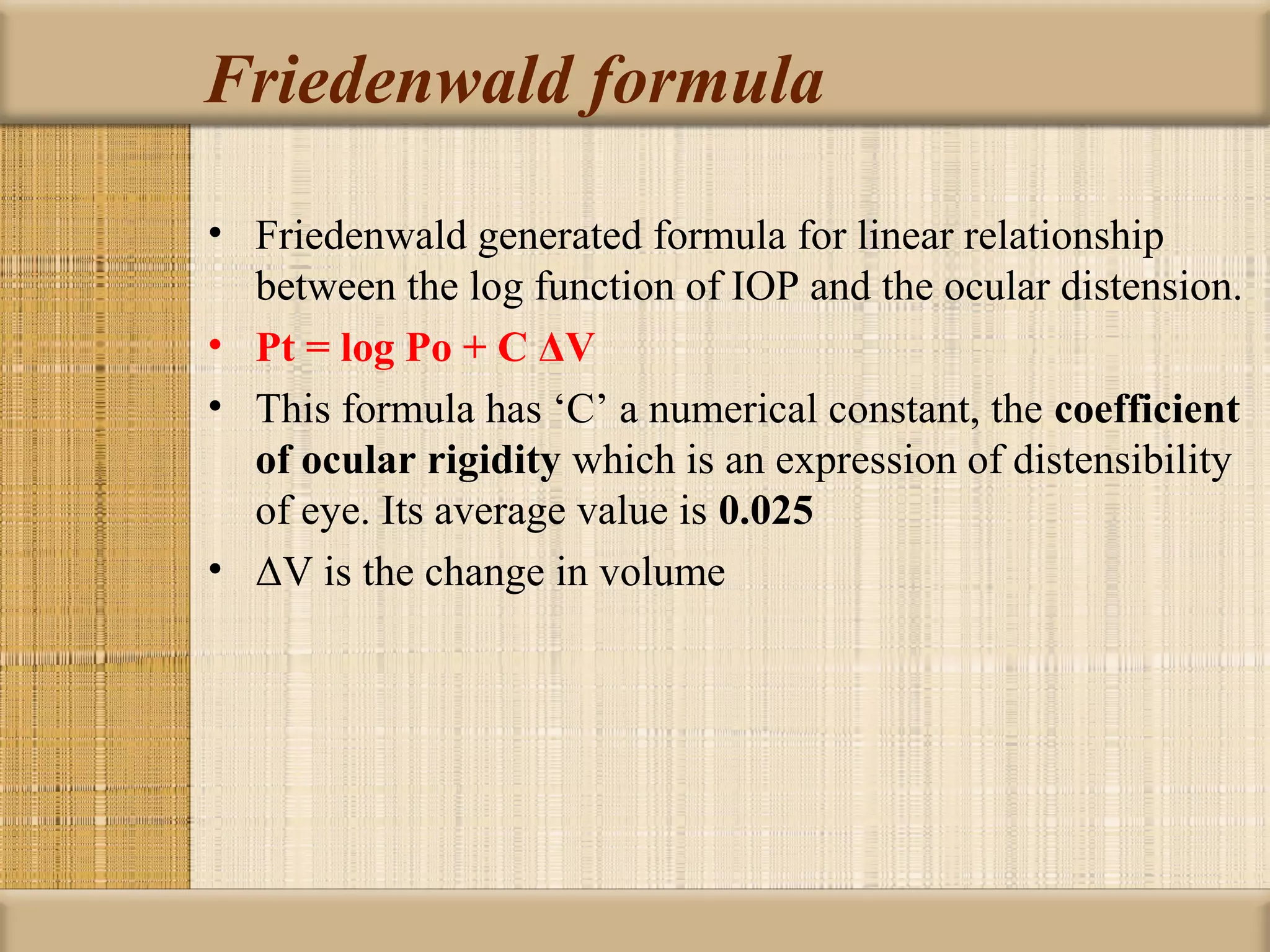
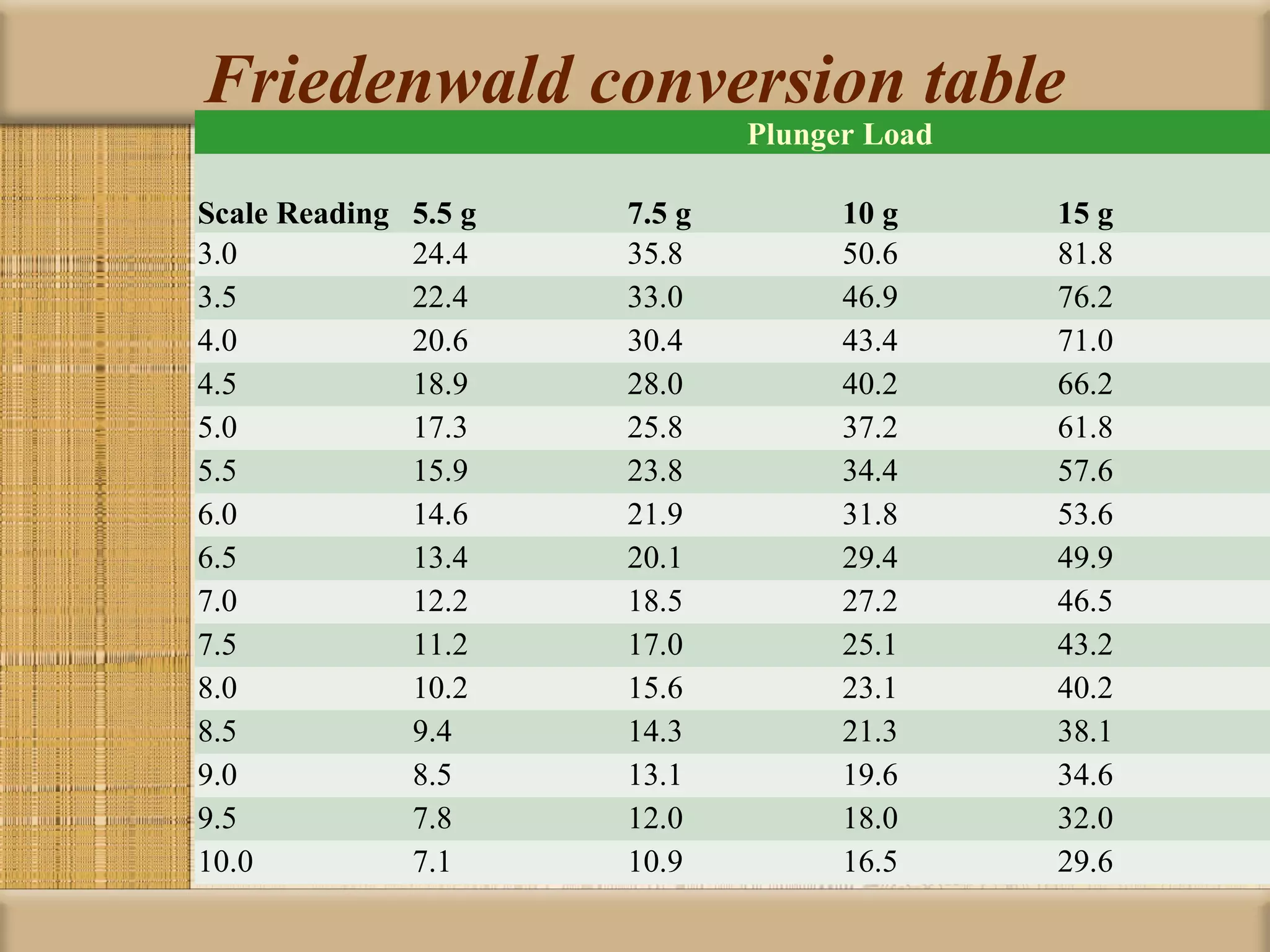
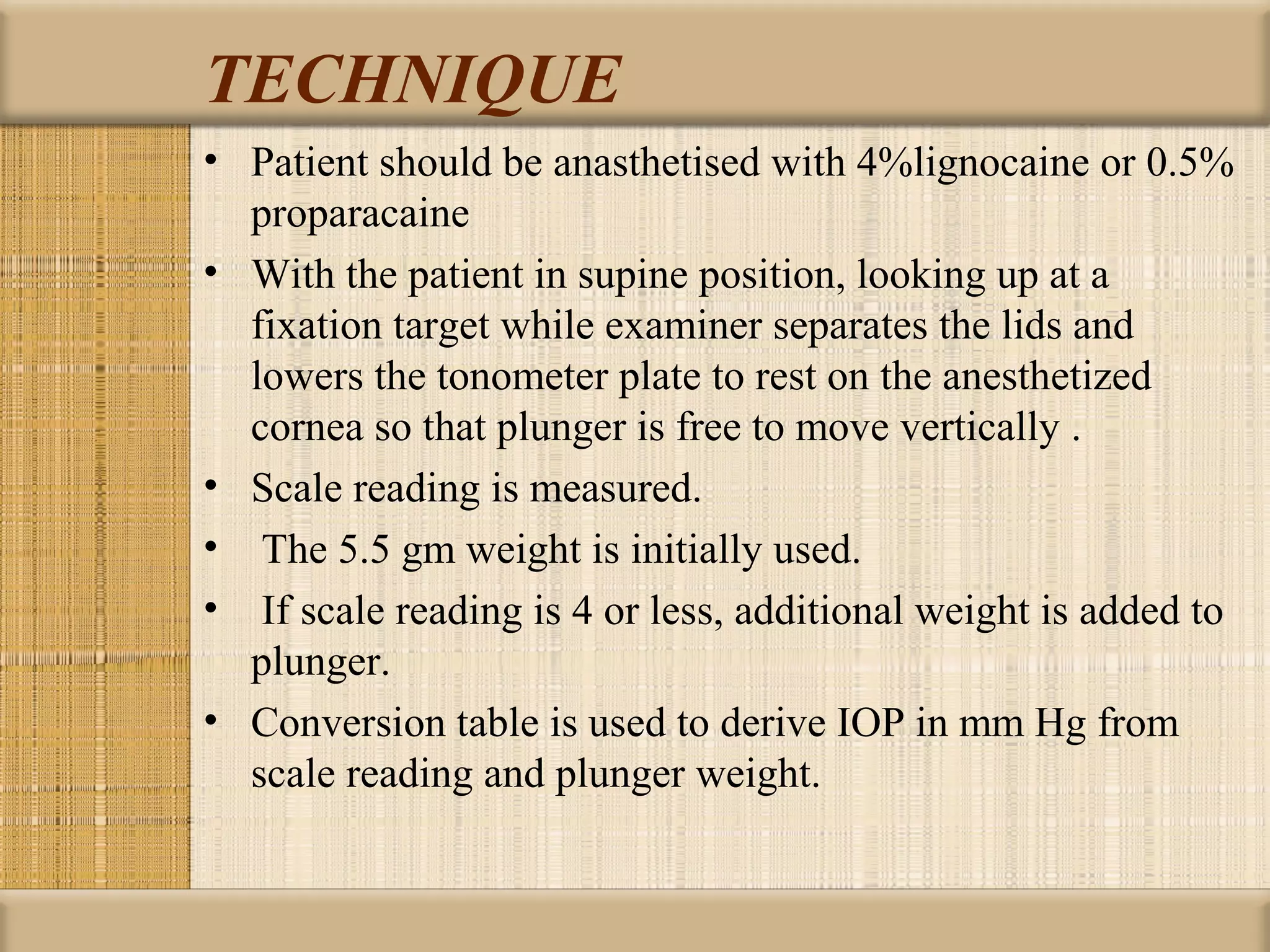
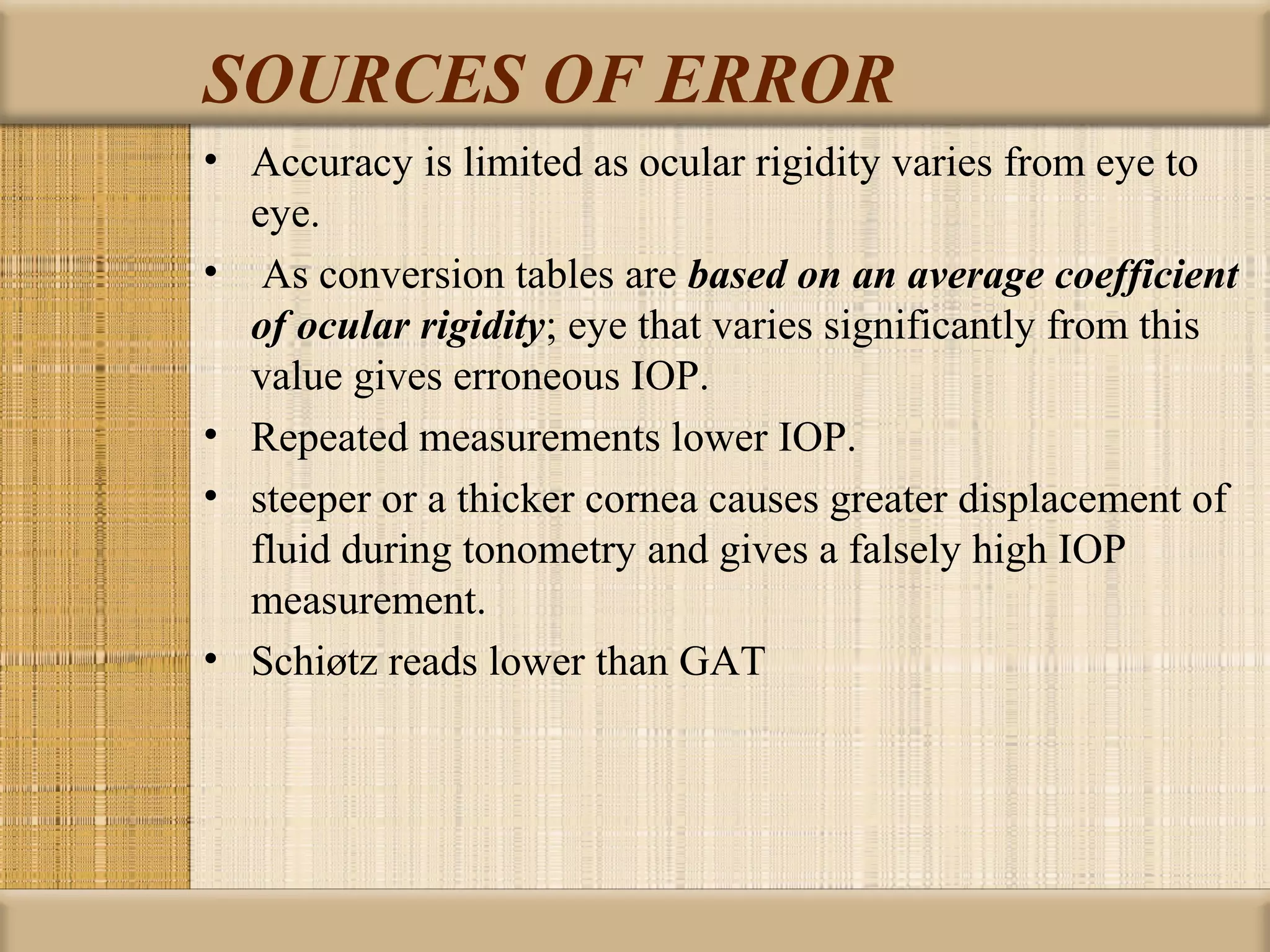
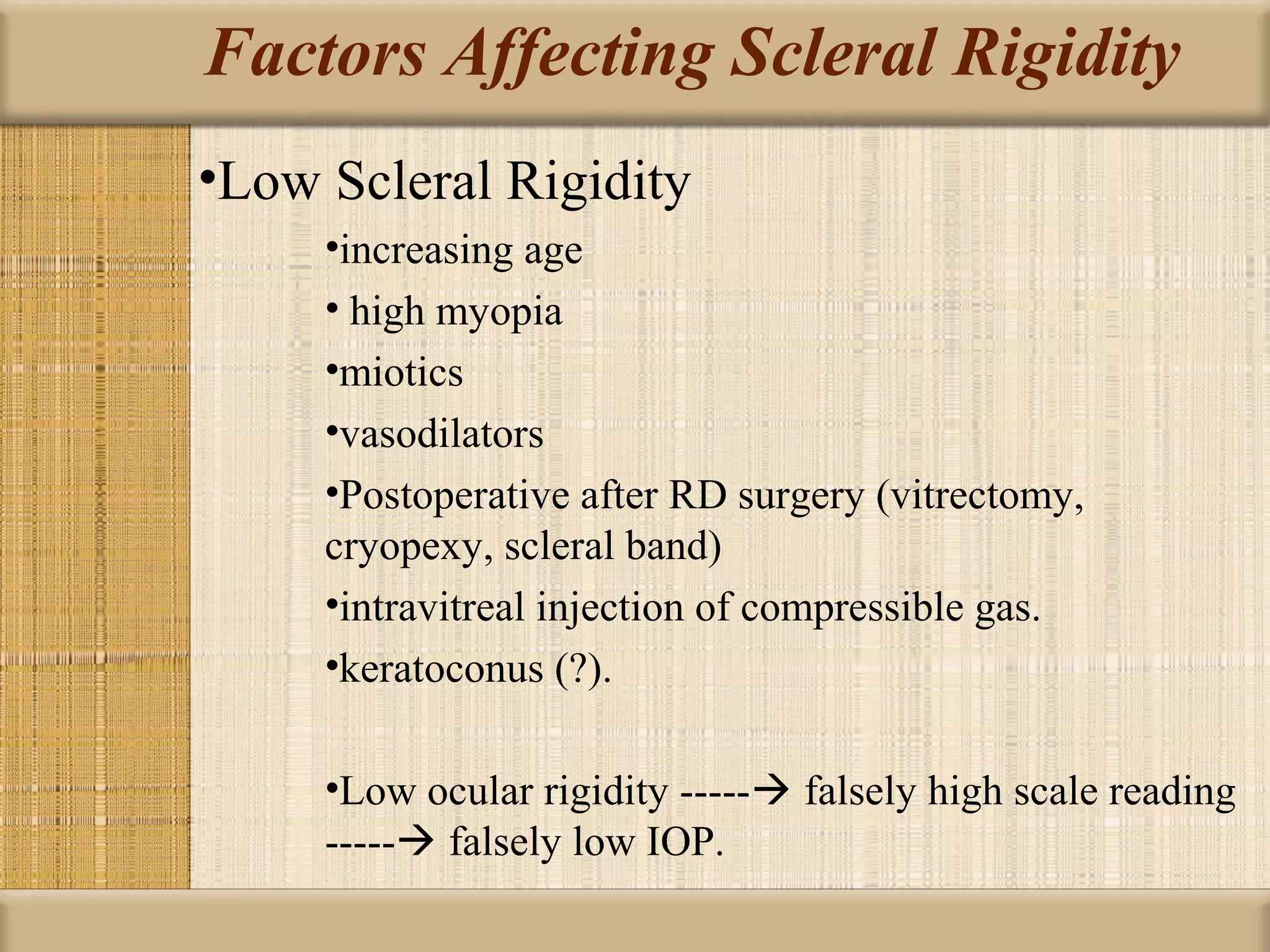
