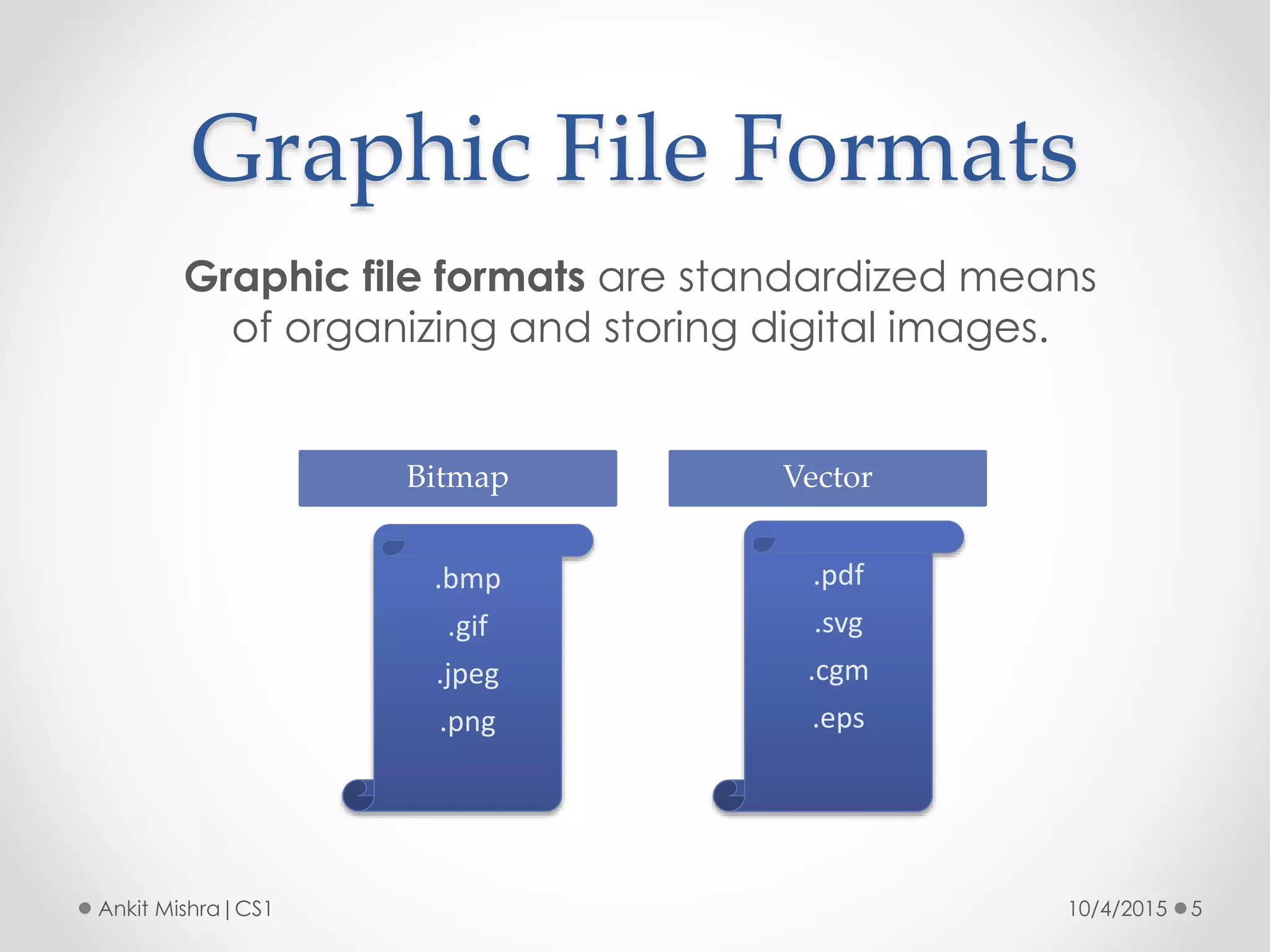
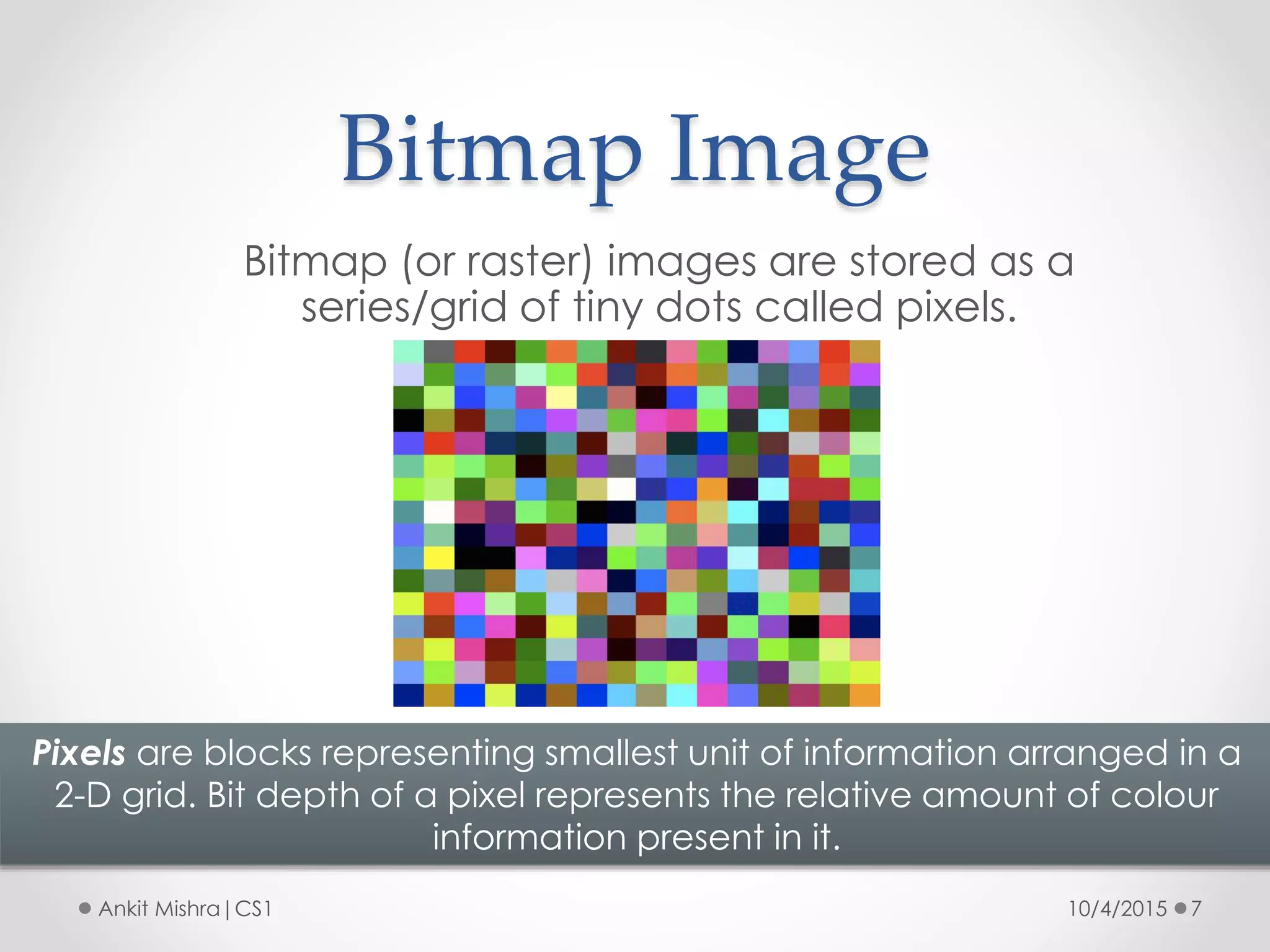
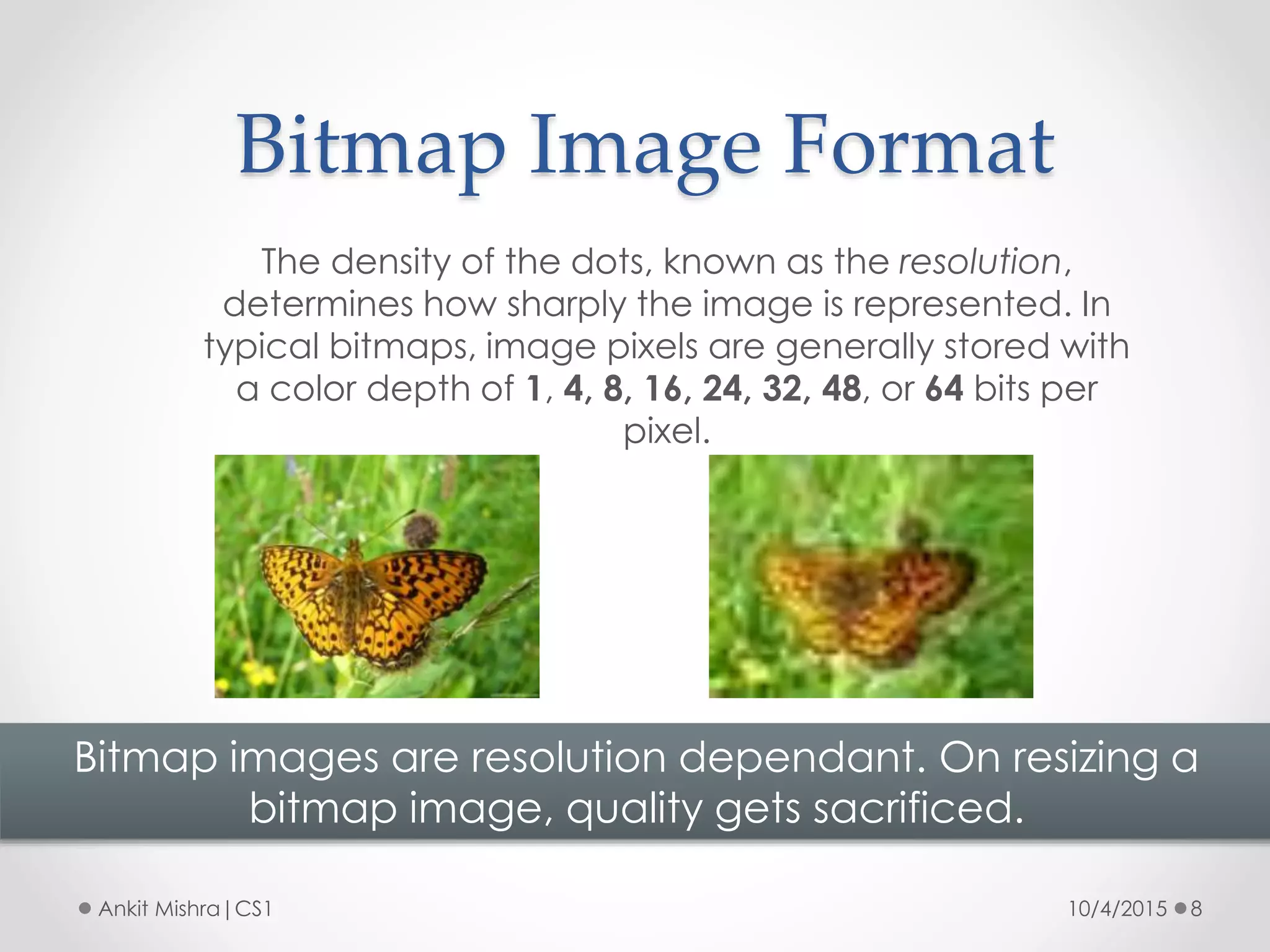