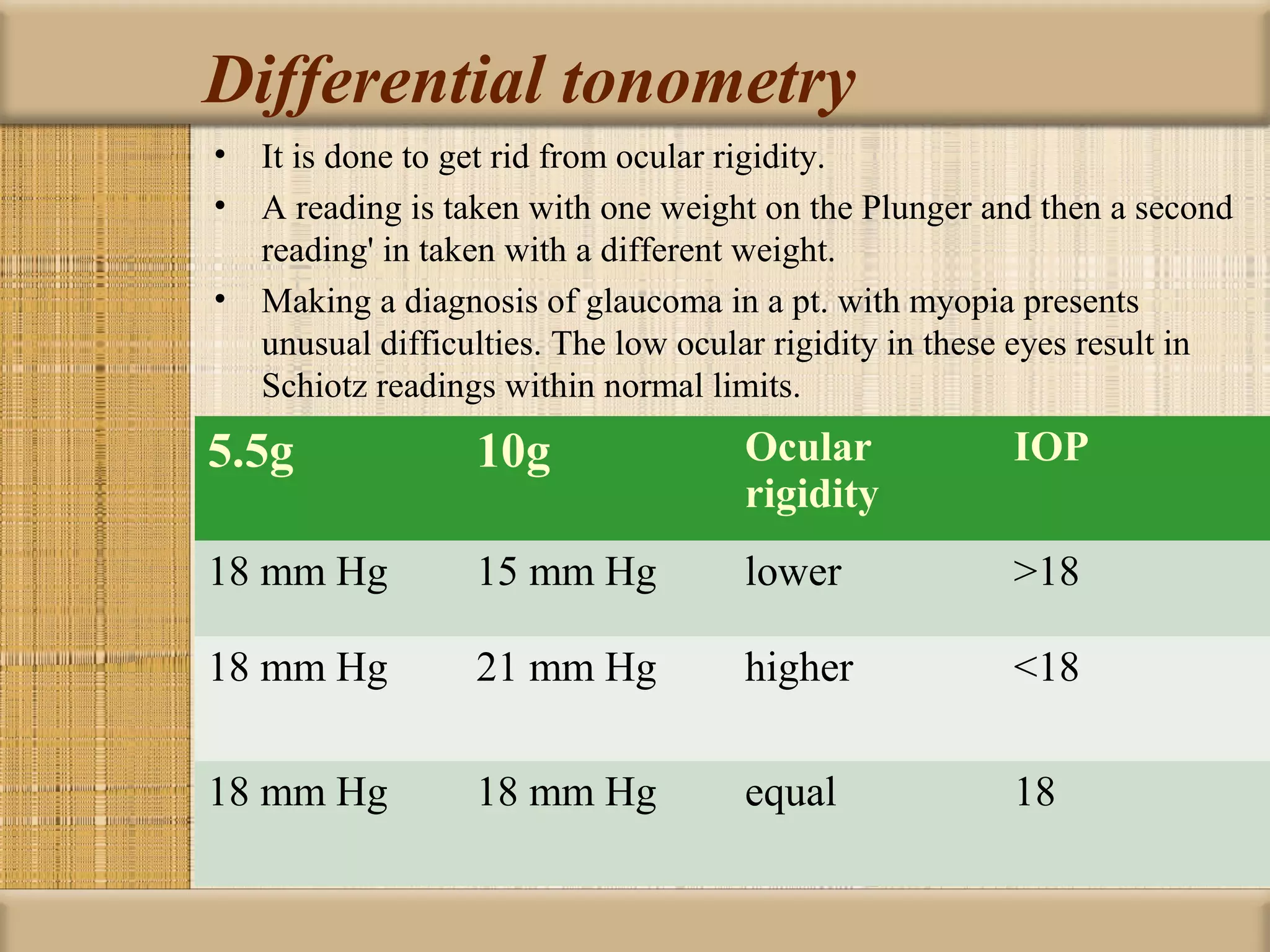
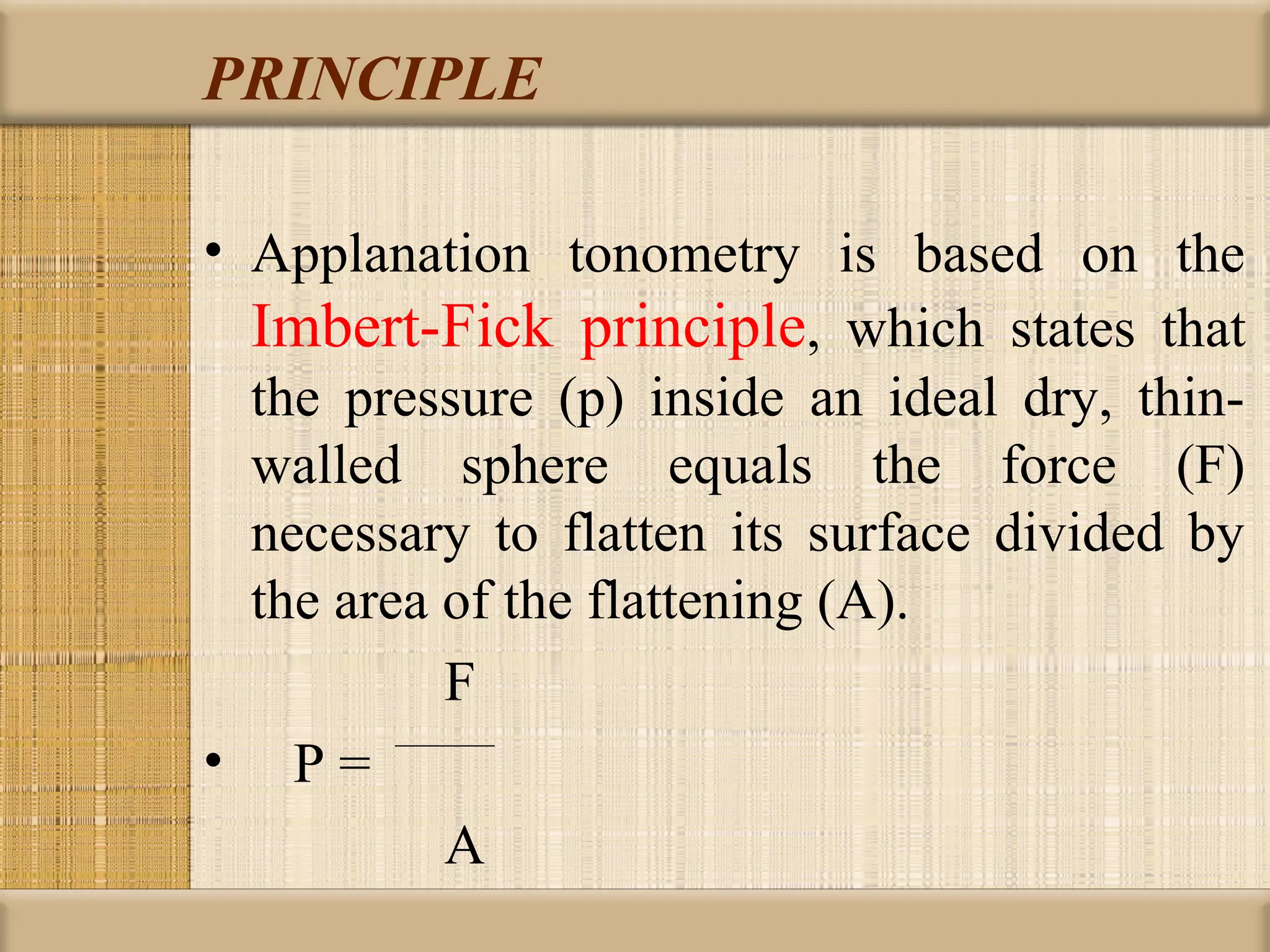
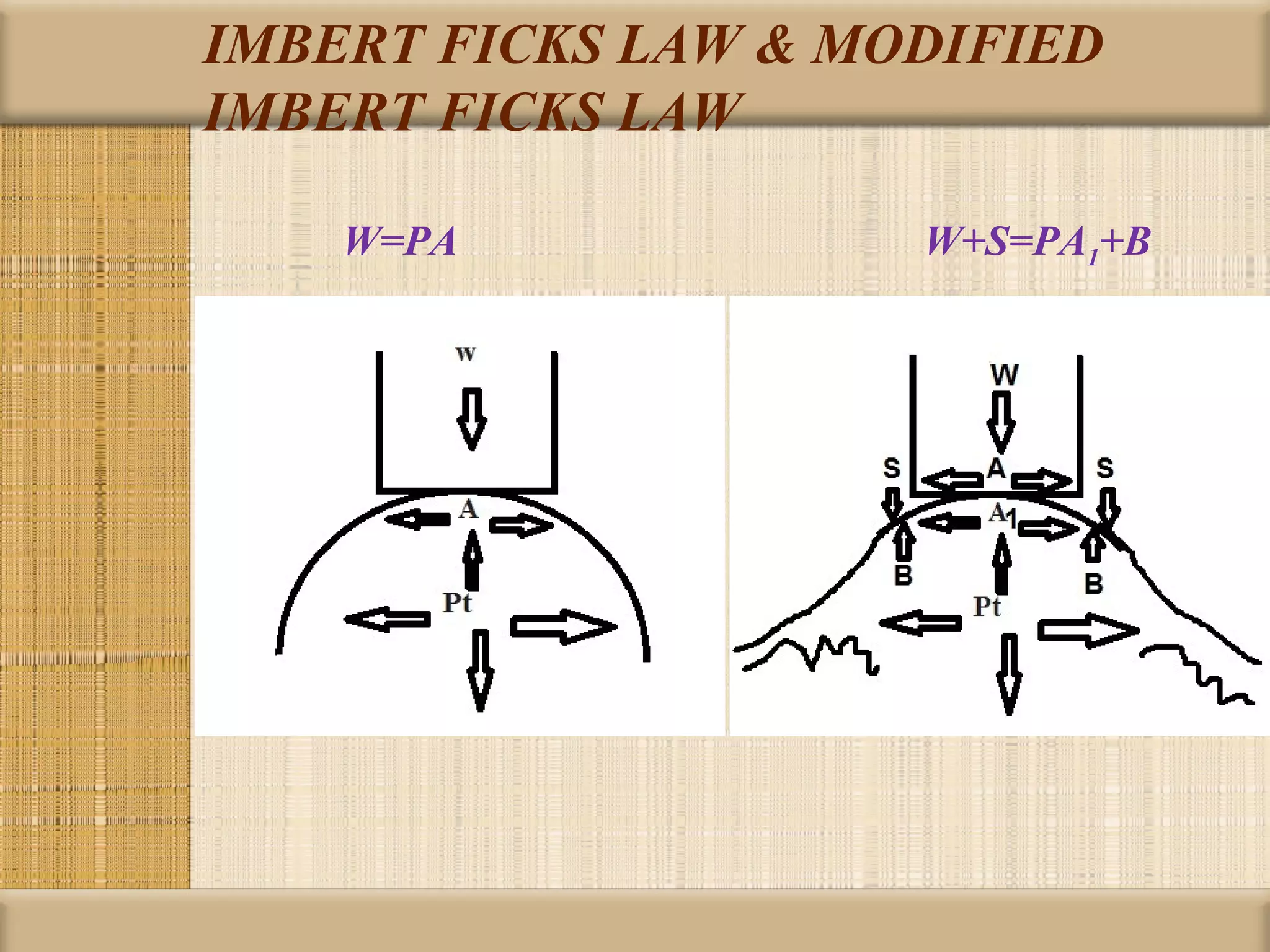
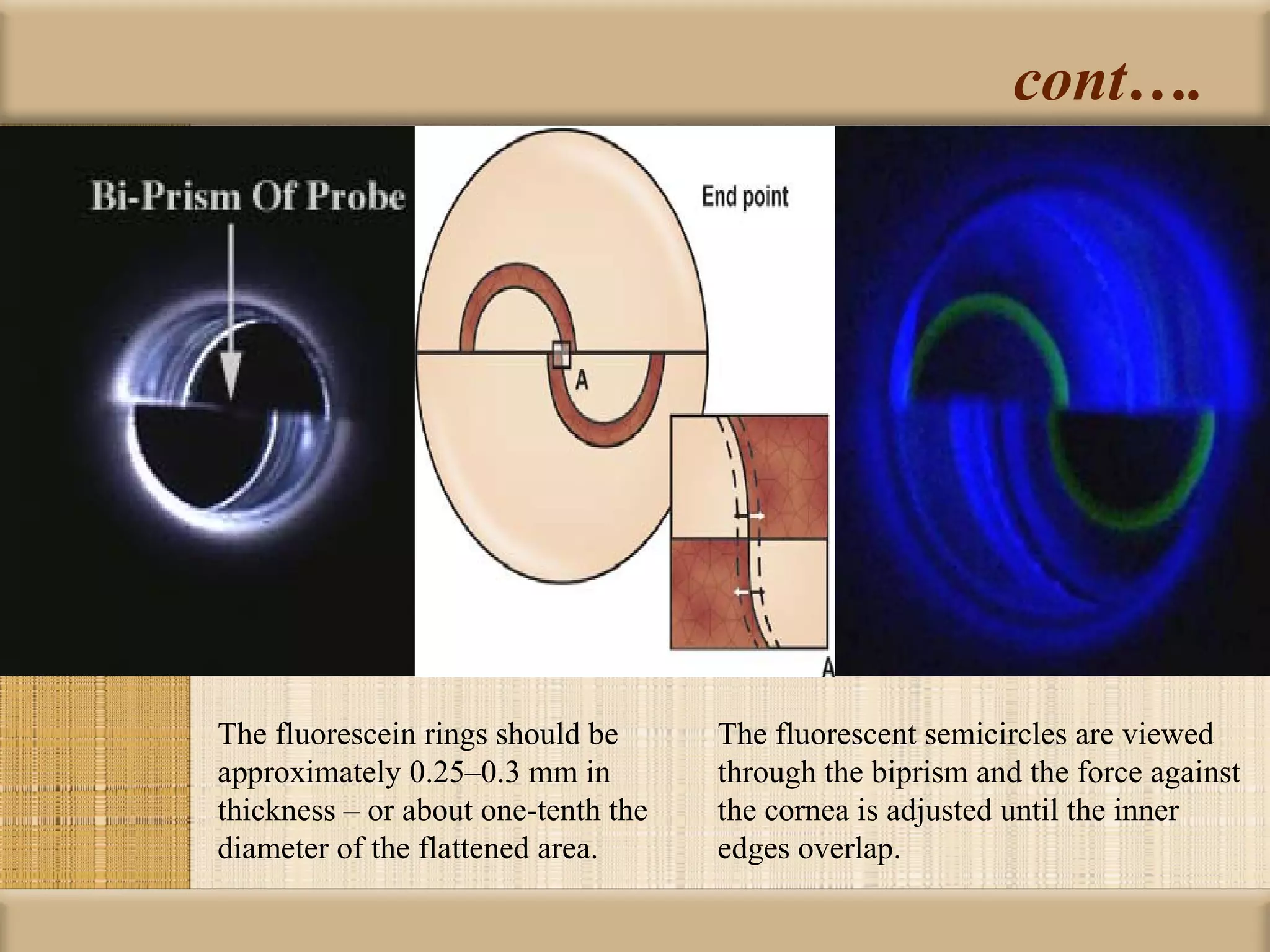
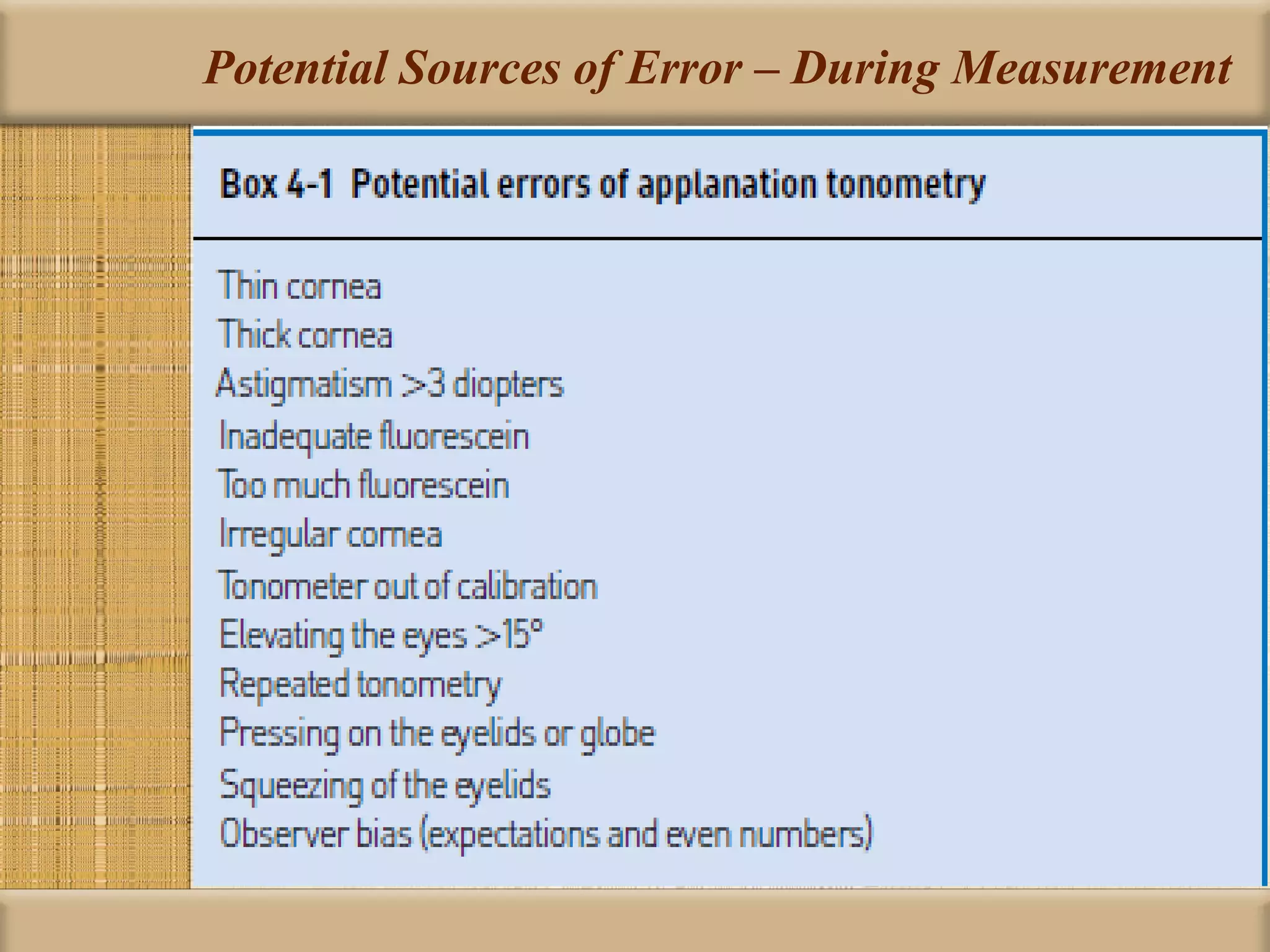
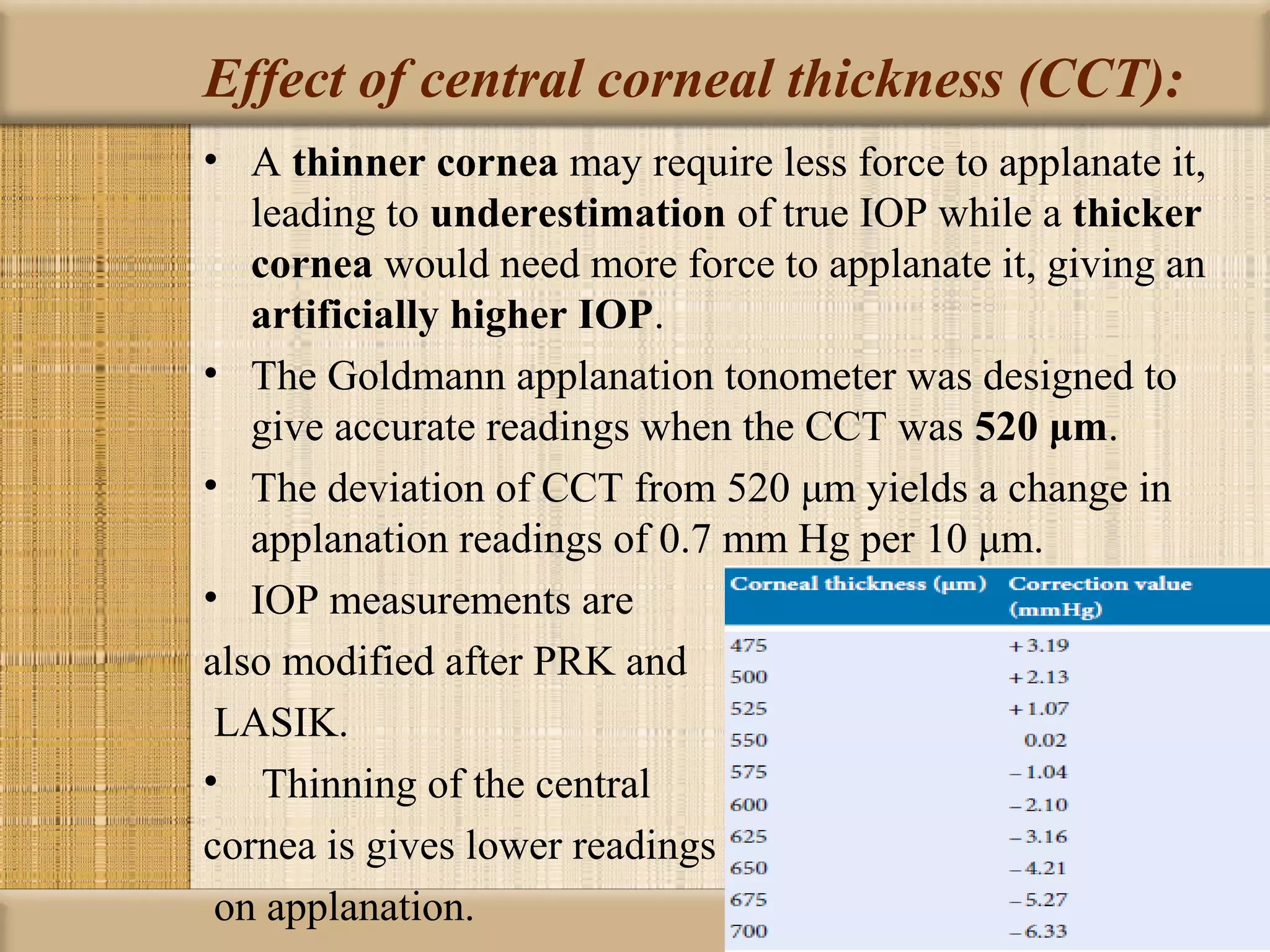
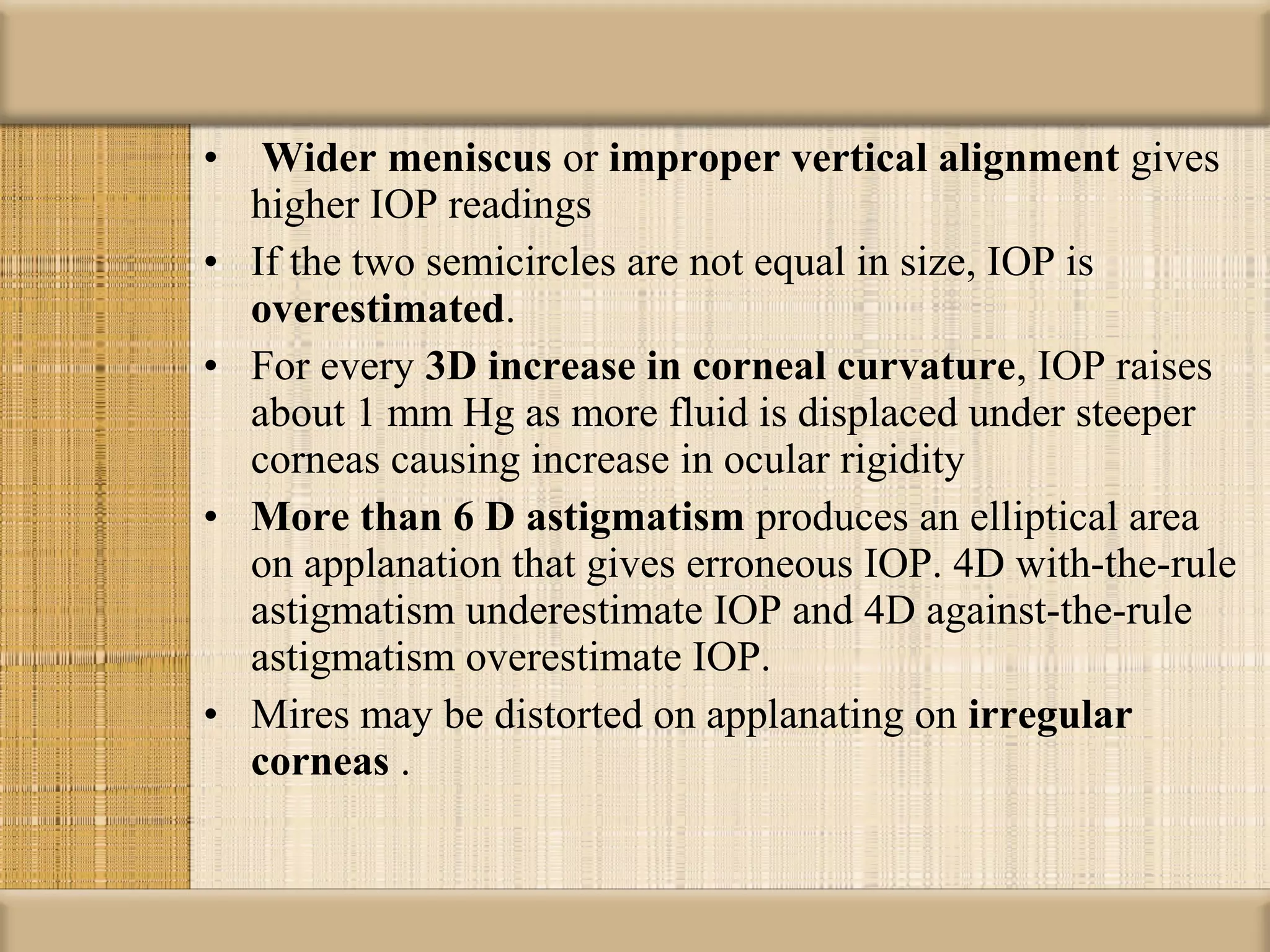
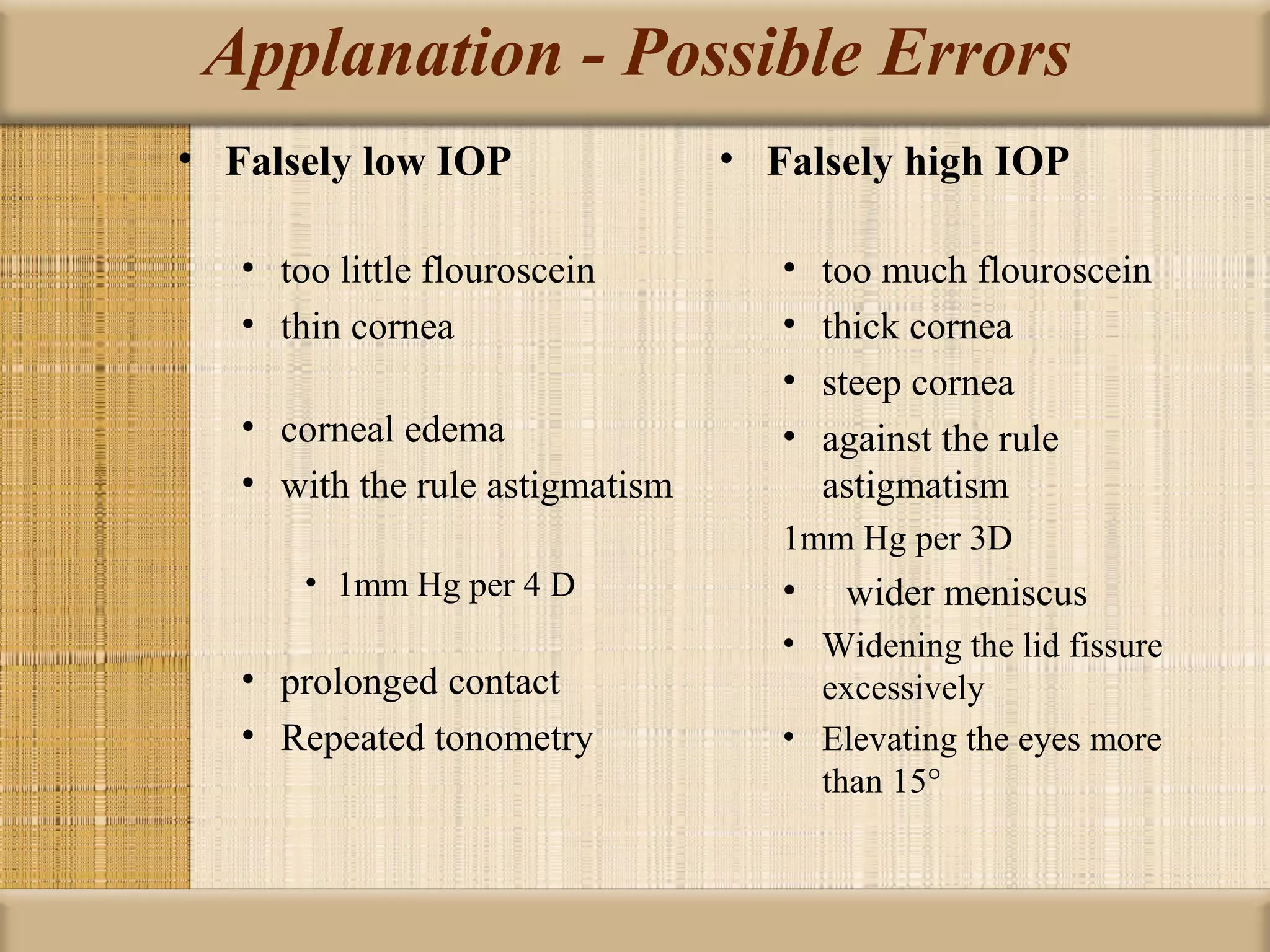
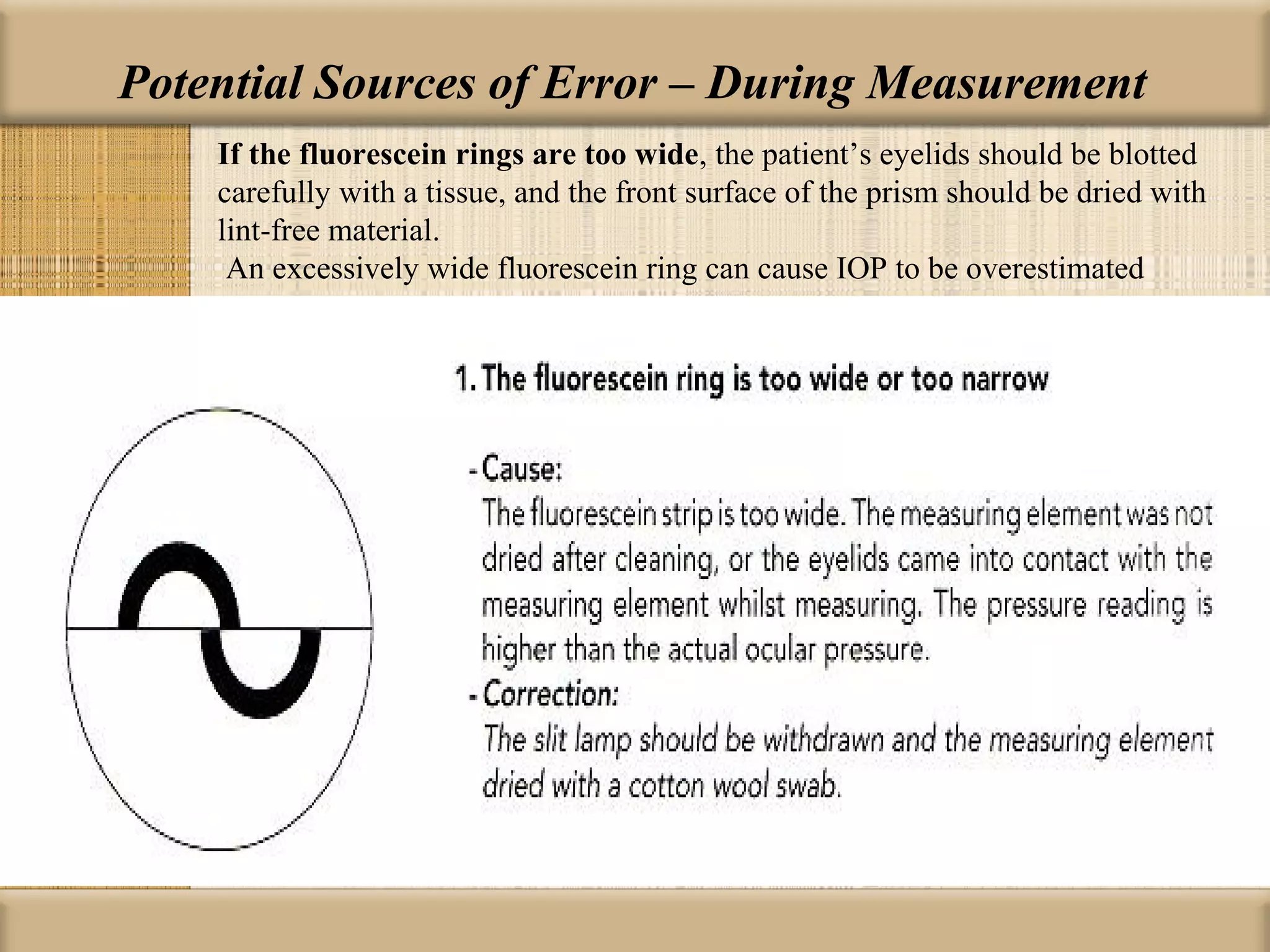
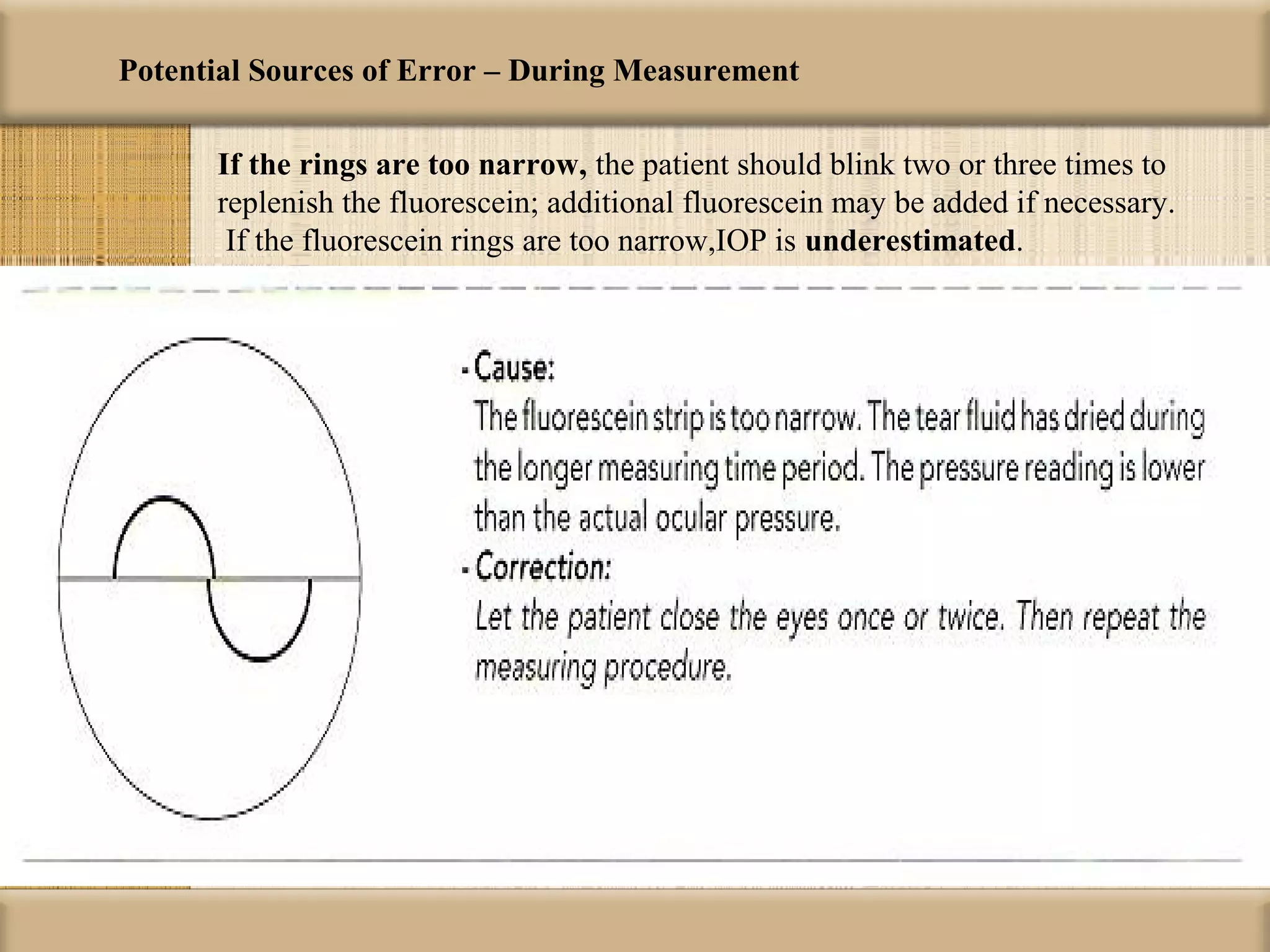
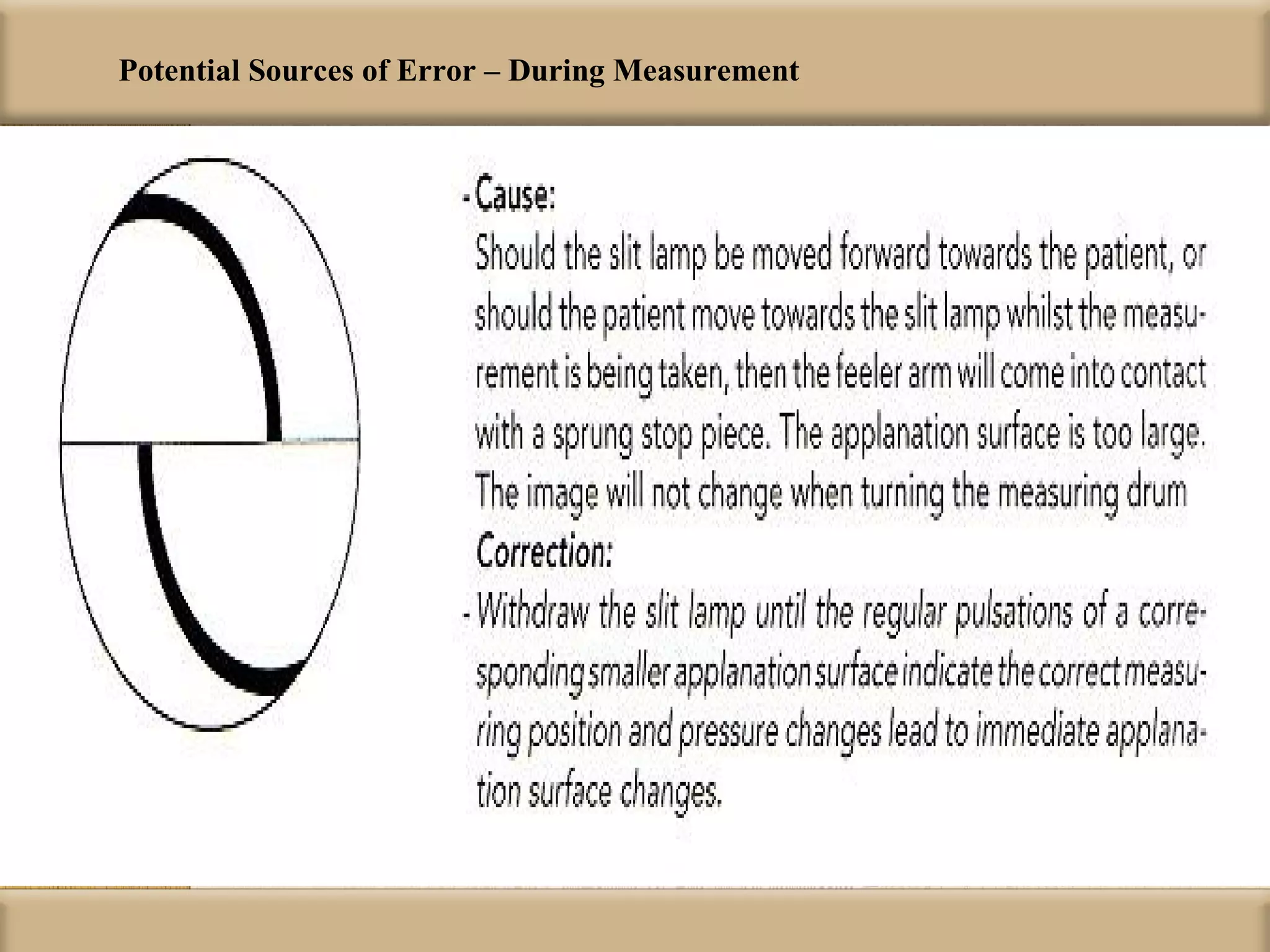