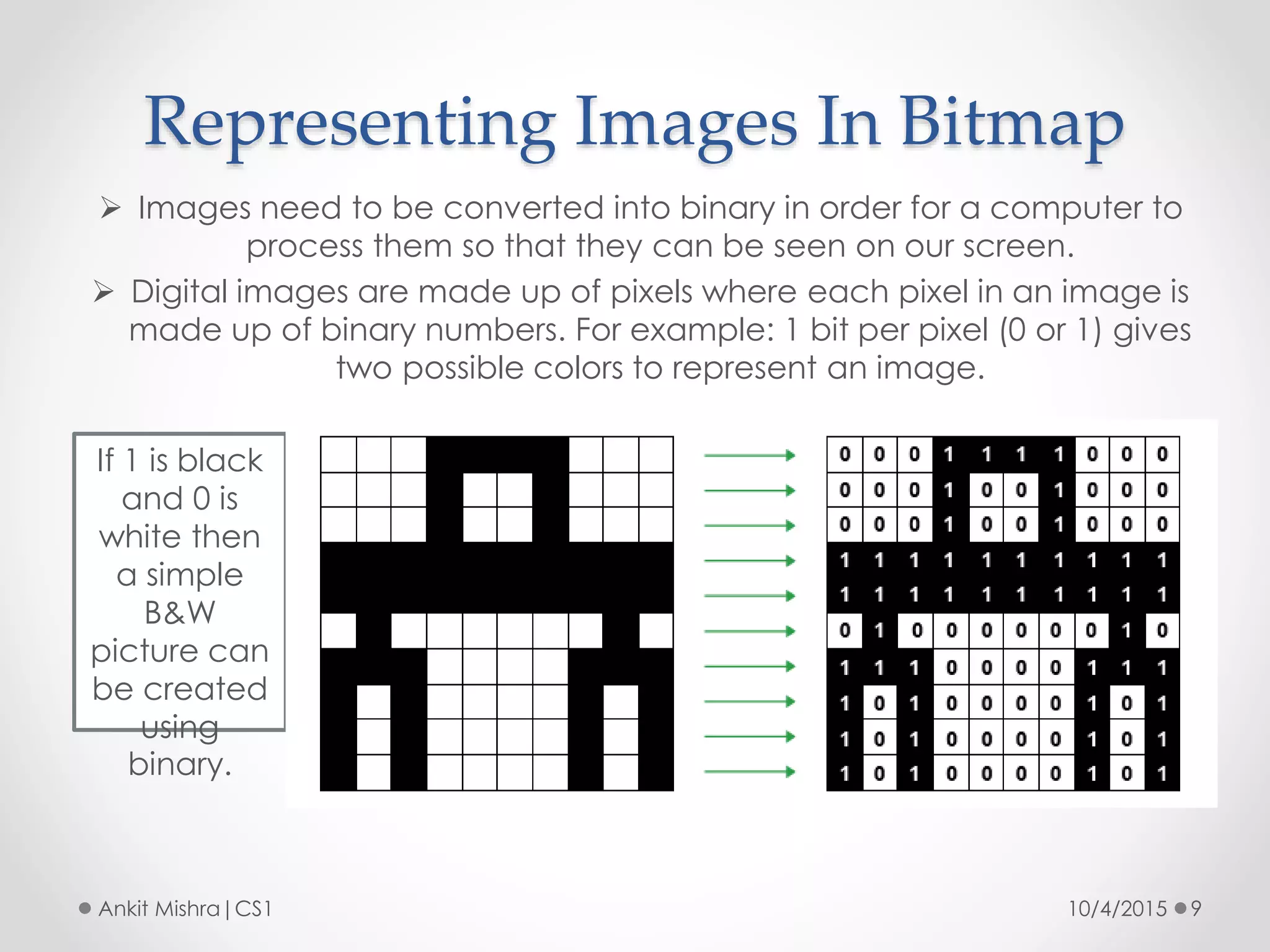
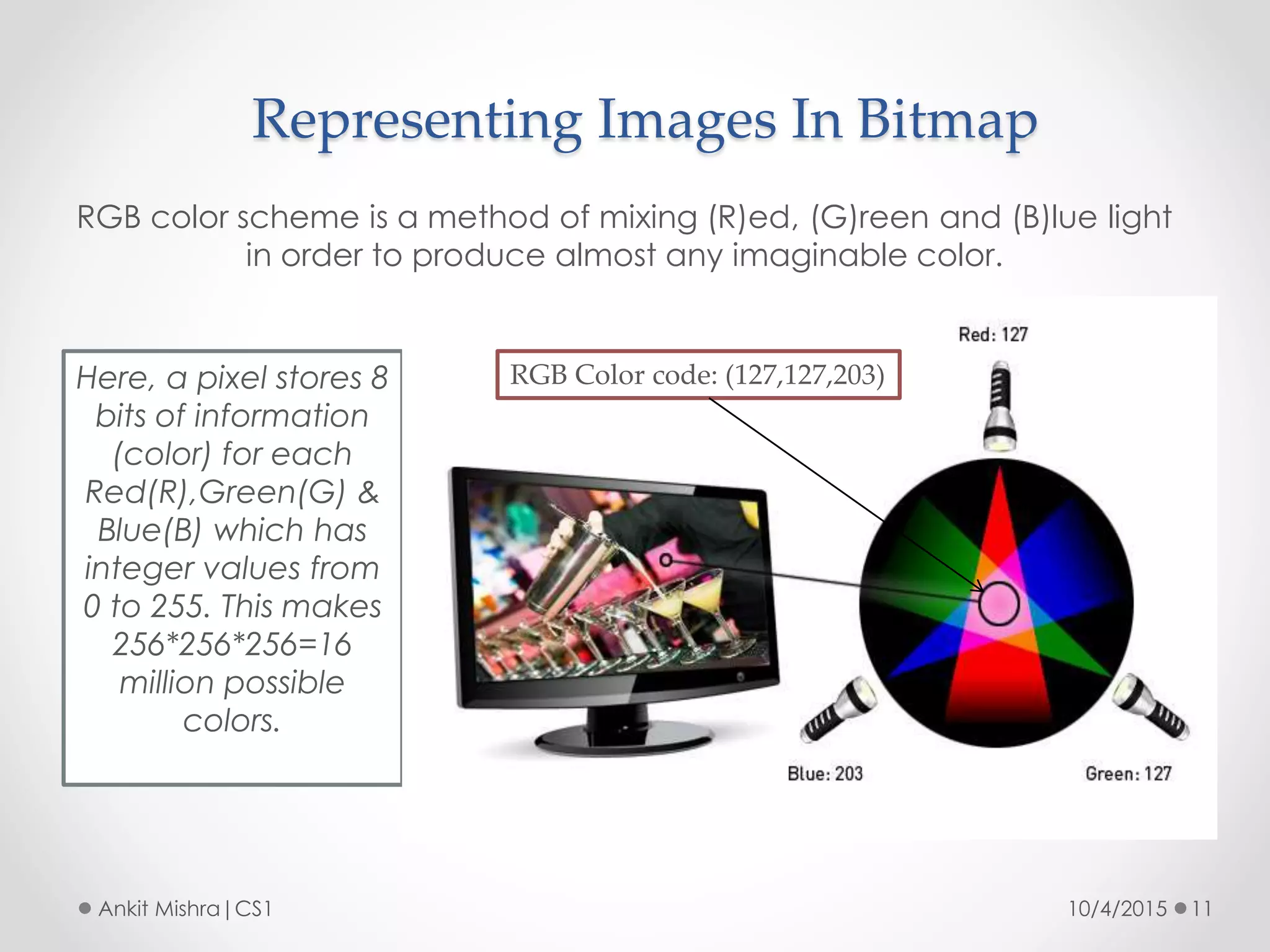
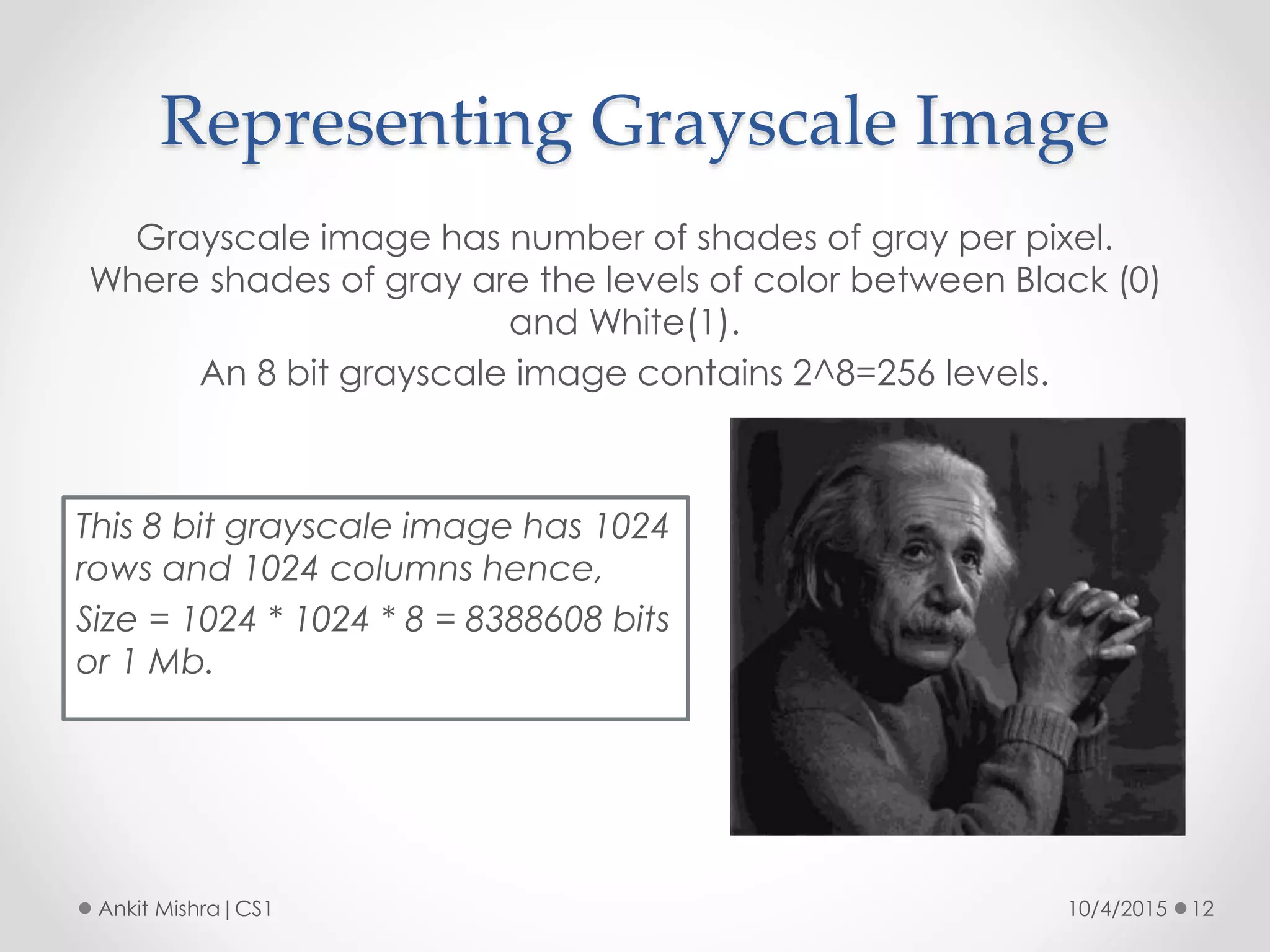