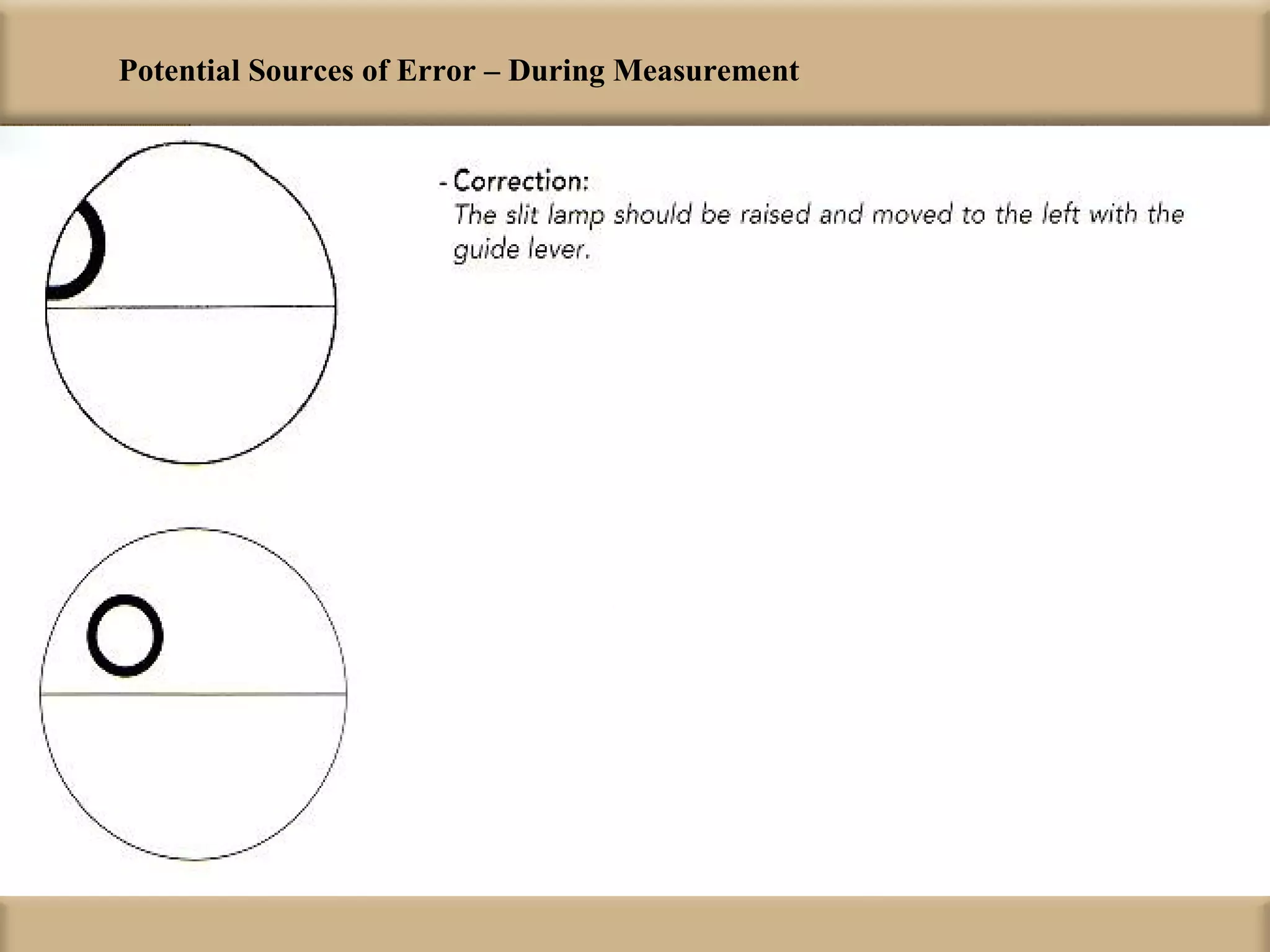
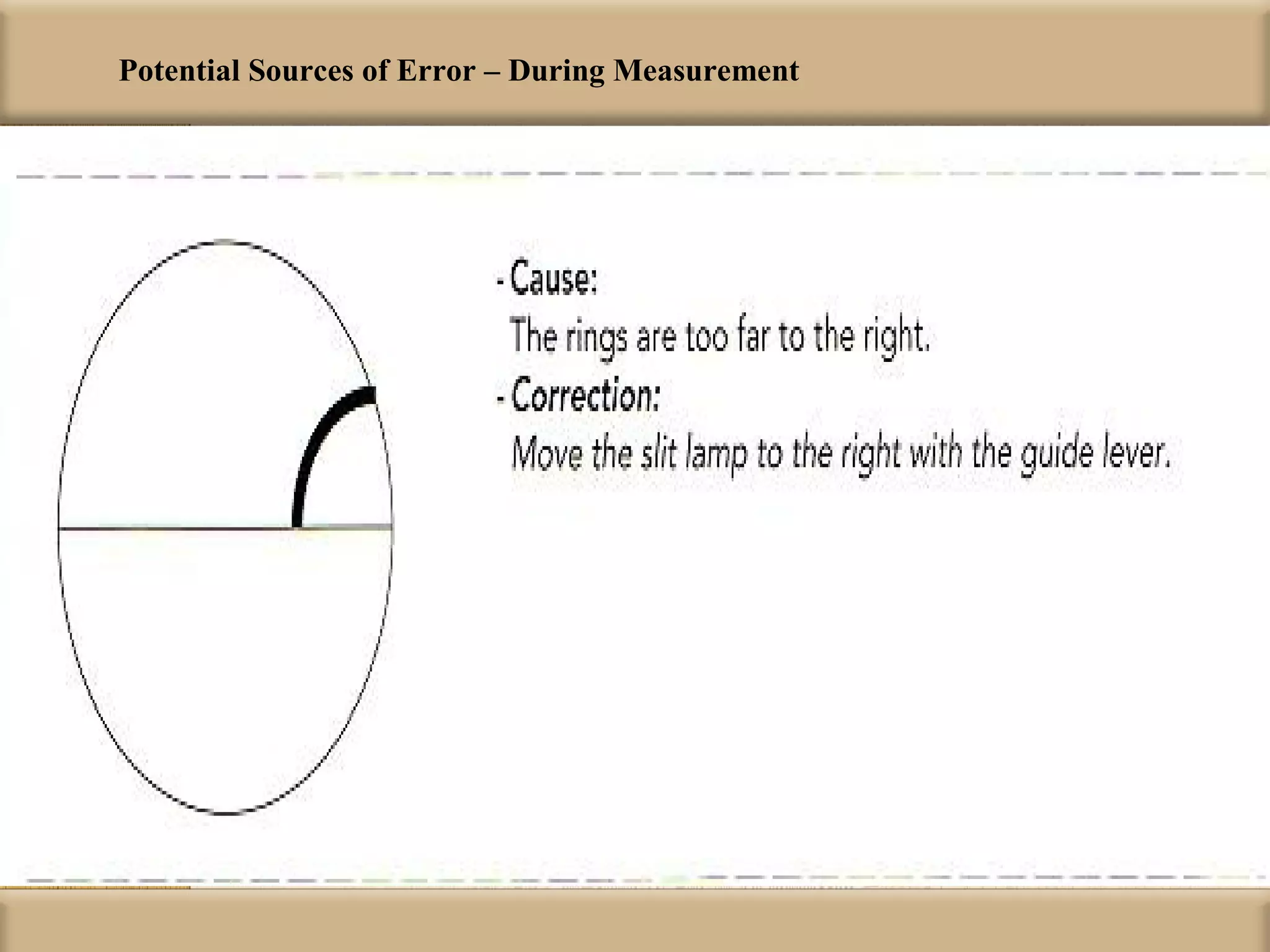
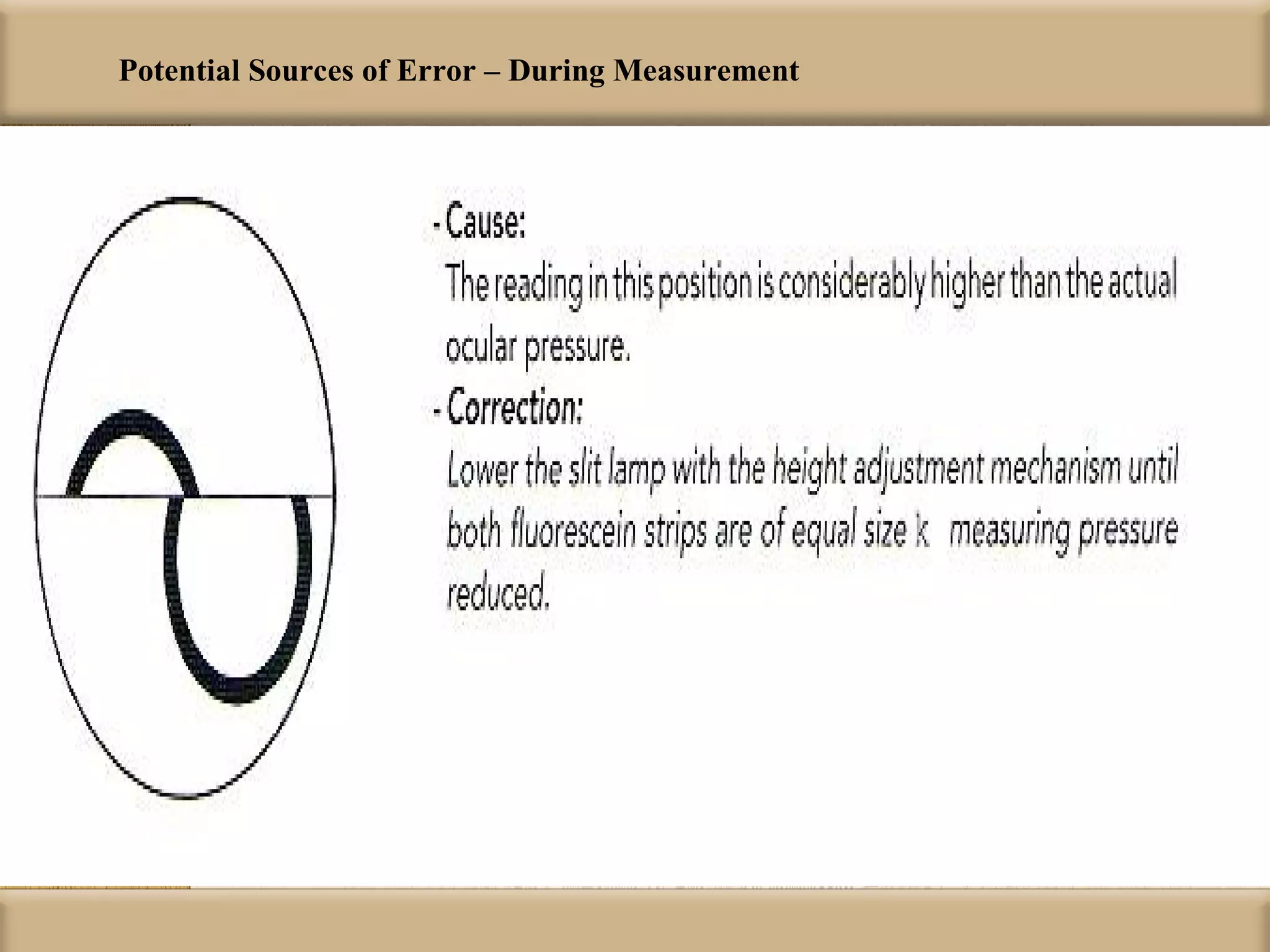
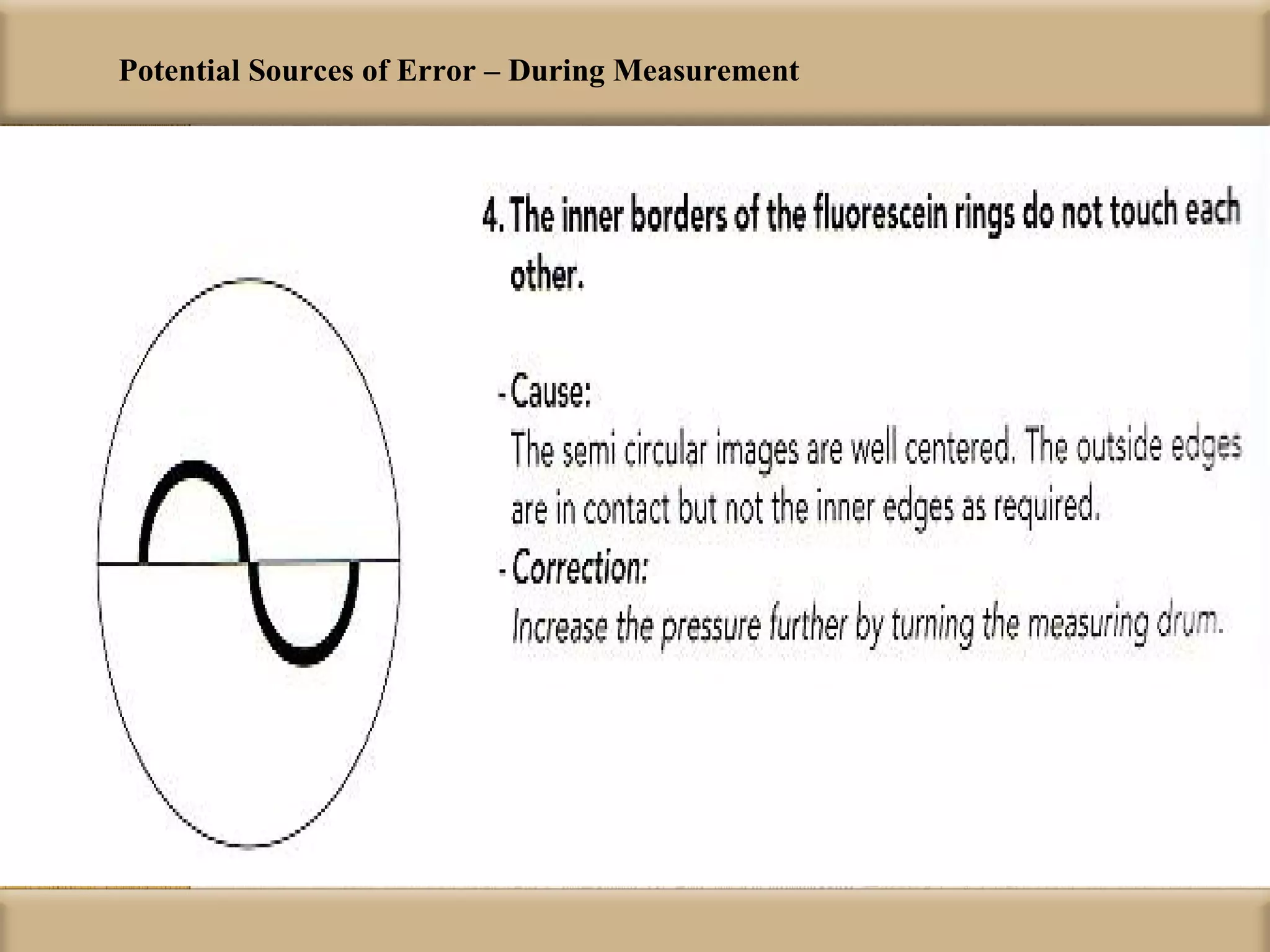
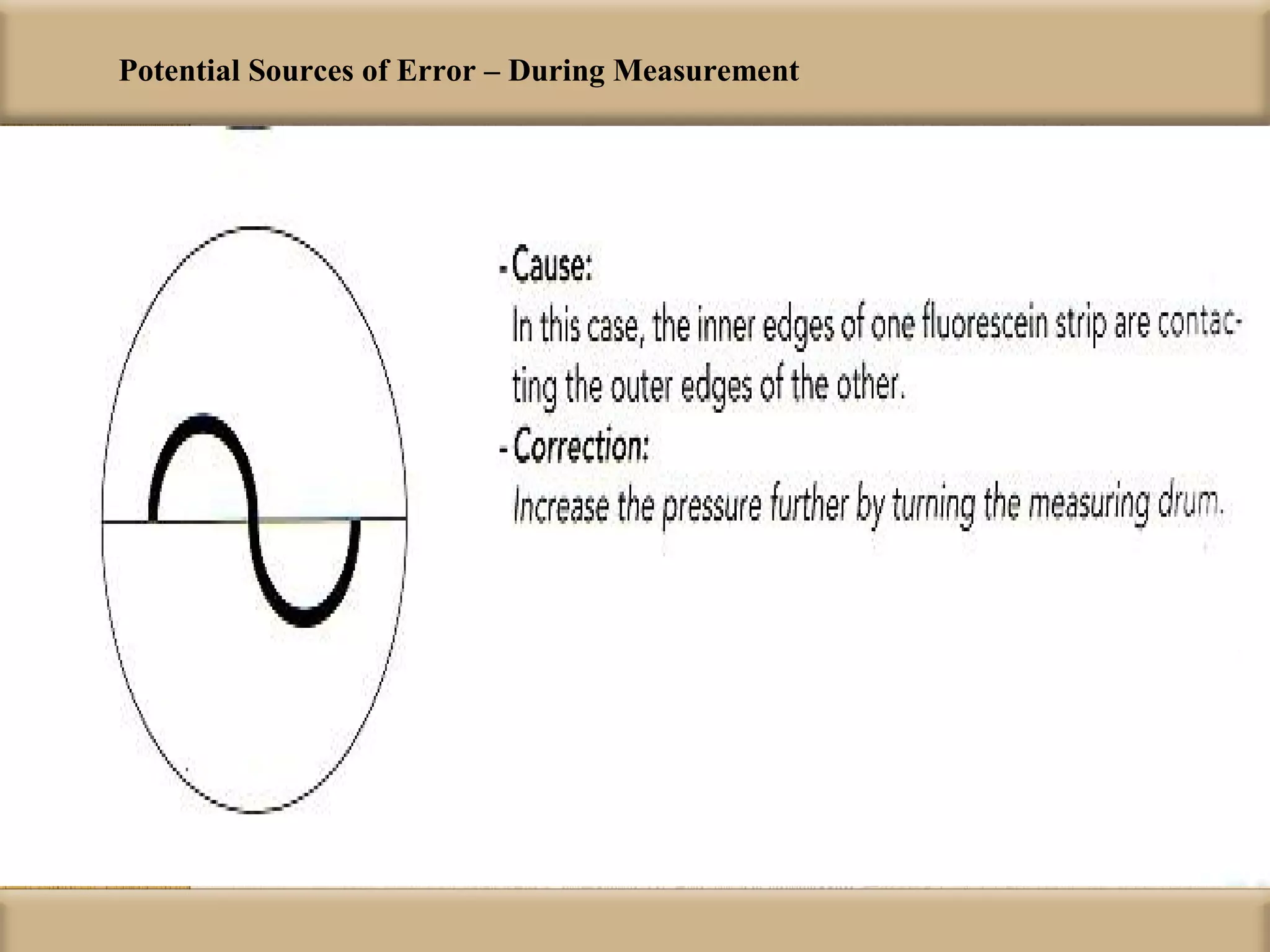
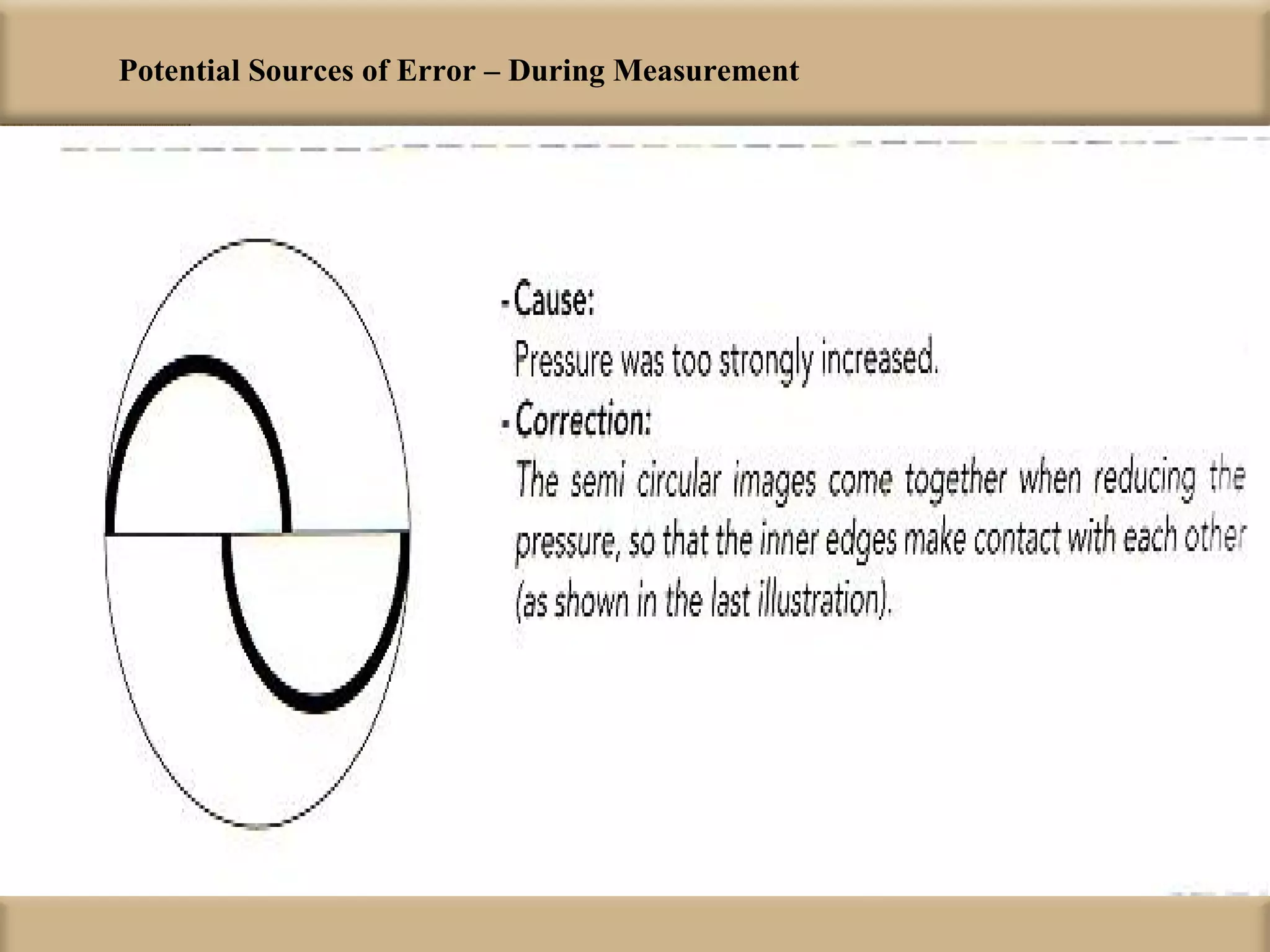
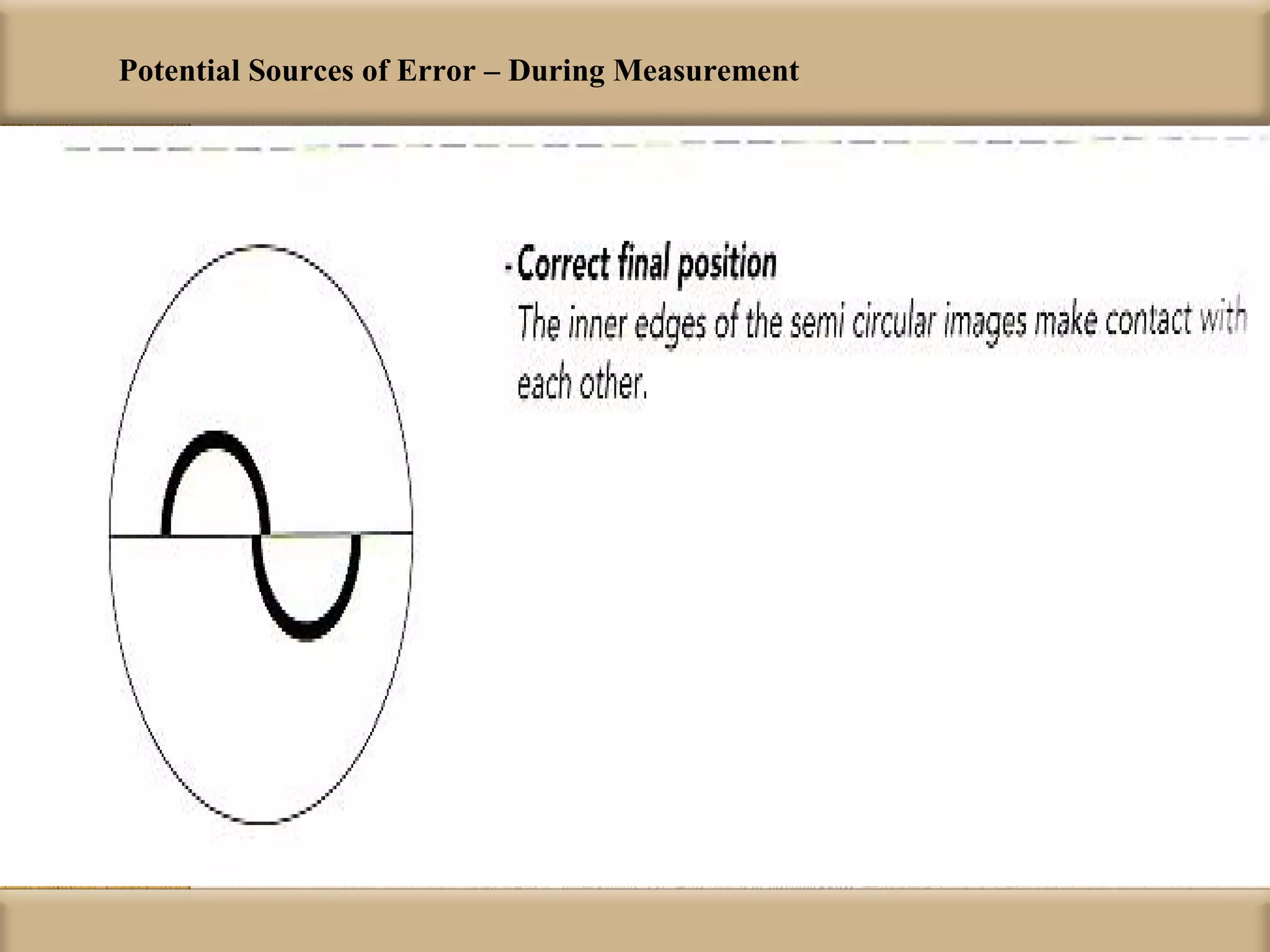
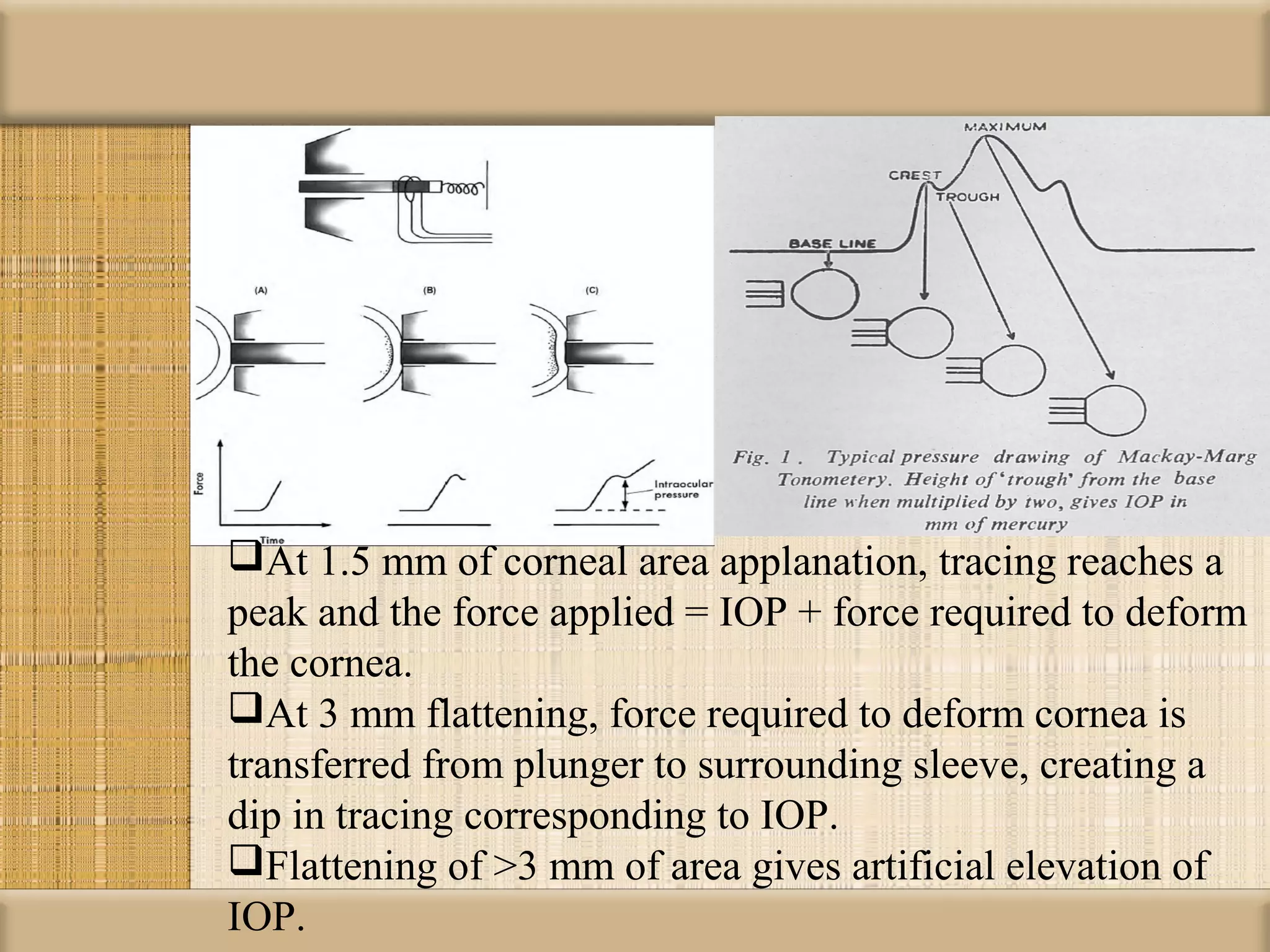
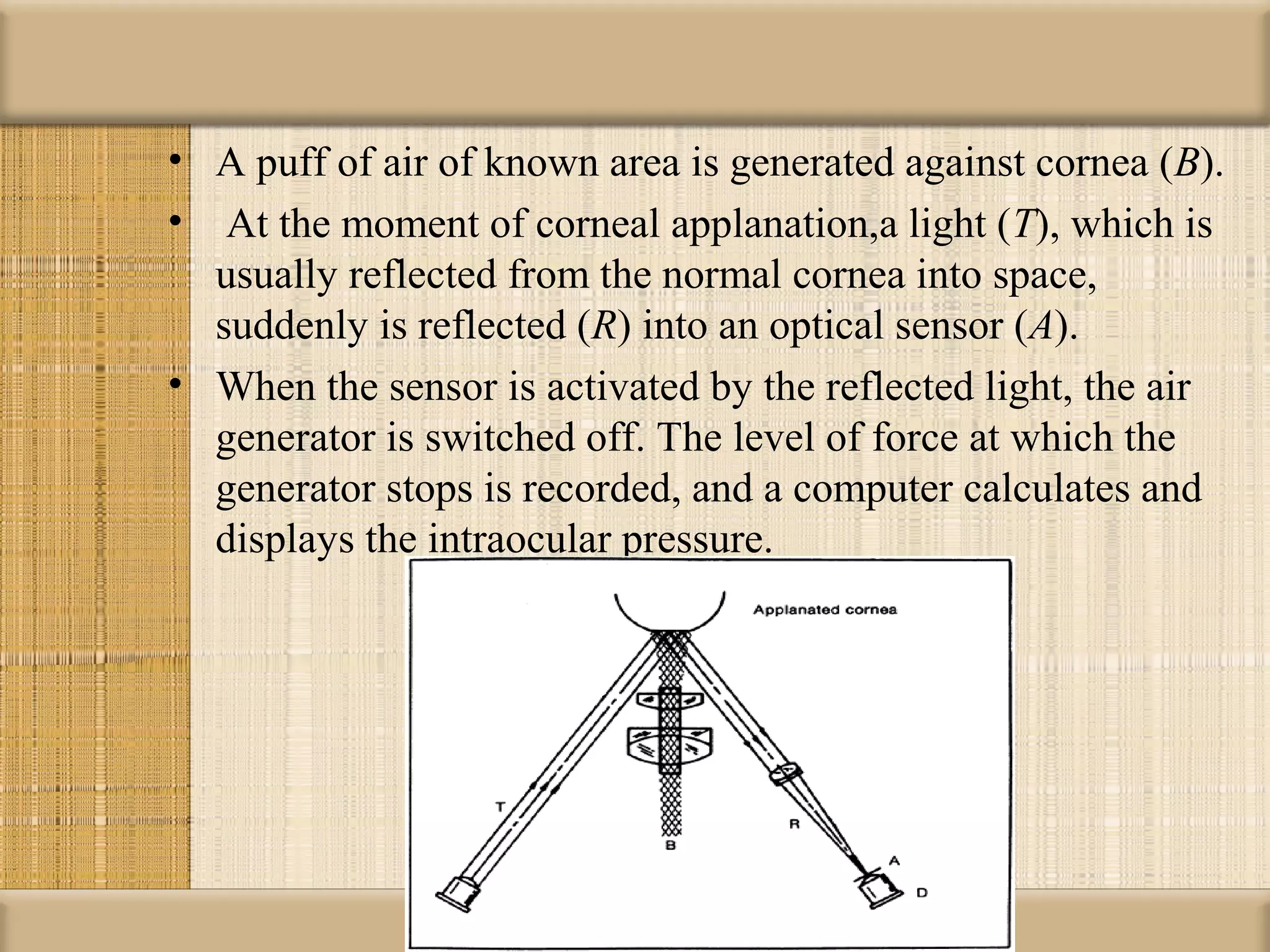
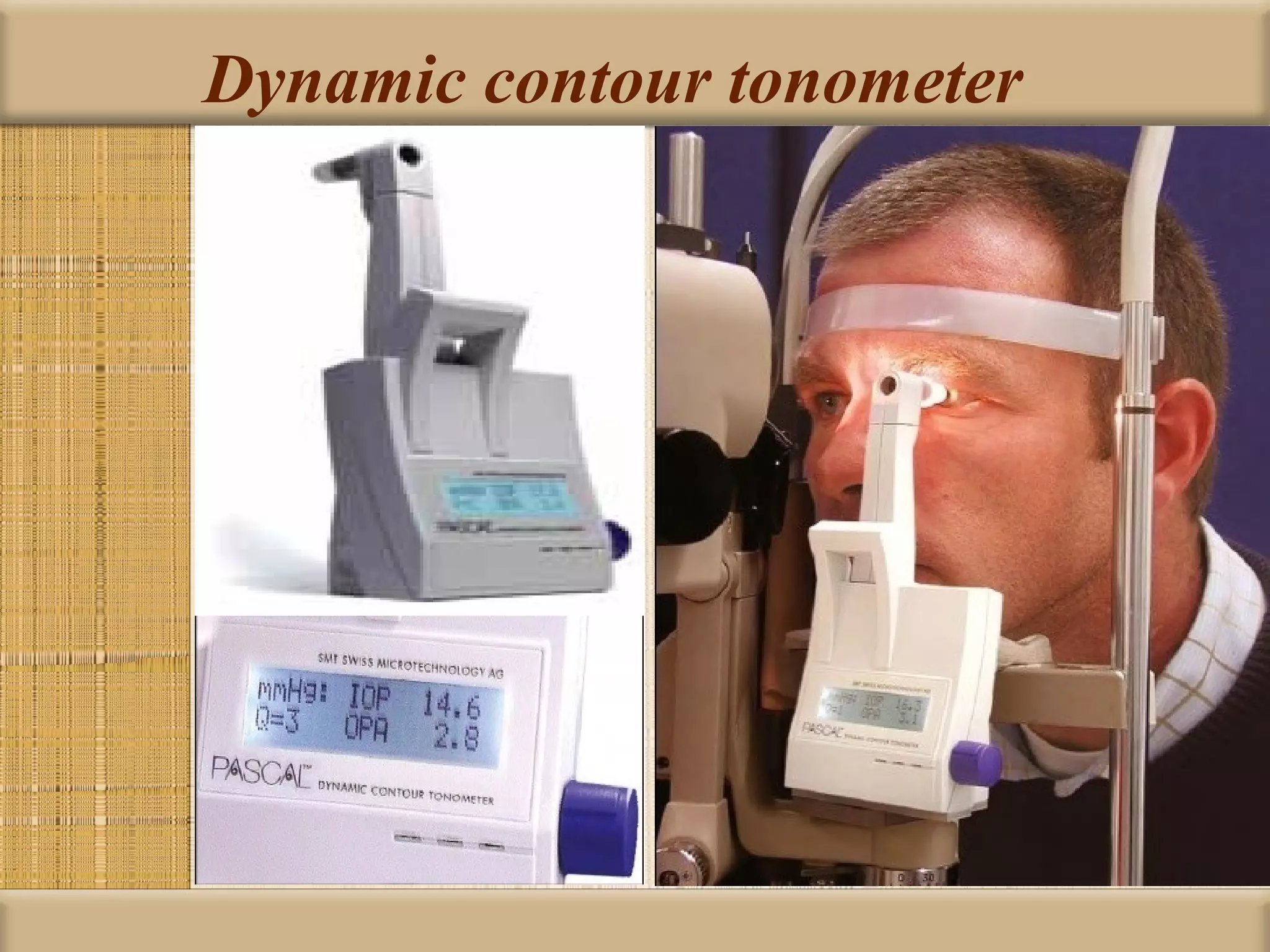