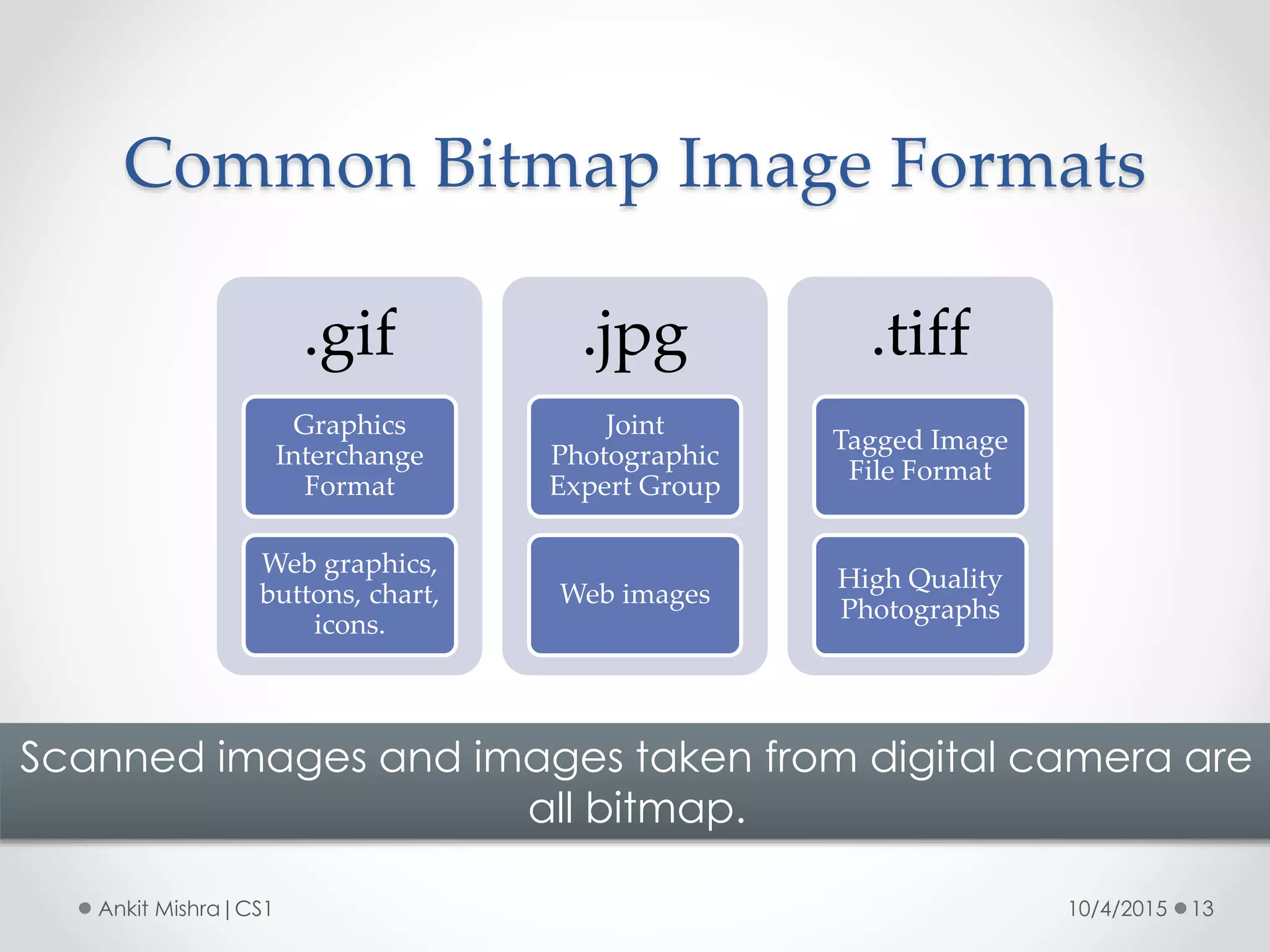
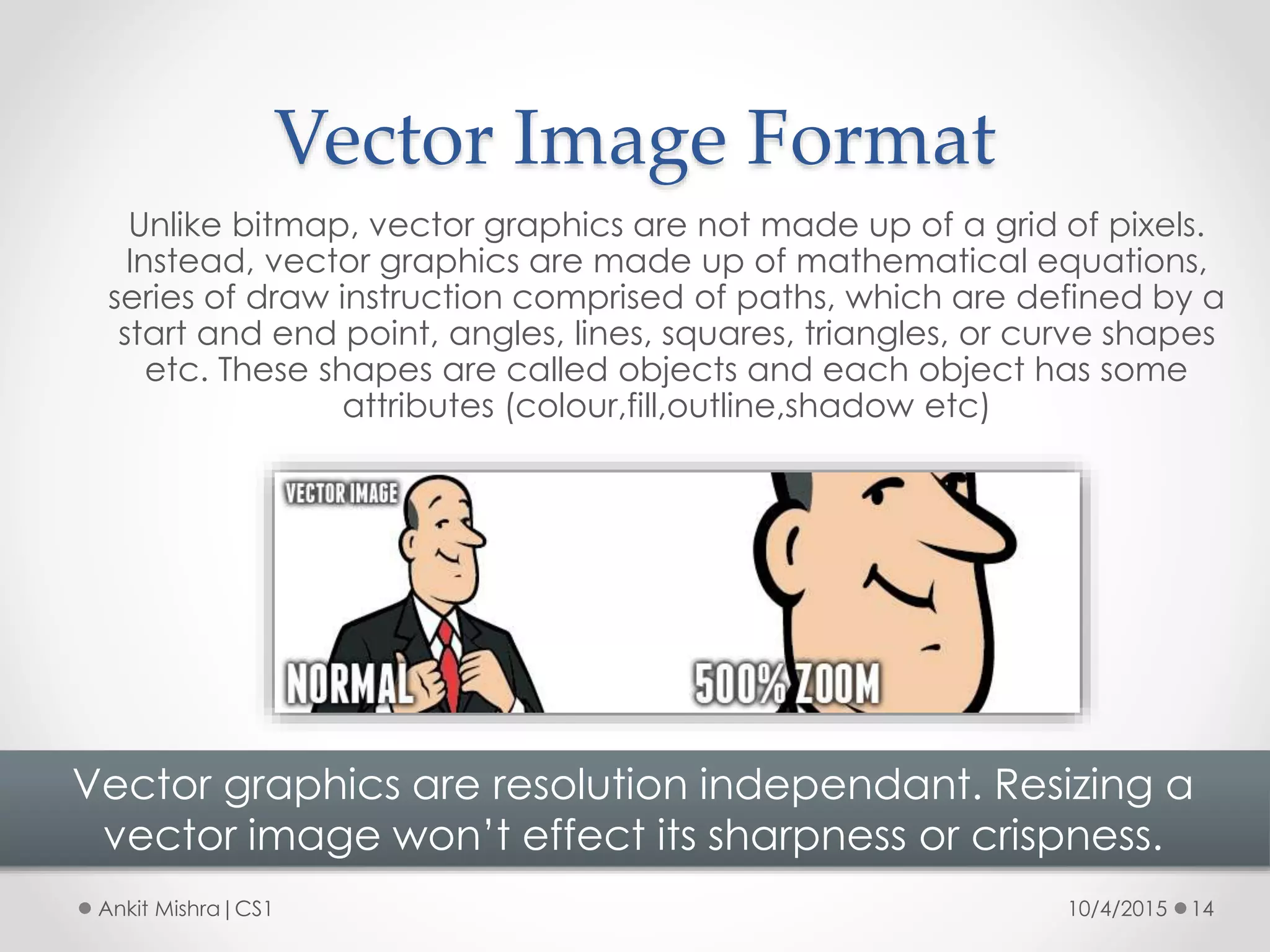
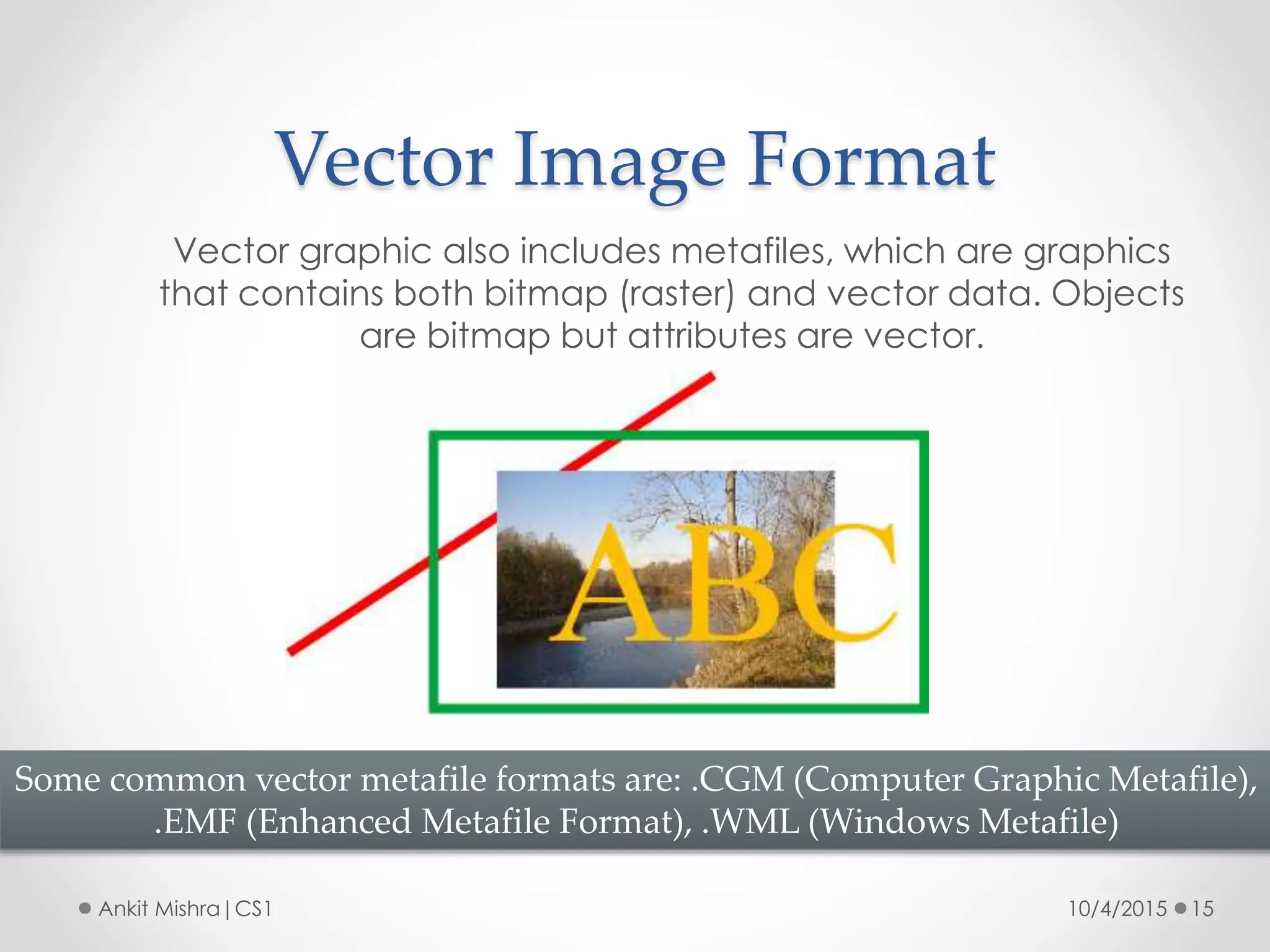