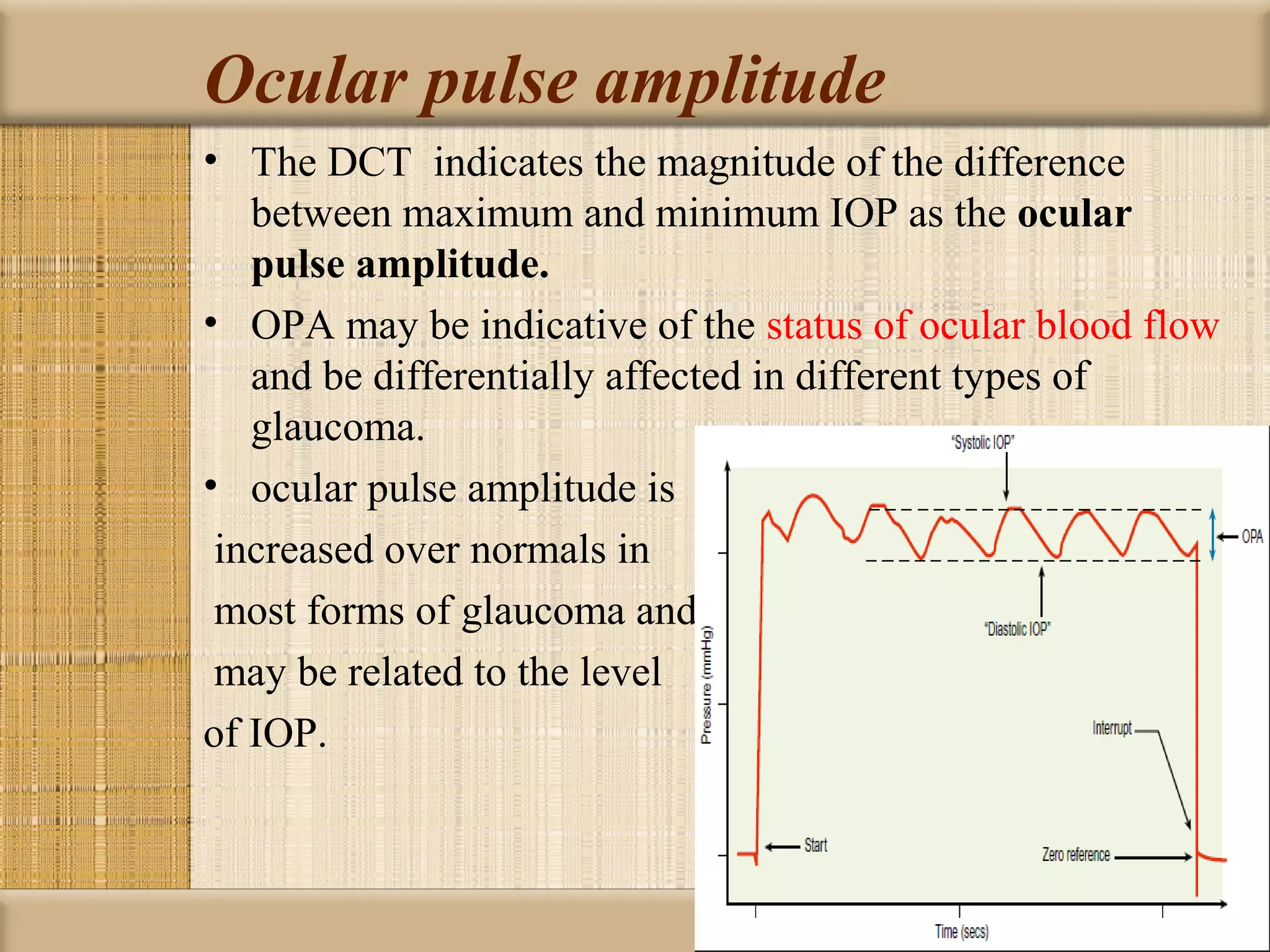
Tonometry is used to measure intraocular pressure (IOP) and is an important test in eye examinations. There are various types of tonometry including indentation, applanation, non-contact, and dynamic methods. The Schiotz tonometer uses weight-based indentation to determine IOP levels, while the Goldmann applanation tonometer flattens a standardized area of the cornea to measure pressure. Accurate tonometry requires consideration of factors like ocular rigidity, corneal thickness, and techniques to minimize IOP changes during measurement. Tonometers must also be properly calibrated and sterilized between patients.