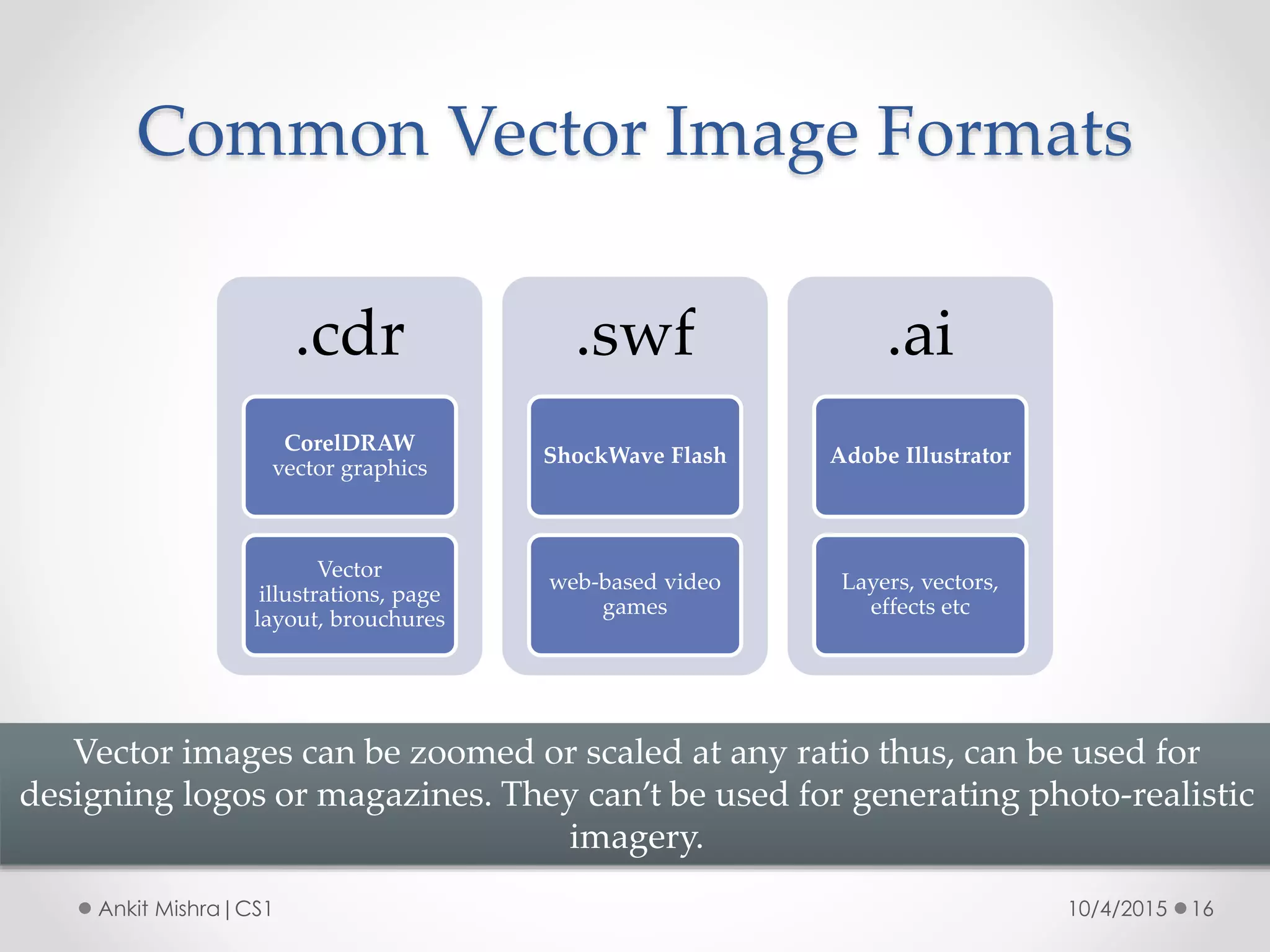
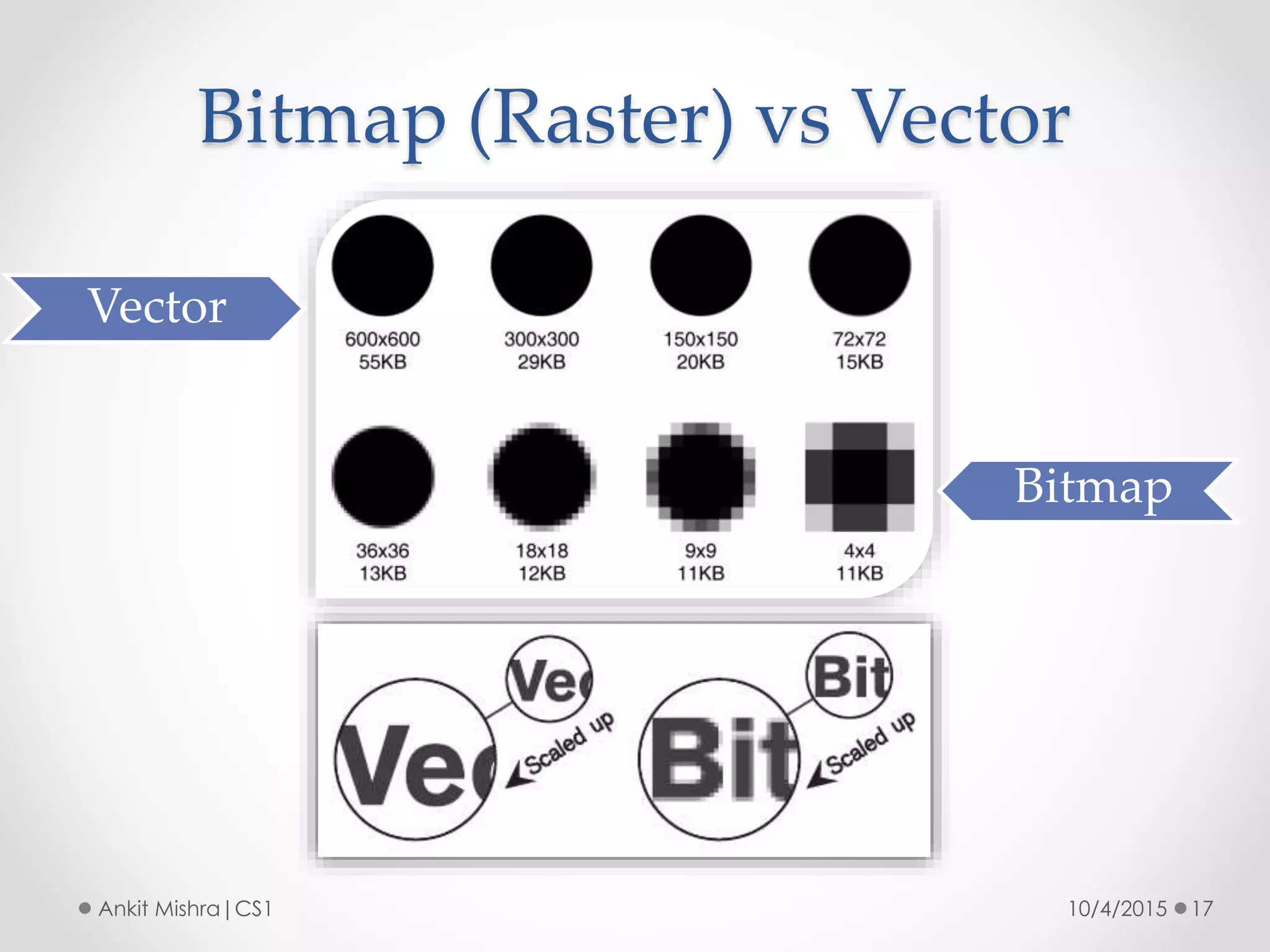
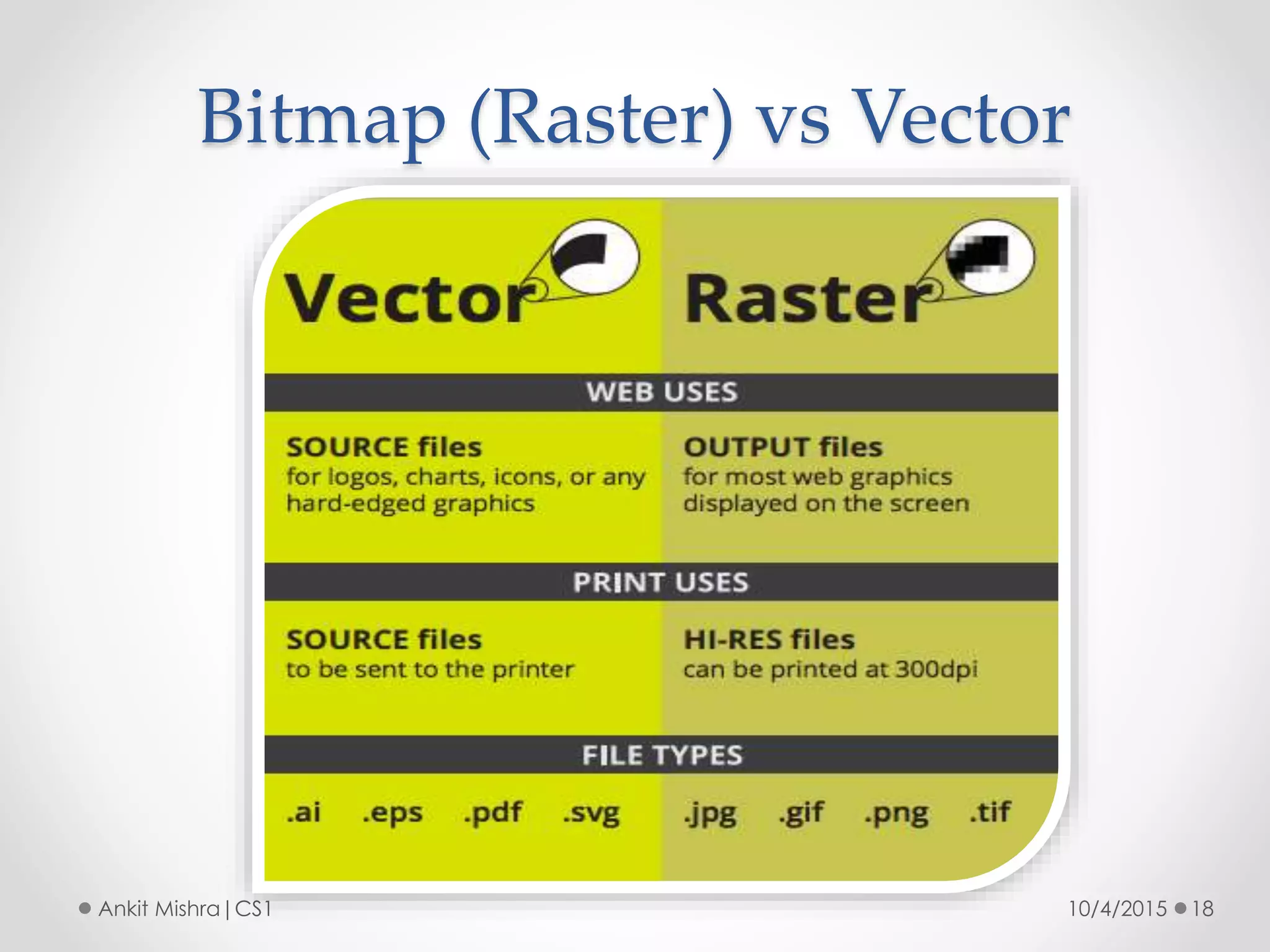
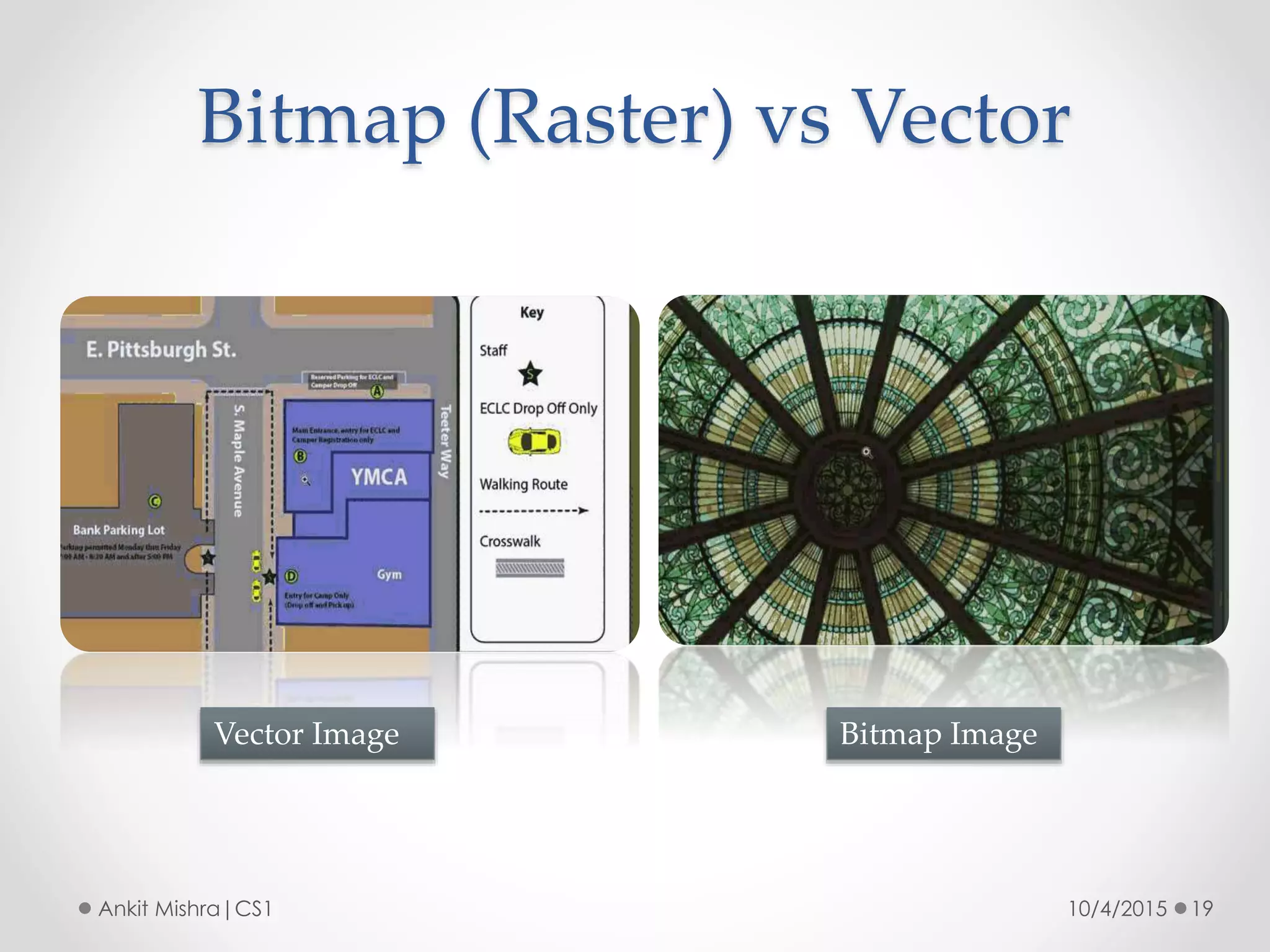
The document provides an introduction to graphic file formats, covering both bitmap and vector image formats, along with their characteristics and uses. Bitmap images, composed of pixels, suffer quality loss when resized, while vector images are based on mathematical equations and maintain quality regardless of scaling. The choice between bitmap and vector formats depends on the nature of the design, with bitmaps suitable for photographic elements and vectors for illustrations with distinct shapes.